Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9FM0 Topic Test - CP - 13 - Hyperbolic Functions MS PDF
9FM0 Topic Test - CP - 13 - Hyperbolic Functions MS PDF
Uploaded by
hardywkingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9FM0 Topic Test - CP - 13 - Hyperbolic Functions MS PDF
9FM0 Topic Test - CP - 13 - Hyperbolic Functions MS PDF
Uploaded by
hardywkingCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic Test
Pearson Edexcel GCE Mathematics (9FM0)
Paper 01 & 02 - Core Pure
Hyperbolic Functions – Mark Scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
Pearson: helping people progress, everywhere
Pearson aspires to be the world’s leading learning company. Our aim is to help everyone progress in their
lives through education. We believe in every kind of learning, for all kinds of people, wherever they are in
the world. We’ve been involved in education for over 150 years, and by working across 70 countries, in 100
languages, we have built an international reputation for our commitment to high standards and raising
achievement through innovation in education. Find out more about how we can help you and your
students at: www.pearson.com/uk
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Core Pure: Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
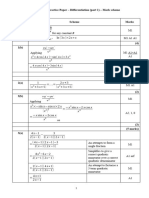
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
1 7 sinh x 14 (e x − e − x )
− = 5 x −x − x −x = 5 M1
cosh x cosh x e +e e +e
14 − (e x − e− x ) = 5(e x + e− x ) 6e x − 14 + 4e− x = 0 A1
3e2 x − 7e x + 2 = 0 (3e x − 1)(e x − 2) = 0 M1
1 A1
ex = or 2
3
x = ln( 13 ) or ln2 B1ft
(5)
Alternative Write 7 – sinhx = 5coshx, then use exponential substitution M1
(i) 7 − 12 (e x − e− x ) = 52 (e x + e− x )
Then proceed as method above.
Alternative (7sechx − 5)2 = tanh 2 x = 1 − sech 2 x M1
(ii)
50sech 2 x − 70sechx + 24 = 0 A1
2(5sechx − 3)(5sechx − 4) = 0 M1
sechx= 53 or sechx= 54 A1
x = ln( 13 ) or ln2 B1ft
(Total 5 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Core Pure: Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
2(a)
(Total 8 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Core Pure: Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
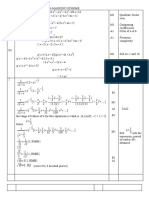
3 1 1
dy 1 (1 + x 2 ) 2 − x 2 (1 + x 2 ) − 2
= .
dx x2 (1 + x 2 )
−
1
1 + x2 M1M1A1
1 1
−
(1 + x ) − x 2 (1 + x )
2 2 2 2
1
NB =
(1 + x 2 )
3
(1 + x 2 ) 2
1
= * A1*
1 + x2
(Total 4 marks)
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
4 e x − e− x 10
5 x −x + 7 = x −x B1
e +e e +e
5(e − e ) + 7(e x + e− x ) = 10
x −x
5(e2 x − 1) + 7(e2 x + 1) = 10e x M1
12e − 10e + 2 = 0
2x x
A1
6e2 x − 5e x + 1 = 0 (3e x − 1)(2e x − 1) = 0 M1
x = ln( 13 ), ln( 12 ) A1
(Total 5 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
5 (a) e x − e− x
e x − e− x e2 x − 1
tanhx = x 2 − x or x or M1
e +e e + e− x e2 x + 1
2
2
e x − e− x (e 2 x + e −2 x + 2) − (e 2 x + e −2 x − 2)
1 − tanh x = 1 − x
2
−x = dM1
e + e (e x + e − x ) 2
2e x .2e− x
=
(e x + e− x ) 2
4
= x − x 2 = sec h 2 x * A1*
(e + e )
(3)
(b) Ignore any imaginary solutions in (b)
e − e e + e− x
x −x x
4 − 3 =3 M1
2 2
e x − 7e− x = 6
e2 x − 6e x − 7 = 0 M1
(e x + 1)(e x − 7) = 0 e x = ... M1
x = ln 7 or awrt 1.95 A1
(4)
(Total 7 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
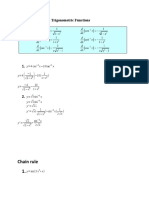
6
dy x
(a) (i) = + arcsin x M1 A1
dx (1 − x 2 )
(2)
(ii) 1 2 3 + B1
At given value derivative = + =
3 6 6
(1)
(b) dy 6e 2x M1 A1
=
dx 1 + 9e 4 x
6 M1
= −2 x
e + 9e2 x
3 M1
=5
2 (e
2x −2 x
+ e ) + 42 (e 2 x − e −2 x )
dy 3 A1* cso
=
dx 5cosh 2 x + 4sinh 2 x
(5)
(Total 8 marks)
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
7(a)
x2 − 2 x + 3 = ( x − 1)2 + 2 M1A1
1
dx = arsinh ( f ( x) ) M1
( x − 1) 2 + 2
2
x − 1 1
ars inh = arsinh A1
2 1 2
(4)
(b) e sinh x = e
2x 2x
( e −e
x
2
−x
) M1
1
2 (e3 x − e x ) A1
(e3 x − e x ) dx = 12 ( 13 e3 x − e x )
1 1
1
2
0
0 M1
= 1
2 ( 1
3 e −e )−
3 1 1
2 ( 1
3 e −e
0 0
)
e3 e 1
= − + A1
6 2 3
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
8(a) y = arcoth x coth y = x
or e.g. B1
u = arcoth x coth u = x
cosh y dx sinh 2 y − cosh 2 y 1
x= = 2 = − M1
sinh y dy sinh y sinh 2 y
dx
= −cosech 2 y = 1 − coth 2 y
dy
dy 1 1
= = * A1* (3)
dx 1 − coth y 2
1 − x2
dy 1
y = ( arcoth x ) = 2 ( arcoth x )
2
(b) B1
dx 1 − x2
d2 y
dx 2
=
2
1 − x2
(1 − x )
2 −1
+ 4 xarcoth x (1 − x )
2 −2
M1
(
2 1 − x2 ) 1
+ 2arcoth x 2 x
= 4 xarcothx + 2
2
d y 1− x
2
=
(1 − x ) (1 − x2 )
2 2
dx 2 2 A1
d2 y 2 4 xarcothx + 2 2arcoth x
(1 − x ) 2
− 2x
dy
= 1− x ( )
− 2x
( )
1− x
2 2 2
dx dx
1 − x2
M1
or
d2 y dy
(1 − x2 ) dx 2
=
2
1− x 2
+ 2x
dx
d2 y
(1 − x2 ) dx 2
dy
− 2x =
2
dx 1 − x 2
A1 cso (5)
(Total 8 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
A level Further Mathematics Topic Test – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
9 (a) dy 1 − 12 1
=2x B1, M1
dx 1 + ( x )2
dy 1
x 2
−1
1
= 2 = A1
dx 1+ x 2 x(1 + x) (3)
(b) 4
1
dx = 2ar sinh x 1
4
4 M1
1
4
x( x + 1)
= 2ar sinh 2 − 2ar sinh( 12 ) M1
= 2 ln(2 + 5 ) - 2ln( 12 + 5
) M1
4
(2 + 5) 2(2 + 5) 2( 5 + 2)( 5 − 1) (3 + 5)
2 ln = 2 ln = 2 ln = 2 ln M1
( + ( ))
1
2
5
4
(1 + 5) ( 5 + 1)( 5 − 1) 2
(3 + 5)(3 + 5) 14 + 6 5 7 3 5
= ln = ln = ln + A1 A1
4 4 2 2 (6)
Alternative dy 1 − 12
(i) Use sinhy = x and state cosh y = x B1
dx 2
for part (a)
1 −1 1 − 12 M1
dy 2 x x
2
= = 2
dx 1 + sinh 2 y 1 +
( x ) 2
dy 1
x 2 −1
1 A1
= 2 =
dx 1+ x 2 x(1 + x)
Alternative dx M1
(i) Use x = tan 2 , = 2 tan sec2 to give 2 sec d = 2 ln(sec + tan
d
for part (b)
= 2ln(sec + tan tan = 1 i.e. use of limits
tan = 2
M1
2
then proceed as before from line 3 of scheme
Alternative 1 x + 12
(ii) for part Use [( x + 12 ) 2 − 14 ]
dx = arcosh 1
2
M1
(b)
= arcosh 9 − arcosh( 32 ) M1
= ln(9 + 80 ) - ln( 32 + 12 5 ) M1
(9 + 80) 2(9 + 80)(3 − 5)
= ln = ln , M1
( 32 + 12 5) (3 + 5)(3 − 5)
2(9 + 4 5)(3 − 5) 7 3 5
= ln = ln + A1 A1
(3 + 5)(3 − 5) 2 2
(Total 9 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
A level Further Mathematics Topic Test – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
10(a)
(Total 9 marks)
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
2
11 (a) ar sinh 2 x, + x M1A1, A1
1 + 4 x2
(3)
2
2x
arsinh2 xdx = xar sinh 2 x 0
2
2
(b) − dx M1 A1ft
0
0 1 + 4x2
2
xar sinh 2 x 0 − (1 + 4 x 2 ) 2
2 1 1
= M1 A1
2 0
= 2arsinh2 2 − [ 32 − 12 ] DM1
= 2 ln(3 + 2 2) − 1
M1 A1
(7)
(Total 10 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
12 (a) f(x) = 5cosh x – 4sinh x = 5 12 (e x + e− x ) − 4 12 (e x − e− x ) M1
= 12 (e x + 9e− x ) A1 cso (2)
(b) 1
2 (e x + 9e− x ) = 5 e2 x − 10e x + 9 = 0 M1 A1
So e x = 9 or 1 and x = ln9 or 0 M1 A1
(4)
Integral may be written
x
2e
(c) 2x dx B1
e +9
2 ex
This is arctan M1 A1
3 3
Uses limits to give 23 arctan1 − 23 arctan( 13 ) = 23 4 − 23 6 = 18
*
DM1 A1cso
(5)
(Total 11 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
Question
Scheme Marks
Number
15 + 2 x − x 2 = 16 − ( x − 1)
2
13 (a) (i) B1
1 x −1
dx = arcsin M1 A1
16 − ( x − 1) 4
2
5
x − 1 1
arcsin 4 = arcsin1 − arcsin 2 dM1
3
= A1 (5)
3
(ii) e x + e− x e x − e− x
5cosh x − 4sinh x = 5 − 4 B1
2 2
e x + 9e − x e x 9e − x
= or + M1
2 2 2
e2 x + 9
= * A1* (3)
2e x
du
(b) u = ex = ex B1
dx
2e x 2u du
dx = . M1
e2 x + 9 u +9 u
2
2 u
= arctan ( + c ) dM1
3 3
2 ex
= arctan ( +c ) A1 (4)
3 3
(Total 12 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
9FM0 Practice Paper – Hyperbolic Functions – Mark scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2023
You might also like
- Edexcel GCE Core 3 Mathematics C3 6665 Advanced Subsidiary Jan 2009 Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesEdexcel GCE Core 3 Mathematics C3 6665 Advanced Subsidiary Jan 2009 Marking Schemerainman875No ratings yet
- Differentiation Part 1 MSDocument8 pagesDifferentiation Part 1 MSAlizaman AlibhaiNo ratings yet
- Kluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Document9 pagesKluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Rex KalNo ratings yet
- 1920F4T1M1MSDocument8 pages1920F4T1M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- C4 e MSDocument4 pagesC4 e MSshah143No ratings yet
- NSGHS 2010 2U Trial SolutionsDocument11 pagesNSGHS 2010 2U Trial SolutionsYon Seo YooNo ratings yet
- Midterm2009 MarkingschemeDocument5 pagesMidterm2009 MarkingschemeRabiah100% (1)
- 1920F4T2M1MSDocument11 pages1920F4T2M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- 15-16 Spring MidtermDocument8 pages15-16 Spring MidtermAmeer Hazim Ghazi Assa’dNo ratings yet
- 2017-2-Joh-Batu Pahat-ADocument7 pages2017-2-Joh-Batu Pahat-AMichelles JimNo ratings yet
- Bol1 CodigoDocument13 pagesBol1 CodigospamtonkrisNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3Document8 pagesMark Scheme June 2007 6665 Core Mathematics C3AhmedNo ratings yet
- Core Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiarynbergman_barrettNo ratings yet
- Solomon A MS - C3 Edexcel PDFDocument4 pagesSolomon A MS - C3 Edexcel PDFThamina AktherNo ratings yet
- SMK Methodist Sibu, Sarawak AnsDocument7 pagesSMK Methodist Sibu, Sarawak Ansvinethirra nantha kumarNo ratings yet
- اسئلة سنوات سكند كالكولس 1 موقع الفريد في الفيزياء .Document51 pagesاسئلة سنوات سكند كالكولس 1 موقع الفريد في الفيزياء .tharmohammed512No ratings yet
- Differentiation: Skills CheckDocument11 pagesDifferentiation: Skills CheckThomas NgangaNo ratings yet
- N2 Mathematics November 2016 MemorandumDocument11 pagesN2 Mathematics November 2016 MemorandumKhodani Given MukhumuliNo ratings yet
- 5e0270e6-Diff Calc PEP 2 S2 2019 MSDocument16 pages5e0270e6-Diff Calc PEP 2 S2 2019 MSArjun DubeNo ratings yet
- Second Summer 21 22Document8 pagesSecond Summer 21 22Galia Mohammad EssaNo ratings yet
- January 2009 MS - C3 OCR MEIDocument4 pagesJanuary 2009 MS - C3 OCR MEIPapersNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument5 pagesDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsRyan TuyanNo ratings yet
- G 1 1 P - C M (3 0 S) : Final Practice Exam Answer KeyDocument34 pagesG 1 1 P - C M (3 0 S) : Final Practice Exam Answer KeyHatdogNo ratings yet
- 2016 MYE 3E AMath Marking SchemeDocument9 pages2016 MYE 3E AMath Marking SchemeZhao Yu QingNo ratings yet
- Maclaurin SerieskeyDocument6 pagesMaclaurin Serieskeymbjanjua35No ratings yet
- 2019 Sem 2 Kte Kulim, Kedah (A)Document4 pages2019 Sem 2 Kte Kulim, Kedah (A)Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Free State Maths Test March 2024 MemoDocument5 pagesGR 11 Free State Maths Test March 2024 MemotryhardeillyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - SolutionsDocument17 pagesMathematics - SolutionsMichelli YonathaNo ratings yet
- 2020 1 Me Munsyi Abdullah ADocument7 pages2020 1 Me Munsyi Abdullah ALIANG HUI YI MoeNo ratings yet
- 2019 2 Ked Ktek MSDocument4 pages2019 2 Ked Ktek MSPeng Peng KekNo ratings yet
- Functions Revision WorksheetDocument28 pagesFunctions Revision WorksheetKLNo ratings yet
- Solomon J MSDocument4 pagesSolomon J MSSachitra WijethungaNo ratings yet
- Ans&Sol JEE (Main) 2024 Ph-1 (31!01!2024) Evening (ActualPaper)Document26 pagesAns&Sol JEE (Main) 2024 Ph-1 (31!01!2024) Evening (ActualPaper)Pratika SinghNo ratings yet
- Test 3 - SMJKCH (Kota Bharu) - AnsDocument8 pagesTest 3 - SMJKCH (Kota Bharu) - AnsLIM YEE WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- M1A-P - Z Apo Ctov Ytest1Document4 pagesM1A-P - Z Apo Ctov Ytest1UCCJANo ratings yet
- Solomon E MS - C2 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon E MS - C2 EdexcelMelody NationNo ratings yet
- E1 2016-2-Terengganu-ADocument5 pagesE1 2016-2-Terengganu-APeng Peng KekNo ratings yet
- 2223F4T1M1MSDocument8 pages2223F4T1M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment Mat183Document22 pagesLab Assignment Mat183Ammar AnuarNo ratings yet
- MAT 1300 Midterm 2 Booklet Solutions PDFDocument41 pagesMAT 1300 Midterm 2 Booklet Solutions PDFdongmianjunNo ratings yet
- January 2007 MS - C3 EdexcelDocument7 pagesJanuary 2007 MS - C3 Edexceljohn mNo ratings yet
- MAT 1300 Midterm 2 Test Package Solutions Fall 2019 1 PDFDocument150 pagesMAT 1300 Midterm 2 Test Package Solutions Fall 2019 1 PDFdongmianjunNo ratings yet
- 5b. Mixed Exam-Style Questions On Exponentials and Logarithms - AnswersDocument2 pages5b. Mixed Exam-Style Questions On Exponentials and Logarithms - Answerswaleedkhan567799No ratings yet
- JEE MAIN QP 09 April 2024 An MathematicsDocument8 pagesJEE MAIN QP 09 April 2024 An Mathematicsvamshimanikanta06No ratings yet
- C3 Practice Paper A5 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesC3 Practice Paper A5 Mark SchemegenmissNo ratings yet
- First Year Higher Secondary Model Examination, June 2022: Answer KeyDocument3 pagesFirst Year Higher Secondary Model Examination, June 2022: Answer KeyYADUKRISHNAN K NAIRNo ratings yet
- 2016 mm34 Exam 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2016 mm34 Exam 1 SolutionsSunny XiaNo ratings yet
- AdrianoDocument1 pageAdrianoLuis MorienteNo ratings yet
- ST Paul 2019 Answer P1Document7 pagesST Paul 2019 Answer P1g-22255924No ratings yet
- Duhok Polytechnic University Technical College of Engineering Highway and Bridge Subject: Calculus II Lecturer's Name: Abdulaziz RASHIDDocument27 pagesDuhok Polytechnic University Technical College of Engineering Highway and Bridge Subject: Calculus II Lecturer's Name: Abdulaziz RASHIDJayHatNo ratings yet
- Kulai (A) P1 19Document7 pagesKulai (A) P1 19Jean TanNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems Course: ARJUN: Target: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2022Document11 pagesDaily Practice Problems Course: ARJUN: Target: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2022Anubhooti JainNo ratings yet
- A Jjeb P 425 1 Maths GuideDocument19 pagesA Jjeb P 425 1 Maths Guidewasswa derickNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 MELAKA SMK Gajah Berang - MATHS QADocument6 pages2014 2 MELAKA SMK Gajah Berang - MATHS QASK67% (3)
- Serie EquationsDocument2 pagesSerie EquationsZA9OF FFNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Resueltos Del Hermano de MieDocument8 pagesEjercicios Resueltos Del Hermano de MieROSA LUZ DEPAZ APESTEGUINo ratings yet
- Editor de EcuacionesDocument1 pageEditor de EcuacionesJasmin Limbania LopezNo ratings yet
- KEY Math 115-009 Calculus 1 Circle One: Grade My Work / Answers Exam 2Document3 pagesKEY Math 115-009 Calculus 1 Circle One: Grade My Work / Answers Exam 2mantaray_09No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Properties of Pure SubstancesZainhumNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Field - DPP 01 - (Parishram 2.0 2023)Document3 pagesElectric Charges and Field - DPP 01 - (Parishram 2.0 2023)2007ameliakimNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Comerical Protos Cf1 Cf15 Cf415 em InglesDocument1 pageCatalogo Comerical Protos Cf1 Cf15 Cf415 em InglesmaxNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric FLANNDocument9 pagesTrigonometric FLANNphysics loverNo ratings yet
- Counter Fort Retaining WallDocument3 pagesCounter Fort Retaining WalljosefNo ratings yet
- Math 230 Section BE1/BB1 Introduction To Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesMath 230 Section BE1/BB1 Introduction To Differential Equationsmaths203No ratings yet
- General Physics: - Scientific Notation - Uncertainty in MeasurementDocument12 pagesGeneral Physics: - Scientific Notation - Uncertainty in MeasurementIchyNo ratings yet
- RM Assignment 2Document15 pagesRM Assignment 2SteveNo ratings yet
- Sombra Contra Las Armadas de La Oscuridad (Ultima Version) - 1-200Document200 pagesSombra Contra Las Armadas de La Oscuridad (Ultima Version) - 1-200cesarcambronero2911No ratings yet
- PM IS 7285 Part 2 FinalDocument10 pagesPM IS 7285 Part 2 FinalSatyadip TeraiyaNo ratings yet
- Cable XHHWDocument3 pagesCable XHHWederNo ratings yet
- Manhole Analysis PDFDocument15 pagesManhole Analysis PDFyoseph dejeneNo ratings yet
- Reverse Type PistonDocument9 pagesReverse Type PistonMirequip Mirequip100% (1)
- Question Bank On Unit ViDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit ViAayushNo ratings yet
- Standards For Suface Electromyography: The European Project Surface EMG For Non-Invasive Assessment of Muscles (SENIAM)Document6 pagesStandards For Suface Electromyography: The European Project Surface EMG For Non-Invasive Assessment of Muscles (SENIAM)mohsin aliNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Archetypal Ontology New Directions in Analytical Psychology 1St Edition Jon Mills PDFDocument63 pagesFull Chapter Archetypal Ontology New Directions in Analytical Psychology 1St Edition Jon Mills PDFjames.harris358100% (10)
- Was Lenin A Communist BengaliDocument16 pagesWas Lenin A Communist Bengalisayuj83No ratings yet
- Fin-Damage of ApfsdsDocument60 pagesFin-Damage of ApfsdsLalNo ratings yet
- Beam TheoryDocument38 pagesBeam Theorynirakaru123No ratings yet
- Reddy Et Al-2012-Hydrological ProcessesDocument15 pagesReddy Et Al-2012-Hydrological ProcessesNoman MirzaNo ratings yet
- PTSP Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesPTSP Objective QuestionsG SrilakshmiNo ratings yet
- Bolts Torque CalculatorDocument4 pagesBolts Torque Calculatorcaod1712No ratings yet
- 7e's - Electron ConfigurationDocument5 pages7e's - Electron ConfigurationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- User Manual - AlexMED Pro Trio 600W Software IIIDocument41 pagesUser Manual - AlexMED Pro Trio 600W Software IIIBelkys LebronNo ratings yet
- IPPP-II (Micro)Document121 pagesIPPP-II (Micro)Tinsaye HayileNo ratings yet
- Elastic Inversion Using Stack Seismic Data: Case Histories in ChinaDocument26 pagesElastic Inversion Using Stack Seismic Data: Case Histories in ChinaAdhita MeryantoNo ratings yet
- P&R Chapter 4 - 1 Steam PipesDocument41 pagesP&R Chapter 4 - 1 Steam PipesMike OtarraNo ratings yet
- Black-Litterman Framework To Test The Effectiveness of Technical Indicators in Portfolio OptimizationDocument14 pagesBlack-Litterman Framework To Test The Effectiveness of Technical Indicators in Portfolio OptimizationKoume UeNo ratings yet
- Technical Aptitude TestDocument4 pagesTechnical Aptitude Testnl_vaishakNo ratings yet
- Physics Full Syllabus Test - 1 (23-24)Document21 pagesPhysics Full Syllabus Test - 1 (23-24)gojosatoru101001No ratings yet