Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Uploaded by
raygelyn apostolCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Devlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsDocument1,241 pagesDevlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsJorge100% (5)
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESlarie_kayne560889% (19)
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesDexter Jess Dag-uman100% (7)
- Life Cycle Assessment of Natural and Mixed Recycled AggregateDocument9 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Natural and Mixed Recycled AggregateBinay DhakalNo ratings yet
- (SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M2 W2Document27 pages(SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M2 W2T Karen WordlabNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BiomoleculesNorie Lyn CARDONA100% (11)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesDocument31 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesMerrie Anne Pascual Bagsic75% (4)
- Q3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Document19 pagesQ3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Lebz RicaramNo ratings yet
- An Extraction of SpinachDocument4 pagesAn Extraction of SpinachDenisse Watt Cuarteros67% (3)
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesSandraNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP Revised 2 BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesDetailed LP Revised 2 BiomoleculesCassy Joy Ellopo RellamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Biomoleculescnjm1104No ratings yet
- DLP ProteinDocument9 pagesDLP ProteinCyrex BuladoNo ratings yet
- CarbsDocument10 pagesCarbsaliemar.tampipiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan With AnnotationDocument8 pagesLesson Plan With AnnotationMarino L. Sanoy100% (1)
- DLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Document6 pagesDLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Abby Castro100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science 10Document12 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10Beryl Andal100% (1)
- LP1 BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesLP1 BiomoleculesInday Selyn100% (1)
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- (KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPDocument6 pages(KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPKaye EstrellaNo ratings yet
- DLL.3rd DemoDocument6 pagesDLL.3rd DemoRhissan Bongalosa Acebuche100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesBiomoleculesEva GarciaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesWORKSHEET Biomoleculesraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week4 (Palawan Division)Document14 pagesDLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week4 (Palawan Division)Maylene VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaPenelope Soria EjadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesLesson-Plan-bio MoleculesJustine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Bio1 LC16Document9 pagesBio1 LC16Evangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 07 - Physical ScienceDocument20 pagesLesson 07 - Physical ScienceJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan School Date Teacher Sec./Time Quarter: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan School Date Teacher Sec./Time Quarter: I. ObjectivesMonalisa TungkagNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesRoxanne Reglos67% (3)
- ELS-DLP Q2-Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument6 pagesELS-DLP Q2-Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeIrish John GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceRodelyn Dahay CalluengNo ratings yet
- CHEM 103M - Compilation of Lecture Notes (Midterms)Document110 pagesCHEM 103M - Compilation of Lecture Notes (Midterms)nuggetNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument3 pagesElementsEva GarciaNo ratings yet
- 5 As Lesson Plan Biomolecules FS 12Document6 pages5 As Lesson Plan Biomolecules FS 12Oniel FajardoNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4 Week 3 BiomoleculesDocument10 pagesScience10 Q4 Week 3 BiomoleculesJomelyn Arzaga100% (4)
- Biology M1 Nature of BiologyDocument25 pagesBiology M1 Nature of BiologyDansNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules: 2 Semester-3 QuarterDocument12 pagesBiological Macromolecules: 2 Semester-3 QuarterDexter Jess Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Document21 pagesQuarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Lynette Licsi100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planjoselyn bergonia100% (1)
- DLP - Day 6-7 (Respiration)Document4 pagesDLP - Day 6-7 (Respiration)kenrick09No ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Chemical Reaction LPDocument23 pagesBiomolecules and Chemical Reaction LPMark TomoNo ratings yet
- DLL-Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesDLL-Cellular RespirationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- DLP GlycolysisDocument3 pagesDLP GlycolysisMichelle NicolasNo ratings yet
- Physical Science M4Document20 pagesPhysical Science M4Aeron GallardoNo ratings yet
- PROTEINS and NUCLEIC ACIDSDocument10 pagesPROTEINS and NUCLEIC ACIDSaliemar.tampipiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument4 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesWelfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Biological MoleculesDocument21 pagesPhysical Science: Biological MoleculesJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Wk6 - 7Document5 pagesSci9 Wk6 - 7Angelicque EserNo ratings yet
- Sacred Heart Diocesan School, Inc: Molave, Zamboanga Del SurDocument3 pagesSacred Heart Diocesan School, Inc: Molave, Zamboanga Del SurEric AbaoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 34-NotesDocument33 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 34-Notes000No ratings yet
- 2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Document5 pages2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Cherrina AguilaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.4Document16 pagesModule 2.4Aletheia Annaliese LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson JanDocument7 pagesCot Lesson JanSittie Asyah Solaiman EdrisNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncNo nameNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade Level Quarter Reference Content StandardDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 9 Grade Level Quarter Reference Content StandardDiana JacintoNo ratings yet
- Judy Chemistry FinalDocument4 pagesJudy Chemistry FinalJudy IntervencionNo ratings yet
- A - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge DemoDocument6 pagesA - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Demoraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Contoso Diversifies Client BaseDocument1 pageContoso Diversifies Client Baseraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Students Will Be Able To Identify Ways They May ReDocument3 pagesStudents Will Be Able To Identify Ways They May Reraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- A - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Final DemoDocument8 pagesA - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Final Demoraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Raygelyn ApostolDocument1 pageActivity 3 - Raygelyn Apostolraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- ENVIBIO - Mam JenDocument2 pagesENVIBIO - Mam Jenraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Biomass As An Alternative For Gas Production: Liliana Pampillón-González and José Ramón Laines CanepaDocument18 pagesBiomass As An Alternative For Gas Production: Liliana Pampillón-González and José Ramón Laines CanepaKhangDươngNo ratings yet
- ОЕКО-ТЕХ MASTER TEXTILE-конвертированDocument1 pageОЕКО-ТЕХ MASTER TEXTILE-конвертированХристина ПавленкоNo ratings yet
- Ugi ReactionDocument12 pagesUgi ReactionFiruj AhmedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oxidation ProcessDocument3 pagesAdvanced Oxidation ProcessBakul HossainNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsesDocument17 pagesAromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsessoujirosettaNo ratings yet
- Yohimbine InjectionDocument1 pageYohimbine InjectionKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds - Vinay Kumar Pandey ASSGNDocument44 pagesAromatic Compounds - Vinay Kumar Pandey ASSGNPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Environmental Assessment: 1. Date 2. Name of Applicant/Petitioner 3. AddressDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Assessment: 1. Date 2. Name of Applicant/Petitioner 3. Addressjonathan smithersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Test BankDocument20 pagesChapter 14 Test BankquynhphamftNo ratings yet
- Fate and Effects of Amphoteric Surfactants in The AquaticDocument5 pagesFate and Effects of Amphoteric Surfactants in The AquaticDenisaMVNo ratings yet
- News Frying Oil Archives - FiltroxDocument35 pagesNews Frying Oil Archives - FiltroxSQF PractitionerNo ratings yet
- 0733E PolyacrilateDocument1 page0733E PolyacrilatenakitaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Plant Design and Economics-Phthalic Anhydride Design Report (Very Good PFD)Document171 pages2019 Plant Design and Economics-Phthalic Anhydride Design Report (Very Good PFD)daraj darajNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Sko3033 PDFDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 Sko3033 PDFFiona Tiwon100% (1)
- Molecules of LifeDocument5 pagesMolecules of LifeGabriela UnoNo ratings yet
- Critical Review On Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in VivoDocument15 pagesCritical Review On Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in VivoasaaguurNo ratings yet
- GRAS Substances (3755-3774)Document6 pagesGRAS Substances (3755-3774)born2dive 9702No ratings yet
- 4714 34335 1 PBDocument14 pages4714 34335 1 PBDarian HerascuNo ratings yet
- 3M Edgesealer 3950Document13 pages3M Edgesealer 3950Imran MustafaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Thermal Pasteurization On Shelf Life and Quality of Kalparasa (Coconut Sap)Document4 pagesEffect of Thermal Pasteurization On Shelf Life and Quality of Kalparasa (Coconut Sap)v s patilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolmengulhounuoNo ratings yet
- Basf Patent PDFDocument7 pagesBasf Patent PDFNabila MGNo ratings yet
- Process For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsDocument5 pagesProcess For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsHarry CortezNo ratings yet
- Sn12, E12 - Exam 2 Practice Problems and KeysDocument40 pagesSn12, E12 - Exam 2 Practice Problems and KeysNguyễn Khánh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (Class 12)Document29 pagesChemistry Project (Class 12)Soumyakanta MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fiberglass Products: Product Line Overview & CapabilitiesDocument16 pagesFiberglass Products: Product Line Overview & CapabilitiesJairo FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueSobi SitjarNo ratings yet
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Uploaded by
raygelyn apostolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Detailed Lesson Plan I N Physical Science 1
Uploaded by
raygelyn apostolCopyright:
Available Formats
DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN PHYSICAL SCIENCE
School Learning SCIENCE
PENHS- Senior High
Area
GRADE 12 Teache REYMARK L. Quarter 3rd
r MALAYAO
Date March 11, 2024 Time 7:30-8:30 am
I. OBJECTIVES
1. Content The learners demonstrate an understanding of the relationship
Standards between the function and structure of biological macromolecules
2. Performanc The learners shall be able to distinguish the structures of different
e Standards biological macromolecules and relate them to their properties
3. Learning a. Explain how the structures of carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic
Competenci acid and proteins, and determine their properties and
es/ functions (S11/12PS-IIIe-22)
Objectives At the end of the lesson, the learners shall be able to:
1. Distinguish between carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic
acids
2. Complete a graphic organizer to summarize the general
characteristics of each biomolecule
3. Express realization on the importance of having a balanced diet
II. CONTENT BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES:
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids
III. LEARNING
MATERIALS
A. References
1. Teacher’s Teaching Guide for Senior High School PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Guide
2. Learner’s
Materials
3. Textbook PHYSICAL SCIENCE, 7th Edition by Whitten, et.al
4. Additional
Materials
from
learning
resource
portal
B. Other Activity sheets, laptop and monitor
Learning
Resources
IV. Teacher’s Activity Students’ Activity
PROCEDURES
Preliminaries Great morning everyone… Great morning, Sir!
Before anything else, may Everyone is present sir.
we all stand for a prayer.
Let’s check if who is absent
from the class?
Now, let me remind you as
we go along with our
lesson, if you have any
question or if you want to
answer please raise your
hands.
Thank you.
A. Reviewing Let’s review what are some
previous two types of polymers we
lesson or discussed before and give Sir, there are two types of polymers:
presenting examples each. Synthetic polymers are derived
the new from petroleum oil, and made by
lesson scientists and engineers.
Examples of synthetic polymers
include nylon, polyethylene,
polyester, Teflon, and epoxy while
Natural polymers occur in nature
and can be extracted. They are
often water-based.
Examples of naturally occurring
polymers are silk, wool, DNA,
cellulose and proteins.
B. Establishin I will be posting a picture
g a purpose and give me your
for the thoughts/ideas about it.
lesson
Sir we are related to the food we ingest
and to be healthy you need to eat good
To explore the lesson more, food.
the students are task to
answer the activity called
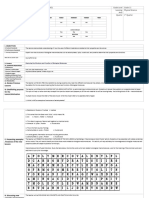
“BioWord Hunting”.
Pre-discussion for the
activity:
Food is a source of
molecules that are F A T S H Y L I P I D P
needed for life. These U P I A T E P R O T E R
are biological N U C L E I C A C I D O
molecules. What you
Y T K T L P D G O G O T
eat belongs to
C A R B O H Y D R A T E
biomolecules. There
A R O A A H L E W V W I
are four biological
molecules that make B I O M O L E C U L E N
up all of life.
The teacher will give
a word hunting
activity to warm up
the students.
Instruction. Look
for the words and
write your Answers:
biomolecule,
carbohydrate, lipid,
protein, and nucleic
acid.
What’s in the Basket?
Students will pass around a basket where
there are keywords/pictures
inside. Once the music stops, the student
holding the basket will get a picture
inside. He/She will identify the
macromolecule found in the food in
the picture.
C. Presenting Presents that organic
examples/ molecules are produced by
instances of living organisms.
the lesson
What are common
elements that are
produced by living Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen
organisms? sir.
What are the four Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and
categories of biomolecules? Nucleic Acid sir.
Very Good! In Addition,
Carbohydrates is the
simplest biomolecules
Contain 3 elements:
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Example:
polysaccharide
Building block:
monosaccharide
Take Note that Protein
provides us with building
blocks for life!
Also regulate most
functions in a cell.
Glycoproteins
(antigens)
Combines w/DNA to
form chromosomes
Antibodies (fights
disease)
Can you give me
examples of proteins? Eggs, fishes, red meat and chicken sir.
Can you give me other
functions of proteins?
Provides structure & strength
(fibers)
Transports molecules in & out cells
Hemoglobin (transports O2)
Enzymes (speeds up rxns)- has –
ase suffix
Acts as hormones (insulin)- many
proteins have suffix of -in
D. Discussing
New Let us proceed with
Concepts & lipids.
Practicing Lipids include:
New Skills # Fats
Oils
Most lipids are made
of just carbon,
hydrogen, and
oxygen.
But unlike
carbohydrates, fats
are more complex &
take much longer
to break down.
So, fats are high-
energy molecules Sir it is made mainly of carbon and
that plants and hydrogen (few oxygen)
animals use to store Fat best method of STORING
energy in reserves forms cell membranes
for longer periods. Insulates body (maintains
What are other functions homeostasis)
of lipids?
Note that Nucleic Acid
Contains C, H, O, N, P
Ex: DNA/RNA
Bldg. Block:
NUCLEOTIDES
Nucleotides consist
of 3 parts:
1. 5-Carbon
Sugar
2. Phosphate
Group
3. Nitrogenous
Base
Activity: BioMac, How Do
They Act?
Each group will be
assigned to a
macromolecule and they
will be given set of guide
questions to answer for 15
minutes. (see attached)
Students present their output.
E. Finding Ask the students, “What
Practical can you say about people
Applications who are on a Students answer may vary.
of Concepts “one type of food diet” (for
and Skills example, they will only eat
in Daily crackers for the whole
Living week).
F. Making Students will watch a video
Generalizati summarizing the lesson.
ons and Then, they will complete a
Abstraction graphic organizer to
s about the summarize all the
Lesson biological macromolecules.
Students present their output.
G. Evaluating Each group will be given
Learning pictures to raise for their
answers. They will identify
the macromolecule
described in each of the
following.
1. The building block is
nucleotides
2. It is composed of C, H,
and O
3. Can function as enzyme,
or antibody
4. Is not soluble in water
5. DNA and RNA are its
examples.
H. Additional Make an acrostic poem
Activities for that describes each of the
Application biological macromolecules. Example:
or P-roteins like keratin and collagen build
Remediatio hair and nails as well as ligaments in skin
R-eactions are sped up with enzymes
such as catalysts
O-xygen and carbon are two elements that
all proteins have
T-he 20 common building blocks called
amino acids make up the molecule
E-xamples of foods that have proteins are
meat, poultry, milk, fish and nuts
I-nsulin is carried by hemoglobin, which
is produced by certain proteins that work
with the circulatory system
Prepared by: Checked by:
REYMARK L. MALAYAO ROWENA VENESA C. PAGALILAUAN
Subject Teacher Head Teacher III
Approved by:
TEODOLFO C. LOPEZ
School Head
You might also like
- Devlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsDocument1,241 pagesDevlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsJorge100% (5)
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESlarie_kayne560889% (19)
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesDexter Jess Dag-uman100% (7)
- Life Cycle Assessment of Natural and Mixed Recycled AggregateDocument9 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Natural and Mixed Recycled AggregateBinay DhakalNo ratings yet
- (SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M2 W2Document27 pages(SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M2 W2T Karen WordlabNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in BiomoleculesNorie Lyn CARDONA100% (11)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesDocument31 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesMerrie Anne Pascual Bagsic75% (4)
- Q3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Document19 pagesQ3 G11 Physical Science Module 7Lebz RicaramNo ratings yet
- An Extraction of SpinachDocument4 pagesAn Extraction of SpinachDenisse Watt Cuarteros67% (3)
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesSandraNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP Revised 2 BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesDetailed LP Revised 2 BiomoleculesCassy Joy Ellopo RellamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Biomoleculescnjm1104No ratings yet
- DLP ProteinDocument9 pagesDLP ProteinCyrex BuladoNo ratings yet
- CarbsDocument10 pagesCarbsaliemar.tampipiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan With AnnotationDocument8 pagesLesson Plan With AnnotationMarino L. Sanoy100% (1)
- DLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Document6 pagesDLP - BIOMOLECULES (Castro, Abegail C.)Abby Castro100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science 10Document12 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10Beryl Andal100% (1)
- LP1 BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesLP1 BiomoleculesInday Selyn100% (1)
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- (KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPDocument6 pages(KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPKaye EstrellaNo ratings yet
- DLL.3rd DemoDocument6 pagesDLL.3rd DemoRhissan Bongalosa Acebuche100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10: Junior High School DepartmentJoanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesBiomoleculesEva GarciaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesWORKSHEET Biomoleculesraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week4 (Palawan Division)Document14 pagesDLL SHS STEM Science Grade 11 - Earth & Life Quarter2 Week4 (Palawan Division)Maylene VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaPenelope Soria EjadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesLesson-Plan-bio MoleculesJustine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Bio1 LC16Document9 pagesBio1 LC16Evangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 07 - Physical ScienceDocument20 pagesLesson 07 - Physical ScienceJoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan School Date Teacher Sec./Time Quarter: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan School Date Teacher Sec./Time Quarter: I. ObjectivesMonalisa TungkagNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesRoxanne Reglos67% (3)
- ELS-DLP Q2-Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument6 pagesELS-DLP Q2-Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeIrish John GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceRodelyn Dahay CalluengNo ratings yet
- CHEM 103M - Compilation of Lecture Notes (Midterms)Document110 pagesCHEM 103M - Compilation of Lecture Notes (Midterms)nuggetNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument3 pagesElementsEva GarciaNo ratings yet
- 5 As Lesson Plan Biomolecules FS 12Document6 pages5 As Lesson Plan Biomolecules FS 12Oniel FajardoNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4 Week 3 BiomoleculesDocument10 pagesScience10 Q4 Week 3 BiomoleculesJomelyn Arzaga100% (4)
- Biology M1 Nature of BiologyDocument25 pagesBiology M1 Nature of BiologyDansNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules: 2 Semester-3 QuarterDocument12 pagesBiological Macromolecules: 2 Semester-3 QuarterDexter Jess Dag-umanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Document21 pagesQuarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Lynette Licsi100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planjoselyn bergonia100% (1)
- DLP - Day 6-7 (Respiration)Document4 pagesDLP - Day 6-7 (Respiration)kenrick09No ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Chemical Reaction LPDocument23 pagesBiomolecules and Chemical Reaction LPMark TomoNo ratings yet
- DLL-Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesDLL-Cellular RespirationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- DLP GlycolysisDocument3 pagesDLP GlycolysisMichelle NicolasNo ratings yet
- Physical Science M4Document20 pagesPhysical Science M4Aeron GallardoNo ratings yet
- PROTEINS and NUCLEIC ACIDSDocument10 pagesPROTEINS and NUCLEIC ACIDSaliemar.tampipiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument4 pagesLesson Guide in Earth and Life Science I. Objectives: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesWelfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Biological MoleculesDocument21 pagesPhysical Science: Biological MoleculesJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Wk6 - 7Document5 pagesSci9 Wk6 - 7Angelicque EserNo ratings yet
- Sacred Heart Diocesan School, Inc: Molave, Zamboanga Del SurDocument3 pagesSacred Heart Diocesan School, Inc: Molave, Zamboanga Del SurEric AbaoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 34-NotesDocument33 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q4 MODULE 34-Notes000No ratings yet
- 2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Document5 pages2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Cherrina AguilaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.4Document16 pagesModule 2.4Aletheia Annaliese LamperougeNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson JanDocument7 pagesCot Lesson JanSittie Asyah Solaiman EdrisNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncDocument10 pagesPhysical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncNo nameNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 9 Grade Level Quarter Reference Content StandardDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 9 Grade Level Quarter Reference Content StandardDiana JacintoNo ratings yet
- Judy Chemistry FinalDocument4 pagesJudy Chemistry FinalJudy IntervencionNo ratings yet
- A - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge DemoDocument6 pagesA - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Demoraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Contoso Diversifies Client BaseDocument1 pageContoso Diversifies Client Baseraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Students Will Be Able To Identify Ways They May ReDocument3 pagesStudents Will Be Able To Identify Ways They May Reraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- A - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Final DemoDocument8 pagesA - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Science - Grade - Rayge Final Demoraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Raygelyn ApostolDocument1 pageActivity 3 - Raygelyn Apostolraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- ENVIBIO - Mam JenDocument2 pagesENVIBIO - Mam Jenraygelyn apostolNo ratings yet
- Biomass As An Alternative For Gas Production: Liliana Pampillón-González and José Ramón Laines CanepaDocument18 pagesBiomass As An Alternative For Gas Production: Liliana Pampillón-González and José Ramón Laines CanepaKhangDươngNo ratings yet
- ОЕКО-ТЕХ MASTER TEXTILE-конвертированDocument1 pageОЕКО-ТЕХ MASTER TEXTILE-конвертированХристина ПавленкоNo ratings yet
- Ugi ReactionDocument12 pagesUgi ReactionFiruj AhmedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oxidation ProcessDocument3 pagesAdvanced Oxidation ProcessBakul HossainNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsesDocument17 pagesAromatic Hydrocarbo N Type of Organic Compound Iupac Name Common Name Chemical Formula / Structure UsessoujirosettaNo ratings yet
- Yohimbine InjectionDocument1 pageYohimbine InjectionKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds - Vinay Kumar Pandey ASSGNDocument44 pagesAromatic Compounds - Vinay Kumar Pandey ASSGNPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Environmental Assessment: 1. Date 2. Name of Applicant/Petitioner 3. AddressDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Assessment: 1. Date 2. Name of Applicant/Petitioner 3. Addressjonathan smithersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Test BankDocument20 pagesChapter 14 Test BankquynhphamftNo ratings yet
- Fate and Effects of Amphoteric Surfactants in The AquaticDocument5 pagesFate and Effects of Amphoteric Surfactants in The AquaticDenisaMVNo ratings yet
- News Frying Oil Archives - FiltroxDocument35 pagesNews Frying Oil Archives - FiltroxSQF PractitionerNo ratings yet
- 0733E PolyacrilateDocument1 page0733E PolyacrilatenakitaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Plant Design and Economics-Phthalic Anhydride Design Report (Very Good PFD)Document171 pages2019 Plant Design and Economics-Phthalic Anhydride Design Report (Very Good PFD)daraj darajNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Sko3033 PDFDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 Sko3033 PDFFiona Tiwon100% (1)
- Molecules of LifeDocument5 pagesMolecules of LifeGabriela UnoNo ratings yet
- Critical Review On Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in VivoDocument15 pagesCritical Review On Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in VivoasaaguurNo ratings yet
- GRAS Substances (3755-3774)Document6 pagesGRAS Substances (3755-3774)born2dive 9702No ratings yet
- 4714 34335 1 PBDocument14 pages4714 34335 1 PBDarian HerascuNo ratings yet
- 3M Edgesealer 3950Document13 pages3M Edgesealer 3950Imran MustafaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Thermal Pasteurization On Shelf Life and Quality of Kalparasa (Coconut Sap)Document4 pagesEffect of Thermal Pasteurization On Shelf Life and Quality of Kalparasa (Coconut Sap)v s patilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Mengulhounuo Keretsu Class: 12 (Science) School: Maple Tree SchoolmengulhounuoNo ratings yet
- Basf Patent PDFDocument7 pagesBasf Patent PDFNabila MGNo ratings yet
- Process For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsDocument5 pagesProcess For The Production of Sucrose Esters of Fatty AcidsHarry CortezNo ratings yet
- Sn12, E12 - Exam 2 Practice Problems and KeysDocument40 pagesSn12, E12 - Exam 2 Practice Problems and KeysNguyễn Khánh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (Class 12)Document29 pagesChemistry Project (Class 12)Soumyakanta MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Fiberglass Products: Product Line Overview & CapabilitiesDocument16 pagesFiberglass Products: Product Line Overview & CapabilitiesJairo FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Separation and Purification TechniqueSobi SitjarNo ratings yet