Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye Surgery
Eye Surgery
Uploaded by
SamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lasik: Eyeglasses Contact LensesDocument3 pagesLasik: Eyeglasses Contact Lensesvandana singhNo ratings yet
- LASIK SurgeryDocument10 pagesLASIK Surgerymandukhai tsogtsaikhanNo ratings yet
- LASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaDocument18 pagesLASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaFawaz Bin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Activity3 (Refraction-Errors)Document8 pagesActivity3 (Refraction-Errors)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Lasik What Is Lasik?Document6 pagesLasik What Is Lasik?Lai Kong HuiNo ratings yet
- Lasik What Is Lasik?Document6 pagesLasik What Is Lasik?Lai Kong HuiNo ratings yet
- Eye SurgeryDocument4 pagesEye SurgeryJihad Elias ChahlaNo ratings yet
- LASER THERAPY PresentationDocument31 pagesLASER THERAPY Presentationapi-3741769100% (5)
- Ocular Laser Therapy 12-5-14Document31 pagesOcular Laser Therapy 12-5-14Prasetiyo WilliamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Terapi Refraksi LaserDocument6 pagesJurnal Terapi Refraksi LaserKim NayoungNo ratings yet
- LASIK Consent 2019-3-2Document9 pagesLASIK Consent 2019-3-2Kumar VjNo ratings yet
- Script For Waves and OpticsDocument5 pagesScript For Waves and OpticsjzbdNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument6 pagesRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureDocument16 pagesCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)Document29 pagesSanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)sanchit2418No ratings yet
- Reference Summary: X-Plain LasikDocument0 pagesReference Summary: X-Plain LasikUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Refraction and AccommodationDocument80 pagesRefraction and Accommodationapi-19916399100% (2)
- Ochiul Si Bolile SaleDocument7 pagesOchiul Si Bolile SaleRares PopeiaNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument41 pagesThe Eyerheanna0076No ratings yet
- Activity1 (Cataract)Document9 pagesActivity1 (Cataract)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Laser Surgery of The Eye: A Safe, Precise TechniqueDocument4 pagesLaser Surgery of The Eye: A Safe, Precise TechniquedabhimanishNo ratings yet
- Lasik BrochureDocument8 pagesLasik BrochurePratik ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Cataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGDocument8 pagesCataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGboogeyman6dimakutaNo ratings yet
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNNo ratings yet
- 03 LasikSeminar Revised by KASDocument36 pages03 LasikSeminar Revised by KASapi-3695929No ratings yet
- CataractsDocument7 pagesCataractsOktovia KakaNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadNo ratings yet
- Nearsightedness (Myopia) Is A Common Vision Condition in Which YouDocument1 pageNearsightedness (Myopia) Is A Common Vision Condition in Which YouAyeesha AbbakuraNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument7 pagesRetinal Detachmentjay dewanagnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument19 pagesRetinal DetachmentJohn Hans CaturasNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNo ratings yet
- Lens CataractDocument16 pagesLens CataractSari RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- Lib-A-23 1-866-366-2020 1Document24 pagesLib-A-23 1-866-366-2020 1Blue62uNo ratings yet
- Reffractive ErrorDocument23 pagesReffractive Errorjyoti singh100% (1)
- Blog 1 PDFDocument1 pageBlog 1 PDFIndore India Eye CareNo ratings yet
- Herzig Lasik GuideDocument14 pagesHerzig Lasik GuideAnthony BNo ratings yet
- Las Vegas Cataract SurgeryDocument2 pagesLas Vegas Cataract SurgeryPaul W. HissNo ratings yet
- Makalah MataDocument13 pagesMakalah MatazahidahrahmanNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument2 pagesRetinal Detachmentwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument17 pagesCataractrhopmaeNo ratings yet
- Wepik Enhancing Visual Acuity A Comprehensive Overview of Lasik Eye Surgery 20230930081942zsawDocument7 pagesWepik Enhancing Visual Acuity A Comprehensive Overview of Lasik Eye Surgery 20230930081942zsawbharti eye foundationNo ratings yet
- Health 1 17Document3 pagesHealth 1 17Rosie SaquinNo ratings yet
- Eye7 Specs Removal BrochureDocument20 pagesEye7 Specs Removal Brochureब्रज किशोर सिंहNo ratings yet
- TimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryDocument1 pageTimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryBaeyerNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Document5 pagesBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Refractive Errors of EyeDocument20 pagesRefractive Errors of EyeKhushi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Eye Care Max: Why Choose Max Eye Care For LASIK? Faqs For Lasik/C-LasikDocument2 pagesEye Care Max: Why Choose Max Eye Care For LASIK? Faqs For Lasik/C-LasikAstha JalanNo ratings yet
- Mata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakDocument74 pagesMata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakYeni AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Visual Optics PresentationDocument33 pagesVisual Optics PresentationSimra WaheedNo ratings yet
- A Patient 'S Guide To Refractive SurgeryDocument7 pagesA Patient 'S Guide To Refractive SurgeryJon HinesNo ratings yet
- Vision, The Human Eye and Correcting Visual DefectsDocument6 pagesVision, The Human Eye and Correcting Visual DefectsjzbdNo ratings yet
- Types of CataractsDocument1 pageTypes of CataractsMj Baltazar ArtamiaNo ratings yet
- Vitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistDocument12 pagesVitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistLesTrechSaNo ratings yet
- Lasik: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLasik: Anatomy and PhysiologyAgung Choro de ObesNo ratings yet
- Eye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsDocument26 pagesEye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsAaron Marcus R. De LeonNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
Eye Surgery
Eye Surgery
Uploaded by
SamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye Surgery
Eye Surgery
Uploaded by
SamCopyright:
Available Formats
(2)
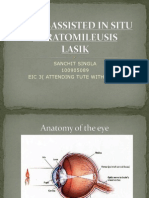
LASIK eye surgery
LASIK eye surgery is the best known and most commonly performed laser refractive
surgery to correct vision problems. Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) can be
an alternative to glasses or contact lenses.
During LASIK surgery, a special type of cutting laser is used to precisely change the
shape of the dome-shaped clear tissue at the front of your eye (cornea) to improve vision
Why it's done
LASIK surgery may be an option for the correction of one of these vision problems:
Nearsightedness (myopia). When your eyeball is slightly longer than normal or
when the cornea curves too sharply, light rays focus in front of the retina and blur
distant vision. You can see objects that are close fairly clearly, but not those that are
far away.
Farsightedness (hyperopia). When you have a shorter than average eyeball or a
cornea that is too flat, light focuses behind the retina instead of on it. This makes
near vision, and sometimes distant vision, blurry.
Astigmatism. When the cornea curves or flattens unevenly, the result is
astigmatism, which disrupts focus of near and distant vision.
If you're considering LASIK surgery, you probably already wear glasses or contact lenses. Your eye doctor will talk with you about
whether LASIK surgery or another similar refractive procedure is an option that will work for you.
Risks
Complications that result in a loss of vision are very rare. But certain side effects of LASIK eye surgery, particularly dry eyes and temporary
visual problems such as glare, are fairly common.
These usually clear up after a few weeks or months, and very few people consider them to be a long-term problem.
You might also like
- Lasik: Eyeglasses Contact LensesDocument3 pagesLasik: Eyeglasses Contact Lensesvandana singhNo ratings yet
- LASIK SurgeryDocument10 pagesLASIK Surgerymandukhai tsogtsaikhanNo ratings yet
- LASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaDocument18 pagesLASIK (Laser Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) :: MyopiaFawaz Bin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Activity3 (Refraction-Errors)Document8 pagesActivity3 (Refraction-Errors)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Lasik What Is Lasik?Document6 pagesLasik What Is Lasik?Lai Kong HuiNo ratings yet
- Lasik What Is Lasik?Document6 pagesLasik What Is Lasik?Lai Kong HuiNo ratings yet
- Eye SurgeryDocument4 pagesEye SurgeryJihad Elias ChahlaNo ratings yet
- LASER THERAPY PresentationDocument31 pagesLASER THERAPY Presentationapi-3741769100% (5)
- Ocular Laser Therapy 12-5-14Document31 pagesOcular Laser Therapy 12-5-14Prasetiyo WilliamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Terapi Refraksi LaserDocument6 pagesJurnal Terapi Refraksi LaserKim NayoungNo ratings yet
- LASIK Consent 2019-3-2Document9 pagesLASIK Consent 2019-3-2Kumar VjNo ratings yet
- Script For Waves and OpticsDocument5 pagesScript For Waves and OpticsjzbdNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument6 pagesRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureDocument16 pagesCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)Document29 pagesSanchit Singla 100905089 Eic 3 (Attending Tute With Eic 2)sanchit2418No ratings yet
- Reference Summary: X-Plain LasikDocument0 pagesReference Summary: X-Plain LasikUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Refraction and AccommodationDocument80 pagesRefraction and Accommodationapi-19916399100% (2)
- Ochiul Si Bolile SaleDocument7 pagesOchiul Si Bolile SaleRares PopeiaNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument41 pagesThe Eyerheanna0076No ratings yet
- Activity1 (Cataract)Document9 pagesActivity1 (Cataract)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Laser Surgery of The Eye: A Safe, Precise TechniqueDocument4 pagesLaser Surgery of The Eye: A Safe, Precise TechniquedabhimanishNo ratings yet
- Lasik BrochureDocument8 pagesLasik BrochurePratik ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Cataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGDocument8 pagesCataract-Case Study - ADOMPINGboogeyman6dimakutaNo ratings yet
- Cataracts The Mayo ClinicDocument6 pagesCataracts The Mayo ClinicJandz MNNo ratings yet
- 03 LasikSeminar Revised by KASDocument36 pages03 LasikSeminar Revised by KASapi-3695929No ratings yet
- CataractsDocument7 pagesCataractsOktovia KakaNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadNo ratings yet
- Nearsightedness (Myopia) Is A Common Vision Condition in Which YouDocument1 pageNearsightedness (Myopia) Is A Common Vision Condition in Which YouAyeesha AbbakuraNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument7 pagesRetinal Detachmentjay dewanagnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Introduction To The Lens and CataractFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument19 pagesRetinal DetachmentJohn Hans CaturasNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNo ratings yet
- Lens CataractDocument16 pagesLens CataractSari RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- Lib-A-23 1-866-366-2020 1Document24 pagesLib-A-23 1-866-366-2020 1Blue62uNo ratings yet
- Reffractive ErrorDocument23 pagesReffractive Errorjyoti singh100% (1)
- Blog 1 PDFDocument1 pageBlog 1 PDFIndore India Eye CareNo ratings yet
- Herzig Lasik GuideDocument14 pagesHerzig Lasik GuideAnthony BNo ratings yet
- Las Vegas Cataract SurgeryDocument2 pagesLas Vegas Cataract SurgeryPaul W. HissNo ratings yet
- Makalah MataDocument13 pagesMakalah MatazahidahrahmanNo ratings yet
- Retinal DetachmentDocument2 pagesRetinal Detachmentwieka mawieNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument17 pagesCataractrhopmaeNo ratings yet
- Wepik Enhancing Visual Acuity A Comprehensive Overview of Lasik Eye Surgery 20230930081942zsawDocument7 pagesWepik Enhancing Visual Acuity A Comprehensive Overview of Lasik Eye Surgery 20230930081942zsawbharti eye foundationNo ratings yet
- Health 1 17Document3 pagesHealth 1 17Rosie SaquinNo ratings yet
- Eye7 Specs Removal BrochureDocument20 pagesEye7 Specs Removal Brochureब्रज किशोर सिंहNo ratings yet
- TimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryDocument1 pageTimRoot - Chapter 10 - Introduction To The Lens and Cataract SurgeryBaeyerNo ratings yet
- Biology - The Eye (Cateracts)Document5 pagesBiology - The Eye (Cateracts)Shannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Refractive Errors of EyeDocument20 pagesRefractive Errors of EyeKhushi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Eye Care Max: Why Choose Max Eye Care For LASIK? Faqs For Lasik/C-LasikDocument2 pagesEye Care Max: Why Choose Max Eye Care For LASIK? Faqs For Lasik/C-LasikAstha JalanNo ratings yet
- Mata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakDocument74 pagesMata Tenang Visus Turun MendadakYeni AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Visual Optics PresentationDocument33 pagesVisual Optics PresentationSimra WaheedNo ratings yet
- A Patient 'S Guide To Refractive SurgeryDocument7 pagesA Patient 'S Guide To Refractive SurgeryJon HinesNo ratings yet
- Vision, The Human Eye and Correcting Visual DefectsDocument6 pagesVision, The Human Eye and Correcting Visual DefectsjzbdNo ratings yet
- Types of CataractsDocument1 pageTypes of CataractsMj Baltazar ArtamiaNo ratings yet
- Vitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistDocument12 pagesVitreous Gel Eye Retinal Detachment OphthalmologistLesTrechSaNo ratings yet
- Lasik: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLasik: Anatomy and PhysiologyAgung Choro de ObesNo ratings yet
- Eye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsDocument26 pagesEye Defects and Latest Technological SolutionsAaron Marcus R. De LeonNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet