Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Repro Hormones
Repro Hormones
Uploaded by
schmooshieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
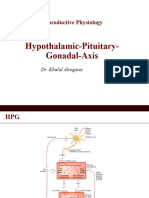
Repro Hormones
Repro Hormones
Uploaded by
schmooshieCopyright:
Available Formats
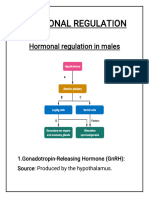
Hormone
Gonadotropi n-Releasing Hormone (GnRH): Hypothal.
Stimulates Release
Norepinephrine
Inhibits Release
Estrogen (female) Inhibins Testosterone (male) Endorphin Dopamine Serotonin
Feedback loop
Actions
Causes LH and FSH release from the Hypophysis
Clinical Relevance
Induces cyclicity, induces ovulation, treats follicular cysts.
Oxytocin: Hypothal.
Smooth Muscle Contractions: estrus, parturition, lactation, ejaculation Behavioral: social, maternal, bonding behavior. GnRH stimulates synthesis and release from pituitary. Females: Follicular phase: estrogen stimulates LH secretion. Males: testosterone Females: Luteal phase: estrogen and progesterone inhibit LH secretion. Males: testosterone inhibits LH secretion Females: Follicular phase: estrogen stimulates LH secretion. Luteal phase: estrogen and progesterone inhibit LH secretion. Inhibin from the gonads inhibits ability of GnRH to promote FSH Ovarian Follicles: progesterone production, follicle maturation and ovulation. Theca Interna: stimulates theca cells to produces androgens by converting cholesterol to pregnenolone. Becomes small luteal cells (secrete progest.) Testis (Leydig cells): stimulates testosterone production. Ovarian Follicles: stimulates estrogen production and follicle growth Granulosa Cells: convert
Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Adenohypophy sis (AP)
Cant give orally Induces milk ejection Induces myometrial contractions: parturition, promote uterine clearance during estrus. Aid semen collection Induce ovulation Treat Follucular cysts hCG: has LH-like activity. Very expensive.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
GnRH stimulates release from pituitary
Inhibin
eCG: placental hormone used to promote FSH activity for superovulation.
Adenohypophy sis (AP)
Estrogen
Actions Behavioral estrus Changes in tubular genitalia Growth of uterus and mammary glands Stimulates uterine activity during parturition Aid in follicular growth and maturation
secretion. androgens to steroids. Stimulates foll. Estrogen in Becomes large luteal cells growth female can (secrete progest.) Superovulation stimulate or Testis (sertoli cells): depress FSH stimulates androgen binding secretion via protein hypothalamus. Clinical Relevance Estrus Synchronization: One dose stimulates LH and ovulation/luteinization of follicles. Prolonged stimulation: results in negative feedback to GnRH/FSH and no formation of large follicles. Check for Neutering: neutered animals will lack gonadal steroids which lead to elevated LH. Can assay LH to see if spayed or not Spayed = high LH Intact = low LH
Progesteron e
You might also like
- Physiology Magdy Sabry Autonomic, Nerve, MuscleDocument104 pagesPhysiology Magdy Sabry Autonomic, Nerve, Musclegmneur100% (4)
- Animal Life Cycles Unit TestDocument3 pagesAnimal Life Cycles Unit Testapi-273897319No ratings yet
- PDocument5 pagesPmedstudNo ratings yet
- The Effect of A Cat's Purr On HealthDocument7 pagesThe Effect of A Cat's Purr On HealthBryan GraczykNo ratings yet
- SIP 2018 FinalDocument32 pagesSIP 2018 Finaljohn clifordNo ratings yet
- Outline For The Quarterly Assessment in Science BiologyDocument8 pagesOutline For The Quarterly Assessment in Science BiologyeiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Hormones: Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GNRH)Document9 pagesReproductive Hormones: Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GNRH)Pooja RnairNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarDocument28 pagesOxytocin, ADH Lecture For 2nd Year MBBS by DR Waeem KausarIMDCBiochemNo ratings yet
- HPG Axis:: A) in FemalesDocument5 pagesHPG Axis:: A) in FemalesHanan Al-HarthiNo ratings yet
- Female HormonesDocument28 pagesFemale HormonesmujahidalmakiNo ratings yet
- Luteinizing HormoneDocument8 pagesLuteinizing HormoneSaba MalikNo ratings yet
- Female HormonesDocument28 pagesFemale Hormonesİlbey Kayra Özçelik100% (1)
- Reproductive HormonesDocument43 pagesReproductive HormonesMunchkin Celina100% (1)
- Hypothalamic Pitutary Gonadal Axis For Female - 111210Document5 pagesHypothalamic Pitutary Gonadal Axis For Female - 111210Okpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Reproductive Pharmacology-By:Dr. DHIREN BHOIDocument77 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Pharmacology-By:Dr. DHIREN BHOIdrdhirenvet100% (9)
- What Is A Hormone?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Hormone?IJSmartNo ratings yet
- Female HormoneDocument43 pagesFemale Hormoneامجد حسين جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CycleDocument78 pagesOvarian CyclefasicaregroupNo ratings yet
- K - 5 & K - 6 Reproduction Hormone (Fisiologi)Document58 pagesK - 5 & K - 6 Reproduction Hormone (Fisiologi)Komalah ChenasammyNo ratings yet
- The Normal Menstrual CycleDocument12 pagesThe Normal Menstrual CycleDheyaa A. SabahNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Hormones and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesReproductive Hormones and Their FunctionsOwolabi PetersNo ratings yet
- Javern M. Supnet RNDocument16 pagesJavern M. Supnet RNGenghis SupnetNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument16 pagesEndocrine GlandsAgatha BayauaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian and Menstrual CyclesDocument7 pagesOvarian and Menstrual CyclesMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Hormones: Biochemistry Department Dr. Mutiara Indah Sari, MkesDocument37 pagesFemale Reproductive Hormones: Biochemistry Department Dr. Mutiara Indah Sari, MkesHabib Al KahfiNo ratings yet
- RS-1 K5-K6 Hormon Repro Pria Dan Wanita, EditDocument57 pagesRS-1 K5-K6 Hormon Repro Pria Dan Wanita, EditfelixNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Biochemistry by ShahidDocument5 pagesReproductive System Biochemistry by ShahidSHAHIDNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineoeDocument62 pagesHY EndocrineoebrownsmilansNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineDocument61 pagesHY EndocrineKiranNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Physiology, Amenorrhea: Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesMenstrual Physiology, Amenorrhea: Page 1 of 5seth10No ratings yet
- Male Feedback MechanismDocument2 pagesMale Feedback Mechanismnelsonalec049No ratings yet
- L3-4. PubertyDocument28 pagesL3-4. Pubertypyinsta7it2No ratings yet
- Andree Oswald CandelarioDocument18 pagesAndree Oswald CandelarioAndree CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Physiology of MenstruationDocument66 pagesGyne - Physiology of MenstruationonijinoNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument33 pagesAnterior Pituitary Glandmarianne.erdooNo ratings yet
- Hormone of Reproductive System (Synthesis and Mechanism of Action)Document38 pagesHormone of Reproductive System (Synthesis and Mechanism of Action)pwfNo ratings yet
- Hormone-A Chemical Substance Produced in The Body That Controls and RegulatesDocument2 pagesHormone-A Chemical Substance Produced in The Body That Controls and RegulatesJohn Cyrus DizonNo ratings yet
- 1,4) HPG and Physiology of AndrogensDocument46 pages1,4) HPG and Physiology of AndrogensBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- MCN Menstrual Cycle LatestDocument8 pagesMCN Menstrual Cycle LatestsophienNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument7 pagesEndocrinologyVijith.V.kumarNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Steroid HormonesDocument4 pagesGonadal Steroid Hormonesrachellouis973No ratings yet
- Abhishek BioDocument10 pagesAbhishek Bioakarshsingh111111No ratings yet
- Diseases of The Pituitary GlandDocument10 pagesDiseases of The Pituitary Glandbalkrishna.narshaiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- PituartaryDocument3 pagesPituartarynancy dasNo ratings yet
- Problem No.1Document34 pagesProblem No.1ayesha bgNo ratings yet
- Hormon ReproDocument36 pagesHormon Reproalvinrinaldi1101No ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland PDFDocument5 pagesPituitary Gland PDFLiv Leyson100% (1)
- Cpy 513 Group 4 PresntationDocument7 pagesCpy 513 Group 4 PresntationOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DDocument17 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DMekuriya BeregaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus & PituitaryDocument61 pagesHypothalamus & PituitaryShreya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDocument57 pagesAnesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDoc SabNo ratings yet
- Periconceptional Period PDFDocument57 pagesPericonceptional Period PDFJamesNo ratings yet
- Opening PrayerDocument37 pagesOpening PrayerHeaven KhyNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis: by Abhinav BhardwajDocument10 pagesHormonal Control of Spermatogenesis: by Abhinav Bhardwajarthurggg429No ratings yet
- Jardine Jade Albert C. Valdez, RMTDocument48 pagesJardine Jade Albert C. Valdez, RMTEj BersalonaNo ratings yet
- (K5-K6) Hormon Repro Pria Dan Wanita, EditDocument53 pages(K5-K6) Hormon Repro Pria Dan Wanita, EditJane Andrea Christiano DjianzonieNo ratings yet
- Gonadotropins: Luteinizing and Follicle Stimulating HormonesDocument4 pagesGonadotropins: Luteinizing and Follicle Stimulating HormoneschintyaNo ratings yet
- LH Concept MapDocument1 pageLH Concept Mapsarahm1171No ratings yet
- SCIENCE Feedback Mechanism in Menstrual CycleDocument6 pagesSCIENCE Feedback Mechanism in Menstrual CycleJasmineNo ratings yet
- Male Sex Hormones FunctionsDocument18 pagesMale Sex Hormones FunctionsPermanand BheemsinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.2 Roles of Hormones in The Reproductive SystemDocument15 pagesLesson 3.2 Roles of Hormones in The Reproductive Systemzaile feline100% (1)
- Basset and Howley 2000Document15 pagesBasset and Howley 2000Susan KNo ratings yet
- Insect RepellentDocument7 pagesInsect RepellentJothi Vel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Nur Robbiyah, Hakimi, Melda Deliana, Siska Mayasari Lubis, Karina Sugih ArtoDocument8 pagesNur Robbiyah, Hakimi, Melda Deliana, Siska Mayasari Lubis, Karina Sugih ArtoTia Amalia Puti RenaeryNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Vibrio Cholerae Effects On Personal Health: Jessica Marie LedesmaDocument17 pagesRunning Head: Vibrio Cholerae Effects On Personal Health: Jessica Marie LedesmaAngel PicoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Brain Plasticity After Stroke FINAL PDFDocument32 pages2 - Brain Plasticity After Stroke FINAL PDFDwi AriyaniNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle & The Transmission Dynamic Versi 1Document14 pagesThe Life Cycle & The Transmission Dynamic Versi 1rayNo ratings yet
- Dystocia Due To Fetal Mummification in A Non Descript Goat A Case StudyDocument4 pagesDystocia Due To Fetal Mummification in A Non Descript Goat A Case StudyAnanta AlfinNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Management of Complications in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease (MND)Document10 pagesPhysiotherapy Management of Complications in Patients With Motor Neuron Disease (MND)YangNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument3 pagesConsiderationAsvogelNo ratings yet
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDocument8 pagesHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of PeriodontiaDocument57 pagesSeminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of Periodontiashreya dasNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Protein Biskuit PrintDocument6 pagesJurnal Protein Biskuit PrintMaz RukhinNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument23 pagesNephrotic SyndromeamlymarsNo ratings yet
- It Is Often Said That Government Spend Too Much Money On Projects To Protect WildlifeDocument1 pageIt Is Often Said That Government Spend Too Much Money On Projects To Protect WildlifeKaungPyae SoneNo ratings yet
- PalpationDocument44 pagesPalpationjenyNo ratings yet
- Components of FoodDocument37 pagesComponents of Foodrathee1966No ratings yet
- Lymphatic Filariasis / Elephantiasis: Wuchereria Bancrofti & Brugia MalayiDocument21 pagesLymphatic Filariasis / Elephantiasis: Wuchereria Bancrofti & Brugia Malayisujit555556677No ratings yet
- Arterial and Venous Supply of Face (2) (Autosaved)Document85 pagesArterial and Venous Supply of Face (2) (Autosaved)megha100% (1)
- D R Johnson Moore Anatomy For Dental Students 3rd Edition 141 180Document40 pagesD R Johnson Moore Anatomy For Dental Students 3rd Edition 141 180ZahraMadaen El mehadbeNo ratings yet
- Monsters in TempestDocument3 pagesMonsters in TempestInesAmoura26No ratings yet
- Active Management of The Third Stage of LabourDocument25 pagesActive Management of The Third Stage of LabourRedroses flowers0% (1)
- Chimpanzees Power PointDocument35 pagesChimpanzees Power Pointjhenriq4No ratings yet
- Gyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & VaginaDocument2 pagesGyne - Case 15 Benign Lesions of The Vulva & Vaginacbac1990No ratings yet
- UrinsryDocument10 pagesUrinsryAzizan HakimNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsAbdiwahab IssackNo ratings yet
- List of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesDocument44 pagesList of English Roots Suffixes and PrefixesJithin VijayanNo ratings yet