Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spelling Test 10 Words Worksheet
Spelling Test 10 Words Worksheet
Uploaded by
Vaishnavi Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Spelling Test 10 Words Worksheet (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views8 pagesSpelling Test 10 Words Worksheet
Spelling Test 10 Words Worksheet
Uploaded by
Vaishnavi SharmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
ASSIGNMENT:4 CO4 (UNIT:4)
Que1) state and explain first law of thermodynamics for
isolated closed and open system?
ANS:System is defined in physics or chemistry, is nothing
more than a collection of objects (or smaller systems)
that can be identified. Usually, the word "system" refers to
a collection that makes thinking about a problem more
convenient. The surrounding is everything else that is
not the system defined. For example, if the system being
studied is a house, the surrounding would be everything
else that is not the house (other houses, the
neighbourhood, the general environment around the
house, etc.). Systems can be described in three different
ways[1]:
°Isolated: this is a system in which no matter or energy is
being exchanged with the surroundings.
°Closed: this is a system in which only energy is being
exchanged with the surroundings.
°Open: this is a system in which both matter and energy is
being exchanged with the surroundings
Ques2) give two classical statement of second
law of thermodynamics?
Ans:According to the second law of
thermodynamics, any naturally occurring
process will always cause the universe’s entropy
(S) to increase. The law simply states that the
entropy of an isolated system will never
diminish over time..
Kelvin-Planck Statement of Second Law of
Thermodynamics
It’s difficult to turn all of the heat emitted by a
heated body into work. The working material of
a heat engine absorbs heat from a hot body,
transforms a portion of it into work, and returns
the remainder to the cold body. No engine can
transform all of the heat from the source into
work without wasting any heat. This indicates
that a sink is required to get continuous work.
Clausius Statement of Second Law of
Thermodynamics
It is impossible to build a technology that can
transmit heat from a colder body to a warmer
body without wasting any energy. In other
words, the refrigerator will not work unless the
compressor is powered by an external source.
Clausius’s assertion is used by heat pumps and
refrigerators.
Kelvin planck statement Clausius statement
Que3) how boilers are classified describe
the construction and working of cochran
boiler with neat sketch?
ANS:The Cochran Boiler is a type of Fire
Tube Boiler along with Lancashire,
Locomotive, Cornish, Simple Vertical,
Scotch Marine boilers. It is an internally
fired, vertically constructed, and multi
tubular type of boiler that is designed
horizontally parallel to the surface. As it
is mentioned that the Cochran Fire Tube
Boiler is an internally fired type, which
means the grate or furnace is constructed
inside the closed container and feeding of
coal or wood will be done externally.
Boiler
types
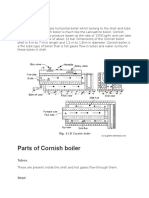
Parts of the Cochran Boiler
1. Boiler Shell
The boiler shell is made of steel plates into a cylindrical form
and it is
riveted or welded together. The ends of the shell are closed by
endplates.
The boiler shell should have enough capacity to store water
and steam.
2. Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber is below the boiler shell for burning
the fuel to
generate steam from the water in the shell.
3. Grate
The grate is a platform in the combustion chamber where fuel is burnt.
The
grate is generally a cast-iron bar and there is space between them so
the air
can pass through it. The surface area of the grate where fire takes place
called a grate surface.
4. Furnace
The furnace is above the grate and below the boiler shell and in the
furnace,
the fuel is burned.
5. Fire Tubes
The fire tubes are the horizontal tube between the combustion
chamber.
The flue gases from the combustion chamber flow to the smokebox via
a
number of fire tubes. These fire pipes are used to exchange heat from
hot
flue gases to water.
6. Fire Hole
It is at the bottom of the combustion chamber for firing fuel inside the
furnace.
7. Chimney
The chimney is provided at the top of the boiler and it is connected to
the
smokebox. These exhaust gases are coming out from fire tubes and pass
through smokebox and exhaust through a chimney.
8. Man Hole
The manhole is for cleaning, repairing and inspecting of the boiler shell.
9. Flue Pipe
Firebox and combustion chamber is connected through a short pipe and
these pipes are called flue pipes. The hot flue gases from the grate flow
into
the combustion chamber via flue pipe.
Application:
Used in refining units
Used in refining units
Also, the Cochran boiler is used in power generation plants where large
quantities of steam from 500 kg/s with high pressures approx. 160 bar
and
high temperatures reach up to 550 oC.
How does Cochran Boiler work?
•First, the coal is fed to grate via a fire hole for a burn.
•The ash formed in burning is collected in ash-pit below the
grate and
it removes manually.
•The hot gases from the grate pass through the combustion
chamber
to horizontal fire tubes and transfer the heat to water by
convection.
•Exhaust gases out from fire tubes pass through smokebox
and
exhaust to the atmosphere via a chimney.
•There is a door in the smokebox for cleaning the fire tunes
and
smokebox. The Cochran boiler has a working pressure of 6.5
bar
and a steam capacity of 3500 kg/hr.
Que4) what is the difference between boiler
mountings and accessories?
Ans: Boiler mountings are components used
for ensuring the safety of boiler operation.
These are generally mounted on the surface of
the boiler.
Control fluid parameters at the inside of the
boiler shell.
The mountings are an essential part of a
boiler, without which boiler operation is
impossible.
Examples: Pressure gauges, Water level
indicator, Safety valves, Stop valve, Fusible
plug, Blow-off cock,
Accessories are the auxiliary items required
for proper operation of boiler and improve the
Boiler efficiency of it.
These are integral parts of the boiler, but not
mounted on it.
Control fluid parameters at outside of the
boiler.
These are not essential parts of the boiler,
without which boiler can operate through at
lower efficiency.
Examples: Superheater, Feed pump, Injector,
Economizer, Steam Separator, Air preheater,
etc.etc.
Question 5) define the following terms
triple point ,critical point ,dryness fraction,
enthalpy of steam ,entropy of Steam?
Ans: 1)The triple point represents a temperature
and pressure combination where all three states
of matter exist in equilibrium.
2)Critical point is the temperature and pressure
combination where the gas form of a substance
can no longer be condensed back to a liquid,
which becomes a supercritical fluid.
3)Dryness fraction is defined as the ratio of mass
of dry steam (vapour) to combined mass of dry
steam (vapour) & mass of liquid in mixture. It is
denoted by x.
4)Enthalpy is the measure of total heat present in
the thermodynamic system where the pressure is
constant. It is represented as. Δ H = Δ E + P Δ V.
where E is the internal energy, P is the pressure
and E is the energy.
5)Entropy quantifies the energy of a substance
that is no longer available to perform useful work.
Because entropy tells so much about the
usefulness of an amount of heat transferred in
performing work, the steam tables include values
of specific entropy (s = S/m) as part of the
information tabulated.
You might also like
- Acids Bases and Salts WksheetDocument2 pagesAcids Bases and Salts WksheetShakwan WatermanNo ratings yet
- Soal Soal HallidayDocument65 pagesSoal Soal HallidayFiza RyanNo ratings yet
- Roller ChainsDocument9 pagesRoller ChainsLister NambatacNo ratings yet
- TE-1 Lab ManualDocument68 pagesTE-1 Lab ManualGurpreet singhNo ratings yet
- Cochran Boiler.Document11 pagesCochran Boiler.nalawadesahil884No ratings yet
- ATD LabDocument32 pagesATD Labneeraj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube BoilerDocument69 pagesFire Tube BoilersadvdsNo ratings yet
- BME ManualDocument32 pagesBME ManualSudhanshuAtkareNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Boiler:: Thermodynamic IIDocument11 pagesBrief History of Boiler:: Thermodynamic IIAhmad CheemaNo ratings yet
- Marine Boiler and Steam Engineering: Prepared by P.Thanga Sabari AP, Marine MSECDocument169 pagesMarine Boiler and Steam Engineering: Prepared by P.Thanga Sabari AP, Marine MSECrickNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesLiterature ReviewSunny ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Boiler and Heat EngineDocument3 pagesBoiler and Heat EngineAjitKumarPandeyNo ratings yet
- Diploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)Document19 pagesDiploma 4 THERMAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL (Copy)AjitKumarPandeyNo ratings yet
- Steam Generators (Boilers) : SubhankarDocument24 pagesSteam Generators (Boilers) : Subhankarশুভঙ্কর মুখার্জীNo ratings yet
- Steam BoilersDocument43 pagesSteam BoilersHolly CrossNo ratings yet
- Cornish BoilerDocument2 pagesCornish Boileranmolkasera100% (1)
- Cornish BoilerDocument3 pagesCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cochran BoilerDocument7 pagesCochran BoilersridharbhsNo ratings yet
- Boiler Book PDFDocument44 pagesBoiler Book PDFmpgzyah100% (5)
- BME Power PlantDocument17 pagesBME Power PlantHimanshu KhadatkarNo ratings yet
- ''Week 2 - Lecture 3-4 - Description of Steam BoilersDocument50 pages''Week 2 - Lecture 3-4 - Description of Steam Boilerstalha 8byt TalhaNo ratings yet
- Boiler: Classification of BoilersDocument7 pagesBoiler: Classification of BoilersSanjeev dahiyaNo ratings yet
- Steam Generators Lecture No.-1Document18 pagesSteam Generators Lecture No.-1rathoraryan2003No ratings yet
- BoilerDocument7 pagesBoilerKunal SupekarNo ratings yet
- Cornish BoilerDocument4 pagesCornish BoilerKhuram IqbalNo ratings yet
- X 4 GH 2 Iop 4 Euyuw Iq ZD FWGGDocument11 pagesX 4 GH 2 Iop 4 Euyuw Iq ZD FWGGdeyllemiNo ratings yet
- 11 Steam Generators 3-2Document26 pages11 Steam Generators 3-2Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- ''Week 1 - Lecture 1-2 - Steam BoilersDocument21 pages''Week 1 - Lecture 1-2 - Steam Boilerstalha 8byt TalhaNo ratings yet
- Essential FeaturesDocument14 pagesEssential FeaturesAhsan AyyazNo ratings yet
- Boilers - Types and ClassificationDocument4 pagesBoilers - Types and ClassificationSharif Muhammad HossainNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesExperiment No. 2: Page 1 of 7Kunal SupekarNo ratings yet
- 1 - Experiment No 1 - SGTC LABDocument13 pages1 - Experiment No 1 - SGTC LABRushi vedeNo ratings yet
- Boilers NotesDocument10 pagesBoilers NotesDr-Bharath Vedashantha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 1-To Study Cochran and Babcock and Wilcox BoilersShahedNo ratings yet
- Continuum Mechanics For EngineersDocument53 pagesContinuum Mechanics For Engineersshushant kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ali RazaDocument12 pagesAssignment-Ali RazaahsanNo ratings yet
- BVF3184 Topic 4 Part 1 - Boiler ComponentsDocument44 pagesBVF3184 Topic 4 Part 1 - Boiler ComponentswidadNo ratings yet
- Steam BoilersDocument34 pagesSteam BoilersSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Faqs For Module3Document4 pagesFaqs For Module3pappuNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3 Heating Surfaces and Boiler HPDocument4 pagesActivity No. 3 Heating Surfaces and Boiler HPAlmer BalidiongNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Measurement of Heating Surface of A Firetube BoilerDocument24 pagesExperiment No. 1 Measurement of Heating Surface of A Firetube BoilerAli Requiso MahmudNo ratings yet
- Boiler Raeding Material - Dec 05Document66 pagesBoiler Raeding Material - Dec 05Dipali AcharyaNo ratings yet
- #To Study On Boiler Selection For "Process Industry" (Minor Project 3rd Year)Document34 pages#To Study On Boiler Selection For "Process Industry" (Minor Project 3rd Year)BHUSHAN MESHRAMNo ratings yet
- Boiler Engineering and Power Plants 3 (2-1) Dr. Abdul GhafoorDocument17 pagesBoiler Engineering and Power Plants 3 (2-1) Dr. Abdul GhafoorUmair KhanNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2. Sketch of Cochran, Lancanshire & Babcock & Wilcox BoilerDocument24 pagesExp - 2. Sketch of Cochran, Lancanshire & Babcock & Wilcox Boilersubir majiNo ratings yet
- Lab 02 FinalDocument13 pagesLab 02 FinalAsh DenemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BoilerDocument26 pagesIntroduction To BoilerEngr Mujahid MehdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Furnaces: Professional Course in English "Process Technology. Equipment and Systems"Document20 pagesUnit 3. Furnaces: Professional Course in English "Process Technology. Equipment and Systems"Nathalia DelgadoNo ratings yet
- ATD Unit-4 NotesDocument44 pagesATD Unit-4 NotesSanjay KatreddyNo ratings yet
- Steam Generators-Fire Tube BoilersDocument11 pagesSteam Generators-Fire Tube BoilersGokulAgNo ratings yet
- Boilers 227 5 2021 0 1 10Document16 pagesBoilers 227 5 2021 0 1 10Anoop AshokNo ratings yet
- Recovery Boiler Equipment and Operation: Thomas M. GraceDocument4 pagesRecovery Boiler Equipment and Operation: Thomas M. GracehabibiNo ratings yet
- Notes Steam Plants - RevisionDocument10 pagesNotes Steam Plants - RevisionKonstantina D. AsimakopoulouNo ratings yet
- Types of BoilerDocument8 pagesTypes of Boilerjay0% (1)
- Unit 1 BoilerDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Boilerdhananjay yadavNo ratings yet
- احمد عمر حسينsecDocument14 pagesاحمد عمر حسينsectdvytecgjynwlniftzNo ratings yet
- ENCON Handbook Fired HeaterDocument18 pagesENCON Handbook Fired HeaterArulvalavan DuraikannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Steam Generators (Boilers)Document55 pagesChapter 4 - Steam Generators (Boilers)rrhoshackNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document17 pagesModule 2Tristan Paul Guerra OrodioNo ratings yet
- Classification of Boilers: Applied ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesClassification of Boilers: Applied ThermodynamicsASHISH PATILNo ratings yet
- Cochran Boiler: It Consists ofDocument4 pagesCochran Boiler: It Consists ofIndra Kumar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Types - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantDocument11 pagesTypes - Of.boilers Draught Thermal - PlantPraveen PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics - WikipediaDocument12 pagesMathematical Physics - WikipediaDAVID MURILLONo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics Lesson 1 - Vector Algebra and Vector Calculus PDFDocument29 pagesClassical Mechanics Lesson 1 - Vector Algebra and Vector Calculus PDFQuoc Hung PhiNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Assignment 4 PDFDocument6 pagesDifferentiation Assignment 4 PDFAmandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- 7 - Displacement - Position - Proximity - Sensor IDocument32 pages7 - Displacement - Position - Proximity - Sensor IKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Low Cost 1.2 G Dual Axis Accelerometer ADXL213: Features General DescriptionDocument12 pagesLow Cost 1.2 G Dual Axis Accelerometer ADXL213: Features General DescriptionMarlon PerinNo ratings yet
- Ushio Elevator Operation ManualDocument615 pagesUshio Elevator Operation Manual朝林檎No ratings yet
- Structural Attachment Elements: Product GroupDocument13 pagesStructural Attachment Elements: Product GroupZoranNo ratings yet
- Office 1Document9 pagesOffice 1Sonti Mani kumarNo ratings yet
- Siemens Industry Online SupportDocument14 pagesSiemens Industry Online SupportkutasNo ratings yet
- 1SAC200017M0002 - B - Contactor and Overload Realy - Guide - 2022Document96 pages1SAC200017M0002 - B - Contactor and Overload Realy - Guide - 2022zunaidi84No ratings yet
- Chem All in One Final AnsweredDocument334 pagesChem All in One Final AnsweredAbhishek GunjalNo ratings yet
- Radiation As A Method of Food PreservationDocument25 pagesRadiation As A Method of Food PreservationvishnuNo ratings yet
- Review Questions in Forensic Ballistics PDF FreeDocument5 pagesReview Questions in Forensic Ballistics PDF FreeRevie Sawadan GaanoNo ratings yet
- Is 12727 PDFDocument14 pagesIs 12727 PDFJanardhana ReddiNo ratings yet
- Thermo MCQDocument23 pagesThermo MCQAnmol ChauhanNo ratings yet
- RT-Lab Based Real-Time Simulation of A Direct Field-Oriented Controller For An Induction MotorDocument6 pagesRT-Lab Based Real-Time Simulation of A Direct Field-Oriented Controller For An Induction MotorMagpie 2023No ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Part 1Document25 pagesChemistry Practical Part 1Hussain bohraNo ratings yet
- Bee Unit4Document66 pagesBee Unit4DOMAKONDA NEHA SE(H)2019No ratings yet
- June 2020 (v3) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry GCSEDocument10 pagesJune 2020 (v3) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry GCSEathmanNo ratings yet
- Dungs Mpa22Document112 pagesDungs Mpa22Piotr MNo ratings yet
- 01 - Kitchenhood Suppression System PDFDocument24 pages01 - Kitchenhood Suppression System PDFGulf JobzNo ratings yet
- Crouzet Miniature V3D 8326Document10 pagesCrouzet Miniature V3D 8326wg0532No ratings yet
- Tds Az 1500 SeriesDocument7 pagesTds Az 1500 SeriesIgor_uhuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationDocument22 pagesEvaluation Exam 17: Kippap EducationMichael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)Document59 pagesCivil Engineering Internship Report (CATIC)TrevorKetso100% (1)
- Factor de ConversionDocument5 pagesFactor de ConversionjmgmNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsDocument10 pagesDynamic Modeling of A PEM Fuel Cell With Temperature EffectsOngolu AbhinavNo ratings yet