Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verbal Tenses Table v3
Verbal Tenses Table v3
Uploaded by
Repollo-Alias Abduscan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Verbal tenses table v3 (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesVerbal Tenses Table v3
Verbal Tenses Table v3
Uploaded by
Repollo-Alias AbduscanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
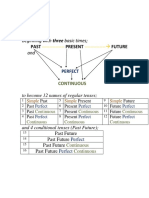
English Verbal tenses
Past Present Future Conditional
2.Past simple 1. Present simple 9. Future simple 13. Conditional
Subject + verb –ed Subject + verb Subject + will + verb Subject+ would+ verb
Subject + irregular verb 3rd person + verb-s
Yesterday, last week,… Everyday, every Monday,...
4.Past continuous 3. Present continuous 10. Future continuous
Subject+ to be+ verb-ing Subject+ to be+ verb-ing Subject + will+ be+ verb-ing
(was/ were) (am/ is/ are) Tomorrow, next week
While, during the afternoon Now, at this moment, …
6.Past perfect 5. Present perfect 11. Future perfect 14. Conditional perfect
Subject + had+ past participle Subject + has/have+ past Subject + will+ have + past Subject+ would+ have+ past
“before” participle participle (3rd column) participle
For, since, … By this time tomorrow, at 3 o’clock
tomorrow
8. Past perfect continuous 7.Present perfect 13. Future perfect continuous
Subject+ had+ been+ verb-ing continuous will+have+to be (been)+v-ing
By…, when…, next summer…
Subject+ has/have+ been +
verb-ing
12. Going to
Subject+ to be+ going to+
infinitive
(am /is/ are)
This afternoon, tomorrow, next
week, next month..
Infinitive: verb
Gerund: verb-ing
Past participle: regular verbs: verb-ed
irregular verbs: 3rd column of the list
Modal verbs: Subject+ modal verb+ infinitive
Modal verbs: can, could, may, might, must, have to, need, should, ought to, will, would.
Past Present Future Conditional
2. Past simple: Se usa para acciones 1. Present simple: Se usa para 9. Future simple: Se usa para 13. Conditional: Se usa para
puntuales y acabadas en el pasado. acciones habituales. acciones en el futuro. hablar de una situación hipotética en el
“He played football last Sunday.” “I “He plays football every Sunday “I will go to university.” “I will live in a presente o futuro. Se usa como forma cortés,
went to Mary’s house last Monday.” morning” “I go to the swimming-pool big house.” “She will be rich” “She educada, para pedir algo.
“He didn’t play football yesterday” everyday.” won’t be poor.” “Will she travel?” “I would go to London, if I had
“Did you go to Mary’s house?” “He doesn’t play football.” “Do you money to pay the ticket.” “I wouldn’t
go to the swimming-pool?” go to Paris.”
“Would you like a cup of tea”
4. Past continuous: Se usa para 3. Present continuous: Se usa 10. Future continuous: Se usa
acciones durativas en el pasado. Se usa para para acciones en el presente. para acciones contínuas, durativas, en el
contrastar una acción más larga con otra más “I’m reading a book now.” “Are you futuro.
corta o puntual. Se usa para describir ‘el telón reading a book?” “He isn’t playing the “By this time tomorrow she will be
de fondo’ de una acción. piano now” driving to Madrid.” “Tomorrow
“While he was painting the house, she Se usa para acciones planificadas y afternoon he will be leaving.”
phoned him.” “Mary was walking on organizadas en el futuro, similar al “going
the sidewalk, suddenly, somebody took to.”
her bag.” “Was she walking on the “He’s seeing Peter this afternoon.”
sidewalk?”
6. Past perfect: Se usa para acciones 5. Present perfect: Se usa para 11. Future perfect: Se usa para 14. Conditional perfect : Se
en el pasado. Cuando queremos marcar la acciones que han empezado en el pasado y acciones acabadas en el futuro. usa para hablar de una situación hipotética
diferencia entre una acción en el pasado y otra llegan hasta el presente. (No existe un tiempo “At 3 o’clock tomorrow, he will have en el pasado.
anterior a esta. En past perfect va la acción equivalente al 100% en castellano) left London.” “I would have told him the truth, if I
‘más antigua’ y en past simple la ‘más “I’ve lived in this house since 1990.” 13. Future perfect continuous: had seen him.” (but I didn’t see him)
nueva.’ (I’m living in this house) se usa para una acción que se estará
“My parents had arrived home, when I “He has worked here for 4 years.” completando en el future, enfatiza la
arrived.” “Has he worked here for 6 years?” “He continuidad.
“When we arrived at the office we saw hasn’t worked here for 7 years” “When she moves to New York next
that somebody had stolen our summer, she will have been teaching
computer.” English for 10 years”.
8. Past perfect continuous: Se 7. Present perfect continuous: 12. Going to: Se usa para acciones
usa en los mismos casos que el past perfect Se usa en los mismos casos que el present planeadas en el futuro.
simple, pero cuando queremos remarcar que perfect, pero cuando queremos remarcar que “I’m going to see Mary this afternoon.”
la acción es durativa, o cuando queremos hacer la acción es durativa, o cuando queremos hacer “She’s going to the cinema with Peter
énfasis en el hecho de que la acción es larga. énfasis en el hecho de que la acción es larga. tonight.” “She isn’t going with Mary.”
“Peter had been talking to her for 2 “I have been living in this house since “Look at those clouds, it’s going to
hours before I arrived.” 1980, and I’m tired, I want to move to rain”
another house.”
You might also like
- Uses of GetDocument3 pagesUses of GetCatalina TranescuNo ratings yet
- Rumus TensesDocument5 pagesRumus TensesNonny Tentia MNo ratings yet
- Institute of Language1Document4 pagesInstitute of Language1Wilmer CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Tarea de InglesDocument4 pagesTarea de InglesCedeño WilmerNo ratings yet
- HandbookDocument1 pageHandbookMUHAMMED FARSIN ENo ratings yet
- Los Angeles de Chimbote Catholic UniversityDocument3 pagesLos Angeles de Chimbote Catholic UniversityAbel Tuesta ThomasNo ratings yet
- Tenses: I. Present 1. Simple Present TenseDocument9 pagesTenses: I. Present 1. Simple Present Tensemichael100% (5)
- Grammar Tenses + Word OrderDocument8 pagesGrammar Tenses + Word Orderbusra dereNo ratings yet
- Review English GrammarDocument17 pagesReview English GrammarVictor BernardesNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Vs Past SimpleDocument24 pagesPast Perfect Vs Past Simpleaalliiccjjaa.statkiewiczNo ratings yet
- 30 Important Grammar PointsDocument4 pages30 Important Grammar PointsMacaNo ratings yet
- 0.3. English Verb Tenses - UsesDocument1 page0.3. English Verb Tenses - UsesTheGaMer ROTNo ratings yet
- PDF 22apr24 0348 SplittedDocument2 pagesPDF 22apr24 0348 SplittedkawieshmatauhasabsNo ratings yet
- Chuyen de Bi Dong, Gian TiepDocument4 pagesChuyen de Bi Dong, Gian Tieptrieunhi2611No ratings yet
- 12 English TenseDocument10 pages12 English TenseKido GroupNo ratings yet
- GramarDocument24 pagesGramaraalliiccjjaa.statkiewiczNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument18 pagesEnglishAna CNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument21 pagesPresent Tenseadinda putriNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH GRAMMAR 5 (Lengkap 15 11 15)Document65 pagesENGLISH GRAMMAR 5 (Lengkap 15 11 15)j chanNo ratings yet
- Name: Beta Gustilawati NPM: 16310048 Class Perth in TuesdayDocument10 pagesName: Beta Gustilawati NPM: 16310048 Class Perth in TuesdayAzahrah Mawaddah IINo ratings yet
- Contracciones: en Argot Se Contrae Going To en Gonna: Un Ejemplo Claro Es La OraciónDocument4 pagesContracciones: en Argot Se Contrae Going To en Gonna: Un Ejemplo Claro Es La Oracióninternet compudellNo ratings yet
- Clase 9 - English 2Document15 pagesClase 9 - English 2casuda1818No ratings yet
- Mixed ConditionalDocument2 pagesMixed ConditionallisaNo ratings yet
- Tense Structure Function ExampleDocument2 pagesTense Structure Function Examplenano yyNo ratings yet
- The Passive, Causative Constructions, Personal and Impersonal Passive Constructions.Document4 pagesThe Passive, Causative Constructions, Personal and Impersonal Passive Constructions.Hugo AguiarNo ratings yet
- Câu Tường Thuật LT-BTDocument5 pagesCâu Tường Thuật LT-BTthuyarmy61No ratings yet
- Future in The PastDocument21 pagesFuture in The PastAlina SemeniukNo ratings yet
- Loi Noi Gian TiepDocument5 pagesLoi Noi Gian TiepNguyễn Bảo Gia HânNo ratings yet
- Sequence of TensesDocument5 pagesSequence of TensesGabriela ScaeteNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Vs Past Simple ExplanationDocument10 pagesPast Continuous Vs Past Simple ExplanationMarianci Roblero gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Sujeto + Said (That) .-Sujeto + Told + C. Indirecto + (That) .Document2 pagesSujeto + Said (That) .-Sujeto + Told + C. Indirecto + (That) .bpxamzNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan English Class - Beginner To Intermediate LevelDocument3 pagesPembahasan English Class - Beginner To Intermediate LevelNendra SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review Packet (Updated) - 2Document9 pagesGrammar Review Packet (Updated) - 2Luke RaffantiNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousSorana PaleuNo ratings yet
- Note NG Pháp TA Nâng CaoDocument10 pagesNote NG Pháp TA Nâng Cao2153801011085No ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: The Ninth Week AssignmentDocument7 pagesBahasa Inggris: The Ninth Week AssignmentRafly RoyanNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech - WorksheetsDocument20 pagesIndirect Speech - WorksheetsDavid KhalatyanNo ratings yet
- Cliff's (Module 3) PDFDocument43 pagesCliff's (Module 3) PDFMario AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Ingles 2Document5 pagesIngles 2Pablo AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Conditional: Complete The Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional: Complete The Conditional Sentencesناكست لافلNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Future-in-the-PastDocument4 pagesModule 13 Future-in-the-PastВиктор ОблоговNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - Indirect-Speech-Practice-Test-No-1 PDFDocument9 pages(123doc) - Indirect-Speech-Practice-Test-No-1 PDFKhánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Semester 1Document7 pagesRangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Semester 1alifiaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesPassive Voiceoj.rj.001No ratings yet
- Past Simple Tense: - (To Be +ing.)Document6 pagesPast Simple Tense: - (To Be +ing.)Miljana KrunicNo ratings yet
- Заняття 5. The Past IndefiniteDocument3 pagesЗаняття 5. The Past IndefiniteІрина МиськівNo ratings yet
- Tenses - TableDocument2 pagesTenses - TableAnuradha MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Seance 02 PDFDocument4 pagesSeance 02 PDFdeux icNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesConditional SentencesrahmatNo ratings yet
- 16 TensissDocument5 pages16 TensissAwfa PrintingNo ratings yet
- Infografía de Proceso Rompecabezas Sencillo ColoridoDocument1 pageInfografía de Proceso Rompecabezas Sencillo ColoridoBrayan BuitragoNo ratings yet
- PastDocument3 pagesPastJhonatan AguilarNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (3) 0Document3 pagesReported Speech (3) 0MariolaNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever Made Mud Pies on a Hot Summer Day?: This Is a Bitty BookFrom EverandHave You Ever Made Mud Pies on a Hot Summer Day?: This Is a Bitty BookNo ratings yet
- Ingles Gramatica Facil Varios AutoresDocument2,091 pagesIngles Gramatica Facil Varios AutoresMelany Nair Uran Martinez100% (1)
- TOEFL EXERCISES Day1 +explanationDocument13 pagesTOEFL EXERCISES Day1 +explanationJenniferNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and PrepositionDocument3 pagesConjunction and Prepositionzurriyata thaibahNo ratings yet
- Syntax 10Document2 pagesSyntax 10Hendra UwaisNo ratings yet
- English SkillDocument42 pagesEnglish SkillRENGANATHAN PNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses and Relative Adverbs Sentence Transformation Rephrasing Exercises - 130432Document3 pagesRelative Clauses and Relative Adverbs Sentence Transformation Rephrasing Exercises - 130432Dewa KagamineNo ratings yet
- B.ingg Kel 6-2Document23 pagesB.ingg Kel 6-2FauziahNo ratings yet
- Connector SummaryDocument18 pagesConnector SummaryledracNo ratings yet
- Gestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeDocument8 pagesGestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeOscar FiscalNo ratings yet
- The Ing As A Noun, Verb, Adjective, Subject, Object, Adverb, or ClauseDocument2 pagesThe Ing As A Noun, Verb, Adjective, Subject, Object, Adverb, or ClauseValentinaNo ratings yet
- 5678 Short No PrepDocument3 pages5678 Short No PrepStephen SuttonNo ratings yet
- Sentence TypesDocument1 pageSentence TypesIsaias FernándezNo ratings yet
- Cronograma de Conteúdos para Aprender Inglês SozinhoDocument6 pagesCronograma de Conteúdos para Aprender Inglês SozinhoEllen LeticiaNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Clauses of Condition (Part 1 and 2)Document7 pagesAdverbial Clauses of Condition (Part 1 and 2)zerguini99No ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Pilihan GandaDocument5 pagesConditional Sentence Pilihan GandaADES SETIA PUTRINo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument32 pagesPronounsSantomi Fitrada100% (2)
- Preface: Test of English For Academics (TOEFA) - Language Center UIN SGD BandungDocument149 pagesPreface: Test of English For Academics (TOEFA) - Language Center UIN SGD BandungRatri HiusenaNo ratings yet
- Basic Writing SkillsDocument141 pagesBasic Writing SkillsFanuel DereseNo ratings yet
- Verb Phrases PRACDocument8 pagesVerb Phrases PRACCristobal Eduardo Castillo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice ExerciseDocument4 pagesActive and Passive Voice ExercisedthaaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Basic Japanese Language (FLES 102) : Basic Word Order and ParticlesDocument4 pagesModule 2 in Basic Japanese Language (FLES 102) : Basic Word Order and ParticlesClarisse EsmoresNo ratings yet
- ConditonalsDocument5 pagesConditonalsGabriel CastellamareNo ratings yet
- Class Notes c1Document14 pagesClass Notes c1la titiNo ratings yet
- Structure Skill 5Document3 pagesStructure Skill 5api-262133173No ratings yet
- Post-Modifiers (Cont'd) : Do Exercise 4.1, 4.2Document17 pagesPost-Modifiers (Cont'd) : Do Exercise 4.1, 4.2twy113No ratings yet
- Seminar 4. Word-Formation in EnglishDocument3 pagesSeminar 4. Word-Formation in EnglishАнастасия СиваничNo ratings yet
- Pearson Readers Grammar Contents WebDocument1 pagePearson Readers Grammar Contents WebitsgiseNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument34 pagesVerbsKen Daniel Oracion100% (1)
- Makalah Adjective ClauseDocument12 pagesMakalah Adjective Clausesaimi duaNo ratings yet