Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guided and Unguided Media in Communication Networks
Guided and Unguided Media in Communication Networks
Uploaded by
717823z1150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesOriginal Title
GUIDED AND UNGUIDED MEDIA IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesGuided and Unguided Media in Communication Networks
Guided and Unguided Media in Communication Networks
Uploaded by
717823z115Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
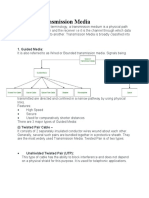
GUIDED AND UNGUIDED MEDIA IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
Guided Media
Guided media refers to the transmission of data through a physical conduit, directing the signal along
a specific path.
TYPES OF GUIDED MEDIA
1. Twisted Pair Cable:
Consists of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together.
Applications: Telephony, local area networks (LANs).
Pros:
- Inexpensive.
- Easy to install and maintain.
- Flexible and lightweight.
Cons:
- Limited bandwidth and distance.
- Susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
2. Coaxial Cable:A single copper conductor at its center, surrounded by a plastic layer for insulation
and a metallic shield.
Applications: Cable television, broadband internet.
Pros:
- Higher bandwidth than twisted pair.
- Less susceptible to EMI.
Cons:
- Bulkier and less flexible than twisted pair.
- More expensive than twisted pair.
3. Fiber Optic Cable
Uses light to transmit data, consists of a core surrounded by cladding and protective layers.
Applications: Long-distance telecommunication, internet backbone, medical imaging.
Pros:
- Very high bandwidth and long-distance capabilities.
- Immunity to EMI.
- Secure from eavesdropping.
Cons:
- Expensive to install and maintain.
- Requires specialized equipment for splicing and termination.
UNGUIDED MEDIA
Unguided media, or wireless communication, involves transmitting data through the air or space
without a physical conduit.
TYPES OF UNGUIDED MEDIA
1. Radio Waves
Uses frequencies from 3 kHz to 1 GHz to transmit data.
Applications: AM/FM radio, television broadcasts, cellular phones.
-Pros:
- Capable of covering large areas.
- Can penetrate buildings and other obstacles.
-Cons:
- Susceptible to interference and signal degradation.
- Limited bandwidth compared to higher frequency methods.
2. Microwaves
Uses frequencies from 1 GHz to 300 GHz, often requiring line-of-sight transmission.
Applications: Satellite communication, wireless LANs, Bluetooth.
Pros:
- Higher bandwidth and data rates than radio waves.
- Suitable for long-distance point-to-point communication.
Cons:
- Requires unobstructed line-of-sight.
- Affected by weather conditions such as rain.
3. Infrared
Uses light waves with frequencies just below visible light.
Applications: Remote controls, short-range communication between devices (e.g., laptops,
smartphones).
Pros:
- High security as signals do not penetrate walls.
- No interference from radio frequency devices.
Cons:
- Limited to very short distances.
- Requires direct line-of-sight.
4. Satellite
Uses satellites in orbit to transmit data over large distances.
Applications: Global positioning systems (GPS), television broadcasts, international
telecommunication.
Pros:
- Can cover vast geographic areas.
- Useful in remote and rural areas.
Cons:
- High latency due to the long distance signals must travel.
- Expensive to deploy and maintain.
You might also like
- Autograph Collection Hotels Technology InfrastructureDocument21 pagesAutograph Collection Hotels Technology InfrastructureVlad MargaritescuNo ratings yet
- Class C ELEMENT II Pool With HighlightsDocument7 pagesClass C ELEMENT II Pool With HighlightsJan Vincent100% (1)
- Communication ChannelsDocument3 pagesCommunication ChannelsMukul BagreNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Guided and Unguided Transmission MediaDocument7 pagesCase Study On Guided and Unguided Transmission Mediakp1981303No ratings yet
- Applications of NetworkDocument20 pagesApplications of NetworkJom JerryNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission MediaDocument3 pagesTypes of Transmission MediaziaullahNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument16 pagesTransmission MediaJames MacalaladNo ratings yet
- Networking Notes (Grade-12 CBSE Computer Science)Document32 pagesNetworking Notes (Grade-12 CBSE Computer Science)Adil DanadNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?Document18 pagesData Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?ychokhatNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 Transmission MediaDocument10 pagesUnit 03 Transmission Mediaroysayanccp05No ratings yet
- Data Transmission MeidaDocument5 pagesData Transmission MeidaRana Sarfraz NawazNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument31 pagesTransmission MediaMOHAMED FAAIZNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument5 pagesTransmission MediaaNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument7 pagesData Transmissionantonially24No ratings yet
- 4 Transmission MediaDocument24 pages4 Transmission MediaRashad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument23 pagesComputer NetworkAyaan SaleemNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission MediaDocument3 pagesTypes of Transmission MediakvbseniorclabNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediumDocument12 pagesTransmission MediumSuryanshuNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument10 pagesData CommunicationMuhammad MaazNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Coaxial CableDocument24 pagesAdvantages of Coaxial CableBurhanudheen KodiyathoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document70 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- Pdf&rendition 1Document9 pagesPdf&rendition 1s22cp042No ratings yet
- Aadi CN1Document6 pagesAadi CN1Aditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Computer Networkspratyay dhondNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaLYF WITH AK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument41 pagesTransmission MediaJasonNo ratings yet
- CN NotesDocument55 pagesCN Notesmegob32763No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledHelen MuriukiNo ratings yet
- Communication Part 3Document39 pagesCommunication Part 3panamasmasNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transmission MediaDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of Transmission MediaKasim WondosenNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument57 pagesComputer NetworkingSaksham Gupta100% (1)
- I.T - Transmission Media (Write-Up)Document19 pagesI.T - Transmission Media (Write-Up)PoopNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Study Material Part-1Document9 pagesUnit-2 Study Material Part-1Himadri BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document84 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- 170 Transmission MediaDocument39 pages170 Transmission Mediahauwauibrahimmagaji532No ratings yet
- Example: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneDocument33 pagesExample: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No #3: What Is Transmission Media?Document5 pagesAssignment No #3: What Is Transmission Media?ArslanNo ratings yet
- To Study About Different Types of Transmission Media. by The End of The Lesson Student CanDocument8 pagesTo Study About Different Types of Transmission Media. by The End of The Lesson Student CanUterus Xbox er f u. RNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 CAP256Document28 pagesLecture9 CAP256vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- MediaDocument19 pagesMediaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission MediaDocument3 pagesTypes of Transmission MediaAli SaiviNo ratings yet
- Data Communications Notes Unit 4Document13 pagesData Communications Notes Unit 4narradoNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Physical Layer: Business Data Communications, 4eDocument33 pagesTopic 4: Physical Layer: Business Data Communications, 4ePeter Tiong Kee YiiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Physical Layer: Business Data Communications, 4eDocument33 pagesTopic 4: Physical Layer: Business Data Communications, 4eSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument7 pagesAdvantages of Optical Fiber Communicationmohammadanas7686No ratings yet
- Assignment of NetworkingDocument13 pagesAssignment of NetworkingJyoti BhanotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Networking UnsecuredDocument58 pagesChapter 1 Networking UnsecuredAnandganesh PolisettiNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Basic Categories of Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesThere Are Two Basic Categories of Transmission MediaAbdirahman ElmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2sahilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CCNDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 CCNsajjadNo ratings yet
- Networking RSDocument60 pagesNetworking RSAnsh FamilyNo ratings yet
- Types of Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesTypes of Transmission MediaHARININo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Networking PDFDocument58 pagesChapter 1-Networking PDFVinod Srivastava100% (1)
- Transmission Media: A. Guided Transmission Media B. Unguided Transmission MediaDocument4 pagesTransmission Media: A. Guided Transmission Media B. Unguided Transmission MediaRonit SahuNo ratings yet
- Network ClassificationDocument2 pagesNetwork ClassificationraghinNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument9 pagesTransmission MediaCatherine KiwalaNo ratings yet
- Guided Vs Unguided Transmission MediaDocument14 pagesGuided Vs Unguided Transmission Mediamuhammad haris aqeelNo ratings yet
- Study of Transmission Media Shaheen OldDocument34 pagesStudy of Transmission Media Shaheen OldAmit Pasi0% (1)
- The Media: Conducted and WirelessDocument28 pagesThe Media: Conducted and WirelessColleen VenderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Transmission MediaDocument24 pagesChapter 3 - Transmission MediaTawanda MukuteNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- 2 - GMDSS Equipment and OperationDocument55 pages2 - GMDSS Equipment and OperationAboody AL-ghamdy100% (1)
- Wa0081. 4Document1 pageWa0081. 4waluyo dosenNo ratings yet
- HotmailDocument520 pagesHotmailmrpobolee100% (1)
- Mbali The GiftedDocument112 pagesMbali The GiftedAviweNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document6 pagesAssignment No 1Hamza Yameen LCM-4063No ratings yet
- CH 2610 12-Oct-2022 691Document4 pagesCH 2610 12-Oct-2022 691MaheshNo ratings yet
- Otr & Pricelist AgustusDocument184 pagesOtr & Pricelist AgustusByeNo ratings yet
- Beacon SATDocument1 pageBeacon SATAngel Ernesto Aguila Michelena100% (1)
- SAES-T-000Document10 pagesSAES-T-000aligul649089No ratings yet
- Cdma 2000Document12 pagesCdma 2000ajayiimaNo ratings yet
- ELECTIVES2Document9 pagesELECTIVES2jjrmllnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Direct Broadcast SatellitesDocument12 pagesLecture 7 Direct Broadcast SatellitesMuhamed El MosalmyNo ratings yet
- KBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race ScheduleDocument2 pagesKBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race SchedulezainNo ratings yet
- Radio Principles Precis 2Document80 pagesRadio Principles Precis 2JOSPHAT YEGONNo ratings yet
- Lora N: Rang e Nav Igatio N)Document33 pagesLora N: Rang e Nav Igatio N)jhunzoldicNo ratings yet
- V L N Subrahmanyam AffidavitDocument2 pagesV L N Subrahmanyam AffidavitdasaribalaNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Harian 1 XI LM Sem 2Document8 pagesPenilaian Harian 1 XI LM Sem 210s230 Rahma AliaNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulationDocument43 pagesAmplitude ModulationAmiel Paul P. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Skdav Govt. Polytechnic Rourkela: Department of Electronics and Telecommunication EngineeringDocument90 pagesSkdav Govt. Polytechnic Rourkela: Department of Electronics and Telecommunication EngineeringSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Study Manual For Amateur Station Operator's Licence Examination IndiaDocument200 pagesStudy Manual For Amateur Station Operator's Licence Examination IndiaDebrup Simongreyman Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- A Review of Television BroadcastingDocument5 pagesA Review of Television BroadcastingMarcNo ratings yet
- Insignia - 24" Class - LED - 720p - Smart - HDTV - Fire TV Edition NS-24DF310NA19Document28 pagesInsignia - 24" Class - LED - 720p - Smart - HDTV - Fire TV Edition NS-24DF310NA19RaNo ratings yet
- Afghanistan - Roadmap BAT-368687Document174 pagesAfghanistan - Roadmap BAT-368687sebghatandarNo ratings yet
- Basic Signal Communication of Bam2Document16 pagesBasic Signal Communication of Bam2Allyza Joyce NatividadNo ratings yet
- Building Telecommunication SystemsDocument2 pagesBuilding Telecommunication SystemsKaguraNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report A&WPDocument28 pagesSeminar Report A&WPVibhanshuNo ratings yet
- RRC 9210 Tactical VHF ECCM 10W Manpack Radio - WB GROUPDocument3 pagesRRC 9210 Tactical VHF ECCM 10W Manpack Radio - WB GROUPOrçun CengizNo ratings yet
- ROK DTH Hammer Operation and Service Guide-SPDocument22 pagesROK DTH Hammer Operation and Service Guide-SPNelson de la RosaNo ratings yet