Professional Documents
Culture Documents
66078ddce8db08001848a6a0 - ## - Chemical Equilibrium
66078ddce8db08001848a6a0 - ## - Chemical Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Rohan PatraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
66078ddce8db08001848a6a0 - ## - Chemical Equilibrium
66078ddce8db08001848a6a0 - ## - Chemical Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Rohan PatraCopyright:
Available Formats
NEET
UTHAAN NEET 2024
Practice Sheet
Chemistry
Chemical Equilibrium
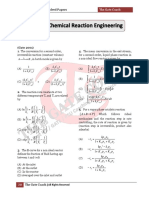
Q1 In a chemical equilibrium A + B ⇌ C + D when The equilibrium constant ‘K’ for the following
one mole of each of the two reactants are dissociation H3 PO4 ⇌ 3H
+
+ PO
3−
4
is:
mixed, 0.6 mole each of the products are (A) K1/K2K3 (B) K1K2K3
formed. The equilibrium constant calculated is (C) K2/K1K3 (D) K1 + K2 + K3
(A) 1 (B) 0.30
Q6 For the equilibrium.
(C) 2.25 (D) 4/9
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2
NOCl(g)
Q2 1 mole of H2 and 2 mole of I2 are taken initially in Kp is related to Kc by the reaction:
a 2 L vessel. The number of moles H2 at (A) Kp = Kc (RT) (B) Kp = Kc (RT)2
equilibrium is 0.2. Then, the number of moles of (C) Kp =
Kc
(D) Kp =
Kc
2
RT
(RT)
I2 and HI at equilibrium are:
(A) 1.2, 1.6 (B) 1.8, 1.0 Q7 PCl5, PCl3, and Cl2 are at equilibrium at 500 K in
(C) 0.4, 2.4 (D) 0.8, 2.0 a closed container and their concentrations are
0.8 × 10–3 mol L–1, 1.2 × 10–3 mol L–1 and 1.2 × 10–3
Q3 Kc for the reaction N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 is K then
mol L–1, respectively. The value of Kc for the
the value of Kc for the reaction 2NH3 ⇌ N2 + 3H2
reaction PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) will be:
will be
(A) 1.8 × 103 mol L–1
(A) K (B) 2K
(B) 1.8 × 10–3 L/mol
(C) 1/K (D) K2
(C) 1.8 × 10–3 mol-1 L
Q4 For the reaction, N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) the (D) 0.55 × 104 mol/ L
equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium
Q8 Calculate Kc for the reversible process given
constant is K2 for the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) ⇌
below. If Kp = 167 and T = 800°C
2NO2(g). What is “K” for the reaction?
1
CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
NO2 (g) ⇌ N 2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 (A) 1.95 (B) 1.85
(A) 1
( K1 K2 ) (C) 1.89 (D) 1.60
(B) 1
(2 K1 K2 )
Q9 What is the unit of Kp for the reaction?
(C) 1
(4 K1 K2 )
CS2(g) + 4H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) + 2H2S(g)
(D)
1
[
1
]
2
(A) atm (B) atm-2
( K1 K2 )
(C) atm2 (D) atm-1
Q5 Consider the equilibrium reactions:
K1
Q10 2HI(g) ⇌ H2(g) + I2(g)
+ −
H3 PO4 ⇌ H + H2 PO
4 The equilibrium constant of the above reaction
K2
H2 PO
−
⇌ H
+
+ HPO
2− is 6.4 at 300 K. If 0.25 mole each of H2 and I2 are
4 4
K3 added to the system, the equilibrium constant
2− + 3−
HPO ⇌ H + PO
4 4 will be:
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
(A) 0.8 (B) 3.2
(C) 1.6 (D) 6.4
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) +
(B) (ii) Kp < Kc
Q11 An increase in pressure would favour the Cl2(g)
forward reaction
(A) N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO(g)
(B) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g) ⇌ 2SO2(g) + Kp not
(C) PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) (C) (iii)
O2(g) defined
(D) H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
Q12 Assertion (A): For the reaction, N2 + O2 ⇌ 2NO,
an increase in pressure at equilibrium does not
affect the reaction.
Reason (R): Σ Moles of gaseous product – Σ
CH3COOC2H5(l) +
moles of gaseous reactant = 0.
H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COOH(l) +
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
(D) C2H5OH(l) (iv) Kp > Kc
true, and Reason (R) is a correct explanation
(assume temperature =
of Assertion (A).
25°C)
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the
true, but Reason (R) is not a correct
explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, and Reason (R) is false.
(A) (A) → (ii); (B) → (i), (iv); (C) → (i),
(D) Assertion (A) is false, and Reason (R) is true.
(iv); (D) → (iii)
Q13 High temperature and high pressure (as per Le (B) (A) → (i), (iv); (B) → (ii); (C) → (i),
Chatelier’s principle) favour (iv); (D) → (iii)
(A) N2 + 2H2 ⇌ 2NH3, ΔH = –Q1 (C) (A) → (i), (iv); (B) → (iii); (C) → (i);
(B) CaCO 3 ⇌ CaO + CO2 , ΔH = +Q2 (D) → (i), (iv)
(C) 3O2 ⇌ 2O3 , ΔH = +Q3 (D) (A) → (iii); (B) → (i), (iv); (C) → (ii);
(D) N2 + O2 ⇌ 2 NO, ΔH = +Q4 (D) → (i), (iv)
Q14 For the homogeneous reaction Q16 The reaction favored at low pressure is:
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) ⇌ 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) (A) H2 ( g) + I2 ( g) ⇌ 2 HI(g)
the equilibrium constant Kc has the unit of (B) PCl5 ( g) ⇌ PCl3 ( g) + Cl 2 ( g)
(A) (Conc) –1 (C) N2 ( g) + O2 ( g) ⇌ 2 NO(g)
(B) Conc (D) N2 ( g) + 3H2 ( g) ⇌ 2 NH3 ( g)
+10
(C) (Conc)
Q17 In the reaction,
(D) it is dimensionless
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + X cal, most
Q15 Match the Column-I with Column-II. favourable conditions of temperature and
pressure for greater yield of SO3 are
Column-I Column-II (A) Low temperature and low pressure
(B) High temperature and low pressure
(C) High temperature and high pressure
(A) N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌2NH3(g) (i) Δ ng > 0
(D) Low temperature and high pressure
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
Q18 For the reaction, is constant in temperature range between T1
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g), the standard free energy and T2, it is readily observed that
is greater than zero. The equilibrium constant (K) (A) Kp > K′P
would be: (B) Kp < K′p
(A) K = 0 (B) K > 1 (C) Kp = K′P
(C) K =1 (D) K <1 (D) Kp =
1
′
Kp
Q19 Which one of the following conditions will favour
Q24 For the reversible reaction,
maximum formation of the product in the
N2(g) +3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) + Heat. The equilibrium
reaction,
shifts in forward direction:
A2(g) + B2(g) ⇌ X2(g) ΔrH = -H kJ
(A) By decreasing the pressure
(A) Low temperature and high pressure
(B) By decreasing the concentrations of N2(g)
(B) Low temperature and low pressure and H2(g)
(C) High temperature and low pressure
(C) By increasing pressure and decreasing
(D) High temperature and high pressure temperature
Q20 A 20 litre container at 400 K contains CO2(g) at (D) By increasing the concentration of NH3(g)
pressure 0.4 atm and an excess of SrO (neglect
Q25 KMnO4 can be prepared from K2MnO4 as per
the volume of solid SrO). The volume of the
the reaction:
containers is now decreased by moving the 2− −
3 MnO + 2H2 O ⇌ 2 MnO + MnO2
4 4
movable piston fitted in the container. The −
+ 4 OH
maximum volume of the container, when The reaction can go to completion by removing
pressure of CO2 attains its maximum value, will OH– ions by adding:
be: (A) HCl (B) KOH
(Given that: SrCO3(s) ⇌ SrO(s) + CO2(g) Kp = 1.6 (C) CO2 (D) SO2
atm)
(A) 2 litre (B) 5 litre
(C) 10 litre (D) 4 litre
Q21 Consider the nitration of benzene using mixed
conc. H2SO4 and HNO3. If a larger amount of
KHSO4 is added to the mixture, the rate of
nitration will be:
(A) Doubled (B) Increase
(C) Decrease (D) Unchanged
Q22 Which of the following statements is correct for
a reversible process in a state of equilibrium?
(A) ΔGº = –2.303 RT log K
(B) ΔGº = 2.303 RT log K
(C) ΔG = –2.303 RT log K
(D) ΔG = 2.303 RT log K
Q23 For a given exothermic reaction, Kp and K´p are
the equilibrium constants at temperature T1 and
T2, respectively. Assuming that heat of reaction
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
Answer Key
Q1 (C) Q14 (B)
Q2 (A) Q15 (A)
Q3 (C) Q16 (B)
Q4 (D) Q17 (D)
Q5 (B) Q18 (D)
Q6 (C) Q19 (A)
Q7 (A) Q20 (B)
Q8 (C) Q21 (C)
Q9 (B) Q22 (A)
Q10 (D) Q23 (A)
Q11 (B) Q24 (C)
Q12 (A) Q25 (C)
Q13 (C)
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
Hints & Solutions
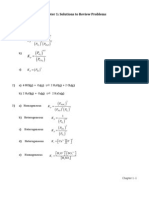
Q1 Text Solution:
Q5 Text Solution:
Q2 Text Solution:
At equilibrium,
[H2 ] = 1 − α = 0. 2
α = 0. 8
[I 2 ] = 2 − α = 1. 2
[HI] = 2α = 1. 6
Q3 Text Solution:
Q6 Text Solution:
Δng
K p = K c (RT )
& Δng = np(g) − nR(g)
Kc
⇒ Kp =
RT
Q7 Text Solution:
Q4 Text Solution:
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
Q8 Text Solution:
Q15 Text Solution:
Q16 Text Solution:
Q9 Text Solution:
Q17 Text Solution:
The given reaction favour the formation of SO3
if temperature is lowered and pressure is
increased.
Q18 Text Solution:
Q10 Text Solution:
The value of equilibrium constant remains
unchanged even on changing the Q19 Text Solution:
concentration of the reaction system. Low temperature and high pressure will favour
the forward reaction as the reaction is
Q11 Text Solution:
exothermic and gaseous number of mole
decreases.
Q12 Text Solution: Q20 Text Solution:
Q13 Text Solution:
Q14 Text Solution:
Q21 Text Solution:
If a large amount KHSO4 is added then conc. of
-
HSO4 ions increases and the reaction will be
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
NEET
shifted in backward direction hence the rate of Q24 Text Solution:
nitration will be slower. The given reaction is exothermic and gaseous
number of moles decreases and hence at low
Q22 Text Solution:
temperature and high pressure favour the
forward reaction.
Q25 Text Solution:
Q23 Text Solution: To disturb the equilibrium in the forward
For an exothermic reaction, if temperature is direction, the hydroxide ions are needed to be
increased the equilibrium constant decreases. removed and that can be done by adding
carbon dioxide.
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
You might also like
- General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10th Edition Petrucci Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesGeneral Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manualrickeybrock6oihx100% (14)
- Finisher Sr5050Document96 pagesFinisher Sr5050EDUARDO PEREYRANo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument29 pagesChemical EquilibriumhertianaNo ratings yet
- Aci318 14Document74 pagesAci318 14Vinicio Cola55% (11)
- My Copyprotein Folding Virtual ActivityDocument7 pagesMy Copyprotein Folding Virtual Activityapi-521781723No ratings yet
- ch15 PDFDocument29 pagesch15 PDFHafidz RafiqiNo ratings yet
- 5.chemical Equilibrium ExerciseDocument37 pages5.chemical Equilibrium ExerciseUday MehtaniNo ratings yet
- Best Questions On Chemical Equilirbium FDocument8 pagesBest Questions On Chemical Equilirbium Flakshit singhalNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium DPP 014728Document11 pagesEquilibrium DPP 014728Yash MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions DetailedDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Solutions DetailedYeonjae JeongNo ratings yet
- 05 Worksheet 3 (Gen Chem) RelevoDocument2 pages05 Worksheet 3 (Gen Chem) Relevocessarine relevoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQDocument22 pagesChemistry MCQAditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Chemical EquilibriumDocument10 pagesUnit 3. Chemical EquilibriumyekcimhadjiamerNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10Th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesGeneral Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10Th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDebraPricemkw100% (14)
- (Download PDF) General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument78 pages(Download PDF) General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Full Chapterbohnkeichuun3100% (8)
- Lec 5chemical EquilibriumDocument25 pagesLec 5chemical Equilibriuma.alsayed6805No ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGkennethleo69No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria - PDFDocument95 pagesChemical Equilibria - PDFshamilsha014No ratings yet
- Full General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10Th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Online PDF All ChapterDocument62 pagesFull General Chemistry Principles and Modern Applications 10Th Edition Petrucci Solutions Manual Online PDF All Chapterestellacime400100% (7)
- 15 Petrucci10e CSMDocument54 pages15 Petrucci10e CSMPhương Ngân HồNo ratings yet
- Chem Eqb.Document5 pagesChem Eqb.Preethi SekarNo ratings yet
- No. of Q 23Document4 pagesNo. of Q 23HappyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equilibrium PDFDocument18 pagesChemistry Equilibrium PDFsirikimurthyNo ratings yet
- Camp 5 - Set 2 Online FileDocument20 pagesCamp 5 - Set 2 Online FileRagu BaguNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Chapter 6Document67 pagesQuick Revision Chapter 6mtul2828No ratings yet
- 2022 CJC H2 CHEM Prelim P1 QP - FINALDocument14 pages2022 CJC H2 CHEM Prelim P1 QP - FINALYanqiao LiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics DPP 03 (Of Lecture 05)Document4 pagesChemical Kinetics DPP 03 (Of Lecture 05)socialworker561No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium 1582Document21 pagesChemical Equilibrium 1582mohammadalirizwan423No ratings yet
- 2019 DHS Prelim H2 Chem P1 ANSDocument6 pages2019 DHS Prelim H2 Chem P1 ANSArthur SoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final Step-C Solutions - Gaseous StateDocument6 pagesChemistry Final Step-C Solutions - Gaseous StateAnas KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium DTS-2Document2 pagesChemical Equilibrium DTS-2hardcoregatesNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz 1 ANSWER KEY 2017Document2 pagesPractice Quiz 1 ANSWER KEY 2017Frezeil RocheNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - DPP 09 - Lakshya JEE 2024Document2 pagesChemical Kinetics - DPP 09 - Lakshya JEE 2024Hrishith SavirNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025Document3 pagesElectrochemistry - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025AkshitEditzNo ratings yet
- DPP-11 - Chemistry Bonding RareDocument4 pagesDPP-11 - Chemistry Bonding RareanandramNo ratings yet
- Unit # 07 (Part - I) : Chemical Equilibrium Exercise # 1Document6 pagesUnit # 07 (Part - I) : Chemical Equilibrium Exercise # 11234vishal mimaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument10 pagesChemical Equilibriumd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Media 1505143131 918696Document18 pagesMedia 1505143131 918696happyNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Chemical EquilibriumDocument105 pages6.0 Chemical EquilibriumTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium, Acids & BasesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium, Acids & BaseswildplayersgamingNo ratings yet
- N2016 H2 P1 Solns For UploadingDocument8 pagesN2016 H2 P1 Solns For UploadingjkNo ratings yet
- Chem 1104Document41 pagesChem 1104Paul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Format PresentasiDocument5 pagesFormat PresentasiHubbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 312 Physical Chemistry: AnswerDocument2 pagesChemistry 312 Physical Chemistry: AnswerParth BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Topic6 ChemicalEquilibriumDocument83 pagesTopic6 ChemicalEquilibriumAishaizlNo ratings yet
- Example 1Document8 pagesExample 1jgolloberNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Chemical Equilibrium 2-09-2019Document114 pages2-1 Chemical Equilibrium 2-09-2019carlos lara rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium (Chemical) HintsDocument4 pagesEquilibrium (Chemical) Hintskartik bankarNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument20 pagesChemical Kineticsvijaylakshmi0727No ratings yet
- CRE GATE Question PaperDocument28 pagesCRE GATE Question PapershashwatNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument28 pages5 PDFTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument28 pages5 PDFTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- CRE GATE Question Paper PDFDocument28 pagesCRE GATE Question Paper PDFChandra prakash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 (Chemical Equilibrium) - 1-2Document31 pagesCh.3 (Chemical Equilibrium) - 1-2Mohamed El-GoharyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Constant NOTESDocument5 pagesEquilibrium-Constant NOTESAlex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium - DPP 04 (Of Lec 05) - Prayas JEE 2025Document3 pagesEquilibrium - DPP 04 (Of Lec 05) - Prayas JEE 2025shashank kumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry DPPDocument4 pagesPhysical Chemistry DPPpediredla.ajithkumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Equilibrium: SolutionsDocument54 pages7 Equilibrium: SolutionsMriganko RoyNo ratings yet
- Admin2 Chemistry 4 Clutch Chemistry Clutch 63 CH 14 Chemical Equilibrium 6839Document17 pagesAdmin2 Chemistry 4 Clutch Chemistry Clutch 63 CH 14 Chemical Equilibrium 6839KarthikNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs - 230307 - 232855 (1) - 27165157Document3 pagesCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM MCQs - 230307 - 232855 (1) - 27165157Karan NigalNo ratings yet
- WPP-1 Without XIIDocument2 pagesWPP-1 Without XIIAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Refrigeration Dryers TG - TI Series: Flow Rate 30.8 To 90 M /minDocument7 pagesRefrigeration Dryers TG - TI Series: Flow Rate 30.8 To 90 M /minSergey SofferNo ratings yet
- Mag-03 and Spectramag-6 Used For Pre-Installation Site SurveysDocument1 pageMag-03 and Spectramag-6 Used For Pre-Installation Site SurveysAbdellah SaadNo ratings yet
- Ritz Vector RSIADocument2 pagesRitz Vector RSIAaungps_sone82No ratings yet
- Lambert Conformal Conic Projection For IndiaDocument4 pagesLambert Conformal Conic Projection For IndiaSantosh RaiNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability: Using SLIDEDocument27 pagesSlope Stability: Using SLIDESaurabh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Compaction Properties: Hygroscopicity, Powder RheologyDocument12 pagesCompaction Properties: Hygroscopicity, Powder RheologyjoshNo ratings yet
- Solutions - : Solute SolventDocument4 pagesSolutions - : Solute SolventLawn94No ratings yet
- The Effect of Manganese On The Microstructure and Properties of All-Wel-Metal DepositsDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Manganese On The Microstructure and Properties of All-Wel-Metal DepositstsoheilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics StudyGuideDocument20 pagesMechanics StudyGuideTs SodariNo ratings yet
- LPI - MaterialsDocument14 pagesLPI - MaterialsizmitlimonNo ratings yet
- Elemen Mesin II GÇô TMS 310-P9Document26 pagesElemen Mesin II GÇô TMS 310-P9Dendi AlcyoneNo ratings yet
- KOM SolutionDocument2 pagesKOM SolutionJay SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fly Wheel Weight ReductionDocument15 pagesFly Wheel Weight ReductionHari KrishNo ratings yet
- Permeability and SeepageDocument9 pagesPermeability and SeepageJames Karl AluraNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying SystemDocument27 pagesPneumatic Conveying SystemRavindra DarjiNo ratings yet
- Accepted PaperDocument12 pagesAccepted PaperKHALEDNo ratings yet
- 08 Viscous FlowDocument40 pages08 Viscous FlowJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- HD 2594Document20 pagesHD 2594Emilio EmiNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Report For PSC Box TemplateDocument25 pagesStructural Design Report For PSC Box TemplateShishir Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Derivation For LSF (Lime Saturation Factor) - VDChariDocument3 pagesDerivation For LSF (Lime Saturation Factor) - VDChariNihar Ranjan Tripathy75% (4)
- ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesElectrolysisRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Design of A Flexible Skin For A Shear Morphing WingDocument16 pagesDesign of A Flexible Skin For A Shear Morphing WingRe DesignNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Air Booster Pump PDFDocument10 pagesPneumatic Air Booster Pump PDFMaxNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Section A: Polymer PrinciplesDocument6 pagesThe Structure and Function of Macromolecules Section A: Polymer PrinciplesTaufik SallehNo ratings yet
- Walter F. Stewart, Stephen S. Woods, Harold Deck Beeson-Safe Use of Oxygen and Oxygen Systems_ Guidelines for Oxygen System Desing, Materials Selection, Operations, Storage, and Transportation (Astm M.pdfDocument113 pagesWalter F. Stewart, Stephen S. Woods, Harold Deck Beeson-Safe Use of Oxygen and Oxygen Systems_ Guidelines for Oxygen System Desing, Materials Selection, Operations, Storage, and Transportation (Astm M.pdfksvvijNo ratings yet
- Acrilem ST190: Product DescriptionDocument2 pagesAcrilem ST190: Product DescriptionMachidon OanaNo ratings yet
- Publications Catalog - October 2016Document113 pagesPublications Catalog - October 2016amir_fortunateNo ratings yet