Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cma Part 1 Section B
Cma Part 1 Section B
Uploaded by
Đồng Thị NgaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cma Part 1 Section B
Cma Part 1 Section B
Uploaded by
Đồng Thị NgaCopyright:
Available Formats
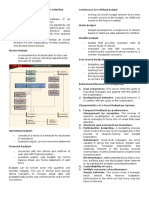
CONTROLLING PROCESS
Major steps in control loop are
POSIVE FEEDBACK FEEDBACK DOUBLE LOOP Establish the budget, or standards of performance
=> NO CORRECTIVE => control based on actual results => result gaps from assumption Measure the actual performance
ACTION => change the plan Analyse and compare actual results with budget
FEEDFORWARD results
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK => control based on forecast results => SINGGLE LOOP Investigate unexpected variances
=> THREE ALTERNATIVE forecast is bad=> take action Result gaps from action => no Devise and implement any necessary corrective
ACTIONS change the plan actions
Review and revise the budget/standards if necessary
PERFORMANCE
PLANNING BUDGETING EVALUATION (1D)
OBJECTIVE – GOALS (ranking/prioritized/ QUANTIFY THE PLAN Actual ~ budget
SMART/ communicated/ harmonized) 1) Master budget: Do nothing/ corrective action/ change budget (plan)
STRATEGIES - BS/P&L/Cashflow
SCHEDULE – TASKS - @ 1 activity level BUDGET MANUAL
Both qualitative and quantitative objective - Financial & non-financial info Budget and control process
2) Budget methodology RESPONSIBILITY CENTER
Budget advantages/ disadv
(adv ~ disavd/ how to prepare/
STRATEGIC PLAN – OPEARTIONAL PLAN Topdown and bottom up Cost center (cost per unit/
how to apply)
CORPORATE PLAN – OPEARTATION PLAN (adv and disadv/ when (what controllable cost only)
- Fixed ~ flexed budget
SINGLE POURPOSE PLAN - Incremental ~ zero buget kind of company) is used Revenue center
STANDING PURPOSE PLAN - Continuous/ rolling budget appropriately) Profit center (rev and cost)
CONTIGENCY PLAN - Project budget Time frame (monthly, Investment center
SHORT TERM PLAN (OPERATIONAL) – LONG TERM - ABB quarterly, half year, full year) (investment amount/ profit
PLAN (STRATEGIC) return => ROI)
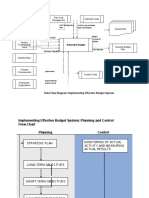
Create master budget
and subbudgets.
Obtain feedback and Get manager buy-in.
revise plan.
Analyze current performance
Take corrective action.
versus expectations.
Examine
variations.
[Type here] [Type here] CHTN My Lien_CMA 1B
STRATEGIC PLANNING
(Corporate strategy – business strategy – departmental strategy)
Set objectives => allocate resource => assign tasks/ schedules
Environmental
obje
Master strategies Tactical Plans
Analysis
• Evaluation of major • Development of long • Development of
interests range plan short range plans
• External • Vison • Operational plans
environments, • Mission • Budgets
opportunities, • Strategies
threats
• Goals
• Internal
• Objectives
environments
strengths and
weakness
Adjust
Monitor Implementation
performance
ANALYSE TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
STAKEHOLDER ANALYSIS
SWOT ANALYSIS SITUATION ANALYSIS
PEST ANALYST (Macro) SWOT analysis, Porter 5 forces, 5 C (company –
PORTER FIVE FORCES (Micro) competitor – customer – collaborators – climate),
COMPLEXITY OF THE BUSINESS PEST analysis
ENVIROMENT SENARIO ANALYSIS (STEEPA)
CHANGES IN BUSINESS BCG – competive analysis (market growth/ market
ENVIRONMENT share)
(Globalization/ Outsourcing BALANCE SCORE CARD
trend) (customer satisfaction/ process efficiency/ growth/
TECHNOLOGY CHANGES financial success)
[Type here] [Type here] CHTN My Lien_CMA 1B
FORECAST TECHNIQUES
TIMES SERIES ANALYSIS LEARNING CURVE
FORECAST TECHNIQUE WITH RISK
Adv: quick, easy (applied for company using more labor cost)
Dis adv: rely on past data, past trend might not (Risk for a security can be measured
Advantage by variability of its historical returns
repeat
Can be used to make a number of decisions or the dispersion of its historical
Make or buy decision returns round their average, or mean,
A. One variable Life cycle costing return. => assigned probability)
a. Trend analysis: trend/ cyclical/ seasonal/ CVP analysis
Development of standard cost Disadv: can not apply for adhoc
irregular
Capital budgeting situation
b. Smoothing data
Development of production plan and labour Method can be used
i. Moving average/ weighted moving
requirement - Expected value
average
Management control - Sensitivity analysis
ii. Exponential smoothing (actual and
forecast): Ft + 1 = aYt + (1 – a)Ft Learning affects quality and improves productivity.
B. >= 2 variables: Y = A + B1X1 + B2X2… Disavd: learning rate is difficult to determined
a. High-low method Learning point:
b. Statistic method th
Incremental method => time to produce the n product - Probability/ Join probability/
i. Test correlation: R2 Cumulative method => average time to produce n product condition probability
ii. Calculate A, B (formula) o Learning rate - Variance/ standard deviation/
iii. Develop model Y = A + BX o Double batch/ unit in batch coefficient of variance
Learning point o Question to be focused
Average Time to produce one unit in 4 batches
B = slope Average time to produce one unit in batch forth
Average time to produce batch forth
A = intercept
R2 : the variation in dependent variables can be Y = a x learning rate
explained by changes in independent variables (a = time to produce first unit / 1st batch)
[Type here] [Type here] CHTN My Lien_CMA 1B
TOP LEVEL PLANNING AND ANALYST
Financial ratio to be analysed Source of fund to be considered
- Profitability - Internal source of fund (Spontaneous liabilities)
- Efficiency including: trade payables/ accruals/ retained
- Liquidity earnings
- Capital structure - External source of fund: loan, new capital
Factors affect the company’s need for
external source of fund
(1) Retention ratio
(2) RAPID sales growth
(3) The company’s profit margin
[Type here] [Type here] CHTN My Lien_CMA 1B
You might also like
- Colorscope ExcelDocument11 pagesColorscope ExcelPriyabrat Mishra100% (1)
- Sop For Warehouse Inventory Management 140119Document9 pagesSop For Warehouse Inventory Management 140119baabdullah100% (3)
- Chapter 8pwr PointDocument53 pagesChapter 8pwr PointĐồng Thị Nga50% (2)
- Acquisition & Interest Date Interest Earned (5%) Interest Income (4%) Premium Amortization Book ValueDocument3 pagesAcquisition & Interest Date Interest Earned (5%) Interest Income (4%) Premium Amortization Book ValueGray JavierNo ratings yet
- BUDGETINGDocument2 pagesBUDGETINGAnna Pamela MarianoNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting MasDocument6 pagesCapital Budgeting MasHainiel ReforzadoNo ratings yet
- Business PlanningDocument2 pagesBusiness Planningmohajansanjoy1975No ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument22 pagesBudgetingAashikkhan50% (2)
- UNDP-Budgeting in Public Sector - OverviewDocument31 pagesUNDP-Budgeting in Public Sector - OverviewPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Functional and Activity Based BudgetingDocument5 pagesFunctional and Activity Based BudgetingBrithney ButalidNo ratings yet
- Effective BudgetingDocument5 pagesEffective Budgetinglyceljoy.sibayanNo ratings yet
- ACT4105 - Class 05 06 07 (Printing)Document24 pagesACT4105 - Class 05 06 07 (Printing)Wong Siu CheongNo ratings yet
- Zero Base BudgetingDocument15 pagesZero Base BudgetingSumitasNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and ControlingDocument22 pagesProject Monitoring and Controlingbassem djediNo ratings yet
- Accounting Chapter 8-Master Budgeting Flashcards - QuizletDocument7 pagesAccounting Chapter 8-Master Budgeting Flashcards - QuizletBisag AsaNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument7 pagesFinancial Planningp.dashaelaineNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlDocument1 page4.1 Budgeting For Planning and ControlLea GerodiazNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management: Short-Term BudgetingDocument12 pagesStrategic Cost Management: Short-Term BudgetingAdrian RoxasNo ratings yet
- Budgeting and Budgetary Control: BudgetDocument20 pagesBudgeting and Budgetary Control: BudgetabhishelNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - Budgeting - Part IIDocument26 pagesWEEK 3 - Budgeting - Part IIvengadeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document17 pagesChapter 8Tran Huong GiangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Monitoring, Evaluation & ControlDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Monitoring, Evaluation & ControlDurish ZakirNo ratings yet
- 08 - Project ControlDocument73 pages08 - Project ControlJJ Welding100% (2)
- Short-Term Planning or Profit Planning - 5 of Financial and Other Resources of The Company InaDocument3 pagesShort-Term Planning or Profit Planning - 5 of Financial and Other Resources of The Company InaAngela GarciaNo ratings yet
- ACCT 102 Management Accounting Master Budget and Responsibility AccountingDocument67 pagesACCT 102 Management Accounting Master Budget and Responsibility Accountingnishikant13No ratings yet
- Project Monitoring and Control 5.2Document30 pagesProject Monitoring and Control 5.2Dangi DilleeRamNo ratings yet
- CORP SC F-0017 Objective KPI Rev.2 2022 (Plant 052C)Document2 pagesCORP SC F-0017 Objective KPI Rev.2 2022 (Plant 052C)Septian Wahyu WidodoNo ratings yet
- Budgeting: Basics and Beyond: Continuing Professional Development ModuleDocument46 pagesBudgeting: Basics and Beyond: Continuing Professional Development ModuleNarissa Mae QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Business Budgeting - Chapter 1Document7 pagesBusiness Budgeting - Chapter 1Udit GuptaNo ratings yet
- FP&A Cheat Sheetv2Document1 pageFP&A Cheat Sheetv2mheryantooNo ratings yet
- F2-15 Flexible Budgets, Budgetary Control and ReportingDocument16 pagesF2-15 Flexible Budgets, Budgetary Control and ReportingJaved ImranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Budgeting: ACCT10001 Accounting Reports and AnalysisDocument38 pagesLecture 9: Budgeting: ACCT10001 Accounting Reports and AnalysisBáchHợpNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 14 Fdocuments - in Project Control Earned Value Management VVIPDocument39 pagesKuliah 14 Fdocuments - in Project Control Earned Value Management VVIPMalik ConsultantNo ratings yet
- P3 BudgetingDocument32 pagesP3 BudgetingJACKSONNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost MGT and Cost ConceptsDocument99 pagesStrategic Cost MGT and Cost ConceptsKendall JennerNo ratings yet
- Budgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqDocument7 pagesBudgeting: By: M. Luqman RafiqsulukaNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring & ControlDocument38 pagesProject Monitoring & ControlSatya KumarNo ratings yet
- Budgeting and The Master BudgetDocument38 pagesBudgeting and The Master BudgetpriyankaNo ratings yet
- Project Control Using EVMDocument40 pagesProject Control Using EVMAbdul NaseerNo ratings yet
- Prof Sunny Sabharwal JgbsDocument28 pagesProf Sunny Sabharwal JgbsVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Joint Impact PlanDocument5 pagesThe Joint Impact PlanhubspotnewsletterNo ratings yet
- Plan Cost Management Estimate Costs Create Work Breakdown StructureDocument3 pagesPlan Cost Management Estimate Costs Create Work Breakdown StructureAnifahchannie PacalnaNo ratings yet
- AF6010 Lecture 10 Budgeting (1) 2Document31 pagesAF6010 Lecture 10 Budgeting (1) 2ehsanNo ratings yet
- The Value of Earned Value Management: PMI Pittsburgh Chapter MeetingDocument26 pagesThe Value of Earned Value Management: PMI Pittsburgh Chapter MeetingAndryaas MamuayaNo ratings yet
- Flexible BudgetDocument3 pagesFlexible BudgetSunita BasakNo ratings yet
- Budget: Prepared By: Joseph R. Mendoza CPA, MBADocument5 pagesBudget: Prepared By: Joseph R. Mendoza CPA, MBApot poootNo ratings yet
- Planning Scheduling Monitoring and Contr-6Document50 pagesPlanning Scheduling Monitoring and Contr-6Daniel CcamaNo ratings yet
- MP124 - Create WBS Budget Plan PDFDocument3 pagesMP124 - Create WBS Budget Plan PDFMadhie JokleNo ratings yet
- Presentation SPM Chapter 3 Approaches To BudgetsDocument34 pagesPresentation SPM Chapter 3 Approaches To Budgetsmdamm090701No ratings yet
- Sales and Operations Planning RapidResponseDocument4 pagesSales and Operations Planning RapidResponseking arjunNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument11 pagesBudgetingCarey DengNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument5 pagesBudgetingishhNo ratings yet
- C - Comprehensive BudgetingDocument8 pagesC - Comprehensive Budgetingian dizonNo ratings yet
- 7 Governance 2016Document10 pages7 Governance 2016aboagyewaahoNo ratings yet
- Project Management Brain Storming Training & PRPDocument58 pagesProject Management Brain Storming Training & PRPAbudi Kasahun100% (1)
- 08 Project ControlDocument73 pages08 Project ControlJJ Welding100% (1)
- 5 BudgetingDocument9 pages5 BudgetingXyril MañagoNo ratings yet
- SAP Result Analysis - Concept: Madhusudhan T CDocument13 pagesSAP Result Analysis - Concept: Madhusudhan T CSUNIL palNo ratings yet
- 5 Approaches To Effective Budgeting Forecasting hc.0046.04.23Document16 pages5 Approaches To Effective Budgeting Forecasting hc.0046.04.23official.waqaslatifNo ratings yet
- ACCA PM BudgetingDocument14 pagesACCA PM BudgetingAysha ZulfiquarNo ratings yet
- Utility PlanningDocument35 pagesUtility PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 11 EVA Formula SheetDocument3 pages11 EVA Formula SheetDileep Kumar MotukuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Production Planning & Control (PPC)Document23 pagesChapter-1: Production Planning & Control (PPC)vitrahulNo ratings yet
- Stock Split and Stock DividendDocument33 pagesStock Split and Stock DividendĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument125 pagesBudgetingĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About The CMA Exam With My Secrets To PassDocument79 pagesAll You Need To Know About The CMA Exam With My Secrets To PassĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Cma Part 1 Section eDocument7 pagesCma Part 1 Section eĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Learning outcome-CMA PART 1Document9 pagesLearning outcome-CMA PART 1Đồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- V ApassingDocument8 pagesV ApassingĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Lit 2-Final 2014 - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesLit 2-Final 2014 - Answer KeyĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Final QuestionsDocument9 pagesFinal QuestionsĐồng Thị Nga100% (1)
- Romanticism - Fri 123Document18 pagesRomanticism - Fri 123Đồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Class: Technology in Teaching EnglishDocument14 pagesWelcome To Our Class: Technology in Teaching EnglishĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Learning Through Inquiry PDFDocument9 pagesLearning Through Inquiry PDFĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Unit 24 Selection and Use of Supplementary Materials and Activities I/ Follow-Up ActivitiesDocument4 pagesUnit 24 Selection and Use of Supplementary Materials and Activities I/ Follow-Up ActivitiesĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Semantic ExercisesDocument5 pagesSemantic ExercisesĐồng Thị NgaNo ratings yet
- Project On Corporate Governance of ITCDocument20 pagesProject On Corporate Governance of ITCViren SinghNo ratings yet
- Classified Advertising: Gulf TimesDocument2 pagesClassified Advertising: Gulf Timesmohamed maharNo ratings yet
- COLLOQUY Talk Talk White PaperDocument15 pagesCOLLOQUY Talk Talk White PaperChiquita FelinaNo ratings yet
- Law of ContractDocument48 pagesLaw of Contractayla josephNo ratings yet
- Resume ASDocument1 pageResume ASSahaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Scope of Financial Engineering and Financial Engineering Vs Financial AnalysisDocument17 pagesMeaning and Scope of Financial Engineering and Financial Engineering Vs Financial AnalysisVikas Sahota67% (3)
- Strategic Management: SNR Degree College, JiganiDocument50 pagesStrategic Management: SNR Degree College, Jiganibu butccmNo ratings yet
- Chinmay STRDocument82 pagesChinmay STRanu jainNo ratings yet
- Home Opportunities Supplier Directory Gebiz Mall My Stuff: Tender DocumentsDocument3 pagesHome Opportunities Supplier Directory Gebiz Mall My Stuff: Tender DocumentsBatu GajahNo ratings yet
- Baye 9e Chapter 01 PDFDocument58 pagesBaye 9e Chapter 01 PDFKim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- Folleto de Las Características Del Programa de FormaciónDocument2 pagesFolleto de Las Características Del Programa de FormaciónacilegnaNo ratings yet
- Asia Amalgamated Holdings Corporation Financials - RobotDoughDocument6 pagesAsia Amalgamated Holdings Corporation Financials - RobotDoughKeith LameraNo ratings yet
- ERP Fit Gap AnalysisDocument20 pagesERP Fit Gap Analysiskarimmebs100% (1)
- Mechanical Integrity PetronasDocument61 pagesMechanical Integrity Petronasdefian100% (6)
- Zomato: IPO NoteDocument15 pagesZomato: IPO NoteManideep KumarNo ratings yet
- Erd 00 23Document39 pagesErd 00 23kattabommanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Registered Insurance Intermediaries As at 7th July 2020-MergedDocument192 pages2020 Registered Insurance Intermediaries As at 7th July 2020-MergedJohn GogoNo ratings yet
- ICICI Pru Smart Kid Premier BrochureDocument14 pagesICICI Pru Smart Kid Premier Brochuredencybk123No ratings yet
- 74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Document20 pages74609bos60479 FND cp2 U4Filip JainNo ratings yet
- Four Derivative DisastersDocument11 pagesFour Derivative DisastersAkhilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Feasib g7 (Final-Unupdated)Document124 pagesFeasib g7 (Final-Unupdated)Donny CherriguineNo ratings yet
- Binary Options e BookDocument74 pagesBinary Options e BookDaniel Santos100% (1)
- Abeyot AberaDocument89 pagesAbeyot AberaOmar ReyanNo ratings yet
- Wack Wack Golf and Country Club Vs NLRCDocument1 pageWack Wack Golf and Country Club Vs NLRCJaps De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Task-1 LO-1: Company BackgroundDocument20 pagesTask-1 LO-1: Company BackgroundDuaa AsjadNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard NpoDocument33 pagesAccounting Standard NpoArifAslamNo ratings yet
- The Strategy Formulation Analytical FrameworkDocument2 pagesThe Strategy Formulation Analytical Frameworkdailydoseoflaw100% (2)