Professional Documents
Culture Documents
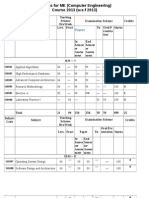
Periods Per Week (60 Min. Each) Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Marks Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total - 150
Periods Per Week (60 Min. Each) Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Marks Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total - 150
Uploaded by
dil17Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periods Per Week (60 Min. Each) Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Marks Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total - 150
Periods Per Week (60 Min. Each) Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Marks Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total - 150
Uploaded by
dil17Copyright:
Available Formats
Class: B.E.
University of Mumbai Branch: Instrumentation
Semester: VII
Elective-I: Expert Systems (Abbreviated as ES) Periods per Week Lecture 04 (60 min. each) Practical 02 Tutorial -Hours Evaluation System Theory 03 Oral --Term Work --Total --Module 1 Contents
Marks 100 25 25 150
Hours 3
Introduction to Expert System What are Expert Systems, Features of Expert System, features of good Expert System, Role of human in Expert System, Expert System organization, Difference between expert system and conventional program, Basic activities of expert system and the areas in which they solve problems, Prospector systems-features, working Expert System Tools Knowledge representation in expert systems-using rules semantic nets, frames, Types of tools available for expert system building and how they are used, Stages in the development of expert system tools, Examples of knowledge engineering Building an Expert Systems Necessary requirements for expert systems development, Justification for expert system development, Task in building expert systems, Stages of expert system development, Choosing a tool for building expert system, Acquiring knowledge from the experts, Examples of the expert systembuilding process, Examples of expert system used in different areas Difficulties in developing an expert system Common pitfalls in-planning an expert system, Scaling with the domain expert during development process. Neural Network Introduction Biological neural networks-neuron physiology, eyes neural network, Artificial neuron models, Neural net architecture (Topologies), Learning in ANN, Characteristics of ANN
26
6 Supervised Learning Single layer networks-perceptrons, Linear separability, Perceptron training algorithm, Modifications multi-layer network-multi-layer discrimination, back propagation algorithm, Classification using back propagation algorithm, Application of back propagation algorithm, Adaptive multiplier networks-algorithm, boosting, prediction network, radial basis functions 7 5 Unsupervised Learning Winner-take all networks, Learning vector quantiser, Co-inter propagation networks, Adaptive response theory 8 5 Associative Networks Non-interactive procedures for association, Hopfield networks, Optimization using Hopfield networks, Brain state in a box network, Boltzmann machines, Hetero associators 9 6 Fuzzy Logic Propositional logic, Membership functions, Fuzzy logic, Fuzzy rule generation, De-fuzzification, Time dependent fuzzy logic, Temporal fuzzy logics, Case study-to use fuzzy logic for processes control problem Theory Examination: 1. Question paper will consist of total 7 questions carrying 20 marks each. 2. Only 5 questions need to be attempted. 3. Q.1 will be compulsory and based on the entire syllabus. 4. Remaining questions will be mixed in nature. 5. In question paper, weightage of each module will be proportional to the number of respective lecture hours as mentioned in the syllabus.
Oral Examination:
Oral examination will be based on entire subject.
Term Work:
Term work consists of minimum six experiments/assignments and a written test. The distribution of the term work shall be as follows, Laboratory work (Experiments and Journal) :15 marks Test (at least one) :10 marks The final certification and acceptance of term work ensures the satisfactory performance of laboratory work and minimum passing in the term-work
Text Books:
1. Stamatios V. Kartalopolous, Understanding Neural Network and Fuzzy Logic, PHI Pvt Ltd. 2. Kishan Mehrotra, Elements of ANN, 2nd Editon, Penram International Publishing (I) Pvt. Ltd.
Reference Books:
27
1. Donald A. Waterman, A Guide to Expert Systems, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company.
28
You might also like
- Virtual Entry Assessment MC 474 With Practice Exam Mail Carrier JobsDocument89 pagesVirtual Entry Assessment MC 474 With Practice Exam Mail Carrier JobsVictor La Cruz75% (4)
- DSM-IV Adult ADHD Symptom Checklist-Self Report Version # 6182Document1 pageDSM-IV Adult ADHD Symptom Checklist-Self Report Version # 6182Chris0% (1)
- Summary and Note Taking With Key Revised EditionDocument16 pagesSummary and Note Taking With Key Revised EditionMuhammad Umar0% (2)
- McClelland Theory of NeedsDocument2 pagesMcClelland Theory of NeedsKanika KapoorNo ratings yet
- Precedent Study GuideDocument5 pagesPrecedent Study GuideNicole Verosil100% (1)
- Adams (2018) PDFDocument5 pagesAdams (2018) PDFBryan TorresNo ratings yet
- IEE 6300: Advanced Simulation Modeling and AnalysisDocument7 pagesIEE 6300: Advanced Simulation Modeling and AnalysisTsega GetnetNo ratings yet
- CSE-401 E Advanced Computer Architecture: 3 1 - Exam: 100 MarksDocument6 pagesCSE-401 E Advanced Computer Architecture: 3 1 - Exam: 100 MarksShivang AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Vtu 5th Sem Open ElectivesDocument10 pagesVtu 5th Sem Open ElectivesRamya ShreeNo ratings yet
- OS - 22 SchemeDocument4 pagesOS - 22 Schemenithyamohan82No ratings yet
- Name of The CourseDocument3 pagesName of The Coursesuraj karayaNo ratings yet
- CE401 7th SemeDocument6 pagesCE401 7th SemeNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- CCIS Systems Thinking IM As of April 1 2021Document141 pagesCCIS Systems Thinking IM As of April 1 2021Valorant Account100% (2)
- Course Plan S2024 CSC-252 Operating Systems (Initial Version)Document3 pagesCourse Plan S2024 CSC-252 Operating Systems (Initial Version)janishab1704No ratings yet
- Sem 1 SyllabusDocument19 pagesSem 1 SyllabusPeterNo ratings yet
- CCIS Systems Thinking IM As of April 1 2021Document139 pagesCCIS Systems Thinking IM As of April 1 2021Lucy FurNo ratings yet
- Systems Modelling and SimulationDocument3 pagesSystems Modelling and Simulationalemu7230No ratings yet
- Distributed Operating Systems SyllabusDocument2 pagesDistributed Operating Systems Syllabuslakshay ahujaNo ratings yet
- HTTP - App - Utu.ac - in - Utuexmanagement - Exammsters - Syllabus - CE2010-Operating System1Document4 pagesHTTP - App - Utu.ac - in - Utuexmanagement - Exammsters - Syllabus - CE2010-Operating System1ꌩꍏꌗꃅꋪꍏꀭ T͡ᎻმƘ๏ԻNo ratings yet
- 21CS44Document4 pages21CS44Edu techNo ratings yet
- DBMS SyllabusDocument4 pagesDBMS SyllabusRishabh PatelNo ratings yet
- Module Outline - OS and SA - 2021Document4 pagesModule Outline - OS and SA - 2021Lets Try FoodsNo ratings yet
- CSE-401 E: Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument8 pagesCSE-401 E: Advanced Computer Architectureprateek4u_27No ratings yet
- MDU B.tech Computer Science 7th Sem SyllabusDocument7 pagesMDU B.tech Computer Science 7th Sem SyllabusManjeet RanaNo ratings yet
- Agent-Based Simulation: Principles of Simulation and The Multi-Agent ApproachDocument42 pagesAgent-Based Simulation: Principles of Simulation and The Multi-Agent ApproachtuanngthanhNo ratings yet
- Elective-II Soft ComputingDocument3 pagesElective-II Soft ComputingCatlin KaraNo ratings yet
- Elective-II Soft Computing PDFDocument3 pagesElective-II Soft Computing PDFKarthi BENo ratings yet
- Outline cs220 OSDocument4 pagesOutline cs220 OSPakeeza QaisarNo ratings yet
- A2S2 - PEAG - en - Fisa Disciplinei - Programare Evolutiva Si Algoritmi Genetici 2016Document5 pagesA2S2 - PEAG - en - Fisa Disciplinei - Programare Evolutiva Si Algoritmi Genetici 2016Harabagiu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Ita3008 Operating-Systems Eth 1.0 37 Ita3008Document2 pagesIta3008 Operating-Systems Eth 1.0 37 Ita3008Groot TenNo ratings yet
- 203CS006-Advances in Software Testing.Document2 pages203CS006-Advances in Software Testing.keerthiksNo ratings yet
- OS 18ec641Document2 pagesOS 18ec641shivalingNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Diploma Engineering Computer Engineering Semester: IV Subject Code: 09CE1405 Subject Name: Operating SystemDocument5 pagesSyllabus of Diploma Engineering Computer Engineering Semester: IV Subject Code: 09CE1405 Subject Name: Operating SystemasgamingNo ratings yet
- MEDocument37 pagesMEMrunal UpasaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Simulation: Book: Jerry Bank's Chapter 1Document28 pagesIntroduction To Simulation: Book: Jerry Bank's Chapter 1Xuân TrườngNo ratings yet
- IS820 Computer SecurityDocument69 pagesIS820 Computer SecuritySHAHID AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Course DescriptionDocument5 pagesOperating Systems Course DescriptionNarasimYNo ratings yet
- 4model PDFDocument83 pages4model PDFاحمد كريم حميدNo ratings yet
- Ce763: Distributed System & Applications (Pe - I) : Teaching Scheme Theory Practical Total CreditDocument5 pagesCe763: Distributed System & Applications (Pe - I) : Teaching Scheme Theory Practical Total CreditpakuNo ratings yet
- OS Course OutlineDocument5 pagesOS Course OutlineAyano BoresaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering SyllabusDocument4 pagesSoftware Engineering Syllabusnagarathnakharvi83No ratings yet
- Sem 620Document40 pagesSem 620Rahul ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning TechniquesDocument162 pagesMachine Learning TechniquesAkhil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument13 pagesExpert SystemsGaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 1Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 1dheerajNo ratings yet
- Visit:: Join Telegram To Get Instant Updates: Contact: MAIL: Instagram: Instagram: Whatsapp ShareDocument3 pagesVisit:: Join Telegram To Get Instant Updates: Contact: MAIL: Instagram: Instagram: Whatsapp ShareMan0% (1)
- How Computers WorkDocument3 pagesHow Computers WorkLaila HassanNo ratings yet
- Cse3008 Introduction-To-Machine - Learning Eth 1.0 2 Cse3008Document2 pagesCse3008 Introduction-To-Machine - Learning Eth 1.0 2 Cse3008RAMIREDDY LAKSHMI PRASANNA 21BCE9890No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Soft Computing - 8th Sem B. Tech - Dr. Debahuti Mishra - 0Document4 pagesLesson Plan-Soft Computing - 8th Sem B. Tech - Dr. Debahuti Mishra - 0Lowry GuettaNo ratings yet
- AI SyllabusDocument4 pagesAI SyllabusVijayKumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument5 pagesCourse OutlineMagarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- Digital VLSI Tes/ng: Sarma Vrudhula Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State UniversityDocument5 pagesDigital VLSI Tes/ng: Sarma Vrudhula Computer Science and Engineering Arizona State Universityishan088No ratings yet
- Expert SystemsDocument13 pagesExpert Systemsanand_seshamNo ratings yet
- CSE6 ThsemDocument11 pagesCSE6 ThsemsimransuriNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 111Document13 pagesUnit IV Part 111raghu RamNo ratings yet
- CS 484 - ParallelProgrammingDocument5 pagesCS 484 - ParallelProgrammingGokul KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Course Description Form: Barrett Hodgson University The Salim Habib CampusDocument8 pagesCourse Description Form: Barrett Hodgson University The Salim Habib CampusSheeraz ArifNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Modeling in Matlab - E.A. ShestovaDocument3 pagesFuzzy Modeling in Matlab - E.A. ShestovaAbduljabbar QureshiNo ratings yet
- SSCD SysDocument3 pagesSSCD SysAbhijeet ThamakeNo ratings yet
- CIT474 Expert SystemsDocument80 pagesCIT474 Expert SystemsOyinkansola AyannugaNo ratings yet
- Expert SystemDocument15 pagesExpert SystemEver GuerraNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For Quantitative AnalysisDocument6 pagesCourse Outline For Quantitative Analysiswondimu teshomeNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesArtificial IntelligenceShubham 'fiddy' MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Gathering User RequirementsDocument17 pagesChapter Six Gathering User RequirementsHamba Abebe100% (1)
- Introduction to Algorithms & Data Structures 3: Learn Linear Data Structures with Videos & Interview QuestionsFrom EverandIntroduction to Algorithms & Data Structures 3: Learn Linear Data Structures with Videos & Interview QuestionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nsdi13 Final164Document14 pagesNsdi13 Final164dil17No ratings yet
- 5960 OSN Chapter6Document11 pages5960 OSN Chapter6dil17No ratings yet
- Transport Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument130 pagesTransport Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down Approachdil17No ratings yet
- Layer 2 Switch SecurityDocument69 pagesLayer 2 Switch Securitydil17No ratings yet
- Sample Calibration ProceduresDocument37 pagesSample Calibration Proceduresdil1750% (2)
- Engineering Periods Per Week (Each of 60 Minutes) Lectures 04 Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total 150Document2 pagesEngineering Periods Per Week (Each of 60 Minutes) Lectures 04 Practical 02 Tutorial - Hours Evaluation System Theory 03 100 Oral - 25 Term Work - 25 Total 150dil17No ratings yet
- PMODocument2 pagesPMOdil17No ratings yet
- IpcDocument3 pagesIpcdil17No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Literature Survey 1.1Document41 pagesChapter 1-Literature Survey 1.1dil17No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Literature Survey 1.1Document41 pagesChapter 1-Literature Survey 1.1dil17No ratings yet
- PID Controller: Control Loop BasicsDocument6 pagesPID Controller: Control Loop Basicsdil17No ratings yet
- Non-Defining Relative ClausesDocument2 pagesNon-Defining Relative ClausesmariaNo ratings yet
- Review On Boarding LiteratureDocument9 pagesReview On Boarding LiteraturebijuchandramohanNo ratings yet
- Augustine Theory of KnowledgeDocument11 pagesAugustine Theory of KnowledgeMUOGBO MICHAEL IZUCHUKWUNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Project Planning PresentationDocument7 pagesUNIT 3 Project Planning PresentationNikhilNo ratings yet
- Creative Thinking SyllabusDocument11 pagesCreative Thinking SyllabusMohd Kamarulzaman OmarNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan - Moon PhasesDocument4 pagesScience Lesson Plan - Moon Phasesapi-215029079No ratings yet
- The Fate of The Ego in AnalyticDocument10 pagesThe Fate of The Ego in AnalyticDanielaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - Part 5Document3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy - Part 5Jesserie NacalabanNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Prepared By: DR / Bahy BoshraDocument73 pagesLeadership: Prepared By: DR / Bahy BoshraNour GafarNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document2 pagesModule 4Jared OlegarioNo ratings yet
- CTET Info BulletinDocument54 pagesCTET Info Bulletinas singhNo ratings yet
- The Act MatrixDocument33 pagesThe Act MatrixMercedes FloresNo ratings yet
- Art UBDDocument13 pagesArt UBDBlue PhoenixNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Asia TEFLDocument9 pagesThe Journal of Asia TEFLEko SepyantoNo ratings yet
- Development of Contextual Relevant CurriculumDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Contextual Relevant CurriculumAzza GhonemNo ratings yet
- The Power of HabitDocument6 pagesThe Power of HabitZOU CARLOTTANo ratings yet
- Ttj1o1 Transportation TechnologyDocument4 pagesTtj1o1 Transportation Technologyapi-204475914No ratings yet
- Operations Research Project PresentationDocument10 pagesOperations Research Project PresentationSarabjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Jargon, Slang, AbbreDocument2 pagesJargon, Slang, AbbreLovely De CastroNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Definition of Terms: NameDocument12 pagesAssignment: Definition of Terms: NameACATALEPSYEPIPHANY WanderlustNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Theoretical FrameworkDocument5 pagesDissertation Theoretical FrameworkCheapPaperWritingServicesOmaha100% (1)
- LITERATURE, A Body of Written Works RelatedDocument3 pagesLITERATURE, A Body of Written Works RelatedalvinNo ratings yet
- BTT Course Outline 2014-2015Document4 pagesBTT Course Outline 2014-2015api-287083255No ratings yet