Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Uploaded by
KASADHA PATRICKCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PRN00936 II Pharmacy First Clinical Pathways v.1.6Document7 pagesPRN00936 II Pharmacy First Clinical Pathways v.1.6Oladimeji Raphael OnibonNo ratings yet
- UTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyDocument26 pagesUTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyAminath MeesanNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping TB in PregnancyDocument1 pageMind Mapping TB in PregnancyAndi Tenri Ola Oddang IINo ratings yet
- Treating Your Infection UtiDocument1 pageTreating Your Infection UtiJames 'jps' SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument23 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsJay AberinNo ratings yet
- How Can You Help Your Patients With An Uncomplicated UTI?: Know?Document1 pageHow Can You Help Your Patients With An Uncomplicated UTI?: Know?gegeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology: Dr. LuDocument2 pagesNephrology: Dr. LuShams JailaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDocument4 pages3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDanilo Pereira Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- UTI TreatmentDocument3 pagesUTI TreatmentMaria RezitadinaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsDrashty DesaiNo ratings yet
- Referat - Syifa Firza UtiDocument28 pagesReferat - Syifa Firza Utimiir ikbalNo ratings yet
- UTI, HSC With QuestionsDocument43 pagesUTI, HSC With QuestionsAlex MatthewNo ratings yet
- Decision Aid For Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Older PeopleDocument4 pagesDecision Aid For Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Older PeopleNeisa SukmaNo ratings yet
- Cystitis & PyelonefritisDocument12 pagesCystitis & PyelonefritisAdinda Raihana SitorusNo ratings yet
- EAU Pocket On Urological Infections 2024Document34 pagesEAU Pocket On Urological Infections 2024kishorechandraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection - Definition, Types, EpidemiologyDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract Infection - Definition, Types, EpidemiologyXerxyllXyreaneLinaoNo ratings yet
- Elderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixDocument36 pagesElderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixRyan Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Does My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesDoes My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract Infectiontsiko111No ratings yet
- Coralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument48 pagesCoralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNJose Ph YuNo ratings yet
- Health AssementDocument13 pagesHealth AssementClarence ViboraNo ratings yet
- UTI UKI Lecture May 2009 Rev 1Document27 pagesUTI UKI Lecture May 2009 Rev 1godlief leghu kondiNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- Educational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaDocument35 pagesEducational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaPH Ph GnsoNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis: It's CysitisDocument8 pagesUrolithiasis: It's CysitisSajeda A. HadiNo ratings yet
- PT Nov 2013 - PP - June16Document2 pagesPT Nov 2013 - PP - June16Anonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle and AUB: Dr. GetnetDocument31 pagesPhysiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle and AUB: Dr. GetnetYiddish hakeNo ratings yet
- Uterin InversionDocument8 pagesUterin InversionZahra AlSaif100% (1)
- Acts Directly On The Smooth Muscle of The Uterus and Increases TheDocument14 pagesActs Directly On The Smooth Muscle of The Uterus and Increases TheKrissyNo ratings yet
- Urological RefferalDocument12 pagesUrological Refferalmichelle octavianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture ISK UKI - Dr. Sahala Panggabean SP - PDDocument25 pagesLecture ISK UKI - Dr. Sahala Panggabean SP - PDBen HonorseekerNo ratings yet
- Vaginitis and Vaginal DischargeDocument52 pagesVaginitis and Vaginal Dischargedrdoaabakhet148No ratings yet
- UTI Treatment Algorithm - Sharp Mesa Vista 2Document3 pagesUTI Treatment Algorithm - Sharp Mesa Vista 2Fitri 1997No ratings yet
- Group 1 Urinarytractinfections 2Document34 pagesGroup 1 Urinarytractinfections 2blessiejamNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Document16 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection A Case Report: DR. Anastasia M Runtunuwu Senior: DR. Christine BelindaDocument25 pagesUrinary Tract Infection A Case Report: DR. Anastasia M Runtunuwu Senior: DR. Christine Belindamartin kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Urinery IncontinsetenceDocument1 pageUrinery IncontinsetenceLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- Form Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterDocument1 pageForm Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterTeenu JobyNo ratings yet
- 13 Gynaecological Conditions in General PracticeDocument64 pages13 Gynaecological Conditions in General Practices14214lscNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Eman Shaker 20182348Document85 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Eman Shaker 20182348زهرة الدوارNo ratings yet
- Female Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecDocument51 pagesFemale Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecalinciopecNo ratings yet
- Làm Gì Khi SDMA TăngDocument1 pageLàm Gì Khi SDMA TăngNguyễn Tấn TàiNo ratings yet
- UTI Leaflet V16 PDFDocument1 pageUTI Leaflet V16 PDFPrecious SorianoNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: Emergency and TraumaDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: Emergency and TraumaJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Tuesday, July 28, 2009 9:25 PMDocument8 pagesTuesday, July 28, 2009 9:25 PMsimonedarlingNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in Children 2021Document19 pagesUrinary Tract Infections in Children 2021azri.hafiziNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Low Abdominal (Pelvic) Pain in Women of Reproductive AgeDocument3 pagesCommon Causes of Low Abdominal (Pelvic) Pain in Women of Reproductive AgeZerry Reza SyahrulNo ratings yet
- Lecture-33 Postpartum HemorrhageDocument50 pagesLecture-33 Postpartum HemorrhageMadhu Sudhan Pandeya100% (2)
- Genital Tract Infections2Document32 pagesGenital Tract Infections2hacker ammerNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence in WomenDocument6 pagesUrinary Incontinence in WomenManju GalagangodageNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionMuhammad Shayan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Managing LUTS BPH For Patients at Risk of Progression - DR RickyDocument37 pagesManaging LUTS BPH For Patients at Risk of Progression - DR RickyafifberlianNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorDocument11 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Bladder Spanish776C547ACFF5Document1 pageBladder Spanish776C547ACFF5cristianNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Women With UtiDocument9 pagesPregnant Women With UtiJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- UTI Patient Leaflet SpanishDocument1 pageUTI Patient Leaflet Spanishovidioch760No ratings yet
- MINDMAP UTI 2Document1 pageMINDMAP UTI 2YeeKee LeeNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- 02 Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pages02 Urinary Tract InfectionElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Management of Urinary Tract Infections (Utis) in Non-Catheterized Long-Term Care Home ResidentsDocument29 pagesManagement of Urinary Tract Infections (Utis) in Non-Catheterized Long-Term Care Home Residentsnz chuksNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Data and Editorial AssociateDocument2 pagesData and Editorial AssociateKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Data Collector - Advert June 2024Document2 pagesData Collector - Advert June 2024KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Job Vacancy - Assistant Bursar PEAS BRIDGE - PEAS UgandaDocument1 pageJob Vacancy - Assistant Bursar PEAS BRIDGE - PEAS UgandaKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Lira Universitys Advertised Jobs 2024 Positions and SpecificationsDocument3 pagesLira Universitys Advertised Jobs 2024 Positions and SpecificationsKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Data ATVrDocument3 pagesData ATVrKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Insulin Prescription FormDocument2 pagesInsulin Prescription FormKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONSDocument5 pagesQUESTIONSKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Call For Abstract - NNF24Document1 pageCall For Abstract - NNF24KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- TPT Campaign - Draft For ST Matia Targets - Working - 19th - May - 2023 - Updated - August 2023Document8 pagesTPT Campaign - Draft For ST Matia Targets - Working - 19th - May - 2023 - Updated - August 2023KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Summery of Key Changes, Updates and Areas of EmphasisDocument11 pagesSummery of Key Changes, Updates and Areas of EmphasisKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Abstraction Tool For PBCs Who Have Not Completed The Contact Tracing and TPT CasDocument15 pagesAbstraction Tool For PBCs Who Have Not Completed The Contact Tracing and TPT CasKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Weekly TB Reporting Template-1Document4 pagesWeekly TB Reporting Template-1KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Lecture I LAB-RLE Estimates in Pregnancy Laboratory Activity' With YouDocument29 pagesNCM107 Lecture I LAB-RLE Estimates in Pregnancy Laboratory Activity' With YouMary Ann G. CorsanesNo ratings yet
- PBT NotesDocument5 pagesPBT NotesYogish HegdeNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Block 4 Unit 3 Non-Communicable Diseases 2Document13 pagesIGNOU Block 4 Unit 3 Non-Communicable Diseases 2erice.researchNo ratings yet
- About The Dangers of Smoking - 14Document14 pagesAbout The Dangers of Smoking - 14Марта БасішинNo ratings yet
- Wa0019.Document12 pagesWa0019.troyganNo ratings yet
- Birth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuDocument38 pagesBirth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuCharles FrankNo ratings yet
- Maternal-Fetal Circadian Communication During PregnancyDocument9 pagesMaternal-Fetal Circadian Communication During PregnancyLeslie AcevesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D and PCOSDocument39 pagesVitamin D and PCOSsyafiraNo ratings yet
- Formation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsDocument32 pagesFormation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument14 pagesChapter 7-Reaching The Age of AdolescenceRC SectionNo ratings yet
- Common Problems of AdolescenceDocument9 pagesCommon Problems of AdolescenceLovemore MulengaNo ratings yet
- Anglais 2022-2023Document16 pagesAnglais 2022-2023Issahh PAMBO EVORANo ratings yet
- G10 Science Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesG10 Science Quiz Beerangel rotaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 GEC 115Document13 pagesModule 1 GEC 115Emil John D. ElefanteNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Nurses' Knowledge and Practice Regarding To Kangaroo Care at Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)Document11 pagesAssessment of Nurses' Knowledge and Practice Regarding To Kangaroo Care at Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)مالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Pclu CasestudyDocument33 pagesPclu CasestudyMarie Francoise BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 of Teenage PregnancyDocument14 pagesChapter 2 of Teenage PregnancyHoney Joy Leopando SabadoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 ApdnDocument10 pagesLab 1 Apdnyeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- 4 - PaediatricsDocument121 pages4 - Paediatricsayeshafarooq60No ratings yet
- Full Download Book Johns Hopkins Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynecology PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Johns Hopkins Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynecology PDFnatividad.donart309100% (29)
- Ondigo - Case Records and Dissertations in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument286 pagesOndigo - Case Records and Dissertations in Obstetrics and GynaecologyAastha JainNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis: Nishalini RavindranDocument6 pagesPhysical Diagnosis: Nishalini RavindranShalini RavNo ratings yet
- S60 - LPL - Noida 3 N-27, Sec-18, Commercial Complex, Near. Atta Market, Noida.120-3029866/3142530 NoidaDocument2 pagesS60 - LPL - Noida 3 N-27, Sec-18, Commercial Complex, Near. Atta Market, Noida.120-3029866/3142530 Noidavimal kumar dwivediNo ratings yet
- Module VI: Social Issues Child MarriageDocument8 pagesModule VI: Social Issues Child MarriageNasreen HasanNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 PassengerDocument9 pagesNCM 102 Passengerlarissedeleon100% (1)
- Astrovega Nov 2023Document43 pagesAstrovega Nov 2023VARA PRASAD100% (1)
- Pathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestDocument16 pagesPathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1028044Document18 pagesNihms 1028044NormanNo ratings yet
- Report Draft 2Document5 pagesReport Draft 2api-533959157No ratings yet
- Assisted Breech Delivery1Document28 pagesAssisted Breech Delivery1swatisinghnigeria100% (4)
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Uploaded by
KASADHA PATRICKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Urinary Tract Infection: Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Uploaded by
KASADHA PATRICKCopyright:
Available Formats
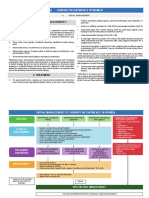
Kijabe OPD Guidelines
Urinary Tract Infection
Key Facts:
• Almost half of all women report at least one UTI sometime during their lifetime (1)
• It is essential to distinguish between simple and complicated and/or upper UTI’s
• All UTI’s in men and pregnant women should be considered to be complicated.
Simple lower urinary tract infections: Complicated/Upper urinary tract
infections:
• Non pregnant women with the following • All men and all pregnant women.
symptoms: • Any patient with the following symptoms in
o Dysuria addition to those of a lower urinary tract
o Frequency infection:
o Urgency o High fever,
o Suprapubic pain o Constitutional symptoms
o Hematuria (cloudy or foul-‐smelling o Flank pain
more common)
Investigations:
• Urinary
Dipstick
–
Nitrates
and
leucocytes
are
an
indicator
of
possible
UTI
(2)
• Urine
culture
–
To
be
considered
in
recurrent
or
complicated
UTI’s
Urine
Microscopy
should
not
be
routinely
performed
for
presumed
UTI
Management
• Exclude
possibility
of
pregnancy
• Consider
STI
as
alternative
diagnosis
(See
STI
guideline)
• Consider
if
requires
consultant
review
(See
box
below)
• Commence
antibiotics
as
per
table
below
(3)
Lower
UTI
Upper
UTI
UTI
Male
UTI
Pregnancy
female
female
First
line
Nitrofurantoin
Ciprofloxacin
500
Ciprofloxacin
500
Nitrofurantoin
100
mg
BD
for
5
mg
BD
for
7
days
mg
BD
for
2
100
mg
BD
for
5
days
weeks
days
*
Second
line
Ciprofloxacin
500
Discuss
with
Levofloxacin
250
Cephalexin
500
mg
BD
for
3
days
consultant
mg
OD
for
10
days
mg
BD
for
7-‐14
days
* except
last
4
weeks
of
pregnancy
Consultant review if any of the following:
• UTI in pregnancy • Concern re pyelonephritis
• Recurrent UTI • Failed first and second line
• Systemically unwell antibiotics.
• Age less than 16
References:
1Foxman
B;
Epidemiology
of
urinary
tract
infections:
incidence,
morbidity,
and
economic
costs.
Dis
Mon.
2003
Feb;49(2):53-‐70.
2.
Walter
LJM
Devill
et
al;
The
urine
dipstick
test
useful
to
rule
out
infections.
A
meta-‐analysis
of
the
accuracy,
June
2004
3.
MOH
guidelines
2014
You might also like
- PRN00936 II Pharmacy First Clinical Pathways v.1.6Document7 pagesPRN00936 II Pharmacy First Clinical Pathways v.1.6Oladimeji Raphael OnibonNo ratings yet
- UTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyDocument26 pagesUTI On A Background of Obstructive NephropathyAminath MeesanNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping TB in PregnancyDocument1 pageMind Mapping TB in PregnancyAndi Tenri Ola Oddang IINo ratings yet
- Treating Your Infection UtiDocument1 pageTreating Your Infection UtiJames 'jps' SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument23 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsJay AberinNo ratings yet
- How Can You Help Your Patients With An Uncomplicated UTI?: Know?Document1 pageHow Can You Help Your Patients With An Uncomplicated UTI?: Know?gegeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology: Dr. LuDocument2 pagesNephrology: Dr. LuShams JailaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDocument4 pages3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDanilo Pereira Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- UTI TreatmentDocument3 pagesUTI TreatmentMaria RezitadinaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsDrashty DesaiNo ratings yet
- Referat - Syifa Firza UtiDocument28 pagesReferat - Syifa Firza Utimiir ikbalNo ratings yet
- UTI, HSC With QuestionsDocument43 pagesUTI, HSC With QuestionsAlex MatthewNo ratings yet
- Decision Aid For Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Older PeopleDocument4 pagesDecision Aid For Diagnosis and Management of Suspected Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Older PeopleNeisa SukmaNo ratings yet
- Cystitis & PyelonefritisDocument12 pagesCystitis & PyelonefritisAdinda Raihana SitorusNo ratings yet
- EAU Pocket On Urological Infections 2024Document34 pagesEAU Pocket On Urological Infections 2024kishorechandraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection - Definition, Types, EpidemiologyDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract Infection - Definition, Types, EpidemiologyXerxyllXyreaneLinaoNo ratings yet
- Elderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixDocument36 pagesElderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixRyan Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Does My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesDoes My Patient Need To Be Screened or Treated For A Urinary Tract Infectiontsiko111No ratings yet
- Coralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument48 pagesCoralie Therese D. Dimacali, MD, FPCP, FPSNJose Ph YuNo ratings yet
- Health AssementDocument13 pagesHealth AssementClarence ViboraNo ratings yet
- UTI UKI Lecture May 2009 Rev 1Document27 pagesUTI UKI Lecture May 2009 Rev 1godlief leghu kondiNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- Educational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaDocument35 pagesEducational Module For Nursing Assistants in Long-Term Care Facilities: Urinary Tract Infections and Asymptomatic BacteriuriaPH Ph GnsoNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis: It's CysitisDocument8 pagesUrolithiasis: It's CysitisSajeda A. HadiNo ratings yet
- PT Nov 2013 - PP - June16Document2 pagesPT Nov 2013 - PP - June16Anonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle and AUB: Dr. GetnetDocument31 pagesPhysiology of The Normal Menstrual Cycle and AUB: Dr. GetnetYiddish hakeNo ratings yet
- Uterin InversionDocument8 pagesUterin InversionZahra AlSaif100% (1)
- Acts Directly On The Smooth Muscle of The Uterus and Increases TheDocument14 pagesActs Directly On The Smooth Muscle of The Uterus and Increases TheKrissyNo ratings yet
- Urological RefferalDocument12 pagesUrological Refferalmichelle octavianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture ISK UKI - Dr. Sahala Panggabean SP - PDDocument25 pagesLecture ISK UKI - Dr. Sahala Panggabean SP - PDBen HonorseekerNo ratings yet
- Vaginitis and Vaginal DischargeDocument52 pagesVaginitis and Vaginal Dischargedrdoaabakhet148No ratings yet
- UTI Treatment Algorithm - Sharp Mesa Vista 2Document3 pagesUTI Treatment Algorithm - Sharp Mesa Vista 2Fitri 1997No ratings yet
- Group 1 Urinarytractinfections 2Document34 pagesGroup 1 Urinarytractinfections 2blessiejamNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Document16 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection A Case Report: DR. Anastasia M Runtunuwu Senior: DR. Christine BelindaDocument25 pagesUrinary Tract Infection A Case Report: DR. Anastasia M Runtunuwu Senior: DR. Christine Belindamartin kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Urinery IncontinsetenceDocument1 pageUrinery IncontinsetenceLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- Form Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterDocument1 pageForm Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterTeenu JobyNo ratings yet
- 13 Gynaecological Conditions in General PracticeDocument64 pages13 Gynaecological Conditions in General Practices14214lscNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Eman Shaker 20182348Document85 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Eman Shaker 20182348زهرة الدوارNo ratings yet
- Female Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecDocument51 pagesFemale Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecalinciopecNo ratings yet
- Làm Gì Khi SDMA TăngDocument1 pageLàm Gì Khi SDMA TăngNguyễn Tấn TàiNo ratings yet
- UTI Leaflet V16 PDFDocument1 pageUTI Leaflet V16 PDFPrecious SorianoNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: Emergency and TraumaDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: Emergency and TraumaJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Tuesday, July 28, 2009 9:25 PMDocument8 pagesTuesday, July 28, 2009 9:25 PMsimonedarlingNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in Children 2021Document19 pagesUrinary Tract Infections in Children 2021azri.hafiziNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Low Abdominal (Pelvic) Pain in Women of Reproductive AgeDocument3 pagesCommon Causes of Low Abdominal (Pelvic) Pain in Women of Reproductive AgeZerry Reza SyahrulNo ratings yet
- Lecture-33 Postpartum HemorrhageDocument50 pagesLecture-33 Postpartum HemorrhageMadhu Sudhan Pandeya100% (2)
- Genital Tract Infections2Document32 pagesGenital Tract Infections2hacker ammerNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence in WomenDocument6 pagesUrinary Incontinence in WomenManju GalagangodageNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionMuhammad Shayan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Managing LUTS BPH For Patients at Risk of Progression - DR RickyDocument37 pagesManaging LUTS BPH For Patients at Risk of Progression - DR RickyafifberlianNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorDocument11 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in Children: Dr. Alia Al-Ibrahim Consultant Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Assistant ProfessorJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Bladder Spanish776C547ACFF5Document1 pageBladder Spanish776C547ACFF5cristianNo ratings yet
- Pregnant Women With UtiDocument9 pagesPregnant Women With UtiJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- UTI Patient Leaflet SpanishDocument1 pageUTI Patient Leaflet Spanishovidioch760No ratings yet
- MINDMAP UTI 2Document1 pageMINDMAP UTI 2YeeKee LeeNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- 02 Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pages02 Urinary Tract InfectionElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Management of Urinary Tract Infections (Utis) in Non-Catheterized Long-Term Care Home ResidentsDocument29 pagesManagement of Urinary Tract Infections (Utis) in Non-Catheterized Long-Term Care Home Residentsnz chuksNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Nocturia, (Excessive Night Urination) Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Data and Editorial AssociateDocument2 pagesData and Editorial AssociateKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Data Collector - Advert June 2024Document2 pagesData Collector - Advert June 2024KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Job Vacancy - Assistant Bursar PEAS BRIDGE - PEAS UgandaDocument1 pageJob Vacancy - Assistant Bursar PEAS BRIDGE - PEAS UgandaKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Lira Universitys Advertised Jobs 2024 Positions and SpecificationsDocument3 pagesLira Universitys Advertised Jobs 2024 Positions and SpecificationsKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Data ATVrDocument3 pagesData ATVrKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Insulin Prescription FormDocument2 pagesInsulin Prescription FormKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONSDocument5 pagesQUESTIONSKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Call For Abstract - NNF24Document1 pageCall For Abstract - NNF24KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- TPT Campaign - Draft For ST Matia Targets - Working - 19th - May - 2023 - Updated - August 2023Document8 pagesTPT Campaign - Draft For ST Matia Targets - Working - 19th - May - 2023 - Updated - August 2023KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Summery of Key Changes, Updates and Areas of EmphasisDocument11 pagesSummery of Key Changes, Updates and Areas of EmphasisKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Abstraction Tool For PBCs Who Have Not Completed The Contact Tracing and TPT CasDocument15 pagesAbstraction Tool For PBCs Who Have Not Completed The Contact Tracing and TPT CasKASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- Weekly TB Reporting Template-1Document4 pagesWeekly TB Reporting Template-1KASADHA PATRICKNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Lecture I LAB-RLE Estimates in Pregnancy Laboratory Activity' With YouDocument29 pagesNCM107 Lecture I LAB-RLE Estimates in Pregnancy Laboratory Activity' With YouMary Ann G. CorsanesNo ratings yet
- PBT NotesDocument5 pagesPBT NotesYogish HegdeNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Block 4 Unit 3 Non-Communicable Diseases 2Document13 pagesIGNOU Block 4 Unit 3 Non-Communicable Diseases 2erice.researchNo ratings yet
- About The Dangers of Smoking - 14Document14 pagesAbout The Dangers of Smoking - 14Марта БасішинNo ratings yet
- Wa0019.Document12 pagesWa0019.troyganNo ratings yet
- Birth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuDocument38 pagesBirth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuCharles FrankNo ratings yet
- Maternal-Fetal Circadian Communication During PregnancyDocument9 pagesMaternal-Fetal Circadian Communication During PregnancyLeslie AcevesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D and PCOSDocument39 pagesVitamin D and PCOSsyafiraNo ratings yet
- Formation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsDocument32 pagesFormation of Bilaminar Germ DiscsStanley OdiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument14 pagesChapter 7-Reaching The Age of AdolescenceRC SectionNo ratings yet
- Common Problems of AdolescenceDocument9 pagesCommon Problems of AdolescenceLovemore MulengaNo ratings yet
- Anglais 2022-2023Document16 pagesAnglais 2022-2023Issahh PAMBO EVORANo ratings yet
- G10 Science Quiz BeeDocument2 pagesG10 Science Quiz Beerangel rotaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 GEC 115Document13 pagesModule 1 GEC 115Emil John D. ElefanteNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Nurses' Knowledge and Practice Regarding To Kangaroo Care at Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)Document11 pagesAssessment of Nurses' Knowledge and Practice Regarding To Kangaroo Care at Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)مالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Pclu CasestudyDocument33 pagesPclu CasestudyMarie Francoise BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 of Teenage PregnancyDocument14 pagesChapter 2 of Teenage PregnancyHoney Joy Leopando SabadoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 ApdnDocument10 pagesLab 1 Apdnyeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- 4 - PaediatricsDocument121 pages4 - Paediatricsayeshafarooq60No ratings yet
- Full Download Book Johns Hopkins Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynecology PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Johns Hopkins Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynecology PDFnatividad.donart309100% (29)
- Ondigo - Case Records and Dissertations in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument286 pagesOndigo - Case Records and Dissertations in Obstetrics and GynaecologyAastha JainNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis: Nishalini RavindranDocument6 pagesPhysical Diagnosis: Nishalini RavindranShalini RavNo ratings yet
- S60 - LPL - Noida 3 N-27, Sec-18, Commercial Complex, Near. Atta Market, Noida.120-3029866/3142530 NoidaDocument2 pagesS60 - LPL - Noida 3 N-27, Sec-18, Commercial Complex, Near. Atta Market, Noida.120-3029866/3142530 Noidavimal kumar dwivediNo ratings yet
- Module VI: Social Issues Child MarriageDocument8 pagesModule VI: Social Issues Child MarriageNasreen HasanNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 PassengerDocument9 pagesNCM 102 Passengerlarissedeleon100% (1)
- Astrovega Nov 2023Document43 pagesAstrovega Nov 2023VARA PRASAD100% (1)
- Pathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestDocument16 pagesPathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1028044Document18 pagesNihms 1028044NormanNo ratings yet
- Report Draft 2Document5 pagesReport Draft 2api-533959157No ratings yet
- Assisted Breech Delivery1Document28 pagesAssisted Breech Delivery1swatisinghnigeria100% (4)