Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Title - An Overview of Powder Metallurgy - Process, Applications, and Advantages
Title - An Overview of Powder Metallurgy - Process, Applications, and Advantages
Uploaded by
hellashah5412Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Title - An Overview of Powder Metallurgy - Process, Applications, and Advantages
Title - An Overview of Powder Metallurgy - Process, Applications, and Advantages
Uploaded by
hellashah5412Copyright:
Available Formats
Title: An Overview of Powder Metallurgy: Process, Applications, and Advantages
Introduction to Powder Metallurgy:
Powder metallurgy (PM) is a versatile manufacturing process that involves the production of
parts from powdered metals or metal alloys. It offers numerous advantages over
conventional methods, such as casting or machining. This article provides an in-depth
exploration of the powder metallurgy process, its applications across various industries, and
the advantages it brings to the table.
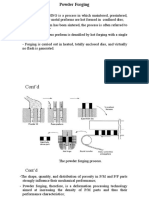
1. Powder Production:
- Powder production is the first step in the powder metallurgy process.
- Methods include atomization, mechanical comminution, and chemical processes.
- Particle size and morphology play a crucial role in determining the properties of the final
product.
2. Powder Compaction:
- Compaction involves pressing the metal powders into a desired shape using a die and
applying high pressure.
- Various techniques like uniaxial pressing, isostatic pressing, and powder injection
molding are employed.
- The density and green strength of the compact are critical parameters controlled during
this stage.
3. Sintering:
- Sintering is the process of heating the compacted powder at elevated temperatures
below its melting point.
- It facilitates the bonding of powder particles, resulting in a solid, coherent mass.
- Factors influencing sintering include temperature, atmosphere, and time.
4. Secondary Operations:
- Secondary operations may include heat treatment, machining, and surface finishing to
achieve the desired properties and surface characteristics.
- These processes enhance the mechanical, physical, and chemical properties of the final
product.
5. Applications of Powder Metallurgy:
- Automotive Industry: PM is extensively used in automotive components such as gears,
bearings, and bushings due to its cost-effectiveness and precision.
- Aerospace Industry: Aerospace applications include engine parts, structural components,
and heat exchangers where lightweight and high strength are critical.
- Medical Sector: Surgical instruments, dental implants, and orthopedic implants benefit
from PM's ability to produce complex shapes with high precision.
- Electronics: PM is utilized in electronic components such as magnetic cores, connectors,
and heat sinks due to its excellent magnetic properties and thermal conductivity.
6. Advantages of Powder Metallurgy:
- Material Utilization: PM allows for near-net-shape manufacturing, minimizing material
waste.
- Complex Geometries: It enables the production of intricate shapes and designs that are
difficult or impossible to achieve through conventional methods.
- Material Diversity: PM can accommodate a wide range of materials, including ferrous and
non-ferrous metals, ceramics, and composites.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Despite initial tooling costs, PM often proves cost-effective for
high-volume production due to reduced machining and assembly requirements.
- Enhanced Properties: Through proper alloying and process control, PM parts exhibit
superior mechanical, magnetic, and corrosion-resistant properties.
Conclusion:
Powder metallurgy is a versatile manufacturing process that continues to gain prominence
across various industries due to its ability to produce complex components with enhanced
properties in a cost-effective manner. Understanding the powder metallurgy process, its
applications, and advantages is crucial for leveraging its full potential in modern
manufacturing.
This overview encapsulates the essence of powder metallurgy, highlighting its significance
as a pivotal technology in the realm of materials science and engineering.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 Chemistry and Measurement Practice Quiz (General Chemistry Ebbing 9E)Document3 pagesChapter 1 Chemistry and Measurement Practice Quiz (General Chemistry Ebbing 9E)God Bless AmericaNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Process PDFDocument2 pagesExtrusion Process PDFSamantha50% (2)
- Powder Metallurgy - Dany DegheadyDocument16 pagesPowder Metallurgy - Dany Degheadydany.degheady08No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesLecture 1 IntroductionguruNo ratings yet
- Conventional Powdered Metal ComponentsDocument15 pagesConventional Powdered Metal ComponentsPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy PDF - Amrita UniversityDocument44 pagesPowder Metallurgy PDF - Amrita UniversityAkshay RajanNo ratings yet
- GoodDocument32 pagesGoodChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- PNC4 - Powder MetallurgyDocument5 pagesPNC4 - Powder MetallurgyAlpNo ratings yet
- Particle SizeDocument38 pagesParticle SizeChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder MetallurgyDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Powder Metallurgyvinslin67% (6)
- New Microsoft Office Word Document2Document10 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Document2Mohammed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Manufacturing-Process Powder-Metallurgy NotesDocument14 pagesMechanical Engineering Manufacturing-Process Powder-Metallurgy NotesSiddheswar BiswalNo ratings yet
- To PM Technology: A Guide For Designers and EngineersDocument30 pagesTo PM Technology: A Guide For Designers and EngineersBasliu DoinaNo ratings yet
- Ali 123Document3 pagesAli 123Zain TabishNo ratings yet
- Recent Technology of Powder Metallurgy and ApplicationsDocument32 pagesRecent Technology of Powder Metallurgy and ApplicationsMuralli Jayaganesan100% (2)
- MME 3518-Powder Metallurgy-1-2Document80 pagesMME 3518-Powder Metallurgy-1-2Mohammed GhisheerNo ratings yet
- Powder Composite Related To Powder Metallurgy: Ordinance Factory Institute of LearningDocument72 pagesPowder Composite Related To Powder Metallurgy: Ordinance Factory Institute of LearningriyamondalNo ratings yet
- EPMA-Final - HIP - Brochure - Introduction To PM HIP TechnologyDocument30 pagesEPMA-Final - HIP - Brochure - Introduction To PM HIP TechnologygillougillouNo ratings yet
- MMR Article - Sachin Malgave, Indo-MIMDocument3 pagesMMR Article - Sachin Malgave, Indo-MIMIndo-MIMNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument6 pagesPowder MetallurgyjayadevakodiNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument24 pagesPowder MetallurgyNitin Gupta100% (1)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument24 pagesPowder MetallurgyMilan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Primary Forming Processes - Dany Degheady (1)Document13 pagesPrimary Forming Processes - Dany Degheady (1)dany.degheady08No ratings yet
- Al-Mno System Powder Production Analysis of Powder 1. Sieve Analysis 2. Tg-Dta AnalysisDocument15 pagesAl-Mno System Powder Production Analysis of Powder 1. Sieve Analysis 2. Tg-Dta Analysisraghavendrajoshi87No ratings yet
- Synopsis On Professional Practice ProjectDocument5 pagesSynopsis On Professional Practice Projectabhishekkumar1_gbpecNo ratings yet
- AME - M1 Ktunotes - inDocument71 pagesAME - M1 Ktunotes - inMadhav P SachithNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Seminar GautamDocument31 pagesPowder Metallurgy Seminar GautamSidhartha GolchhaNo ratings yet
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Metallurgy TechnologyDocument7 pagesThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Metallurgy Technologyankitrao31100% (2)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument26 pagesPowder MetallurgyVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering ProblemDocument6 pagesComplex Engineering ProblemMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (Class15) Powder Metallurgy: Part BDocument8 pagesUnit 8 (Class15) Powder Metallurgy: Part BrajarajanNo ratings yet
- POWDERMETTRALUGYDocument9 pagesPOWDERMETTRALUGYNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document39 pagesChapter 4Ervenjee BascoNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding of Microstructured Components From Plastics, Metals and CeramicsDocument8 pagesInjection Molding of Microstructured Components From Plastics, Metals and CeramicsFabian SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument11 pagesPowder MetallurgyChandan PathakNo ratings yet
- Powder MetallurgyDocument18 pagesPowder MetallurgyBhupendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Powder Met CH 1Document28 pagesPowder Met CH 1thomasvictor2005No ratings yet
- Die PMDocument50 pagesDie PMRajaNo ratings yet
- Uses of Powder Metallurgy in Recent Development in VehiclesDocument9 pagesUses of Powder Metallurgy in Recent Development in VehiclesNishant DeyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - PMDocument46 pagesModule 1 - PMFRANCIS THOMASNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy: Forging Process of Connecting RodDocument24 pagesPowder Metallurgy: Forging Process of Connecting RodDera LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy ThesisDocument5 pagesPowder Metallurgy ThesisPurchaseCollegePapersCanada100% (3)
- Metalurgi Serbuk p3Document3 pagesMetalurgi Serbuk p3nonameNo ratings yet
- Parameter Optimization of Metal Injection Moulding: A ReviewDocument15 pagesParameter Optimization of Metal Injection Moulding: A ReviewKresna Dwi PutrantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document59 pagesChapter 9amonmeizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Powder ForgingmscDocument23 pagesChapter 6 Powder ForgingmscDesalegn DgaNo ratings yet
- MECH202 - 2015-16 FALL - L04 - Powder MetallurgyDocument46 pagesMECH202 - 2015-16 FALL - L04 - Powder MetallurgyDanish IftikharNo ratings yet
- Nptel WeldingDocument233 pagesNptel WeldingThasarathan Ravichandran100% (2)
- Powder MetallurgyDocument4 pagesPowder MetallurgyAndri YanNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument3 pagesMaterialsQlangNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering &: TechnologyDocument4 pagesKhulna University of Engineering &: TechnologyASHIR HASAN NIBIRNo ratings yet
- Unit III - Introduction To Manufacturing EngineeringDocument281 pagesUnit III - Introduction To Manufacturing EngineeringJohnNo ratings yet
- Power Metallurgy and PLC NotesDocument46 pagesPower Metallurgy and PLC NotesFRANCIS THOMASNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mechanical Properties of Sintered and Hot Extruded Aluminium and Aluminium Based Titania CompositesDocument9 pagesAssessment of Mechanical Properties of Sintered and Hot Extruded Aluminium and Aluminium Based Titania CompositesAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- V4i4 1287Document2 pagesV4i4 1287waris rNo ratings yet
- Materials For MoldDocument52 pagesMaterials For MoldSnowy DoveNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy WikDocument11 pagesPowder Metallurgy WiksiswoutNo ratings yet
- Nptel WeldingDocument236 pagesNptel WeldingNishankzattNo ratings yet
- Effect On The Mechanical Properties of Sintering Process of Aluminium Alloys (#651528) - 914969Document7 pagesEffect On The Mechanical Properties of Sintering Process of Aluminium Alloys (#651528) - 914969kahramanNo ratings yet
- Adhesion Promoter Makes Hybrid Components Even Lighter and More RigidDocument6 pagesAdhesion Promoter Makes Hybrid Components Even Lighter and More RigidSebastian AndreoliNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Advantages and LimitationsDocument6 pagesPowder Metallurgy Advantages and LimitationsHafiezul HassanNo ratings yet
- En 934 3Document7 pagesEn 934 3Temur LomidzeNo ratings yet
- Amc Corewell™: Advantages DescriptionDocument1 pageAmc Corewell™: Advantages DescriptionDakhlanNo ratings yet
- Pipes CATALOGUE PDFDocument3 pagesPipes CATALOGUE PDFYusma NurNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry ProjectAadarsh MouryaNo ratings yet
- DensobandDocument1 pageDensobandShamsul Bahrin SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Shell Gadus S3 V460 LeafletDocument2 pagesShell Gadus S3 V460 Leafletluismanuel.g10No ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Physical Properties of Cotton, Bamboo, Viscose and Modal Union Fabric For Kids Wear, Women Wear and Men WearDocument8 pagesComparative Study of Physical Properties of Cotton, Bamboo, Viscose and Modal Union Fabric For Kids Wear, Women Wear and Men WearImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- Modern Blast Furnace IronmakingDocument10 pagesModern Blast Furnace IronmakingNancy Carolina Prieto Martinez100% (2)
- Road Maps Organic Chemistry Set 4 Eklavya @JEEAdvanced - 2024Document13 pagesRoad Maps Organic Chemistry Set 4 Eklavya @JEEAdvanced - 2024puneethrgcNo ratings yet
- PNO52 245 71687 v1 ENDocument8 pagesPNO52 245 71687 v1 ENjtcool74100% (1)
- Reach SVHC List Excel TableDocument14 pagesReach SVHC List Excel Tablebb bamNo ratings yet
- SAE 3000 PsiDocument27 pagesSAE 3000 PsiWilson JustinoNo ratings yet
- Thyssenkrupp Electrical Steel: Why Powercore?Document6 pagesThyssenkrupp Electrical Steel: Why Powercore?Chirag PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PYQDocument33 pagesChemistry PYQelisee alangbaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Effects in High Strength SteelsDocument36 pagesHydrogen Effects in High Strength SteelsNattapong PongbootNo ratings yet
- Ar Ged 04Document1 pageAr Ged 04Bahaa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ansi-Aws A5 - 18-93Document37 pagesAnsi-Aws A5 - 18-93skrkulachiNo ratings yet
- Brake L Specification Text Brake Leur ADocument3 pagesBrake L Specification Text Brake Leur AhjduarteNo ratings yet
- Zeroflame Aquasteel-Certificate-Alicia SeebaluckDocument1 pageZeroflame Aquasteel-Certificate-Alicia SeebaluckGulsher KhanNo ratings yet
- Crystal DefectsDocument35 pagesCrystal DefectsTim_Junsu_266No ratings yet
- Guide To OvermouldingDocument10 pagesGuide To OvermouldingVivek AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Textile Journal ListDocument2 pagesTextile Journal ListNat RajaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2sakinah azizanNo ratings yet
- TecCrete FlooringDocument98 pagesTecCrete FlooringDiaszNo ratings yet
- SMAW 9 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2Document29 pagesSMAW 9 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2Romeo Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Solid Carbide End Mills For 48HRC: Micro Grain 10% Co Grade 2 Flute Iso CodeDocument10 pagesSolid Carbide End Mills For 48HRC: Micro Grain 10% Co Grade 2 Flute Iso CodepromoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument11 pagesChapter IIbale, Arjay D.No ratings yet
- Nomex Arc: Extreme Protection ColorDocument2 pagesNomex Arc: Extreme Protection ColorRobert AndrewNo ratings yet