Professional Documents
Culture Documents
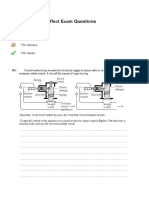
B4 Worksheet3
B4 Worksheet3
Uploaded by
Shalini KulshresthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B4 Worksheet3
B4 Worksheet3
Uploaded by
Shalini KulshresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
– 12 – M19/4/PHYSI/SP3/ENG/TZ1/XX
(Option B continued)
7. (a) Show that during an adiabatic expansion of an ideal monatomic gas the temperature T
and volume V are given by [2]
2
TV 3 constant
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
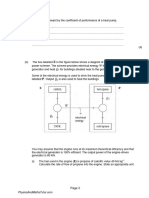
(b) The diagram shows a Carnot cycle for an ideal monatomic gas.
P
A
The highest temperature in the cycle is 620 K and the lowest is 340 K.
(i)
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
(Option B continues on the following page)
– 13 – M19/4/PHYSI/SP3/ENG/TZ1/XX
(Option B, question 7 continued)
(ii) B is 540 J. Calculate the
thermal energy that leaves the gas during one cycle. [2]
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
VC
(iii) Calculate the ratio where VC is the volume of the gas at C and VB is the
VB
volume at B. [2]
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
(c) (i) Calculate the change in the entropy of the gas during the change A to B. [1]
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
(ii) Explain, by reference to the second law of thermodynamics, why a real engine
operating between the temperatures of 620 K and 340 K cannot have an
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
..........................................................................
End of Option B
Turn over
You might also like
- Ib Physics HL Review Packet - ThermodynamicsDocument19 pagesIb Physics HL Review Packet - ThermodynamicsGhenwa DimachkiNo ratings yet
- Solar radiation-WSDocument2 pagesSolar radiation-WSPrisha GargNo ratings yet
- Chem Ib PaperDocument18 pagesChem Ib Paperembededodin0% (1)
- Thermodynamics WsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Wsnturnaoglu25No ratings yet
- 2021 Sda F5 June Test 1Document11 pages2021 Sda F5 June Test 1blueegofxNo ratings yet
- P3 11 TransformersDocument65 pagesP3 11 Transformersisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics coreDocument8 pagesThermal Physics corerohit.makwanaNo ratings yet
- P3 10 Motor EffectDocument58 pagesP3 10 Motor EffectHiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- IB-1 Thermal Properties & Calorimetry PracticeDocument3 pagesIB-1 Thermal Properties & Calorimetry PracticeGajendraNo ratings yet
- Black Body Radiation 3 QPDocument11 pagesBlack Body Radiation 3 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFDocument7 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFMuhammad ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Domestic Uses - Safety 2 QPDocument13 pagesDomestic Uses - Safety 2 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pages3.1 Thermal Physicsmardel11No ratings yet
- 4 Ideal Gas0001Document18 pages4 Ideal Gas0001Pooja MehraNo ratings yet
- Topic 3. Thermal Heating Long QDocument11 pagesTopic 3. Thermal Heating Long Qjh seoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Test - Paper 2Document2 pagesTopic 3 Test - Paper 2IB BaddiesNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPDocument9 pagesThermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPJinYoongLimNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPDocument9 pagesThermal Properties & Temperature 2 QPgopalNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios BIDocument596 pagesEjercicios BIESTEBAN JUNINHO CAICEDO PIEDRANo ratings yet
- 22.2-Thermal Properties and Temperature-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument10 pages22.2-Thermal Properties and Temperature-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDaniel goodchildNo ratings yet
- Black Body Radiation 2 QPDocument16 pagesBlack Body Radiation 2 QPNaeemNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties - 9-18Document25 pagesThermal Properties - 9-18Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties - 9-18Document25 pagesThermal Properties - 9-18Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TestDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- Black Body Radiation 2 QPDocument16 pagesBlack Body Radiation 2 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- P1 - Heat TransferDocument16 pagesP1 - Heat Transferreda100% (1)
- Set 62 - Chapter 2Document12 pagesSet 62 - Chapter 2lelon81No ratings yet
- Energy and Thermal Extra Questions PDFDocument29 pagesEnergy and Thermal Extra Questions PDFsib menoNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Revision Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/AdduDocument8 pagesCapacitors Revision Worksheet: Addu High School Hithadhoo/AdduDhan Bahadhur Mr.Dhan Bahadur BoharaNo ratings yet
- Thermal ExtDocument9 pagesThermal Extrohit.makwanaNo ratings yet
- Induced Potential, Transformers _ National Grid 2 QPDocument16 pagesInduced Potential, Transformers _ National Grid 2 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions PDFDocument9 pagesRevision Questions PDFmwagweNo ratings yet
- P1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandDocument59 pagesP1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandjesudassajNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - TestDocument7 pagesUnit 4 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- 2 HoursDocument17 pages2 HoursOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document11 pagesPaper 4Myat Thura KyawNo ratings yet
- Test Chem 1,2Document7 pagesTest Chem 1,2Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- This Section Consists of Four Questions: B1, B2, B3 and B4. Answer Two QuestionsDocument2 pagesThis Section Consists of Four Questions: B1, B2, B3 and B4. Answer Two QuestionsJorge ChavezNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics ExtendedDocument9 pagesThermal Physics Extendedrohit.makwanaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power-AQADocument16 pagesWork, Energy & Power-AQAmzzha3No ratings yet
- BondingDocument14 pagesBondingMuizzudin AzaliNo ratings yet
- ST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFDocument10 pagesST 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Introductory Electronics) PDFSaleem ShahidNo ratings yet
- SL Topic 1 - 2009 - 2015Document82 pagesSL Topic 1 - 2009 - 2015principal.jakkurNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy 1 QPDocument20 pagesInternal Energy 1 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument20 pagesEnergetics Questionslianchen251110No ratings yet
- P2 Revision Booklet Static Electricity: Medium (Grade C)Document10 pagesP2 Revision Booklet Static Electricity: Medium (Grade C)Prarthana VinothNo ratings yet
- National & Global Energy Resources 2 QPDocument15 pagesNational & Global Energy Resources 2 QPEman RizwanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements & Eqns 2 QP-1Document18 pages3.1 Cons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements & Eqns 2 QP-1youssefelk.egNo ratings yet
- 3 8 1 7-Induced-FissionDocument49 pages3 8 1 7-Induced-FissionSack YomamNo ratings yet
- Reversed Heat Engines QPDocument4 pagesReversed Heat Engines QPYousef ElwakilNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference - Resistance 3 QPDocument13 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference - Resistance 3 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Igcse Electrochemistry Review PDFDocument7 pagesIgcse Electrochemistry Review PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- Water and HydrogenDocument7 pagesWater and HydrogenOkumu KevinsNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 33-05lelon ongNo ratings yet
- SL Topic 2 - 2016 - 2019Document30 pagesSL Topic 2 - 2016 - 2019principal.jakkurNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Internal Resistance PDFDocument16 pages2.4 Internal Resistance PDFschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument20 pagesEnergetics QuestionsKelum100% (1)
- Ib Physics Question Bank Toddle-Topic 3Document4 pagesIb Physics Question Bank Toddle-Topic 3Yousef HuseinNo ratings yet
- Phys p2Document16 pagesPhys p2Kalana GamageNo ratings yet
- Understanding Plastics Engineering Calculations: Hands-on Examples and Case StudiesFrom EverandUnderstanding Plastics Engineering Calculations: Hands-on Examples and Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Global Perspectives Summer TaskDocument3 pagesGlobal Perspectives Summer TaskShalini KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Document15 pagesGrade 9 Mass and Weight 2021-2022Shalini KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Free Fall and Ticker Tape TimerDocument26 pagesAcceleration Due To Free Fall and Ticker Tape TimerShalini KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Study of Simple Pendulum Using Tracker Video Analysis and High Speed Camera: An Interactive Approach To Analyze Oscillatory MotionDocument10 pagesStudy of Simple Pendulum Using Tracker Video Analysis and High Speed Camera: An Interactive Approach To Analyze Oscillatory MotionShalini KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Final - SR Iit N120 (2023-24) - Teaching Schedule With QP Allotment (Code - 06-07-2023)Document80 pagesFinal - SR Iit N120 (2023-24) - Teaching Schedule With QP Allotment (Code - 06-07-2023)baddaaasssNo ratings yet
- Pre-Project Report On "Improving The Properties of Earthen Plaster"Document43 pagesPre-Project Report On "Improving The Properties of Earthen Plaster"rafiq mirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Communication Systemswleum100% (1)
- (1991) Hornik (Neural Netw.)Document7 pages(1991) Hornik (Neural Netw.)MaxNo ratings yet
- Newton S Law of CoolingDocument9 pagesNewton S Law of CoolingJulian Mauricio Cuevas GalloNo ratings yet
- SLM 3 The Six Trigonometric Ratios 22 23Document12 pagesSLM 3 The Six Trigonometric Ratios 22 23Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- CREII-Module-5 - Lecture 22 & 23 PDFDocument16 pagesCREII-Module-5 - Lecture 22 & 23 PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- Bus Duct - Catalog - GERS ViejoDocument12 pagesBus Duct - Catalog - GERS Viejo123peniscolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (CE-860)Document29 pagesLecture 2 (CE-860)MUHAMMAD AHMAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- TRBC Manual - Fourth Edition - 090408 PDFDocument128 pagesTRBC Manual - Fourth Edition - 090408 PDFMatheus Baños100% (1)
- Sartorius Cata Integrated Lab Equipment S 0300 eDocument430 pagesSartorius Cata Integrated Lab Equipment S 0300 eedal_108No ratings yet
- Bubbledeck Voided Flat Slab Solutions: June 2008Document91 pagesBubbledeck Voided Flat Slab Solutions: June 2008Gan Chin PhangNo ratings yet
- NC590 - Construction Planning L2 QP Supp 2019Document8 pagesNC590 - Construction Planning L2 QP Supp 2019fanafisto04No ratings yet
- Ejercicios Ep3 ControlDocument3 pagesEjercicios Ep3 ControlLobo EsteparioNo ratings yet
- The Yamaha NS10 StoryDocument8 pagesThe Yamaha NS10 Storyjsf1200No ratings yet
- SQA-Vb PresentationDocument30 pagesSQA-Vb PresentationObaid UllahNo ratings yet
- The Short Life of Evariste Galois: by Tony RothmanDocument14 pagesThe Short Life of Evariste Galois: by Tony RothmanisraeloNo ratings yet
- MTS 234 Lecture Note MODULE 1Document4 pagesMTS 234 Lecture Note MODULE 1Oladimeji YusufNo ratings yet
- ROCKAL FOAM (28: 30) KG/M: FlammabilityDocument9 pagesROCKAL FOAM (28: 30) KG/M: Flammabilityjustice judgeNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 1 - SolDocument19 pagesEXERCISE 1 - SolmaeNo ratings yet
- Ucmp Unit-5Document77 pagesUcmp Unit-5Rashida BegumNo ratings yet
- HMT Senthil CompressDocument515 pagesHMT Senthil Compresssathiyapriyan2003No ratings yet
- NanotechnologyDocument14 pagesNanotechnologymohan vamsi100% (1)
- John Crane MaterialsDocument46 pagesJohn Crane MaterialsLuis YañezNo ratings yet
- MCA4020-Model Question PaperDocument18 pagesMCA4020-Model Question PaperAppTest PINo ratings yet
- Sheave Manual SMDocument8 pagesSheave Manual SMLutfi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Consultative Group On Sustainable Development Indicators (CGSDI) (R.O.C) PDFDocument1 pageConsultative Group On Sustainable Development Indicators (CGSDI) (R.O.C) PDFbrayanlomasNo ratings yet
- La-Borne CatalogueDocument10 pagesLa-Borne Catalogueronald.wongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Work and EnergyDocument18 pagesLesson 5 Work and EnergyanonymousNo ratings yet
- June 2015 QP - Unit 4 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2015 QP - Unit 4 Edexcel Physics A-LeveltyNo ratings yet