Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work - Power-Energy
Work - Power-Energy
Uploaded by
aiden3inches210Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Work - Power-Energy
Work - Power-Energy
Uploaded by
aiden3inches210Copyright:
Available Formats
WORKSHEET GRADE 9 NAME ……………………………….
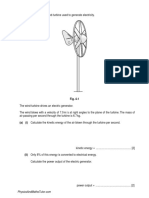
1. Fig. 3.1 shows an aircraft on the deck of an aircraft carrier.
The aircraft accelerates from rest along the deck. At take-off, the aircraft has a speed of 75m/ s. The
mass of the aircraft is 9500kg.
(a) Calculate the kinetic energy of the aircraft at take-off. kinetic energy
= ...........................................................[3]
(b) On an aircraft carrier, a catapult provides an accelerating force on the aircraft. The catapult
provides a constant force for a distance of 150m along the deck.
Calculate the resultant force on the aircraft as it accelerates. Assume that all of the kinetic energy at
take-off is from the work done on the aircraft by the catapult. force
= ...........................................................[2]
2. The diagram shows the energy transferred in a lamp in one second.
Which type of wasted energy is produced by the lamp?
A. chemical potential energy B. electrical energy
C. gravitational potential energy D. thermal energy
3. Which energy resource is not renewable?
A fossil fuel B sunlight C tides D wind
4. An aircraft with a mass of 300 000kg is flying at an altitude of 2000 m with a speed of 100 m / s.
What is the kinetic energy of the aircraft?
A 1.5 × 104 kJ B 1.5 × 106 kJ C 3.0 × 106 kJ D 6.0 × 106 kJ
5. Fig. 3.1 shows a skier taking part in a downhill race.
(a) The mass of the skier, including his equipment, is 75 kg. In the ski race, the total vertical change in
height is 880 m. Calculate the decrease in the gravitational potential energy (g.p.e.) of the skier.
decrease in g.p.e. = ...........................................................[2]
(b) The skier starts from rest. The total distance travelled by the skier during the descent is2800 m.
The average resistive force on the skier is 220 N. Calculate
(i) the work done against the resistive force,
work done = ...........................................................[2]
(ii) the kinetic energy of the skier as he crosses the finishing line at the end of the race.
kinetic energy = ...........................................................[2]
(c) Suggest why the skier bends his body as shown in Fig. 3.1.
...............................................................................................................................................[1]
You might also like
- Ecoscience. .Population,.Resources,.Environment. (1977) .PDF (ProActiveReSEarch)Document1,649 pagesEcoscience. .Population,.Resources,.Environment. (1977) .PDF (ProActiveReSEarch)ragod2100% (7)
- Sph4u Solutions (Unit 2)Document0 pagesSph4u Solutions (Unit 2)Voormila NithianandaNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Questions Energy Work and Power AnswersDocument11 pagesPast Paper Questions Energy Work and Power AnswersAnuj SamantNo ratings yet
- Cee 102L Sim SDL Manual - Week-1-9 PDFDocument362 pagesCee 102L Sim SDL Manual - Week-1-9 PDFRyuuki Lacia100% (1)
- Edexcel M2 NotesDocument32 pagesEdexcel M2 Notestajoar ananNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion Q&ADocument8 pagesEnergy Conversion Q&AGkid GkidNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Worksheet 1Document5 pagesWork Energy Worksheet 1TheOnesNo ratings yet
- Change in Energy and Energy Transformations AnsDocument33 pagesChange in Energy and Energy Transformations Anslokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- U6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ADocument14 pagesU6 Work Energy Power Topic Test ApixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Phys Int CC CH 9 - Energy - Answers PDFDocument6 pagesPhys Int CC CH 9 - Energy - Answers PDFSyanlla TaboraNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions (60 Marks)Document6 pagesAnswer All Questions (60 Marks)Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power ERDocument6 pagesEnergy, Work & Power EREman Gurmani100% (2)
- Physics Worksheet - Grade 10Document14 pagesPhysics Worksheet - Grade 10Faran AssifNo ratings yet
- 2022 Part 1 Physics and BiologyDocument11 pages2022 Part 1 Physics and BiologyFloraNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument5 pagesEnergyAsmeerNo ratings yet
- P2 Energy ReviseDocument6 pagesP2 Energy ReviseSamuel ChenNo ratings yet
- Model Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationDocument22 pagesModel Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationKrishna ShahNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 03 QP PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 03 QP PDFWai HponeNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkDocument10 pagesConservation of Energy: Physics 20 Unit C: Energy and WorkUnzal FatehullahNo ratings yet
- TestDocument6 pagesTesthongling24No ratings yet
- THERMO 2 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 2022 W - SolutionsDocument6 pagesTHERMO 2 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 2022 W - SolutionsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Turbo MachinesDocument2 pagesAssignment 1: Turbo MachineskookoNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument38 pagesIlovepdf Mergedmilaray47No ratings yet
- EASADocument10 pagesEASAvivaboyNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 01 QPDocument9 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 01 QPabdullahthaher04No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 01 QPDocument9 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 01 QPShakiraNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-03Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-03lelon ong0% (1)
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work Power Efficiency AnswerDocument4 pagesTutorial Work Power Efficiency AnswerNicole Nicole100% (1)
- 11th PT-1Document6 pages11th PT-1ABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledOlajuwonNo ratings yet
- Copia de Ejercicios EnergiaDocument4 pagesCopia de Ejercicios EnergiajosefinarNo ratings yet
- Physics 100: Solutions To Homework Assignment #6: Section 1. Warm-Up! Fill-in-the-Blanks (1 PT Each)Document6 pagesPhysics 100: Solutions To Homework Assignment #6: Section 1. Warm-Up! Fill-in-the-Blanks (1 PT Each)Razvan Gaina100% (1)
- HB Classroom Physics Class 12 2015Document40 pagesHB Classroom Physics Class 12 2015himadri.banerji60No ratings yet
- 5Document4 pages5akshayatejomurthulaNo ratings yet
- 1.7 WK 1 TheoryDocument10 pages1.7 WK 1 TheoryMaira setiaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument40 pagesRevisionshrija nooporNo ratings yet
- 1 MARK Work Power Energy Problems For UploadingDocument5 pages1 MARK Work Power Energy Problems For UploadingfotickNo ratings yet
- The First Quiz of Fluid Mechanics in Spring SemesterDocument3 pagesThe First Quiz of Fluid Mechanics in Spring Semester林冠呈No ratings yet
- 1.7 WK 3 TheoryDocument12 pages1.7 WK 3 TheoryMaira setiaNo ratings yet
- Change in Energy - Energy TrasformationDocument25 pagesChange in Energy - Energy Trasformationlokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- QB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power ADocument11 pagesQB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power AmarufinoNo ratings yet
- CLINT E. MOSENABRE FluidsDocument5 pagesCLINT E. MOSENABRE FluidsClint MosenabreNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument5 pagesWork and EnergyAdam ChiangNo ratings yet
- British School of Kampala: Year 9 Physics AssignmentDocument7 pagesBritish School of Kampala: Year 9 Physics AssignmentElsie VanpraetNo ratings yet
- Topic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyDocument3 pagesTopic 7: Kinetics: Momentum: The Quantity of Motion Possessed by A Moving BodyTom ManNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Energy Work Power ProblemsDocument4 pagesEnergy Work Power ProblemsNudratNo ratings yet
- Physics 122 Problem SetDocument86 pagesPhysics 122 Problem SetCarmen DraghiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X MCQDocument13 pagesPhysics Class X MCQRohit MishraNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument7 pagesContinuekenfackNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 PhysicsDocument2 pagesGrade 10 PhysicsTinotenda ChatindoNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment SampleDocument2 pagesPhysics Assignment SampleRimjhimNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document6 pagesHW 3Stephanie TeoNo ratings yet
- HW6-Energy Stores and Transfers-1 (学生版) - 021544Document12 pagesHW6-Energy Stores and Transfers-1 (学生版) - 021544Jun WuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch06Document2 pagesTutorial Ch06khxrsvrgb6No ratings yet
- Y2 Workbook Final PDFDocument177 pagesY2 Workbook Final PDFMelody RbayNo ratings yet
- Sos Secondary SchoolDocument6 pagesSos Secondary Schoolsanjayashrestha777No ratings yet
- % CJ - Effective Jet Velocity in M/s % U - Flight Velocity in M/s % Mdota - Mass Flow Rate of Air in Kg/s % Sigma - U/cj No UnitDocument2 pages% CJ - Effective Jet Velocity in M/s % U - Flight Velocity in M/s % Mdota - Mass Flow Rate of Air in Kg/s % Sigma - U/cj No UnitJaya Kumar R KNo ratings yet
- WORK-POWER-ENERGY - Solved ProblemsDocument6 pagesWORK-POWER-ENERGY - Solved ProblemsZain Ul AbidinNo ratings yet
- (201 Marks) : (1 Mark)Document49 pages(201 Marks) : (1 Mark)Manav NairNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Uniform Circular MotionDocument37 pages2.4 Uniform Circular MotionMartinNo ratings yet
- Cie As Physics 9702 Theory v1Document18 pagesCie As Physics 9702 Theory v1Fasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Work Power Energy RevisionDocument71 pagesYr 9 Work Power Energy RevisionJunho RyooNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document26 pagesLecture 6rookeeNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 8 WorkDocument5 pagesDLL Grade 8 WorkIrish Joy Aguadera - NamuagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Work Energy PowerDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Work Energy PowerSiti Juwairiah ZainurinNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics For Open Systems or Flow ProcessDocument32 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics For Open Systems or Flow ProcessGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Matt UrenbmetcDocument5 pagesMatt UrenbmetcMatthew UrenNo ratings yet
- Richard J. Blakely-Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications (Stanford-Cambridge Program) (1995) PDFDocument461 pagesRichard J. Blakely-Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications (Stanford-Cambridge Program) (1995) PDFDwi AgustiyaniNo ratings yet
- Efficiency and Power - IIDocument4 pagesEfficiency and Power - IIjahangir0% (1)
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Notes PDFDocument78 pages081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Notes PDFKrish NarayananNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework #2 PDFNataly Yisel ArizaNo ratings yet
- Aits 1718 PT I Adv Paper 2 Ans SolDocument14 pagesAits 1718 PT I Adv Paper 2 Ans SolSangeeta MishraNo ratings yet
- Exam Question ZCA101 2008 2009Document10 pagesExam Question ZCA101 2008 2009sirraxNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch05 02 WADocument3 pagesGr10 Rev Ch05 02 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- A2 42 GravitationDocument45 pagesA2 42 GravitationJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Igcse Y9 Physics 2013-14 v2Document19 pagesIgcse Y9 Physics 2013-14 v2Shaikh Usman Ai100% (1)
- Work Energy UnderstandingDocument12 pagesWork Energy Understandingmbs_13_1953100% (2)
- Space ScienceDocument17 pagesSpace Sciencehuylimala0% (1)
- Work and Energy Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesWork and Energy Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersSCIENCE WORK [AMP] ActivitiesNo ratings yet
- Application of Vector Product and Dot ProductDocument11 pagesApplication of Vector Product and Dot Productnishan_ravinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 06 PDFNisa ArpyantiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and MachineryDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics and Machineryபாலரத்தினம் தமிழன்No ratings yet
- Mod Phys Book - Work and E TESTDocument5 pagesMod Phys Book - Work and E TESTtekya57No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Note)Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Note)SANLU HTUTNo ratings yet