Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Uploaded by
Ishan Nautiyal 9 binsarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- E-Assessment QuestionsDocument189 pagesE-Assessment Questionsnaveen100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockDocument27 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockSunnu MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Review QuestionsMarina XuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 14 - PhysicsDocument7 pagesAssignment 14 - Physicsdivi tyagiNo ratings yet
- VIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyDocument3 pagesVIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyRani PandeyNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Document32 pages12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- EMI 2 (Main)Document4 pagesEMI 2 (Main)Jotika DeviNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 ACDocument8 pagesCh. 7 ACAawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- Csec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeDocument9 pagesCsec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeNadia PowellNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Alternating CurrentDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Alternating Currentsarikapurwar0135No ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorDocument4 pagesAlternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- PCM Final 12 Dps G NoidaDocument13 pagesPCM Final 12 Dps G Noidasudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Semiconductors - DPP 02Document3 pagesSemiconductors - DPP 02mv7602456No ratings yet
- CH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTDocument3 pagesCH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTPatel 0786No ratings yet
- #NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismDocument8 pages#NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismZombie GamerNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedSanyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 45 QuestionsDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity 45 Questionsajiyasingh232000No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityaishwarya meenaNo ratings yet
- CH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Document4 pagesCH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Electric Current - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)Document5 pagesElectric Current - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)pragnakrishnan5No ratings yet
- Current Electricity 2Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity 2nrg8619No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - (EMI & AC) - AssignmentDocument13 pagesPHYSICS - (EMI & AC) - Assignmentmalani.swastikNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Parallel AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesSingle Phase Parallel AC CircuitsFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Document11 pagesBasics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Pratik AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Physics: PCCP DivisionDocument98 pagesPhysics: PCCP DivisionAyushNo ratings yet
- Fitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityDocument4 pagesFitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityKeerthivasav 12No ratings yet
- Ac & Emw, Appl-Derivaties, Gen Principal &process-IsolationDocument25 pagesAc & Emw, Appl-Derivaties, Gen Principal &process-Isolationjiknown6No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- Pinnaacle Classes: V V V V XDocument9 pagesPinnaacle Classes: V V V V Xpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Ee Power-Electronics PDFDocument42 pagesEe Power-Electronics PDFPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01Document5 pagesAlternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01daksh singhNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyDocument5 pagesStudent Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyCraftoastNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-20: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDocument6 pagesJEE Main Level Practice Test-20: For JEE & NEET AspirantsJeet GovindNo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: JEE-ProblemsDocument4 pagesExercise - V: JEE-ProblemsTejas SalviNo ratings yet
- Chapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)Document8 pagesChapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)dummymail6383No ratings yet
- Chapter #10Document15 pagesChapter #10Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 1Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity 1NK NikhilNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument5 pagesAlternating CurrentHe HeNo ratings yet
- Current 06-POWER - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics)Document3 pagesCurrent 06-POWER - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics)SAKSHI JHANo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDocument19 pagesPhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Emi Jee ExamDocument2 pagesEmi Jee ExamPythagorasPhysics Academy2No ratings yet
- Major Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1Document13 pagesMajor Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1DeaDShoT 618No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Document6 pagesPhysics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Malik Babar Iqbal AwanNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Document22 pagesAptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Navyadeepika. KokkiralaNo ratings yet
- Physics SampleDocument102 pagesPhysics Sampleshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- DPP 3Document11 pagesDPP 3mstudy1009No ratings yet
- EC Network AnalysisDocument70 pagesEC Network AnalysisSamarth UrankarNo ratings yet
- Spotlight Phase-2 (2023-24) Day-3 PPT PhysicsDocument14 pagesSpotlight Phase-2 (2023-24) Day-3 PPT Physicsnarendra05101995No ratings yet
- Power Electronics PDFDocument41 pagesPower Electronics PDFAnand KalNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity-02-Objective SolvedDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12thJE 1 - D06 Aug 2019Document14 pages12thJE 1 - D06 Aug 2019HARSHITNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MCQS & CASE STUDYDocument7 pagesChapter 7 MCQS & CASE STUDYShubham ChhabraNo ratings yet
- SR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21Document18 pagesSR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21kumarNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument3 pagesElectricityUncle IrodovNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025Document4 pagesCurrent Electricity - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025AkshitEditzNo ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 4 - PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 4 - PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- 04-AC-Self Evalution Test-SolutionDocument2 pages04-AC-Self Evalution Test-SolutionMuhammad Arslan AsifNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- O&m SPVDocument9 pagesO&m SPVsingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- PS817Document8 pagesPS817arness22No ratings yet
- Dual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcDocument4 pagesDual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcRoberto SNo ratings yet
- Thermo Co2 BB - 150Document128 pagesThermo Co2 BB - 150vishwajeet vimalNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGDocument3 pagesPowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGanon_370743546No ratings yet
- HSC NCTB Book Physics 2nd Part PDFDocument151 pagesHSC NCTB Book Physics 2nd Part PDFlishadNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistryhehe xdNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- PU, Slicone, NBR SealDocument28 pagesPU, Slicone, NBR SealJirakom LimmongkolkulNo ratings yet
- Telescopic Line ENDocument154 pagesTelescopic Line ENDaniel FríasNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide Kurzanleitung Instruction de Service Guía de Referencias Rápidas Guida Di Riferimento RapidoDocument402 pagesQuick Reference Guide Kurzanleitung Instruction de Service Guía de Referencias Rápidas Guida Di Riferimento RapidoRoger RiveroNo ratings yet
- HPR Flow Switch Replacement Hyperformance Plasma Systems: Field Service BulletinDocument4 pagesHPR Flow Switch Replacement Hyperformance Plasma Systems: Field Service BulletinAung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- Finall Structurall Report For PrintDocument66 pagesFinall Structurall Report For Printpoojitha100% (1)
- Horiz. DC Motor PDFDocument178 pagesHoriz. DC Motor PDFPedro RiveraNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 MHD Part-2Document12 pagesUnit-3 MHD Part-2amit621988No ratings yet
- UNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldsDocument54 pagesUNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldscharlieNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines ExamDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines ExamBapeNo ratings yet
- Catologo Lennox Cbx32mv - Elite SeriesDocument28 pagesCatologo Lennox Cbx32mv - Elite SeriesCharlie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Waste SegregationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Waste SegregationDeepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Thermo MCQDocument23 pagesThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LatinDocument3 pagesLatinpdrharigmailcomNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's LawDocument19 pagesApplied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's LawAhmadNo ratings yet
- Self-Powered Griller Using Thermoelectric Generator Peltier Module With Backup Power SourceDocument6 pagesSelf-Powered Griller Using Thermoelectric Generator Peltier Module With Backup Power SourceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phase - DiagramsDocument22 pagesPhase - Diagramskundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report ON Accelerometer Sensors..: Presented By:-Sarthak PatnaikDocument24 pagesA Seminar Report ON Accelerometer Sensors..: Presented By:-Sarthak Patnaikshas112No ratings yet
- TIP2955 TIP3055: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsDocument4 pagesTIP2955 TIP3055: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsI am number 4No ratings yet
- Modulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Document8 pagesModulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Angel RuizNo ratings yet
- Design Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingDocument3 pagesDesign Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingKhem Thapa0% (1)
- Dynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsDocument10 pagesDynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsOngolu AbhinavNo ratings yet
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Uploaded by
Ishan Nautiyal 9 binsarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Current Electricity - DPP 06 (Of Lec 10) - Lakshya JEE 2025
Uploaded by
Ishan Nautiyal 9 binsarCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE
Lakshya JEE (2025)
Physics
DPP: 6
Current Electricity
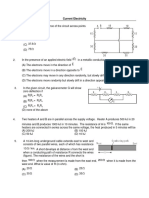
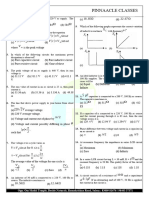
Q1 In the diagrams, all light bulbs are identical, all (B) 6.75 V
cells are ideal and identical. In which circuit (C) 13.5 V
bulbs are dimmest. (D) 27 V
(A)
Q3 A 60-watt bulb operates on 220 V supply. The
current flowing through the bulb is _________.
(A) 11
3
A
3
(B) 11 A
(B)
(C) 8A
(D) 6A
Q4 ′ n′ identical bulbs, each designed to draw a
(C) power P from a certain voltage supply are
joined in series across the supply. The total
power which they will draw is
(A) P
(D) (B) nP
(C) P2
n
(D) Pn
Q5 An electric heater and an electric bulb are
Q2 A torch bulb rated as 4.5 W, 1.5 V is rated 500 W, 220 V and 100 W, 220 V
connected as shown in the figure. The emf of respectively. Both are connected in series to a
the cell of internal resistance 2.67Ω, need to 220 V a.c. mains. Calculate power consumed
make the bulb glow at full intensity is ______. by (i) heater (ii) bulb.
Q6 Two bulbs A and B are connected as shown.
When is switch ′ S′ closed then which of them
will fuse? (100 V ∼ 50 W)(100 V ∼ 40 W)
(A) 4.5 V
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
shunt of resistance 1. 2Ω. Then its new range is
n times the original range. The value of n is
(A) 49 (B) 50
(C) 51 (D) 52
Q11 In an ammeter 0.2 % of current passes through
(A) Bulb A galvanometer coil. If resistance of the coil is 20
(B) Bulb B Ω, then resistance of the ammeter is?
1 1
(C) Both A and B will fuse (A) 100 Ω (B) 50 Ω
1
(D) Neither A nor B will fuse (C) 25 Ω (D) 15 Ω
Q7 Three electric bulbs of 200 𝑊, 200 𝑊 and 400 Q12 A galvanometer having coil resistance 60Ω
𝑊 are connected as shown in figure. The gives full scales deflection when 40 mA current
resultant power of the combination is pass through it. If it is to be converted into a
Voltmeter of range 50 volt , then the value of
resistance to be connected in series with coil is.
(A) 555 Ω
(B) 1250 Ω
(C) 1190 Ω
(D) 1280 Ω
Q13 A galvanometer of resistance 50Ω is connected
to a cell of emf 3 Volt, along with another
(A) 800 W (B) 400 W
resistance 2950Ω in series. Full scale deflection
(C) 200 W (D) 600 W
of 30 division is obtained. In order to reduce
Q8 Figure of merit of galvanometer is given by deflection to 20 division, the value of extra
(Symbols have their usual meanings) resistance needed in series is.
NAB k
(A) k
(B) (A) 4050 Ω
NAB
A NAk
(C) kNB
(D) B
(B) 450 Ω
(C) 6050 Ω
Q9 A galvanometer coil has 24 turns, and 14 Ω
(D) 1500 Ω
resistance when number of turns increased to
30 , its resistance becomes 21 Ω. Its voltage Q14 Resistance of galvanometer is 40Ω . It has 30
sensitivity. division in the scale and 3 × 10−3 A current is
(A) Increases by 25% needed to produce one division deflection.
(B) Decreases by 25% What value of resistance is required to convert
(C) Decreases by 16. 6% it into a Voltmeter of range 45 volt?
(D) Increases by 30% (A) 500 Ω as shunt
(B) 460 Ω as shunt
Q10 A galvanometer coil has resistance 60Ω. If it is
(C) 500 Ω in series
converted into an ammeter by connecting a
(D) 460 Ω in series
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
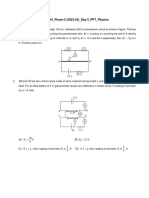
Q15 The coil resistance of a galvanometer is 100Ω
and it gives full scale deflection when 1 mA
current pass through it. The value of resistance
needed which can convert this galvanometer
into an ammeter which gives full scale
deflection when 10 A current pass through the
ammeter, is
If the filament in light bulb A burns out, then
(A) 0. 3 Ω
which of the following is true for light bulb B?
(B) 0. 03 Ω
(A) It is turned off
(C) 0. 1 Ω
(B) Its brightness does not change
(D) 0. 01 Ω
(C) It gets dimmer
Q16 A micro ammeter has resistance of 100 Ω and (D) It gets brighter
full scale deflection current 50 μA. It is to be
Q19 A 100 W bulb B1, and two 60 W bulbs B2 and B3,
converted into a Voltmeter of range 10V. The
are connected to a 250 V source, as shown in
value of resistance needed is approximately
the figure. If W1, W2 and W3 are the output
equal to.
powers of the bulbs B1, B2 and B3, respectively.
(A) 200 Ω
Then,
(B) 20, 000 Ω
(C) 2000 Ω
(D) 200, 000 Ω
Q17 When a galvanometer is shunted by 5 Ω
resistance gives full scale deflection for 250 mA
current and when a resistance 1050 Ω is
connected is series with galvanometer, it gives
full scale deflection for 25 volt. The value of
resistance of galvanometer is approximately (A) W1 > W2 = W3
equal to (B) W1 > W2 > W3
(A) 20 Ω (C) W1 < W2 = W3
(B) 48 Ω (D) W1 < W2 < W3
(C) 50 Ω
(D) 60 Ω Q20 Two batteries, one of emf 18 volt and internal
resistance 2 Ω and the other of emf 12 volt and
Q18 A circuit consists of a battery, a resistor R and internal resistance 1 Ω, are connected as shown.
two light bulbs A and B as shown. The ideal voltmeter V will record a reading of
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
Temperature coefficient of resistance of the coil
is
(A) 6.3 × 10–4 K–1
(B) 4.3 × 10–4 K–1
(C) 8.3 × 10–4 K–1
(D) 2.3 × 10–4 K–1
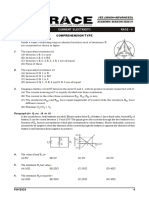
Q23 In the circuit shown, the meter bridge is in its
(A) 15 volt (B) 30 volt balanced state. The meter bridge wire has a
(C) 14 volt (D) 18 volt resistance 0.1 Ω/cm. The value of unknown
resistance X and the current drawn from the
Q21 AB is a wire of uniform resistance. The
battery of negligible resistance is
galvanometer G shows no current when the
length AC = 20 cm and CB = 80 cm. The
resistance R is equal to
(A) 6 Ω, 5 A
(A) 2 Ω (B) 8 Ω
(B) 10 Ω, 0.1 A
(C) 20 Ω (D) 40 Ω
(C) 4 Ω, 1.0 A
Q22 Figure shows a meter bridge. Wire AC has (D) 12 Ω, 0.5 A
uniform cross-section. The length of wire AC is
Q24 In the network shown the potential difference
100 cm. X is a standard resistor of 4 Ω and Y is a
between A and B is (R = r1 = r2 = r3 = 1 Ω, E1 = 3 V,
coil. When Y is immersed in melting ice the null
E2 = 2 V, E3 = 1 V)
point is at 40 cm from point A. When the coil Y
is heated to 100°C, a 78 Ω resistor has to be
connected in parallel with Y in order to keep the
bridge balanced at the same point.
(A) 1 V (B) 2 V
(C) 3 V (D) 4 V
Q25 In the circuit shown here, E1 = E2 = E3 = 2 V and R1 =
R2 = 4 ohms. What is the current (in A) flowing
between points A and B through battery E2?
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
Answer Key
Q1 (C) Q14 (D)
Q2 (C) Q15 (D)
Q3 (B) Q16 (D)
Q4 (D) Q17 (C)
Q5 13. 98 W, 69. 89 W Q18 (D)
Q6 (B) Q19 (D)
Q7 (C) Q20 (C)
Q8 (B) Q21 (C)
Q9 (C) Q22 (C)
Q10 (C) Q23 (C)
Q11 (C) Q24 (B)
Q12 (C) Q25 2
Q13 (D)
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
You might also like
- E-Assessment QuestionsDocument189 pagesE-Assessment Questionsnaveen100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockDocument27 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering by Pawan Chandani Sir 1679927943592-UnlockSunnu MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Review QuestionsMarina XuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 14 - PhysicsDocument7 pagesAssignment 14 - Physicsdivi tyagiNo ratings yet
- VIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyDocument3 pagesVIBRANT - Class - 10 - DPPs PhyRani PandeyNo ratings yet
- CurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Document3 pagesCurrentElectricity Basichomeworksheet-4Shreyansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Document32 pages12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- EMI 2 (Main)Document4 pagesEMI 2 (Main)Jotika DeviNo ratings yet
- Ch. 7 ACDocument8 pagesCh. 7 ACAawesh BackupsNo ratings yet
- Csec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeDocument9 pagesCsec Electrical and Electronic Technolohy PDF FreeNadia PowellNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Alternating CurrentDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 - Alternating Currentsarikapurwar0135No ratings yet
- Alternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorDocument4 pagesAlternating Current: AC Voltage Applied To A ResistorAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- PCM Final 12 Dps G NoidaDocument13 pagesPCM Final 12 Dps G Noidasudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Semiconductors - DPP 02Document3 pagesSemiconductors - DPP 02mv7602456No ratings yet
- CH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTDocument3 pagesCH 3 MCQ PHYSICS CLASS 12TH ASSIGNMENTPatel 0786No ratings yet
- #NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismDocument8 pages#NEET DPYQ Test Paper - 4 - Electricity & MagnetismZombie GamerNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MergedSanyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 45 QuestionsDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity 45 Questionsajiyasingh232000No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument4 pagesElectricityaishwarya meenaNo ratings yet
- CH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Document4 pagesCH # 13 (Current Electricity) - Physics 12 (TC)Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Electric Current - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)Document5 pagesElectric Current - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Abhimanyu 2.0 (Telugu)pragnakrishnan5No ratings yet
- Current Electricity 2Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity 2nrg8619No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - (EMI & AC) - AssignmentDocument13 pagesPHYSICS - (EMI & AC) - Assignmentmalani.swastikNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Parallel AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesSingle Phase Parallel AC CircuitsFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Document11 pagesBasics of Network Theory - Practice Sheet 01Pratik AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Physics: PCCP DivisionDocument98 pagesPhysics: PCCP DivisionAyushNo ratings yet
- Fitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityDocument4 pagesFitjee Paper Class 10 ElectrcityKeerthivasav 12No ratings yet
- Ac & Emw, Appl-Derivaties, Gen Principal &process-IsolationDocument25 pagesAc & Emw, Appl-Derivaties, Gen Principal &process-Isolationjiknown6No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddDocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - Exercise - MCQ - Bc-OddRaaghav SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocument12 pagesCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- Pinnaacle Classes: V V V V XDocument9 pagesPinnaacle Classes: V V V V Xpinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Ee Power-Electronics PDFDocument42 pagesEe Power-Electronics PDFPriya DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01Document5 pagesAlternating Current - Practice Sheet - UCH25DPP01daksh singhNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyDocument5 pagesStudent Copy. DPP No. 21 - Current ElectrictyCraftoastNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-20: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDocument6 pagesJEE Main Level Practice Test-20: For JEE & NEET AspirantsJeet GovindNo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: JEE-ProblemsDocument4 pagesExercise - V: JEE-ProblemsTejas SalviNo ratings yet
- Chapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)Document8 pagesChapter-19 Alternating Current and Electromagnetic Waves (PG 359 - 366)dummymail6383No ratings yet
- Chapter #10Document15 pagesChapter #10Malik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity 1Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity 1NK NikhilNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument5 pagesAlternating CurrentHe HeNo ratings yet
- Current 06-POWER - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics)Document3 pagesCurrent 06-POWER - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics)SAKSHI JHANo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDocument19 pagesPhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Emi Jee ExamDocument2 pagesEmi Jee ExamPythagorasPhysics Academy2No ratings yet
- Major Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1Document13 pagesMajor Test - 2 GR-XII JEE 1DeaDShoT 618No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Document6 pagesPhysics Notes Prepared by Babar Iqbal Awan Unit 13Malik Babar Iqbal AwanNo ratings yet
- Aptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Document22 pagesAptransco Electronic Engn 2011 Previous Paper 5c60dbb7Navyadeepika. KokkiralaNo ratings yet
- Physics SampleDocument102 pagesPhysics Sampleshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- DPP 3Document11 pagesDPP 3mstudy1009No ratings yet
- EC Network AnalysisDocument70 pagesEC Network AnalysisSamarth UrankarNo ratings yet
- Spotlight Phase-2 (2023-24) Day-3 PPT PhysicsDocument14 pagesSpotlight Phase-2 (2023-24) Day-3 PPT Physicsnarendra05101995No ratings yet
- Power Electronics PDFDocument41 pagesPower Electronics PDFAnand KalNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity-02-Objective SolvedDocument9 pagesCurrent Electricity-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 12thJE 1 - D06 Aug 2019Document14 pages12thJE 1 - D06 Aug 2019HARSHITNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 MCQS & CASE STUDYDocument7 pagesChapter 7 MCQS & CASE STUDYShubham ChhabraNo ratings yet
- SR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21Document18 pagesSR Physics PH V Pet-6 (Adv) QP DT 05.07.21kumarNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument3 pagesElectricityUncle IrodovNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025Document4 pagesCurrent Electricity - DPP 03 (Of Lec 06) - Lakshya JEE 2025AkshitEditzNo ratings yet
- XII - Revision Sheet - 4 - PhysicsDocument2 pagesXII - Revision Sheet - 4 - PhysicsVipin VNo ratings yet
- 04-AC-Self Evalution Test-SolutionDocument2 pages04-AC-Self Evalution Test-SolutionMuhammad Arslan AsifNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- O&m SPVDocument9 pagesO&m SPVsingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- PS817Document8 pagesPS817arness22No ratings yet
- Dual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcDocument4 pagesDual Ingecon Sun U B Series Family at 1500vdcRoberto SNo ratings yet
- Thermo Co2 BB - 150Document128 pagesThermo Co2 BB - 150vishwajeet vimalNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGDocument3 pagesPowerLogic PM800 Series - PM810MGanon_370743546No ratings yet
- HSC NCTB Book Physics 2nd Part PDFDocument151 pagesHSC NCTB Book Physics 2nd Part PDFlishadNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistryhehe xdNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Reference: Serway, Raymond A. & Jerry S. Faughn (2002) - Holt Physics. Holt, Rinehart and WinstonLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- PU, Slicone, NBR SealDocument28 pagesPU, Slicone, NBR SealJirakom LimmongkolkulNo ratings yet
- Telescopic Line ENDocument154 pagesTelescopic Line ENDaniel FríasNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide Kurzanleitung Instruction de Service Guía de Referencias Rápidas Guida Di Riferimento RapidoDocument402 pagesQuick Reference Guide Kurzanleitung Instruction de Service Guía de Referencias Rápidas Guida Di Riferimento RapidoRoger RiveroNo ratings yet
- HPR Flow Switch Replacement Hyperformance Plasma Systems: Field Service BulletinDocument4 pagesHPR Flow Switch Replacement Hyperformance Plasma Systems: Field Service BulletinAung Naing OoNo ratings yet
- Finall Structurall Report For PrintDocument66 pagesFinall Structurall Report For Printpoojitha100% (1)
- Horiz. DC Motor PDFDocument178 pagesHoriz. DC Motor PDFPedro RiveraNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 MHD Part-2Document12 pagesUnit-3 MHD Part-2amit621988No ratings yet
- UNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldsDocument54 pagesUNIT 11-PHY 131-Chapter 16-Electric Forces and FieldscharlieNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines ExamDocument5 pagesElectrical Machines ExamBapeNo ratings yet
- Catologo Lennox Cbx32mv - Elite SeriesDocument28 pagesCatologo Lennox Cbx32mv - Elite SeriesCharlie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Waste SegregationDocument6 pagesAutomatic Waste SegregationDeepak ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Thermo MCQDocument23 pagesThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LatinDocument3 pagesLatinpdrharigmailcomNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's LawDocument19 pagesApplied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's LawAhmadNo ratings yet
- Self-Powered Griller Using Thermoelectric Generator Peltier Module With Backup Power SourceDocument6 pagesSelf-Powered Griller Using Thermoelectric Generator Peltier Module With Backup Power SourceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phase - DiagramsDocument22 pagesPhase - Diagramskundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report ON Accelerometer Sensors..: Presented By:-Sarthak PatnaikDocument24 pagesA Seminar Report ON Accelerometer Sensors..: Presented By:-Sarthak Patnaikshas112No ratings yet
- TIP2955 TIP3055: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsDocument4 pagesTIP2955 TIP3055: Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsI am number 4No ratings yet
- Modulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Document8 pagesModulo 4 b2 Ame Question Quiz Part1Angel RuizNo ratings yet
- Design Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingDocument3 pagesDesign Steps As Per NBC For Structrual Analysis of Residential BuildingKhem Thapa0% (1)
- Dynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsDocument10 pagesDynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsOngolu AbhinavNo ratings yet