Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook (Bryan) Hodder (S
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook (Bryan) Hodder (S
Uploaded by
Sonal SinglaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook (Bryan) Hodder (S
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook (Bryan) Hodder (S
Uploaded by
Sonal SinglaCopyright:
Available Formats
G) The particulate nature of matter
• Co re
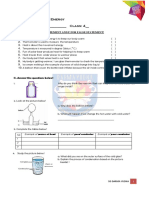
1 A sa mpl e of a solid subst ance, which had been cooled t o - s•c, was put Into a test-tube .
The t est-tube was then heated in a water bath . The temperature of the substa nce was taken every
5 minutes fo r an ho ur. The results o btained are shown below.
Time/min 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 so 55 60
Temperaturel°C -5 -1 13 28 45 62 76 79 82 82
a Plot the results o n the graph paper below, putting time on the ho ri zo ntal axis and temperature
o n the verti cal ax is.
/4/
b What is the melting poi nt of the substance? ... /1/
c What Is the bo iling point of the substa nce? ... /1/
d Describe w hat is happening t o the particles of the subst ance after 50 minutes.
/2/
0 Ph otocopying prohibited Cambri dge IGCSE Ch emistry Work book
Core/Extended
2 Imagi ne that you are a wa t er molecul e in an ice cu be. Describe what happens to you as the ice cu be
is heated up to a temperatu re of ,oo~c.
/6/
3 a Explai n the meaning of each of the fo llowing t erms.
; melting ... /1/ ;, condensation ... /1/
ii chemi cal cha nge .. /1/ ' eva po ratio n . /1/
, ; d issolving .. /1/
iii su blimation ... /1/
b W hich of the t erms given In pa rt a best describes w hat is taking place in each of the fo llowing?
i The formation of wa t er droplets on the inside of a w indow on a cold day.
/1/
ii The formation of liq uid potassium chloride from solid potassi um chloride
using strong heat ·· ························ ·-·······-·····--·····-·····--·····-··· /1/
iii The formation of iodi ne vapour from solid iod ine o n heating. /1/
iv Adding sugar t o hot co ff ee t o sweeten t he drink .. /1/
• Core/Extended
4 Use ideas about ki netic theory to explain the fo llowing :
a Diffu sio n does not occur in so lids.
/2/
b Gases ca n be compressed more t han liquids.
/2/
c It is possible fo r a liquid t o flow but a solid cannot.
/2/
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook Photcxopying prohibited O
1 THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER
• Extended
5 W hen t he fo llowi ng experiment is set up, a clo ud of f ine w hite powder ca n be seen as t he ammonia
gas reacts with the hydroge n chl oride gas.
rnttonwool10ilked rnttoowocilOilked
inmncmtrated in corKe<1trated
hydrochloric add ammonialciutioo
Hydrogen ch lo ride particles are more than twice as heavy as ammon ia pa rticles.
a Wh ich of the particles w ill move faste r? ···-·······-·----·-··-···-·····--·······-···---···--···---···--· /1/
b At wh ich poi nt, A to E, alo ng the tube will t he w hite clo ud be see n? Explai n your
answer in te rm s of t he movement of t he particles.
/2/
c How do the particles of hydrogen chloride and ammonia gas move along the tube?
/1/
Exam focus
1 a i Give two properties shown by:
/2/
a liquid .. /2/
a gas. . /2/
ii Draw d iagrams in the boxes below to show how the particles are arranged in each of the
physical states.
b
DOD
The melting an d boiling points of five
substances are given in the table.
liquid
Substan ce
Oxygen
Meltin l!noint/K Ba ilin, n oint/K
55 90
/3/
(Take room temperature as 298K) Bromine 2"6 332
Mercury 234 630
Phosphorus 3 17 553
l,= 1808 3023
0 Photocopyi ng prohibited Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook
Extended
i What is the melting point of mercury in °C? ... /1}
ii Which element/ sis a gas at room temperature? .. /1]
iii Which element/sis a solid at room temperature? . /1]
iv Which of the elements will boil first if the temperature is raised from room
temperature? /11
[Total: 13]
2 Use the kinetic theory to explain the following.
a Walking along the street in front of a coffee shop, it is possible to smell the coffee.
/2/
b When laying railway track, gaps have to be left between the lengths of track.
/2/
c When a tea bag is placed in a cup of hot water, the colour of the water changes.
/2/
d In cold weather, the amount of water found running down the inside of windows increases.
/2/
e A bubble of methane rises from the bottom of the Pacific Ocean. As it rises, the bubble gets bigger.
/2/
f Pollen grains are mixed with water and obseived under a microscope. Dust particles in the air are
also observed in the same way.
i What would the pollen grains and dust particles be doing?
11/
ii What causes the grains and dust particles to behave in the way you have described in part i?
/2/
[Tota/: 13]
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook Photcxopyingproh ibited O
You might also like
- Agitator Support DesignDocument3 pagesAgitator Support DesignSabir Nasim100% (2)
- Ch04 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCh04 SolutionsNasser SA100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook 2nd Edition PDFDocument97 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook 2nd Edition PDFfran86% (14)
- Particulate Nature of Matter - WorksheettDocument10 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter - Worksheettssohxq100% (4)
- GPA Sampling Method (Scope, Definition, Principles, Safety)Document27 pagesGPA Sampling Method (Scope, Definition, Principles, Safety)Candra Aditya Wiguna100% (2)
- Vdocuments - MX Elcometer Fitz Atlas 2 of Coating DefectsDocument1 pageVdocuments - MX Elcometer Fitz Atlas 2 of Coating DefectsEdgarDavidDiazCamposNo ratings yet
- API Standard 2000 - Venting Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Storage Tanks: Nonrefrigerated and RefrigeratedDocument5 pagesAPI Standard 2000 - Venting Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Storage Tanks: Nonrefrigerated and RefrigeratedNicolas CardonaNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Sayyidina Othman, Chemistry 9701 Test On Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesSekolah Menengah Sayyidina Othman, Chemistry 9701 Test On Chemical BondingKoo Keung EngNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Chemistry-CMPDocument5 pagesUnit 5 - Chemistry-CMPsmitakamath6686No ratings yet
- I Bas 102 2023-24Document14 pagesI Bas 102 2023-24bamiy54090No ratings yet
- 0620 w12 Ms 32 PDFDocument6 pages0620 w12 Ms 32 PDFafriliawsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAlfredo MartinNo ratings yet
- U WIe TG7 T6 VNLZLBV 8 C 86Document5 pagesU WIe TG7 T6 VNLZLBV 8 C 86tanishabhattacharjee31No ratings yet
- Genchem2 - Q3 - 1ST Summative TestDocument2 pagesGenchem2 - Q3 - 1ST Summative TestRIZZA MARBELLANo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry p2 June 2015Document21 pagesCsec Chemistry p2 June 2015dela250% (10)
- Diels AlderDocument3 pagesDiels AldermmmsaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-10 SURFACE CHEMISTRY MINI 2023Document6 pagesUNIT-10 SURFACE CHEMISTRY MINI 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- GPAT 13 P'ceuticsDocument29 pagesGPAT 13 P'ceuticsGANESH KUMAR JELLANo ratings yet
- Quiz Science HeatDocument3 pagesQuiz Science HeatlinaNo ratings yet
- First Year Higher Secondary Examination June 2022 CHEMISTRY - ANSWER KEY (Unofficial)Document7 pagesFirst Year Higher Secondary Examination June 2022 CHEMISTRY - ANSWER KEY (Unofficial)Ashkar AshrafNo ratings yet
- +2 Chemistry Answer Key April 2021Document8 pages+2 Chemistry Answer Key April 2021Arsh UmarNo ratings yet
- The Preparation and Characterization of An X-Type Zeolite: An Experiment in Solid-State ChemistryDocument6 pagesThe Preparation and Characterization of An X-Type Zeolite: An Experiment in Solid-State ChemistryMuddasar SafdarNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Surface ChemistryDocument4 pagesCH 19 Surface Chemistryshivanijain4443No ratings yet
- Vincent, Fleury - Report - Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument16 pagesVincent, Fleury - Report - Types of Chemical ReactionsVincent FleuryNo ratings yet
- Topical KCSE Mock Chemistry Answers15 SchoolsDocument129 pagesTopical KCSE Mock Chemistry Answers15 Schoolsdorismakena67No ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter: Core CurriculumDocument2 pages1 States of Matter: Core CurriculumTRSeven100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument11 pagesChemistry Lab ReportteniNo ratings yet
- The Bullvalene Story. The Conception of Bullvalene, A Molecule That Has No Permanent StructureDocument4 pagesThe Bullvalene Story. The Conception of Bullvalene, A Molecule That Has No Permanent StructureThirumalai DNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Beatty SecondaryDocument35 pages2020 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Beatty SecondaryUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry t2 sp01Document8 pages11 Chemistry t2 sp01yogesh.No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: Mrs. C. Williams-Massey Third From ChemistryDocument15 pagesCovalent Bonding: Mrs. C. Williams-Massey Third From ChemistryJoshua BrownNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 5Document10 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 5Ûdây RäjpütNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Required PracticalDocument5 pagesCatalyst Required PracticalyoNo ratings yet
- As and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 4 Hydrolysis Student Teacher Technician WorksheetsDocument5 pagesAs and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 4 Hydrolysis Student Teacher Technician WorksheetsonehllznNo ratings yet
- Qn. No. Part - A MarksDocument13 pagesQn. No. Part - A MarkslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry - 5359493 (1644335237664)Document1 pageSurface Chemistry - 5359493 (1644335237664)Kingro SimNo ratings yet
- 0620 w04 QP 1 PDFDocument16 pages0620 w04 QP 1 PDFFaithNo ratings yet
- Water Softening IndustryDocument4 pagesWater Softening IndustryArslanAliNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chem ch1 Questions PDFDocument2 pagesIGCSE Chem ch1 Questions PDFRajesh100% (1)
- Chemistry: Important Questions Before Half Yearly ExamDocument14 pagesChemistry: Important Questions Before Half Yearly ExamSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- AQA Chem 1 Answers ch12Document4 pagesAQA Chem 1 Answers ch12Ellie AndersonNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document20 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2dilemNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Chapters 2 and 3 Study Guide NameDocument3 pagesPhysical Science: Chapters 2 and 3 Study Guide Namevaulted armorNo ratings yet
- (Source: MJC/2018) : JPJC/JC1 H1 Biology/TA1/2024Document11 pages(Source: MJC/2018) : JPJC/JC1 H1 Biology/TA1/2024aliciathrowaway666No ratings yet
- 22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Eight: Criticality AccidentsDocument4 pages22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Eight: Criticality AccidentsmsakowskNo ratings yet
- SURFACE CHEMISTRY - CBSE QsDocument19 pagesSURFACE CHEMISTRY - CBSE QsShahzadNo ratings yet
- 2010 Holy Innocents Chemistry PrelimDocument29 pages2010 Holy Innocents Chemistry PrelimSONo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document32 pagesUnit 6yoomin2005824No ratings yet
- Worksheet ATP 5Document9 pagesWorksheet ATP 5pranavi jagarlamudiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2016 Chemistry Set 1Document5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper Solution 2016 Chemistry Set 1Savan PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ChemistryDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Chemistryrohitskv4545No ratings yet
- 5 Estructura Quimica de Los Carbones-Tema 1Document125 pages5 Estructura Quimica de Los Carbones-Tema 1elisamd1234No ratings yet
- Eng 2005Document5 pagesEng 2005AryanNo ratings yet
- Fabian 5Document3 pagesFabian 5FabianNo ratings yet
- Atoms 9Document8 pagesAtoms 9kintujojoNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverDocument12 pagesPhysical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverBonga DubeNo ratings yet
- Cy1104 - Engineering Chemistry Unit - 2 Surface Chemistry and Catalysis Lecture PlanDocument28 pagesCy1104 - Engineering Chemistry Unit - 2 Surface Chemistry and Catalysis Lecture PlanBeuna.No ratings yet
- Scholastica: Mock 1Document14 pagesScholastica: Mock 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2004 45 MinutesDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistry Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2004 45 MinutesVarun PanickerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5selambante shiferawNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PAPER-01 (Solved) Class - XII AnswersDocument7 pagesSAMPLE PAPER-01 (Solved) Class - XII AnswersAnonymous VGjeJJwxNo ratings yet
- Chem G10-Quiz1 19-5-2020Document13 pagesChem G10-Quiz1 19-5-20201211200107No ratings yet
- Block Copolymers: Synthetic Strategies, Physical Properties, and ApplicationsFrom EverandBlock Copolymers: Synthetic Strategies, Physical Properties, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Wind Pressure: Project: Chimney at GoaDocument11 pagesCalculation of Wind Pressure: Project: Chimney at GoaHemant SonawadekarNo ratings yet
- Multistage Centrifugal Pump Operation & Maintenance ManualDocument11 pagesMultistage Centrifugal Pump Operation & Maintenance ManualHazrin HasanNo ratings yet
- Essential Vibration Theory, Setup & Analysis: UnbalanceDocument9 pagesEssential Vibration Theory, Setup & Analysis: UnbalanceAntony JuwonoNo ratings yet
- 7e LP - ConductionDocument13 pages7e LP - ConductionKresha LluismaNo ratings yet
- NAF-Check Tilting Disc Check Valves FK 30.70 (11) GB: CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesNAF-Check Tilting Disc Check Valves FK 30.70 (11) GB: CharacteristicsRobovenNo ratings yet
- Sensor Conductividad Con-BtaDocument4 pagesSensor Conductividad Con-BtaMayerly Giraldo AvilaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Si Units Thermodynamics 6 EditionDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Si Units Thermodynamics 6 EditionIllion IllionNo ratings yet
- Design Pressure Vessel & HEDocument175 pagesDesign Pressure Vessel & HEDavid Lambert100% (3)
- Chemical KineticsDocument116 pagesChemical KineticsSai Vishnu GainiNo ratings yet
- Studi Karakteristik Gerakan Dan Operabilitas Anjungan Pengeboran Semi-Submersible Dengan..Document10 pagesStudi Karakteristik Gerakan Dan Operabilitas Anjungan Pengeboran Semi-Submersible Dengan..naufalNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in The Interpretation: of Dissolved Gas Analysis in TransformersDocument2 pagesRecent Developments in The Interpretation: of Dissolved Gas Analysis in TransformersheroNo ratings yet
- Igcse 41 EnergytransfersDocument32 pagesIgcse 41 EnergytransfersHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Helical Coil HeatDocument205 pagesHelical Coil Heatemergingengineer100% (1)
- Unit 19: They'Re in The Park: Part 1: Theory English Pronunciation VietnameseDocument8 pagesUnit 19: They'Re in The Park: Part 1: Theory English Pronunciation Vietnamesenguyen lynNo ratings yet
- Z Pengaruh Kondisi Permukaana Lekat Lapisan Pelindung (Effects ofDocument13 pagesZ Pengaruh Kondisi Permukaana Lekat Lapisan Pelindung (Effects ofPenghuni SurgaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics Important NumericalsDocument4 pages1st Year Physics Important NumericalsMian Ejaz80% (5)
- Study of Temperature Load On Structure's: Dr. Amit Bijon Dutta & Er. Tapas SarkarDocument5 pagesStudy of Temperature Load On Structure's: Dr. Amit Bijon Dutta & Er. Tapas SarkarquanNo ratings yet
- Taleem City Institute: Ameenpur, Faisalabad 03126987979Document22 pagesTaleem City Institute: Ameenpur, Faisalabad 03126987979AbdulRehman KhokharNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument1 pageStrength of Materialsdhana555No ratings yet
- Overcoming Paint Film DefectsDocument7 pagesOvercoming Paint Film DefectsMahmood H NaqviNo ratings yet
- Btech Metta Mme 3 Sem Principle of Extractive Metallurgy Pmt3i001 2018Document2 pagesBtech Metta Mme 3 Sem Principle of Extractive Metallurgy Pmt3i001 2018Manas ranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Pre FormulationDocument15 pagesPre FormulationMeghana JNo ratings yet
- Condenser Vacuum Improvement Stage-IDocument23 pagesCondenser Vacuum Improvement Stage-Inetygen1100% (4)
- Air Cooler - DesignDocument7 pagesAir Cooler - Designkarthipetro100% (1)
- Free Water Jet Cutting GuideDocument11 pagesFree Water Jet Cutting GuideRuham Pablo ReisNo ratings yet