Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0001s 4
0001s 4
Uploaded by
michaelfletcher510 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page004s hydrolic formulas x6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document004s hydrolic formulas x6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page0001s 4
0001s 4
Uploaded by
michaelfletcher51004s hydrolic formulas x6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
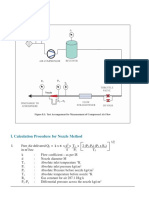
Formulas
Velocity of oil flow in pipe: Gas Formulas:
V = GPM x 0.3208 ÷ A PSIG (PSI Gage) = PSIA - 14.7
A = GPM x 0.3208 ÷ V PSIA (PSI Absolute) = PSIG + 14.7
GPM = A x V ÷ 0.3208
Isothermal
V = Oil velocity in feet per second
GPM = Flow in gallons per minute P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
A = Inside area of pipe in square inches. P1 = Pre-charge Pressure + 14.7
Rule of thumb: V1 = Intial Gas Volume
Pump suction lines 2 to 4 feet/second P2 = System Pressure + 14,7
Pressure lines up to 500 PSI - 10 to 15 fps V2 = Compressed Gas Volume
Pressure lines 500 to 3000 PSI - 15 to 20 fps
Pressure lines over 3000 PSI - 25 fps P1, V1 are initial pressure and volume; P2 and V2 are
All oil lines in air-over-oil system - 4 fps final conditions.
fps = feet per second Note:
Barlow formula (hoop stress): Isothermal operatiion occurs when compression or
expansion is slow enough to allow transfer of heat out
P=2xtxS÷D of or into the accumulator.
P = Working pressure in PSI with a 4:1 Design Factor
t = Wall thickness, in inches Adiabatic
S = Allowable stress (12,500 with a 4:1 Design Factor) P1 x V1 x T2 = P2 x V2 x T1
D = Outside diameter, in inches. P1 x V1 ÷ T1 = P2 x V2 ÷ T2
D = √ A/.7854
Atmosphere: P1 = Pre-charge Pressure + 14.7
V1 = Intial Gas Volume
Atmospheric pressure is 14.7 psi at sea level P2 = System Pressure + 14.7
One Bar is equal to 14.5 psi (Atmos. - 1.01 Bar) V2 = Compressed Gas Volume
The pressure created by one fooot of water is .433 psi T1 = Initial Temp. Absolute (Rankine)
T2 = Increased Temp. Absolute (Rankine)
Atmospheric Ratio = 14.7 ÷ PSI = 33.9 ÷ (X)
T1, P1 and V1 are initial temperature, pressure and
Atmospheric will lift water 33.9 feet
volume and, T2, P2 and V2 are final conditions.
1 inch Hg = .491 psi
14.7 psi = 29.92 hg Note:
Y inch Hg Absolute = (29.92 - Y) x .491 = PSI Adiabatic operatiion occurs when compression or
PSI = lbs ÷ in2 expansion is rapid so that there is no transfer of heat.
Hg = Inches of mercury The adiabatic equation is used where compression or
expansion occurs in less than 1 minute.
Filtration:
1 Micron = .000039" Rule of thumb:
149 Micron = 100 Mesh Compressibility of hydraulic oil: Volume reduction is
74 Micron = 200 Mesh approximately 0.5% for every 1000 PSI pressure.
44 Micron = 325 Mesh Compressibility of water: Volume reduction is about
Beta 75 = 98.7% 0.3% for every 1000 PSI pressure.
Beta 100 = 99%
Rankine = Fahrenheit + 460
Beta 200 = 99.5%Gas
Kelvin = Celsius + 278
Beta Ratio = Upstream Count ÷ Downstream Count
Celsius to Fahrenheit = (C + 17.78) x 1.8 = Fahrenheit
Efficiency Percent (%) = 1 - (1 ÷ Beta Ratio) x 100 Fahrenheit to Celsius = F - 32 ÷ 1.8 = Celsius
Intial Gas Volume - Compressed Gas = Usual Oil
43 Parker Hannifin Corporation
Mobile Cylinder Division
Youngstown, OH
You might also like
- Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pagesBasic HVAC Formulas - Tech Tipgauravgujar24100% (1)
- 300 MW Thermal Power Plant Training Material For OperatorsDocument360 pages300 MW Thermal Power Plant Training Material For OperatorsCarlos Huaman100% (6)
- Troubleshooting and Repairing LCD TVsDocument195 pagesTroubleshooting and Repairing LCD TVsManoranjan Yadav95% (21)
- Pressure LectureDocument75 pagesPressure LecturezhainogNo ratings yet
- 07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipDocument2 pages07-11 Basic HVAC Formulas - Tech TipAslam100% (2)
- 03 FundamentalsDocument32 pages03 FundamentalsKavi BhandariNo ratings yet
- Determination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesDocument6 pagesDetermination of Certified Relieving CapacitiesGustavo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Vapor Power Cycles - CompleteDocument97 pagesChapter 1 Vapor Power Cycles - CompleteAdnan NimachwalaNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Back Pressure: Burst PressureDocument15 pagesDefinitions: Back Pressure: Burst PressuremecambNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: Induction TuningDocument39 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: Induction TuningloganathanpalaniNo ratings yet
- ZM KV Idag eDocument6 pagesZM KV Idag elutfi awnNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewermaylynXiXNo ratings yet
- Correlaciones de GasDocument29 pagesCorrelaciones de GasKathlyn GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 0 Basic Principle of Pneumatic CircuitsDocument76 pages0 Basic Principle of Pneumatic CircuitsBayu RafliNo ratings yet
- PressionDocument33 pagesPressionebrahim ftiesNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression FundamentalsDocument50 pages02-Gas Compression FundamentalsVikram JitNo ratings yet
- MMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - ProblemDocument13 pagesMMC 16101 - Compressor - 01 - Problemyasin kocaboğaNo ratings yet
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC FormulasAshok Kumar S100% (4)
- I. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle MethodDocument3 pagesI. Calculation Procedure For Nozzle Methodome solNo ratings yet
- 02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Document47 pages02-Gas Compression Fundamentals-1Muhammad Asad100% (4)
- Lecture 3 Fluid StaticsDocument89 pagesLecture 3 Fluid StaticsMark LobrigoNo ratings yet
- PSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipDocument4 pagesPSV Sizing: The Relief Load Can Be Calculated Directly, in Pounds Per Hour, From The Following RelationshipAfees OlajideNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving - BellimoDocument30 pagesEnergy Saving - BellimoNguyễn Thành NamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power FormulaDocument20 pagesFluid Power FormulaEka Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- 8.assessment of CompresorsDocument14 pages8.assessment of CompresorsPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFSaraswatapalit0% (1)
- Standard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument11 pagesStandard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CyclejjNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 by Sta. Maria Chapter 3 Solution ManualDocument7 pagesThermodynamics 1 by Sta. Maria Chapter 3 Solution ManualAllen MalabarbasNo ratings yet
- Accumulator SizingDocument6 pagesAccumulator Sizingtankimsin100% (2)
- Condenser ProblemsDocument12 pagesCondenser ProblemsJagdeesh R100% (1)
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerPamee BautistaNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Fluid Power FormulaDocument10 pagesMiscellaneous Fluid Power FormulaRicardo Vargas GraciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NumericalsDocument36 pagesChapter 2 NumericalsAASHISH KATUWALNo ratings yet
- Actual Free Air Discharge (P2-P1) V Po T: Coal Boiler Air Compressor PerformanceDocument2 pagesActual Free Air Discharge (P2-P1) V Po T: Coal Boiler Air Compressor Performancesiruslara6491No ratings yet
- Boiler FormulasDocument5 pagesBoiler FormulasAnonymous 6Mb7PZjNo ratings yet
- Ice Plant Test RigDocument9 pagesIce Plant Test Rigramniwas123No ratings yet
- Unit 3 ReviewDocument34 pagesUnit 3 ReviewزهديابوانسNo ratings yet
- Q 22.5 GPM D 1'' C 120 (Galvanized Iron)Document14 pagesQ 22.5 GPM D 1'' C 120 (Galvanized Iron)Neil Allison Najorda CabilbilNo ratings yet
- Control System TemperatureDocument5 pagesControl System TemperatureGourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesTAIMUR NASIRNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Pressure MeasurementDocument86 pagesUnit 2 - Pressure MeasurementNilesh LuhariyaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFDocument94 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning PDFYash ShahNo ratings yet
- 4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1Document1 page4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1rinabiswasNo ratings yet
- FD3 CalculationsDocument36 pagesFD3 Calculationssudhiruday31No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reversed Carnot CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Reversed Carnot CyclejjNo ratings yet
- Process Calculations & Fan Audit Module in Cement IndustryDocument99 pagesProcess Calculations & Fan Audit Module in Cement IndustryNITITN ASNANINo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System: By: Engr. Yuri G. MellizaDocument47 pagesRefrigeration System: By: Engr. Yuri G. MellizaJohnRay LominoqueNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta MariaDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Chapter 3 Solution Sta MariaJean PD81% (21)
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Fortification of White Flat Bread WithDocument8 pagesFortification of White Flat Bread WithRadwan AjoNo ratings yet
- 064640Document314 pages064640venalum90No ratings yet
- Phoneway - All Models Manual - V-1-0Document104 pagesPhoneway - All Models Manual - V-1-0PauloSNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 p57-87Document31 pagesVol 2 p57-87Andrés LladosaNo ratings yet
- Active Directory - Forest, Tree, DomainDocument5 pagesActive Directory - Forest, Tree, DomainshaileshNo ratings yet
- Radwin TDM Backhaul Over Unlicensed BandsDocument5 pagesRadwin TDM Backhaul Over Unlicensed BandsVisakh VijayNo ratings yet
- Cortex-M3/M4 ArchitectureDocument37 pagesCortex-M3/M4 Architecturesuhaskakade0075745No ratings yet
- Three Moment Equation PaperDocument9 pagesThree Moment Equation PaperAkash SoodNo ratings yet
- Statistical Models in Simulation: Course LeaderDocument23 pagesStatistical Models in Simulation: Course LeadershyNo ratings yet
- 3rd&4thsemsyllabus PDFDocument139 pages3rd&4thsemsyllabus PDFVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Time Value ProblemDocument8 pagesTime Value ProblemPrantik RayNo ratings yet
- FRST Quarter Exam PR 2Document3 pagesFRST Quarter Exam PR 2Katie MarianoNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 9 Math Q1 Week 5Document3 pagesDLL Grade 9 Math Q1 Week 5Cris JanNo ratings yet
- Machine-Learning Analysis For The Iris Dataset: ArticleDocument16 pagesMachine-Learning Analysis For The Iris Dataset: ArticleBarrey WaneNo ratings yet
- Action and PerceptionDocument19 pagesAction and PerceptionjieliNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarDocument6 pagesFiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarVivek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Favrholdt, David. On Neils BohrpdfDocument153 pagesFavrholdt, David. On Neils BohrpdfTheresa TurnerNo ratings yet
- Barton Flotrac 308 User ManualDocument16 pagesBarton Flotrac 308 User ManualJose Fernando Davila VigoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 5: Multiplying Decimals and Mixed Decimals With Factors Up To 2 Decimal PlacesDocument13 pagesQuarter 1 Week 5: Multiplying Decimals and Mixed Decimals With Factors Up To 2 Decimal PlacesKharren NabasaNo ratings yet
- 3do m2Document4 pages3do m2asfghNo ratings yet
- 10 1109@10 923789 PDFDocument13 pages10 1109@10 923789 PDFAyu Oka WiastiniNo ratings yet
- Soldred Brass HookDocument3 pagesSoldred Brass HookdadahineNo ratings yet
- ITEM ANALYSIS Grade 6 DIAGNOSTICDocument23 pagesITEM ANALYSIS Grade 6 DIAGNOSTICFrancis Decena100% (1)
- Glycosidase Enzymes Stabilization Through Immobilization Onto Nanoparticulated Bimodal OrganosilicasDocument1 pageGlycosidase Enzymes Stabilization Through Immobilization Onto Nanoparticulated Bimodal Organosilicasdadang71No ratings yet
- How To Prepare Storage For ASMDocument3 pagesHow To Prepare Storage For ASMspizaroNo ratings yet
- Sadtem - Catalogue - Transformateurs de Courant Intérieurs - 2009Document24 pagesSadtem - Catalogue - Transformateurs de Courant Intérieurs - 2009ZorbanfrNo ratings yet
- MDS9000 - Troubleshooting GuideDocument560 pagesMDS9000 - Troubleshooting Guidegopi123456uNo ratings yet
- Cs 109Document1 pageCs 109paul13136No ratings yet