Professional Documents
Culture Documents
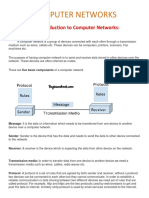
Network
Network
Uploaded by
bazengampole64Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network
Network
Uploaded by
bazengampole64Copyright:
Available Formats
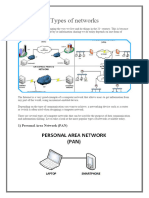
Networks can be classified into various types based on their scale, purpose,
topology, and technology. Here are some common types:
1. **Local Area Network (LAN)**: LAN is a network that covers a small geographical
area, typically within a single building or campus. It's commonly used in homes,
offices, schools, etc.
2. **Wide Area Network (WAN)**: WAN spans a large geographical area, connecting
LANs and other networks across cities, countries, or even continents. The internet
is the largest WAN.
3. **Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)**: MAN covers a larger geographical area than
a LAN but smaller than a WAN, usually within a city or metropolitan area. It can
connect multiple LANs.
4. **Wireless LAN (WLAN)**: WLAN uses wireless technology, such as Wi-Fi, to
connect devices within a limited area. It's common in homes, offices, cafes, etc.
5. **Personal Area Network (PAN)**: PAN is a network formed around an individual
person, typically connecting personal devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets,
etc.
6. **Client-Server Network**: In this type of network, devices are divided into
client and server roles. Clients request services or resources from servers, which
provide them. It's commonly used in businesses and organizations.
7. **Peer-to-Peer Network (P2P)**: In a P2P network, all devices have equal status
and can act as both clients and servers. They can directly communicate and share
resources without a central server.
8. **Virtual Private Network (VPN)**: VPN is a secure network that uses encryption
and tunneling protocols to provide privacy and security over a public network, such
as the internet. It's often used for remote access to corporate networks or to
bypass geo-restrictions.
9. **Intranet**: An intranet is a private network within an organization that uses
internet technologies to share information, collaboration tools, and other
resources among employees.
10. **Extranet**: An extranet extends an intranet to selected external users, such
as customers, partners, or suppliers, allowing them limited access to certain
resources or services.
These are just a few examples, and there are many other specialized types of
networks tailored to specific needs and applications.
You might also like
- Unit-1 NotesDocument24 pagesUnit-1 NotesMOGILIPURI KEERTHINo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and NetworkDocument25 pagesComputer Communication and Networkmhatet_ignacioNo ratings yet
- Ict doc2Document7 pagesIct doc2leenatahir93No ratings yet
- Ict doc2Document7 pagesIct doc2leenatahir93No ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument2 pagesNetworkingShankar DakoliaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument5 pagesComputer NetworkGalih ApNo ratings yet
- Submodule Introduction To Communication NetworksDocument18 pagesSubmodule Introduction To Communication Networksmohamedmwakuzimu9966No ratings yet
- ComputernetworkDocument2 pagesComputernetworksujan DhekeNo ratings yet
- Chap1Genaralities on networkDocument5 pagesChap1Genaralities on networkngangfobiziNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument18 pagesComputer Networksacharyay72No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document35 pagesUnit 1trapti191967No ratings yet
- Q.B For It SkiilsDocument15 pagesQ.B For It SkiilsSwapnil ShirkeNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument44 pagesSeminar ReportShubham KhotkarNo ratings yet
- Info Tech Jonathan 2024Document4 pagesInfo Tech Jonathan 2024marshalee.whorms.r4No ratings yet
- Activity 7 - Dela Cruz, Tehillah Mae ADocument17 pagesActivity 7 - Dela Cruz, Tehillah Mae ATehillah CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Communication TechnologiesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Communication TechnologiesTsepiso MohaleNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument9 pagesTypes of NetworksTishya PansariNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 Chapter 1Document21 pagesCcna1 Chapter 1Simona SmnNo ratings yet
- Networks & The Effects of Using ThemDocument16 pagesNetworks & The Effects of Using Themtaha imranNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - (Web-Application) - Accesibility and Networking NotesDocument24 pagesUnit-4 - (Web-Application) - Accesibility and Networking Noteselliecoral10No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument12 pagesComputer NetworkvictoriousNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Fundamentals Lecture Note.Document45 pagesComputer Network Fundamentals Lecture Note.muhammadalameenabdullahi89No ratings yet
- COA Chapter 4Document33 pagesCOA Chapter 4dagneNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Network?Document55 pagesWhat Is A Computer Network?AnuNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Document9 pagesActivity 1 1. What Is Computer Networks?Katrina Mae VillalunaNo ratings yet
- SCT Unit - 1Document21 pagesSCT Unit - 1Evil PsythonNo ratings yet
- STD VII - Lesson 1 - Computer Networking.Document11 pagesSTD VII - Lesson 1 - Computer Networking.arjunbendre1982No ratings yet
- CN MaterialDocument8 pagesCN Materialmaruthi maheshNo ratings yet
- Networking FundamentalsDocument19 pagesNetworking FundamentalsJerald Pacheco JoseNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Web Analytics Unit-2: Fundamentals of Computer NetworkingDocument20 pagesSocial Media and Web Analytics Unit-2: Fundamentals of Computer NetworkingNAUSHAD SHEKHNo ratings yet
- CSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeDocument11 pagesCSC 325 Exam Question Marking SchemeFaisal AliNo ratings yet
- It Era 4Document27 pagesIt Era 4jules200303No ratings yet
- Computer Unit 5Document52 pagesComputer Unit 5Jayesh BoroleNo ratings yet
- DCN Unit 1saqDocument9 pagesDCN Unit 1saqsravan kumarNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument4 pagesComputer NetworkingOgbo IsuNo ratings yet
- Q.1 To 10. NTDocument13 pagesQ.1 To 10. NTninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument4 pagesComputer NetworkingOgbo Isu100% (1)
- Hardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument14 pagesHardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDagneWalleNo ratings yet
- dccn1Document86 pagesdccn1indiankillerfreefireNo ratings yet
- 1 1Document35 pages1 1tafadzwa sidNo ratings yet
- CN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterDocument44 pagesCN 3rd Year Unit 1notes by MasterNikhil kumarNo ratings yet
- Session Four Manging Computer Network TechnologiesDocument53 pagesSession Four Manging Computer Network Technologieshalilmohamed830No ratings yet
- CN-lecture 4 Types of EtworkDocument8 pagesCN-lecture 4 Types of EtworkⲤʟᴏᴡɴᴛᴇʀ ᏀᴇɪꜱᴛNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks (Core) : CA5CRT14 Theory:3 Hrs. Per Week Credits:4 Unit 1: (10 HRS.)Document178 pagesComputer Networks (Core) : CA5CRT14 Theory:3 Hrs. Per Week Credits:4 Unit 1: (10 HRS.)PranayNo ratings yet
- 1 Computer Networks 1Document114 pages1 Computer Networks 1NishikantNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)Document14 pagesQuarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)PRESIDENT ELPIDIO QUIRINO NHSNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument3 pagesComputer NetworksTirath SinghNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer NetworkingDocument5 pagesBasics of Computer NetworkingJaime Jr CarlosNo ratings yet
- CN NotesDocument32 pagesCN Notessameerahmadkhan130No ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument12 pagesTypes of NetworksDeshaun AugustusNo ratings yet
- Types of Network: Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhDocument15 pagesTypes of Network: Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhNavneet NandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Types of NetworksDocument17 pagesUnit 4: Types of NetworksSJ ShahidNo ratings yet
- Data Network SH11-12Document26 pagesData Network SH11-12Edwin VillaNo ratings yet
- Name Five (5) Network Types. Differentiate and Give The Function of Each Type. Local Area Network (LAN)Document1 pageName Five (5) Network Types. Differentiate and Give The Function of Each Type. Local Area Network (LAN)miyukiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document65 pagesUnit 3Prabin ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Computer Network TypesDocument16 pagesComputer Network TypesFatimah FaqihiNo ratings yet
- Portable Private Wifi: Sg5 Project ProposalDocument9 pagesPortable Private Wifi: Sg5 Project ProposalcampusTourNo ratings yet
- CcnaDocument21 pagesCcnaYoo Hoo BinNo ratings yet