Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity Notes
Electricity Notes
Uploaded by
dhruvagg3210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesElectricity Notes
Electricity Notes
Uploaded by
dhruvagg321Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
ELECTRICITY
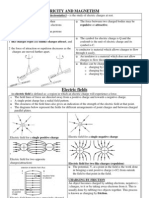
Properties of electric charge
● Electric charge is a scalar quantity. It can be of two types
only : positive and negative.
● Like charges repel each other while unlike charges attract each
other.
● Additivity of charge : The total charge of the body is the
algebraic sum of all the individual contributions by various
charges present on it, each being taken with its proper sign.
● Conservation of electric charge : Electric charge can neither
be created nor be destroyed.
● Quantisation of charge : Every charge is an integral multiple
of a certain smallest amount of charge that exists in nature.
This property of charge is called quantisation.Hence, the
charged bodies will have charges which are integral multiples
of the charge on electron
(e = 1.6 × 10 19 C.)
Q=±ne
● Charge is always associated with mass
● Charge is transferable
❖ Conductors and insulators
Electrical conductivity depends on how tightly the electrons
are bound to the nucleus of the atom. Some materials
have electrons that are tightly bound to the nucleus and are
not free to travel within the substance. These materials are
called insulators. Materials that have electrons in the
outermost regions of the atom that are free to travel are
called conductors.
Metals are good conductors as they have large number of
free electrons.
★ How clouds get charged?
During the development of a thunderstorm, the air
currents move upward while the water droplets move
downward. In such a condition, a churning cloud
formation causes water vapour molecules to collide,
resulting in a transfer of electrons between these
molecules. Cooling causes water vapour molecules to
condense into water droplets. The atoms in these
droplets hold onto electrons more readily than atoms in
water vapour, and thus the droplets become negatively
charged. Being heavier, these negatively charged water
droplets accumulate at the bottom of the cloud, causing
the bottom of the cloud to become negatively charged.
The top of the cloud, containing the rising water vapour,
becomes positively charged.
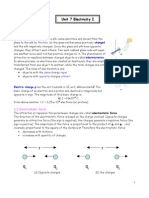
● Coulombs law : The force of attraction or repulsion between
two point charges q1 and q2 at rest is directly proportional to
the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the
square of the distance r between them and it always acts
along the line joining the charges.
where K is a constant of proportionality sometimes called electrical constant
or Coulombs constant.
For vacuum, the coulombs constant K = 1
—-----------=9 × 109 Nm2 C2
in SI system
4πε0
USES OF STATIC ELECTRICITY
● Photocopier : The electrostatic force that charged particles exert on one another plays
the central role in an office copier. The copying process is called xerography.
● Laser and Inkjet Printer
Electric potential
Electric potential at a point A in an electric field is the work done per unit positive test
charge in transporting it from infinitely far away to the point A
Current Electricity
Electric current : The rate of flow of electric charge through any
cross-section is called electric current.
●
● Electric current is a scalar quantity
● SI Unit of electric current : Ampere (A) ; 1 Ampere = 1
coulomb / sec = 1 C s-1
● Terminal voltage (V) : It is the potential difference across
the terminals of the source of emf (like battery) in the
external closed circuit
You might also like
- CXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesCXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and Magnetismdela278% (9)
- Electricity ReviewerDocument5 pagesElectricity Reviewertadashihamada021No ratings yet
- Electricity: By: Saurabh SinghDocument15 pagesElectricity: By: Saurabh SinghSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 ElectricityDocument30 pages1 ElectricitySajid AmanullahNo ratings yet
- Lesson#1 - Electric ChargesDocument14 pagesLesson#1 - Electric Chargesjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceDocument53 pagesElectrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceNo PainNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electric FieldsDocument132 pagesElectricity and Electric FieldsWebby ZimbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Electricity TheoryDocument15 pagesChapter - Electricity TheoryAisil JNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument36 pagesElectricitylunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Electricity IDocument9 pagesUnit 7 Electricity Itwy113No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 21 Part 2 - May 12Document21 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 21 Part 2 - May 12Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument18 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsYashwanthNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesElectrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsSONY SAB HDNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema TRDocument219 pagesPlus Two Physics Full Chapters-Seema TRanjimarv43No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Elecric Field-UpdateDocument53 pagesChapter 23 - Elecric Field-Updatewaelabood51No ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Physics 2Document3 pagesReviewer For General Physics 2Ezel MayNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Basic ConceptsDocument34 pages1.1 Basic ConceptsBORASCA EZEKIELNo ratings yet
- 2020 Wts 12 Electrostatics & EletricityDocument41 pages2020 Wts 12 Electrostatics & Eletricitylethabothebe079No ratings yet
- Aanhin Ko Ang Mahal Na Araw Kung Mahal Kita Araw ArawDocument7 pagesAanhin Ko Ang Mahal Na Araw Kung Mahal Kita Araw ArawJuan Carlos Viaje PimentelNo ratings yet
- Jack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsDocument6 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content PhysicsLoraNo ratings yet
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument23 pagesElectric Forces and Electric FieldsbrianhguyNo ratings yet
- Phy Notes 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPhy Notes 1 PDFDeepika VNo ratings yet
- Physics 1.8Document14 pagesPhysics 1.8Priya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Revision NotesDocument16 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 12 Revision NotesAryan ParasharNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge, Coulomb's Law-2Document20 pagesElectric Charge, Coulomb's Law-2christianrizelgNo ratings yet
- 5-7 PhysicsDocument93 pages5-7 PhysicsJohn SeñeresNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Physics All in One Notes by Seema ElizabethDocument219 pagesHsslive Xii Physics All in One Notes by Seema ElizabethQWERtyNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Part 1Document21 pagesElectricity - Part 1Anonymous CommentatorNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Physics by Byju'sDocument56 pages12th Grade Physics by Byju'sSoham ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document67 pagesChapter 23lucky03081981No ratings yet
- شابتر 1Document41 pagesشابتر 1HanNo ratings yet
- AP10006 Physics II: ElectricityDocument38 pagesAP10006 Physics II: Electricity白卡持有人No ratings yet
- Physics Grade - Xii: ElectrostaticsDocument51 pagesPhysics Grade - Xii: Electrostaticskarthikeyan annamalaiNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument76 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldGladys Lambayong100% (1)
- Physics Unacademy Iconic NotesDocument52 pagesPhysics Unacademy Iconic NotesSANJAY J100% (2)
- Electric DipoleDocument29 pagesElectric DipoleDr-Amr HesseinNo ratings yet
- Natsci2 Under Mr. Pili: ElectricityDocument27 pagesNatsci2 Under Mr. Pili: Electricityhhnflaws29No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and Magnetismkhrisannmiller12No ratings yet
- Electric Forces and FieldDocument39 pagesElectric Forces and FieldRado JaNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thDocument24 pagesElectricity - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thsyedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- Phys 91173 ReviseDocument8 pagesPhys 91173 ReviseBenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23, Part I: Electrical Charge. Coulomb's Law About Force Between Two Point Charges. Application of Coulomb's LawDocument13 pagesChapter 23, Part I: Electrical Charge. Coulomb's Law About Force Between Two Point Charges. Application of Coulomb's LawFaraz HumayunNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics by J Tiong PDFDocument31 pagesEngineering Economics by J Tiong PDFRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document18 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!ramanan13No ratings yet
- 1.1 Electrical Quantities and Units: Circuit, and Each Component of The Circuit Is Known As An ElementDocument19 pages1.1 Electrical Quantities and Units: Circuit, and Each Component of The Circuit Is Known As An ElementAbrha FtsumNo ratings yet
- X Class Physics ElectricityDocument7 pagesX Class Physics ElectricityPaarth BansalNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument31 pagesELECTROSTATICSSweet Krisyl LopezNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument9 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsSrushti ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document26 pagesLecture 8ansat5.ansatNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 02Document31 pagesElectrostatics 02nithin_v90No ratings yet
- ChargeDocument4 pagesChargeRana IslamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Stem ADocument29 pagesLesson 1 Stem AWen SeulNo ratings yet
- Engg Utilities 1Document39 pagesEngg Utilities 1ricaosio91No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Force Discharge Potential Notes Class 12 PDF DownloadDocument7 pagesElectrostatics Force Discharge Potential Notes Class 12 PDF DownloadGokul ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument47 pagesElectric FieldUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- +2 Physics Full Material E.MDocument90 pages+2 Physics Full Material E.MBalajiNo ratings yet
- CoulombsDocument47 pagesCoulombsTrishia LimpinNo ratings yet
- Check Point Notes - ElectricityDocument70 pagesCheck Point Notes - ElectricityaghayousufproNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MidtermDocument30 pagesQuiz 2 MidtermJoamerel Malonzo De LeonNo ratings yet
- A Simple Closed-Loop Active Gate Voltage Driver For Controlling Di - DT and DV - DT in IGBTs PDFDocument18 pagesA Simple Closed-Loop Active Gate Voltage Driver For Controlling Di - DT and DV - DT in IGBTs PDFzeevko1249No ratings yet
- Diss Hat Ecke 2016Document90 pagesDiss Hat Ecke 2016tran phamNo ratings yet
- For Accuracy and Safety: Globally ApprovedDocument4 pagesFor Accuracy and Safety: Globally ApprovedPedro LopesNo ratings yet
- SWAS OverviewDocument16 pagesSWAS OverviewtuyencntnNo ratings yet
- PDS4 2Document2 pagesPDS4 2akhyar98No ratings yet
- 8 MYP Physics Sem 2 29 Apr 2015 v01Document18 pages8 MYP Physics Sem 2 29 Apr 2015 v01kailaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Effect of Cutting Fluids in Turning Operation: Gokul Gopan, Smitha G. NairDocument6 pagesCase Study On Effect of Cutting Fluids in Turning Operation: Gokul Gopan, Smitha G. NairAnonymous l5PQDDkNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On The Thermal Performance of A Composite Board inDocument10 pagesNumerical Study On The Thermal Performance of A Composite Board inPedro MuttoniNo ratings yet
- Created by .. Shatakshi RDocument23 pagesCreated by .. Shatakshi RShatakshi RampureNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Insitu StressesDocument33 pagesCH 9 Insitu StressesALIKNFNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of A High-Speed PMSGDocument13 pagesOptimal Design of A High-Speed PMSGHuynh Thanh AnhNo ratings yet
- Is.7634.2.2012 0Document26 pagesIs.7634.2.2012 0Jagadeesh PuppalaNo ratings yet
- Es 103 - Module 9 - Moving LoadsDocument36 pagesEs 103 - Module 9 - Moving Loadsyrbbwababa05No ratings yet
- Investigation of Premature Pavement Distresses On Typical National Highway ProjectDocument28 pagesInvestigation of Premature Pavement Distresses On Typical National Highway ProjectProf. Prithvi Singh Kandhal100% (2)
- Asme SawDocument3 pagesAsme Sawhalil ozgunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Traffic Analysis TechniquesDocument48 pagesChapter 8 - Traffic Analysis TechniquesAhmad Daher67% (3)
- Hemiwedge Cartridge Valve Brochure April 2010Document8 pagesHemiwedge Cartridge Valve Brochure April 2010Heri SetyantoNo ratings yet
- Ultra Life ER14250 DatasheetDocument2 pagesUltra Life ER14250 DatasheetArslan AwanNo ratings yet
- Linear Differential Equation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesLinear Differential Equation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaZaw Moe Khine100% (1)
- Lab Exercise No. 6: Ideal Gas Law: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesLab Exercise No. 6: Ideal Gas Law: Department of Mechanical EngineeringJino BalingNo ratings yet
- MEC910 - Mid Term - Sem I 08-09Document7 pagesMEC910 - Mid Term - Sem I 08-09sh1999No ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesMidterm ExamRachel BasistoNo ratings yet
- UT ProbeDocument16 pagesUT ProbeHenry CruzNo ratings yet
- Thyratron PreambleDocument23 pagesThyratron PreamblealtamiroNo ratings yet
- Lego Little MechanismDocument9 pagesLego Little MechanismsudheerNo ratings yet
- Jit Term 3 FinalDocument82 pagesJit Term 3 Finalpreciousrebotile133No ratings yet
- Astm C 136 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm C 136 PDFJuan Jesus Garcia Reyes100% (2)
- Tesla ReceiversDocument5 pagesTesla ReceiversharishkumarsinghNo ratings yet
- Holes Crossword Puzzle AnswersDocument1 pageHoles Crossword Puzzle AnswersJAIME GERBOLÉS RIBASNo ratings yet