Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Uploaded by
bowieslyimCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 8K Light Multiple Choice TestDocument3 pages8K Light Multiple Choice Testapi-3698146100% (4)
- Rme Exam CoverageDocument1 pageRme Exam CoverageMarc100% (4)
- Heat Run Test For TransformerDocument8 pagesHeat Run Test For TransformerHosni Mohamed KassimNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 2)Document15 pagesUnit 14 Unit Test (Level 2)bowieslyimNo ratings yet
- 8J - Quick QuizDocument3 pages8J - Quick QuizMatthew ToppingNo ratings yet
- PhysicDocument36 pagesPhysicselbywNo ratings yet
- F TestDocument7 pagesF TestAbid SharifNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Test - ADocument8 pagesUnit 3 Test - Aapi-535415281No ratings yet
- CH 14.3 Quiz & AnsDocument6 pagesCH 14.3 Quiz & AnsAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)Document7 pagesKnowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)api-535415281No ratings yet
- 10s Student Copy UnitTest - D09-Apr-2021Document2 pages10s Student Copy UnitTest - D09-Apr-2021Yash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Task 3 Answers To Textbook QuestionsDocument4 pagesYear 7 Science Task 3 Answers To Textbook QuestionsTadmore Tutors TuitonNo ratings yet
- 5 6154457525488977613Document5 pages5 6154457525488977613ankith sNo ratings yet
- UH Science 44Document7 pagesUH Science 44yuniNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument10 pagesPhysics SQPSai VedantNo ratings yet
- Junoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIDocument186 pagesJunoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIkisuisoffbeatNo ratings yet
- 09 PU 2 IMP Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pages09 PU 2 IMP Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- CPP-2 - Wave Optics PDFDocument2 pagesCPP-2 - Wave Optics PDFADITYA TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Human Eye Test PaperDocument4 pagesHuman Eye Test PaperDeepak SalwaniNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Document12 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Umbra Screen: Opaque SphereDocument6 pagesUmbra Screen: Opaque SphereFilip MilisovNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionCinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- 15 Detecting EnvironmentDocument106 pages15 Detecting EnvironmenttoperissaNo ratings yet
- SR PHY SaqDocument12 pagesSR PHY SaqtattikotasatishNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Physics 10Document8 pagesTerm 2 Physics 10abcdNo ratings yet
- GR10 OT CumulativeDocument9 pagesGR10 OT CumulativenaeblahblahNo ratings yet
- Light - Worksheet 2 SCDocument7 pagesLight - Worksheet 2 SC。无名。。No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticssaniyainam74No ratings yet
- CW 1Document3 pagesCW 1ELECTRONIC BOY SHAURYANo ratings yet
- Kuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)Document11 pagesKuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)黑No ratings yet
- Class 12 CH 9 Ray & Wave OpticsDocument7 pagesClass 12 CH 9 Ray & Wave OpticsKumar PratikNo ratings yet
- Optics 27 YearsDocument15 pagesOptics 27 YearssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 1st YearDocument3 pagesCH 9 1st Yearfahad.qureshi7799No ratings yet
- Light Knowledge Organiser Quiz - Eco Black and WhiteDocument3 pagesLight Knowledge Organiser Quiz - Eco Black and White200651625No ratings yet
- Depth Reconstruction With Deep Neural Networks (Part 1)Document66 pagesDepth Reconstruction With Deep Neural Networks (Part 1)xuanhan1019No ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 29 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 29 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22abcdNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Wave Optics QB1Document12 pagesCh-11 Wave Optics QB1Angel SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 OpticsDocument24 pagesUnit 6 OpticsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- Photometry: Fundamental Physics Lab Journal O-6Document7 pagesPhotometry: Fundamental Physics Lab Journal O-6Phie-phie elexNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light FINALDocument9 pagesRefraction of Light FINALPrakritiNo ratings yet
- Edunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MDocument5 pagesEdunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MVIKRAM CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- x8ni27VJ6MxLGNaWJSrn PDFDocument21 pagesx8ni27VJ6MxLGNaWJSrn PDFPriya JindalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Notes - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Notes - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAshida AjmalNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument12 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- REFRACTION OF LIGHT by Prakash ProtectedDocument42 pagesREFRACTION OF LIGHT by Prakash ProtectedprakashNo ratings yet
- Yaan Ushni: Surjct: ScienceDocument6 pagesYaan Ushni: Surjct: ScienceSahej Kaur AroraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Wave Optics Class XiiDocument2 pagesAssignment Wave Optics Class XiiAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample 6 PhyDocument4 pagesSample 6 PhyFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences - Paper 1Document19 pagesPhysical Sciences - Paper 1Alaia McDonaldsNo ratings yet
- FSC Ch#10 (Series Test-9) 2017-2018Document2 pagesFSC Ch#10 (Series Test-9) 2017-2018chanochinkoNo ratings yet
- PRETEST - Electromagnetic Waves, Light & Optics WORDDocument9 pagesPRETEST - Electromagnetic Waves, Light & Optics WORDMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- 1 WoDocument4 pages1 Womayankt2147No ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 eDocument17 pagesNSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 e托普斯No ratings yet
- Human Eye & The Colorful World - Daily Home Assignment 03Document2 pagesHuman Eye & The Colorful World - Daily Home Assignment 03Smayan SethiNo ratings yet
- Phy3 2Document19 pagesPhy3 2Y AdaNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 5 (Physics)Document7 pagesPractice Sheet 5 (Physics)Parnika GuptaNo ratings yet
- XII - I PreBoard - PHYSICSDocument12 pagesXII - I PreBoard - PHYSICSBhawesh Kumar SoniNo ratings yet
- 02 03 Physical Optics 62-84Document6 pages02 03 Physical Optics 62-84eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Yenepoya Pu CollegeDocument20 pagesYenepoya Pu Collegeshaxm098No ratings yet
- Wave Optics Exercise (161-172) .PMDDocument12 pagesWave Optics Exercise (161-172) .PMDHemendra PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics NotesDocument44 pagesWave Optics NotesPrerna JhaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement Current Electromagnetic RadiationDocument23 pagesThe Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement Current Electromagnetic RadiationMadhav patilNo ratings yet
- Dose LimitsDocument3 pagesDose LimitsBOOBOONo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Element Builder: Element Builder Gizmo Shows An Atom With A SingleDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Element Builder: Element Builder Gizmo Shows An Atom With A SingleMicah Webster-Bass100% (1)
- Gain and The Threshold of Three-Dimensional Quantum-Box LasersDocument7 pagesGain and The Threshold of Three-Dimensional Quantum-Box LasersNitika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Some Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70Document4 pagesSome Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70KentNo ratings yet
- AC6 Module11Document22 pagesAC6 Module11Fred BorjaNo ratings yet
- Fisher and Paykel Service ManualDocument92 pagesFisher and Paykel Service ManualAnonymous GxeR0L50% (2)
- Richard Wolf 2271Document39 pagesRichard Wolf 2271Akram AlwahibiNo ratings yet
- Seismic WavesDocument31 pagesSeismic WavesYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Melcs Science8Document8 pagesMelcs Science8Nurpayda AbangNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Completion CertificateDocument13 pagesEmergency Lighting Completion CertificateKuljinder VirdiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesAlternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNo ratings yet
- TEST LEVEL 2 - DIPOLE MOMENT AND E, V DUE TO DIPOLE - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesTEST LEVEL 2 - DIPOLE MOMENT AND E, V DUE TO DIPOLE - Attempt ReviewHardik GoyalNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Ordering Data: 7ME65204HC132AA2: Process ConnectionDocument2 pagesDatasheet For Ordering Data: 7ME65204HC132AA2: Process ConnectionTR JJNo ratings yet
- See WFM: Wire Feed Module (Optional) K924-5 Remote Control (Optional)Document1 pageSee WFM: Wire Feed Module (Optional) K924-5 Remote Control (Optional)Coordinador - MantenimientosNo ratings yet
- 09 - Ohms - LawDocument2 pages09 - Ohms - Lawchie CNo ratings yet
- Motor Gradder 2 PDFDocument54 pagesMotor Gradder 2 PDFJose Cruz Martinez Medina100% (1)
- Hsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsDocument16 pagesHsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsAdith DeepakNo ratings yet
- PARTS LIST Model MH-5, MHT-5, MHC-5Document4 pagesPARTS LIST Model MH-5, MHT-5, MHC-5Brian PortillaNo ratings yet
- Abb DriveDocument3 pagesAbb DriveShatrughna SamalNo ratings yet
- HPM10000 72V Test ResultsDocument2 pagesHPM10000 72V Test ResultsakseerNo ratings yet
- THIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Document2 pagesTHIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Edelyn Unay92% (13)
- ATS22C21Q: Lembar Data ProdukDocument3 pagesATS22C21Q: Lembar Data ProdukHASTUNGKARA groupNo ratings yet
- MindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadDocument32 pagesMindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadRocky Clark100% (21)
- Product Information Packet: 25HP, 1775RPM, 3PH, 60HZ, 284T, 1054M, TEFC, F1Document13 pagesProduct Information Packet: 25HP, 1775RPM, 3PH, 60HZ, 284T, 1054M, TEFC, F1Wilfredo MolinaNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - QuizDocument16 pagesEM Waves - QuizApril Joy LascuñaNo ratings yet
- High End Fed1Document7 pagesHigh End Fed1Weerut Srhidhara100% (1)
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Uploaded by
bowieslyimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 1)
Uploaded by
bowieslyimCopyright:
Available Formats
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
vel
Unit 14 Unit test
1
Name: ____________________________ ( ) Total marks: 50 marks
Class: ____________________________ Time: 35 min
Note:
1 Attempt ALL questions.
2 Write your answers in the spaces provided on the Answer Sheet.
A True or false questions (5 marks, 1 mark each)
Write ‘T’ for a true statement and ‘F’ for a false statement.
1 Light coming from a distant star reaches our eyes as divergent rays.
2 The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the reflecting
surface.
3 A kaleidoscope makes use of reflection of light.
4 A chopstick immersed in water appears to bend because of refraction of light.
5 When light enters a medium from air, the refractive index of that medium
determines how much the light bends.
B Multiple-choice questions (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1 Which of the following are luminous objects?
(1) A firefly (2) Eyes of a cat in (3) Lava
the dark
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
E2 Which of the following statements is correct?
A Image formed at infinity by a convex lens cannot be seen clearly.
B The angle of refraction is always equal to the angle of incidence.
New Mastering Science -1- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
C We can see non-luminous objects when they refract light into our eyes. vel
D Parallel light rays converge after passing a concave lens.
1
New Mastering Science -2- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
E3 Which of the following is a correct ray diagram for a convex lens? vel
A B 1
C D
4 Which of the following are the applications of reflection of light?
(1) Spectacles for long sight
(2) Mirrors in solar power plants
(3) Driving mirrors
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
E5 In which of the following situations does refraction of light occur?
(1) Light enters water from air at an angle.
(2) Light passes through a concave lens.
(3) Light enters a glass block from air at an angle larger than the critical angle.
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
E6 What is the approximate magni-
fication of the image formed by
the magnifying glass in the right
photo?
A 1/4
B 1/2
C 2
New Mastering Science -3- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
D 4 vel
1
New Mastering Science -4- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
E7 The photo below shows a polar bear. vel
1
The polar bear appears white because
A its fur absorbs almost all colours of light.
B its fur reflects almost all colours of light.
C it gives out white light.
D it is covered with snow.
8 Which of the following statements about light are correct?
(1) Light is a kind of electromagnetic radiation.
(2) Light travels at about 300 000 000 m s-1 in a vacuum.
(3) Light may change direction when it travels from one medium to another
medium.
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
9 What kind of electromagnetic radiation is
used to take the photo on the right?
A Visible light
B Ultraviolet radiation
C X-rays
D Gamma rays
10 Which of the following statements about microwaves is INCORRECT?
A Microwaves can be used as Wi-Fi signals.
B Water molecules absorb microwaves and vibrate vigorously.
C Octopus cards communicate with Octopus sensors by microwaves.
D Microwaves are possibly cancer causing.
New Mastering Science -5- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
vel
C Fill in the blanks (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1
Complete the following sentences.
1 The a is an imaginary line perpendicular to a reflecting surface.
E2 A person underwater has a full view of the environment above the water. This
view is called the b .
E3 The diminished images formed by convex lenses are always c , while those
formed by concave lenses are always d .
4 A microscope consists of e lenses which are used for producing magnified
images of tiny specimens.
5 When a beam of white light passes through a prism, a visible f is formed.
6 Red, green and g are the primary colours of light. Mixing any two of them
E can produce magenta, h or cyan light.
7 The characteristic marks on a banknote are printed in i ink. These marks
glow under lamps that emit j .
D Questions (25 marks)
E1 Jamie is doing an experiment using the set-up shown in the diagram below. Light
enters a semicircular glass block and results in a reflected ray and a refracted ray.
a Label the angle of incidence as A, the angle of reflection as B, and the
angle of refraction as C in the diagram on the answer sheet. (3 marks)
b When Jamie moves the ray box along the direction shown in the diagram,
how does the angle of refraction change? (1 mark)
c When the incident ray hits the point O at an angle larger than a certain
value, the refracted ray disappears. Name this phenomenon. (1 mark)
d Write the TWO necessary conditions for the phenomenon stated in c to
New Mastering Science -6- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
occur. (2 marks) vel
1
New Mastering Science -7- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
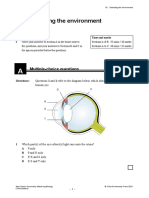
2 We are able to see things clearly only when light coming from them converges vel
on the retina. The diagram below shows the eye of a person suffering from an
eye defect.
1
retina
a Can this person see near objects clearly? (1 mark)
b Draw a ray diagram with a suitable optical device on the answer sheet to
show how his eye defect can be corrected. (4 marks)
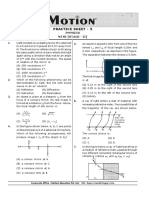
3 In the following rays diagrams, two light rays enter media X and Y at the same
angle separately.
air air
X Y
a Which medium has a higher refractive index? Explain briefly. (2 marks)
b It is known that one of the two media is glass, and the other is diamond.
What are X and Y respectively? (2 marks)
4 Sandy puts a plane mirror on the left of a digital clock and sees the following
image in the mirror.
a States the laws of reflection. (2 marks)
b What is the time as shown on the clock? (1 mark)
c State the nature of the image that helps you answer b. (1 mark)
d Sketch the image after 35 minutes on the answer sheet. (2 marks)
e If Sandy moves the plane mirror to under the clock at the time of b, what
would be the image she see? Sketch the image in the answer sheet.
(2 marks)
f Explain why plane mirrors are often used in home designs. (1 mark)
New Mastering Science -8- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
- End - vel
1
New Mastering Science -9- Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
Unit 14 Light, colours and beyond vel
Unit test
Answer sheet
1
Name: ____________________________ ( ) Marks: _______/50
Class: ____________________________
A True or false questions (5 marks, 1 mark each)
1 __________ 2 __________ 3 __________ 4 __________ 5 __________
B Multiple-choice questions (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1 __________ 2 __________ 3 __________ 4 __________ 5 __________
6 __________ 7 __________ 8 __________ 9 __________ 10 __________
C Fill in the blanks (10 marks, 1 mark each)
a ______________________________ b ______________________________
c ______________________________ d ______________________________
e ______________________________ f ______________________________
g ______________________________ h ______________________________
i ______________________________ j ______________________________
D Questions (25 marks)
1 a
New Mastering Science - 10 - Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
b __________________________________________________________________
vel
c __________________________________________________________________
1
d __________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
2 a __________________________________________________________________
3 a
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
b Medium X: ________________________________________________________
Medium Y: ________________________________________________________
4 a __________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
b __________________________________________________________________
c __________________________________________________________________
New Mastering Science - 11 - Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
d
vel
1
f __________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
- End -
New Mastering Science - 12 - Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
Unit 14 Light, colours and beyond vel
Unit test
Answers
1
A True or false questions (5 marks, 1 mark each)
1 F 2 F 3 T 4 T 5 T
B Multiple-choice questions (10 marks, 1 mark each)
1 B 2 A 3 B 4 C 5 D
6 C 7 B 8 D 9 C 10 C
C Fill in the blanks (10 marks, 1 mark each)
a normal b fish-eye view
c inverted / real d erect / virtual
e convex f spectrum
g blue h yellow
i fluorescent j ultraviolet radiation
D Questions (25 marks)
1 a
A B
Each correct label 3×1m
b Increase. 1m
c Total internal reflection. 1m
d Light travels from a medium of higher refractive index to a
medium of lower refractive index. 1m
The angle of incidence is larger than the critical angle. 1m
New Mastering Science - 13 - Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
14 Light, colours and beyond
Le
2 a No. 1m vel
b
1
Divergent light rays from a near object 1m
Correct type of lens 1m
Correct bending of light rays, focus on retina 2×1m
3 a Medium Y. 1m
Light ray bends more as it travels from air to medium Y when
comparing with medium X. 1m
b Medium X: glass 1m
Medium Y: diamond 1m
4 a The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of
incidence. 1m
The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie on the
same plane. 1m
b 8:51 1m
c The image is laterally inverted. 1m
d 2m
e 2m
f Plane mirrors can make a room look bigger. 1m
- End -
New Mastering Science - 14 - Unit test 14
© Oxford University Press 2019
You might also like
- 8K Light Multiple Choice TestDocument3 pages8K Light Multiple Choice Testapi-3698146100% (4)
- Rme Exam CoverageDocument1 pageRme Exam CoverageMarc100% (4)
- Heat Run Test For TransformerDocument8 pagesHeat Run Test For TransformerHosni Mohamed KassimNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Unit Test (Level 2)Document15 pagesUnit 14 Unit Test (Level 2)bowieslyimNo ratings yet
- 8J - Quick QuizDocument3 pages8J - Quick QuizMatthew ToppingNo ratings yet
- PhysicDocument36 pagesPhysicselbywNo ratings yet
- F TestDocument7 pagesF TestAbid SharifNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Test - ADocument8 pagesUnit 3 Test - Aapi-535415281No ratings yet
- CH 14.3 Quiz & AnsDocument6 pagesCH 14.3 Quiz & AnsAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)Document7 pagesKnowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)api-535415281No ratings yet
- 10s Student Copy UnitTest - D09-Apr-2021Document2 pages10s Student Copy UnitTest - D09-Apr-2021Yash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Task 3 Answers To Textbook QuestionsDocument4 pagesYear 7 Science Task 3 Answers To Textbook QuestionsTadmore Tutors TuitonNo ratings yet
- 5 6154457525488977613Document5 pages5 6154457525488977613ankith sNo ratings yet
- UH Science 44Document7 pagesUH Science 44yuniNo ratings yet
- Physics SQPDocument10 pagesPhysics SQPSai VedantNo ratings yet
- Junoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIDocument186 pagesJunoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIkisuisoffbeatNo ratings yet
- 09 PU 2 IMP Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pages09 PU 2 IMP Ray Optics & Optical InstrumentsBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- CPP-2 - Wave Optics PDFDocument2 pagesCPP-2 - Wave Optics PDFADITYA TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Human Eye Test PaperDocument4 pagesHuman Eye Test PaperDeepak SalwaniNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Document12 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Umbra Screen: Opaque SphereDocument6 pagesUmbra Screen: Opaque SphereFilip MilisovNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionCinara RahimovaNo ratings yet
- 15 Detecting EnvironmentDocument106 pages15 Detecting EnvironmenttoperissaNo ratings yet
- SR PHY SaqDocument12 pagesSR PHY SaqtattikotasatishNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Physics 10Document8 pagesTerm 2 Physics 10abcdNo ratings yet
- GR10 OT CumulativeDocument9 pagesGR10 OT CumulativenaeblahblahNo ratings yet
- Light - Worksheet 2 SCDocument7 pagesLight - Worksheet 2 SC。无名。。No ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument3 pagesWave Opticssaniyainam74No ratings yet
- CW 1Document3 pagesCW 1ELECTRONIC BOY SHAURYANo ratings yet
- Kuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)Document11 pagesKuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)黑No ratings yet
- Class 12 CH 9 Ray & Wave OpticsDocument7 pagesClass 12 CH 9 Ray & Wave OpticsKumar PratikNo ratings yet
- Optics 27 YearsDocument15 pagesOptics 27 YearssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 1st YearDocument3 pagesCH 9 1st Yearfahad.qureshi7799No ratings yet
- Light Knowledge Organiser Quiz - Eco Black and WhiteDocument3 pagesLight Knowledge Organiser Quiz - Eco Black and White200651625No ratings yet
- Depth Reconstruction With Deep Neural Networks (Part 1)Document66 pagesDepth Reconstruction With Deep Neural Networks (Part 1)xuanhan1019No ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 29 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 29 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22abcdNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Wave Optics QB1Document12 pagesCh-11 Wave Optics QB1Angel SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 OpticsDocument24 pagesUnit 6 OpticsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- Photometry: Fundamental Physics Lab Journal O-6Document7 pagesPhotometry: Fundamental Physics Lab Journal O-6Phie-phie elexNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light FINALDocument9 pagesRefraction of Light FINALPrakritiNo ratings yet
- Edunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MDocument5 pagesEdunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MVIKRAM CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- x8ni27VJ6MxLGNaWJSrn PDFDocument21 pagesx8ni27VJ6MxLGNaWJSrn PDFPriya JindalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Notes - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Notes - Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAshida AjmalNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument12 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- REFRACTION OF LIGHT by Prakash ProtectedDocument42 pagesREFRACTION OF LIGHT by Prakash ProtectedprakashNo ratings yet
- Yaan Ushni: Surjct: ScienceDocument6 pagesYaan Ushni: Surjct: ScienceSahej Kaur AroraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Wave Optics Class XiiDocument2 pagesAssignment Wave Optics Class XiiAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample 6 PhyDocument4 pagesSample 6 PhyFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences - Paper 1Document19 pagesPhysical Sciences - Paper 1Alaia McDonaldsNo ratings yet
- FSC Ch#10 (Series Test-9) 2017-2018Document2 pagesFSC Ch#10 (Series Test-9) 2017-2018chanochinkoNo ratings yet
- PRETEST - Electromagnetic Waves, Light & Optics WORDDocument9 pagesPRETEST - Electromagnetic Waves, Light & Optics WORDMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- 1 WoDocument4 pages1 Womayankt2147No ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 eDocument17 pagesNSSBIO3E Chapter Test Ch15 e托普斯No ratings yet
- Human Eye & The Colorful World - Daily Home Assignment 03Document2 pagesHuman Eye & The Colorful World - Daily Home Assignment 03Smayan SethiNo ratings yet
- Phy3 2Document19 pagesPhy3 2Y AdaNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 5 (Physics)Document7 pagesPractice Sheet 5 (Physics)Parnika GuptaNo ratings yet
- XII - I PreBoard - PHYSICSDocument12 pagesXII - I PreBoard - PHYSICSBhawesh Kumar SoniNo ratings yet
- 02 03 Physical Optics 62-84Document6 pages02 03 Physical Optics 62-84eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Yenepoya Pu CollegeDocument20 pagesYenepoya Pu Collegeshaxm098No ratings yet
- Wave Optics Exercise (161-172) .PMDDocument12 pagesWave Optics Exercise (161-172) .PMDHemendra PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics NotesDocument44 pagesWave Optics NotesPrerna JhaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement Current Electromagnetic RadiationDocument23 pagesThe Laws of Electromagnetism Maxwell's Equations Displacement Current Electromagnetic RadiationMadhav patilNo ratings yet
- Dose LimitsDocument3 pagesDose LimitsBOOBOONo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Element Builder: Element Builder Gizmo Shows An Atom With A SingleDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Element Builder: Element Builder Gizmo Shows An Atom With A SingleMicah Webster-Bass100% (1)
- Gain and The Threshold of Three-Dimensional Quantum-Box LasersDocument7 pagesGain and The Threshold of Three-Dimensional Quantum-Box LasersNitika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Some Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70Document4 pagesSome Terms To Remember For Midterm Exam Elec 70KentNo ratings yet
- AC6 Module11Document22 pagesAC6 Module11Fred BorjaNo ratings yet
- Fisher and Paykel Service ManualDocument92 pagesFisher and Paykel Service ManualAnonymous GxeR0L50% (2)
- Richard Wolf 2271Document39 pagesRichard Wolf 2271Akram AlwahibiNo ratings yet
- Seismic WavesDocument31 pagesSeismic WavesYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- Melcs Science8Document8 pagesMelcs Science8Nurpayda AbangNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Completion CertificateDocument13 pagesEmergency Lighting Completion CertificateKuljinder VirdiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesAlternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNo ratings yet
- TEST LEVEL 2 - DIPOLE MOMENT AND E, V DUE TO DIPOLE - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesTEST LEVEL 2 - DIPOLE MOMENT AND E, V DUE TO DIPOLE - Attempt ReviewHardik GoyalNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Ordering Data: 7ME65204HC132AA2: Process ConnectionDocument2 pagesDatasheet For Ordering Data: 7ME65204HC132AA2: Process ConnectionTR JJNo ratings yet
- See WFM: Wire Feed Module (Optional) K924-5 Remote Control (Optional)Document1 pageSee WFM: Wire Feed Module (Optional) K924-5 Remote Control (Optional)Coordinador - MantenimientosNo ratings yet
- 09 - Ohms - LawDocument2 pages09 - Ohms - Lawchie CNo ratings yet
- Motor Gradder 2 PDFDocument54 pagesMotor Gradder 2 PDFJose Cruz Martinez Medina100% (1)
- Hsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsDocument16 pagesHsslive-Xii-Physics-1. Electric Charges and Field & Potential and CapacitorsAdith DeepakNo ratings yet
- PARTS LIST Model MH-5, MHT-5, MHC-5Document4 pagesPARTS LIST Model MH-5, MHT-5, MHC-5Brian PortillaNo ratings yet
- Abb DriveDocument3 pagesAbb DriveShatrughna SamalNo ratings yet
- HPM10000 72V Test ResultsDocument2 pagesHPM10000 72V Test ResultsakseerNo ratings yet
- THIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Document2 pagesTHIRD PERIODICAL TEST IN SCIENCE Grade 5Edelyn Unay92% (13)
- ATS22C21Q: Lembar Data ProdukDocument3 pagesATS22C21Q: Lembar Data ProdukHASTUNGKARA groupNo ratings yet
- MindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadDocument32 pagesMindTap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bank DownloadRocky Clark100% (21)
- Product Information Packet: 25HP, 1775RPM, 3PH, 60HZ, 284T, 1054M, TEFC, F1Document13 pagesProduct Information Packet: 25HP, 1775RPM, 3PH, 60HZ, 284T, 1054M, TEFC, F1Wilfredo MolinaNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - QuizDocument16 pagesEM Waves - QuizApril Joy LascuñaNo ratings yet
- High End Fed1Document7 pagesHigh End Fed1Weerut Srhidhara100% (1)