Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MPL Notes
MPL Notes
Uploaded by
DawitCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MPL Notes
MPL Notes
Uploaded by
DawitCopyright:
Available Formats
PRINCIPLES OF FLIGHT - I
Aerodynamics is the study of the behavior of air as it interacts with solid Avionics: Modern Cessna 172s are often equipped with advanced avionics
objects, such as an aircraft, car, or building. It involves analyzing the suites, such as the Garmin G1000 integrated flight deck.
forces and the resulting motion of objects moving through the air, as well Instrumentation: Includes standard flight instruments, navigation, and
as understanding how air moves around these objects. The key principles communication equipment, which may vary depending on the model and
and concepts in aerodynamics include: customization.
Lift: The force that acts perpendicular to the relative motion of the object Variants
through the air. In the case of an airplane wing, lift is the force that allows
Cessna 172: The basic model, which has seen numerous updates over the
the plane to rise and stay in the air.
decades.
Drag: The force that opposes the motion of the object through the air. It
Cessna 172P: A model introduced in the early 1980s with various
acts parallel and opposite to the direction of motion, slowing the object
improvements.
down.
Cessna 172S Skyhawk SP: A more recent model with enhanced
Thrust: The force that propels an object forward through the air. In an
performance and features.
aircraft, thrust is typically generated by engines.
Use and Popularity
Weight: The force due to gravity acting on the object, pulling it
downward. Training: Widely used by flight schools around the world due to its
forgiving flight characteristics and reliability.
Personal Use: Popular among private pilots for recreational flying and
The Cessna 172, also known as the Skyhawk, is one of the most popular
cross-country trips.
and widely produced aircraft in the world. Here are the detailed
specifications and characteristics of the Cessna 172: Commercial Use: Utilized for aerial photography, survey work, and light
transport.
General Overview
The Cessna 172's longevity and widespread use are a testament to its solid
Role: Civil utility aircraft, primarily used for flight training, personal use,
design, versatility, and reliability. It remains a quintessential aircraft for
and light commercial use.
training new pilots and for general aviation enthusiasts.
Manufacturer: Cessna Aircraft Company, a subsidiary of Textron
Aviation.
First Flight: June 12, 1955.
Introduction: 1956.
Number Built: Over 44,000 units, making it the most produced aircraft in
history.
Design and Features
Configuration: High-wing monoplane with a fixed tricycle landing gear.
Construction: Primarily all-metal, with some composite materials used in
later models.
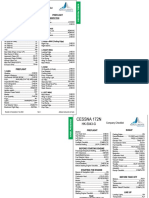
Dimensions
Length: 27 ft 2 in (8.28 m).
Wingspan: 36 ft 1 in (11.00 m).
Height: 8 ft 11 in (2.72 m).
Wing Area: 174 sq ft (16.2 m²).
Performance
Maximum Speed: Approximately 140 knots (259 km/h, 161 mph).
Cruise Speed: Around 122 knots (226 km/h, 140 mph).
Stall Speed: 48 knots (89 km/h, 55 mph) with flaps down.
Range: About 696 nautical miles (1,289 km, 801 miles) with standard fuel
tanks.
Service Ceiling: 14,000 feet (4,267 m).
Rate of Climb: 720 feet per minute (3.7 m/s).
Powerplant
Engine: Typically equipped with a single Lycoming O-320 or IO-360
engine.
Horsepower: Varies by model, generally around 160 to 180 hp.
Capacity
Seating: 4 (pilot and three passengers).
Maximum Takeoff Weight (MTOW): 2,550 lb (1,157 kg).
Empty Weight: Approximately 1,700 lb (770 kg), depending on the
specific model and configuration.
Fuel Capacity: Typically, 56 gallons (212 liters).
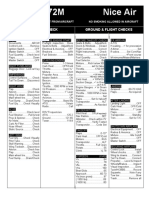
Avionics and Systems
You might also like
- Cessna 172 Skyhawk ChecklistDocument2 pagesCessna 172 Skyhawk Checklistfedor andres82% (33)
- The Basic Aerobatic Manual: With Spin and Upset Recovery TechniquesFrom EverandThe Basic Aerobatic Manual: With Spin and Upset Recovery TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 & 175 Parts Catalog (1956-1962)Document445 pagesCessna 172 & 175 Parts Catalog (1956-1962)NOE GLEZ. V.No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Aircraft WingDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Aircraft WingSai RahulNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Wing AssignmentDocument8 pagesAerodynamics Wing Assignmentosca7100% (1)
- C172 Training Manual SAMPLE 1jul2011Document34 pagesC172 Training Manual SAMPLE 1jul2011Danielle Bruckert100% (3)
- Cessna 172 SP ChecklistDocument12 pagesCessna 172 SP ChecklistTim Morgan100% (39)
- Cessna 172 SkyhawkDocument4 pagesCessna 172 SkyhawkJames Russell S. SanchoNo ratings yet
- CRUZ - Prelim ResearchDocument22 pagesCRUZ - Prelim ResearchRev Xavier CruzNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument4 pagesDesignCatherine MerillenoNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172Document11 pagesCessna 17246mjsswcwfNo ratings yet
- SudhirReddyKonayapalli YSujatha A 61Document8 pagesSudhirReddyKonayapalli YSujatha A 61Zain Ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- El Camino Del Guerrero, CONCLUSIÓNDocument14 pagesEl Camino Del Guerrero, CONCLUSIÓNELECTRONICA SISTEMAS AVIONICSNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172Document19 pagesCessna 172Yan NaingNo ratings yet
- Gliding: SoaringDocument6 pagesGliding: Soaringhòa đỗNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Typical Wing Rib For Passenger AircraftDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Typical Wing Rib For Passenger Aircraftjacob ellyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Aerodynamic Profiles Used and Their ApplicationDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of Aerodynamic Profiles Used and Their Applicationanand maniNo ratings yet
- Skydiving GlossaryDocument12 pagesSkydiving GlossaryAlina Maria MiuNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 - WikipediaDocument18 pagesCessna 172 - Wikipediaakshay patelNo ratings yet
- S2Document13 pagesS2Mukesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Concepts Prelim Stuff Examples of An Aircraft - Non-Acrobatic Operation Includes Any ManeuverDocument8 pagesConcepts Prelim Stuff Examples of An Aircraft - Non-Acrobatic Operation Includes Any ManeuverFejlean Angelica AntineoNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument52 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsJelly MortonNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 DesignDocument20 pagesCessna 172 Designwillmike100% (2)
- Citation X ImprovementsDocument12 pagesCitation X ImprovementsDoor UR100% (1)
- Lift To Drag: AileronsDocument6 pagesLift To Drag: AileronsSyed Qasim ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Hovercraft PDFDocument4 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Hovercraft PDFAniket UgleNo ratings yet
- Design and Finite Element Analysis of Aircraft Wing Using Ribs and SparsDocument8 pagesDesign and Finite Element Analysis of Aircraft Wing Using Ribs and SparsashwinNo ratings yet
- Rana Anurag Aeromodelling Lab Final Report 08Document18 pagesRana Anurag Aeromodelling Lab Final Report 08Anurag RanaNo ratings yet
- GlidingDocument4 pagesGlidingPhương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Micro UAVDocument8 pagesMicro UAVMOST PASONNo ratings yet
- DESIGN 2 REVIEWER MidtermsDocument19 pagesDESIGN 2 REVIEWER MidtermsRalph A. PastranaNo ratings yet
- Design of Bomber Aircraft: Department of Aeronautical Engineering Gojan School of Business and TechnologyDocument51 pagesDesign of Bomber Aircraft: Department of Aeronautical Engineering Gojan School of Business and TechnologyThilak KumarNo ratings yet
- 'Aeronautical 'Trade Project' by LewishDocument36 pages'Aeronautical 'Trade Project' by LewishLewishNo ratings yet
- Ijirt159812 PaperDocument12 pagesIjirt159812 PaperSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Aliya - Aviation PresentationDocument48 pagesAliya - Aviation PresentationahmedshahbazafsarNo ratings yet
- Gliding: SoaringDocument5 pagesGliding: SoaringVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument52 pagesChapter 9 Aircraft Landing Gear Systemsjeremyallan.ligeroNo ratings yet
- GE ELECTIVE FINALS Landscape Microsoft OneNote OnlineDocument31 pagesGE ELECTIVE FINALS Landscape Microsoft OneNote OnlineJune CostalesNo ratings yet
- Design and Finite Element Analysis of Ai PDFDocument7 pagesDesign and Finite Element Analysis of Ai PDFRaja Sekhar BattuNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Types and DesignDocument24 pagesAircraft Types and DesignNataliaNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear StructureDocument12 pagesLanding Gear StructureRayhan AlfaridziNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Evaluation of Polyhedral Swept Back High Wing Chuck Glider For Better L/D RatioDocument12 pagesDesign and Performance Evaluation of Polyhedral Swept Back High Wing Chuck Glider For Better L/D RatioTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- C-172 EFM ManualDocument9 pagesC-172 EFM ManualM BNo ratings yet
- Futuristic Aircraft Wing Configurations PresentationDocument31 pagesFuturistic Aircraft Wing Configurations PresentationAswith R ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-SpDocument12 pagesDesign and Testing of A Winglet Airfoil For Low-Spelouen.wurmserNo ratings yet
- The Fascinating World of Aircraft A Look Into The Main PartsDocument8 pagesThe Fascinating World of Aircraft A Look Into The Main Partsersain05.krgNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of A ParagliderDocument3 pagesAerodynamics of A Paraglider18th Attack SquadronNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Aircraft Wing J Nose Panel Using Mono and Multi Core Composite MaterialsDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis of Aircraft Wing J Nose Panel Using Mono and Multi Core Composite MaterialsstaedtlerpNo ratings yet
- A2A C172 Pilot's ManualDocument102 pagesA2A C172 Pilot's Manualbagarie275% (4)
- IEEE Paper ID 2589Document18 pagesIEEE Paper ID 2589Zianur HaqiNo ratings yet
- Aerothon 2019: Fixed Wing: Team: Squad Alpha 9Document13 pagesAerothon 2019: Fixed Wing: Team: Squad Alpha 9Saad Anwar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Computational Analysis of The Aerodynamic Performance of NACA 4412 and NACA 23012 AirfoilsDocument11 pagesComputational Analysis of The Aerodynamic Performance of NACA 4412 and NACA 23012 AirfoilsSubash DhakalNo ratings yet
- Sae Aero Design West Report, Polytechnic Institute of NYU, 213 PDFDocument30 pagesSae Aero Design West Report, Polytechnic Institute of NYU, 213 PDFShiva KarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- AERODYNAMICSDocument3 pagesAERODYNAMICSfedihaj548No ratings yet
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument120 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsAldwin Ipac Naguiat100% (2)
- Aircraft Landing Gear SystemsDocument120 pagesAircraft Landing Gear SystemsJoshua Christopher RamirezNo ratings yet
- App-C4-Design of Sailplanes PDFDocument32 pagesApp-C4-Design of Sailplanes PDFmiguelNo ratings yet
- Design Consideration and Construction of A BiplaneDocument9 pagesDesign Consideration and Construction of A BiplaneIJMER100% (1)
- App c4 Design of SailplanesDocument32 pagesApp c4 Design of SailplanesfakeNo ratings yet
- MH-RF2: A Cargo Aircraft With Giant Structure and Full of Modern TechnologyDocument69 pagesMH-RF2: A Cargo Aircraft With Giant Structure and Full of Modern Technologyjohn tanvirNo ratings yet
- Swept, Diamond and Delta WingsDocument21 pagesSwept, Diamond and Delta WingsHan Thu AungNo ratings yet
- An Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLFrom EverandAn Aviator's Field Guide to Middle-Altitude Flying: Practical skills and tips for flying between 10,000 and 25,000 feet MSLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 10. ExamDocument5 pages10. ExamDawitNo ratings yet
- COM NoteDocument1 pageCOM NoteDawitNo ratings yet
- Quizlet-Com-668523Document52 pagesQuizlet-Com-668523DawitNo ratings yet
- Eduprojecttopics Com Product Stock Management System Project ReportDocument12 pagesEduprojecttopics Com Product Stock Management System Project ReportDawitNo ratings yet
- GeForce Experience PC Build DIY DirectionsDocument3 pagesGeForce Experience PC Build DIY DirectionsDawitNo ratings yet
- Amt 4101 Activity 1Document14 pagesAmt 4101 Activity 1Brendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Checklist C 172Document2 pagesChecklist C 172KARLSSONNo ratings yet
- SACAA Eagle Air Student Information BrochureDocument23 pagesSACAA Eagle Air Student Information BrochureAnurag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Special Airworthiness Information Bulletin: FAA Aviation SafetyDocument3 pagesSpecial Airworthiness Information Bulletin: FAA Aviation SafetySkoltzAllaniNo ratings yet
- Cessna ActuatorDocument11 pagesCessna ActuatorCTN2010No ratings yet
- C-172 Cessna Skyhawk Quick Reference Normal Operating ChecklistDocument1 pageC-172 Cessna Skyhawk Quick Reference Normal Operating ChecklistPatrick ReisNo ratings yet
- C172 Emergency ProceduresDocument3 pagesC172 Emergency ProceduresAConPCNo ratings yet
- Company Checklist: Normal V - Speeds (Kias) PreflightDocument6 pagesCompany Checklist: Normal V - Speeds (Kias) PreflightJhan Carlo FrancoNo ratings yet
- Service BulletinDocument7 pagesService BulletinBikers BillNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesCessna 172 - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediakarasuilyas123No ratings yet
- TwinDisc Hitachi Nico Marine Transmissions CapacityTableDocument42 pagesTwinDisc Hitachi Nico Marine Transmissions CapacityTablemari adi100% (1)
- CESSNA 172-R Pilot and Flight Crew FamiliarizationDocument67 pagesCESSNA 172-R Pilot and Flight Crew Familiarizationgiuseppe751No ratings yet
- C172 Nav II ChecklistDocument2 pagesC172 Nav II Checklisterik_xNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172 Checklist: C-172 Preflight Inspection C-172 FirstDocument5 pagesCessna 172 Checklist: C-172 Preflight Inspection C-172 FirstGaston Moschen100% (1)
- C172S NavIII Emergencies Checklist-3Document1 pageC172S NavIII Emergencies Checklist-3Matthew BarrowsNo ratings yet
- C172M QRH (VH-JZJ) v1.1Document49 pagesC172M QRH (VH-JZJ) v1.1alphaNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172M Nice Air: Ground & Flight Checks Pre-Flight CheckDocument2 pagesCessna 172M Nice Air: Ground & Flight Checks Pre-Flight CheckMajved Ariel HassanNo ratings yet
- 1 - About CAA Indigo Cadet Pilot ProgrameDocument3 pages1 - About CAA Indigo Cadet Pilot ProgrameAman GhumanNo ratings yet
- Plane Power Reference GuideDocument1 pagePlane Power Reference GuideSkySupplyUSANo ratings yet
- C172S ChecklistDocument13 pagesC172S ChecklistBrandonrjoNo ratings yet
- Cessna172RG Checklist Revised 11-6-12Document24 pagesCessna172RG Checklist Revised 11-6-12alphaNo ratings yet
- Cessna 150 CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesCessna 150 Characteristicsr521999No ratings yet
- Cessna 172S (C172) - Normal and Emergency ChecklistsDocument2 pagesCessna 172S (C172) - Normal and Emergency ChecklistsalphaNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172, 182, 206 SEB-34-16Document18 pagesCessna 172, 182, 206 SEB-34-16Alex AbadNo ratings yet
- Lista de Chequeo 172 NDocument4 pagesLista de Chequeo 172 NJorge Heli Garzon MarinNo ratings yet
- Analog C172 S-R Normal-Emergency ChecklistDocument2 pagesAnalog C172 S-R Normal-Emergency Checklistengin arNo ratings yet