Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sta210 Hypothesis Testing
Sta210 Hypothesis Testing
Uploaded by
Athirah IsaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sta210 Hypothesis Testing
Sta210 Hypothesis Testing
Uploaded by
Athirah IsaCopyright:
Available Formats
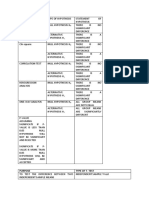
HYPOTHESIS TESTING Nota Tiera
TRADITIONAL METHOD P-VALUE METHOD
1. State the hypotheses and identify the 1. State the hypotheses and identify the
claim. claim.
2. Find the critical value(s) from the 2. Compute the test value.
appropriate table. 3. Find the P-value.
3. Compute the test value. 4. Make the decision.
4. Make the decision to reject or not 5. Summarize the results.
reject the null hypothesis.
5. Summarize the results.
HYPOTHESIS-TESTING COMMON PHRASES
> <
Is greater than Is less than
Is above Is below
Is higher than Is lower than
Is longer than Is shorter than
Is bigger than Is smaller than
Is increased Is decreased or reduced from
¿ ≠
Is equal to Is not equal to
Is the same as Is different from
Has not changed from Has changed from
Is the same as Is not the same as
OUTCOMES OF A HYPOTHESIS-TESTING SITUATION
I. Claim is H 0
Reject H 0 Do not reject H 0
There is enough evidence to There is not enough
reject the claim. evidence to reject the claim.
HYPOTHESIS TESTING Nota Tiera
II. Claim is H 1
Reject H 0 Do not reject H 0
There is enough evidence to There is not enough
support the claim. evidence to support the
claim.
OUTCOMES OF A HYPOTHESIS-TESTING SITUATION FOR TWO SPECIFIC CASES
I. Claim is H 0
Reject H 0 Do not reject H 0
There is enough evidence to There is not enough
reject the claim. evidence to reject the claim.
(a) Decision when claims is H 0 and H 0 is rejected.
II. Claim is H 1
Reject H 0 Do not reject H 0
There is enough evidence to There is not enough
support the claim. evidence to support the
claim.
(b) Decision when claim is H 1 and H 0 is not rejected
DECISION RULE WHEN USING A P-VALUE
If P-value ≤ α , reject the null hypothesis.
If P-value ¿ α , do not reject the null hypothesis.
You might also like
- Btech 1 SemDocument320 pagesBtech 1 SemAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Document13 pagesStatistics & Probability Q4 - Week 1-2Rayezeus Jaiden Del Rosario50% (2)
- UGRD NCM6100 2016S Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocument10 pagesUGRD NCM6100 2016S Theoretical Foundations of NursingRcel BalmesNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 8 Testing of HypothesisDocument51 pagesLecture Notes 8 Testing of HypothesisFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 - 2Document54 pagesChapter3 - 2Hafzal Gani67% (3)
- Day 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingDocument14 pagesDay 9 - Module Hypothesis TestingJoven JaravataNo ratings yet
- Wading Deeper Into The River of GodDocument134 pagesWading Deeper Into The River of Godg.galan100% (1)
- Testing MeansDocument8 pagesTesting MeansboNo ratings yet
- Topik 3 Tes HipotesisDocument46 pagesTopik 3 Tes HipotesisSharnella Janet YapfrineNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis111 PDFDocument3 pagesHypothesis111 PDFjonnydeep1970virgilio.itNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Test1Document31 pagesHypothesis Test1Mario Mora GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Betsy FarberDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing Betsy FarberPungkodi KrishnamaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Part I)Document79 pagesChapter 5 (Part I)Natasha GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument45 pagesHypothesis Testingrushilgoelme20a1053No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 4 PDFQuoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Unit II Hypothesis 1Document32 pagesUnit II Hypothesis 1AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Tests of SignificanceDocument60 pagesTests of SignificancegirmaNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationDocument8 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc. Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel FoundationJasmine BalbinNo ratings yet
- QMMDocument54 pagesQMMgladwin thomasNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - Hypothesis TestingDocument29 pagesLec 7 - Hypothesis TestingABDUR -No ratings yet
- One-Tailed Test Two-Tailed TestDocument18 pagesOne-Tailed Test Two-Tailed Testkassandra panganibanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6. Introduction To Hypothesis TestingDocument20 pagesCHAPTER 6. Introduction To Hypothesis TestingDiệp Anh Hà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument60 pagesHypothesis TestingLaiba ZahirNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses TestingDocument70 pagesHypotheses TestingRajesh JayachandranNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument26 pagesHypothesis TestingGenevieve Bacomo50% (4)
- The P - Value Method of Hypothesis TestingDocument3 pagesThe P - Value Method of Hypothesis TestingCaren JabonNo ratings yet
- Maths ProbStats 12 Digital NotesDocument24 pagesMaths ProbStats 12 Digital NotesganapathyramasubramaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Fundamental of Hypothesis TestingDocument26 pagesCh. 9 Fundamental of Hypothesis TestingUmang ShahNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Hypothesis Testing: - Average Price of A Kilogram of Shrimp in The Philippines IsDocument26 pagesFundamental of Hypothesis Testing: - Average Price of A Kilogram of Shrimp in The Philippines IsJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing and P Value: BY DR Zahid Khan Senior Lecturer King Faisal University, KSADocument16 pagesHypothesis Testing and P Value: BY DR Zahid Khan Senior Lecturer King Faisal University, KSAMayur SomvanshiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesistes Ting and PvaluesDocument16 pagesHypothesistes Ting and Pvalueszbashir786No ratings yet
- Testing HypothisisDocument41 pagesTesting HypothisisProtikNo ratings yet
- Ch11 HypothesesDocument21 pagesCh11 HypothesesNguyen Minh TrangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Fundamental of Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Fundamental of Hypothesis TestingMadhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Betsy FarberDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing Betsy FarberMichael McneilNo ratings yet
- L7-Hypothesis TestingDocument44 pagesL7-Hypothesis TestingAhmed EbisoNo ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006nishant1090No ratings yet
- Unlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006Document15 pagesUnlocking The Mysteries of Hypothesis Testing: Brent Griffin Revised Fall 2006ValanArasuNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document32 pagesUnit 11Kundan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document89 pagesChapter 4Afifa SuibNo ratings yet
- Handouts HyphotesisDocument1 pageHandouts HyphotesisBuddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- This Can Be Answered by Hypothesis TestingDocument19 pagesThis Can Be Answered by Hypothesis TestingJohnby BalasabasNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 Hypothesistesting Diffvariable w11 12Document65 pagesChapter6 Hypothesistesting Diffvariable w11 12Muhamad FarizNo ratings yet
- Type I and II ErrorsDocument35 pagesType I and II ErrorsMarwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hipotese Toetse: Eensteekproef Hypothesis Testing: One SampleDocument16 pagesHipotese Toetse: Eensteekproef Hypothesis Testing: One SampleGregorNo ratings yet
- Test of HypothesisDocument48 pagesTest of HypothesismahendaecNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing - LVC UpdatedDocument54 pagesHypothesis Testing - LVC UpdatedGURUPADA PATINo ratings yet
- Framing The Testable HypothesisDocument48 pagesFraming The Testable HypothesisTaruna BajajNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing 08052022 070212pmAhmed Hassan QureashiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Test FullDocument41 pagesHypothesis Test Fullanindya_kunduNo ratings yet
- One-And Two-Sample Tests of Hypotheses: E 10.1 (Tomato)Document6 pagesOne-And Two-Sample Tests of Hypotheses: E 10.1 (Tomato)Anonymous 8wAMvyQMfNo ratings yet
- Purpose Type of T-TestDocument3 pagesPurpose Type of T-TestPriyanka BobbyNo ratings yet
- Test of HypothesisDocument31 pagesTest of HypothesisJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Biostat Hypothesis TestingDocument67 pagesBiostat Hypothesis Testingshimeles teferaNo ratings yet
- MGMT 222 Ch. V-1Document30 pagesMGMT 222 Ch. V-1Asteway Mesfin100% (1)
- Business Statistics-3Document28 pagesBusiness Statistics-3raynedhakhadaNo ratings yet
- QMI Lecture 7Document54 pagesQMI Lecture 7patrng1No ratings yet
- Week8 Handout 2020Document17 pagesWeek8 Handout 2020Mohammad Rajih BihNo ratings yet
- Foundation Studies General Mathematics B: Hypothesis Testing NotesDocument62 pagesFoundation Studies General Mathematics B: Hypothesis Testing NotesBu-Hilal Alsuwaidi89% (9)
- Unit 7Document9 pagesUnit 7Adam wondwoseNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction TO Ypothesis Esting: o o o oDocument1 pageNtroduction TO Ypothesis Esting: o o o oRein BulahaoNo ratings yet
- INferential StatisticsDocument34 pagesINferential StatisticsNhelia Santos BañagaNo ratings yet
- Homo Interrogans: Questioning and the Intentional Structure of CognitionFrom EverandHomo Interrogans: Questioning and the Intentional Structure of CognitionNo ratings yet
- Textbook Global Perspectives On Stem Cell Technologies 1St Edition Aditya Bharadwaj Eds Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Global Perspectives On Stem Cell Technologies 1St Edition Aditya Bharadwaj Eds Ebook All Chapter PDFnelson.mcclary359100% (11)
- Investigating Reaction RatesDocument5 pagesInvestigating Reaction RatesAgus SalimNo ratings yet
- Science and Truth-Intro IDocument4 pagesScience and Truth-Intro IShotornotNo ratings yet
- IVSemModernWorld PDFDocument115 pagesIVSemModernWorld PDFJishnuNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 - Semifinals - Jan Week 1 To 2Document17 pagesPractical Research 1 - Semifinals - Jan Week 1 To 2Jay DhelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Phitron RoboticsDocument3 pagesChapter-3 Phitron RoboticsDave Joseph CondeNo ratings yet
- John Munby Communicative Syllabus Design Cambridge University Press 1978Document118 pagesJohn Munby Communicative Syllabus Design Cambridge University Press 1978Chloe EisenheartNo ratings yet
- Woman in AstronomyDocument56 pagesWoman in AstronomyKarelNo ratings yet
- Hofstede Never Studied Culture: Rachel F. BaskervilleDocument14 pagesHofstede Never Studied Culture: Rachel F. BaskervilleEvilheart Darktheory D'knightNo ratings yet
- Comparing Bacteria Growth On Door HandlesDocument4 pagesComparing Bacteria Growth On Door HandlesPrateek KNo ratings yet
- de Vaus Chapters 1 and 2Document43 pagesde Vaus Chapters 1 and 2Tamal ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionSyed Omar SayreNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics Library Information ScienceDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics Library Information ScienceWillYouWriteMyPaperForMeSingapore100% (1)
- GP1 - Accuracy and PrecisionDocument4 pagesGP1 - Accuracy and PrecisionMark Anthony AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document10 pagesUnit - 1Prashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Needs Assessment Laboratorium Biologi Pada Madrasah Aliyah: Negeri (Man) Di Kota Banjarmasin Ahmad SalabiDocument27 pagesNeeds Assessment Laboratorium Biologi Pada Madrasah Aliyah: Negeri (Man) Di Kota Banjarmasin Ahmad SalabiHanum DwiratriNo ratings yet
- Annex 2 Proposal Writing GuidelinesDocument4 pagesAnnex 2 Proposal Writing GuidelinesHenok GelanehNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2: Embedding Action Research For Reflective TeachingDocument11 pagesField Study 2: Embedding Action Research For Reflective TeachingCharize Anne MendozaNo ratings yet
- Research Methedology 2Document13 pagesResearch Methedology 2Vidhi JainNo ratings yet
- Importance of The Problems of World View: Alhassanain (P) Network For Islamic Heritage and ThoughtDocument25 pagesImportance of The Problems of World View: Alhassanain (P) Network For Islamic Heritage and Thoughtwww.alhassanain.org.englishNo ratings yet
- Nitatekeleza: NitafanikiwaDocument8 pagesNitatekeleza: Nitafanikiwaapi-280917049No ratings yet
- Ellis Model Information Seeking BehaviourDocument22 pagesEllis Model Information Seeking BehaviourRiki Cesc AriantoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Design: An Imperative For Odissi Dance TeachersDocument16 pagesCurriculum Design: An Imperative For Odissi Dance TeachersRohini DandavateNo ratings yet
- Essay 08 - The Four ElementsDocument3 pagesEssay 08 - The Four ElementsGeoff BoswellNo ratings yet
- BRM (Notes)Document9 pagesBRM (Notes)Rahul GhosaleNo ratings yet
- Julie Thompson Klein - Resources For Interdisciplinary Studies PDFDocument7 pagesJulie Thompson Klein - Resources For Interdisciplinary Studies PDFQuintus SertoriusNo ratings yet