Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Muscles
Introduction To Muscles
Uploaded by
Maria Jesus Bustamante MussoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAnatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetAlaka71% (17)
- The Cubonomicon v1Document43 pagesThe Cubonomicon v1javandarNo ratings yet
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- Body Mechanics: Psoas Major FunctionDocument15 pagesBody Mechanics: Psoas Major FunctiontokionasNo ratings yet
- SAP 4.7 Installation TutorialDocument54 pagesSAP 4.7 Installation Tutorialrajeev.ashokan8023100% (34)
- 1 Musculoskeletal Mind MapDocument1 page1 Musculoskeletal Mind Mapvn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- Reading Assignment 4Document17 pagesReading Assignment 4John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- 1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument5 pages1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemLeo Mari Go LimNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- GCSE PE Paper 1 ContentDocument18 pagesGCSE PE Paper 1 Contentshiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Handout Part IIDocument4 pagesMuscular System Handout Part IIDeenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- MM ProjectDocument3 pagesMM ProjectdeuceNo ratings yet
- CHP 11Document71 pagesCHP 11Sophia YounNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument2 pagesMuscle Systemapi-428138727No ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument3 pagesLocomotion and MovementYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Upgrade Now InviteDocument1 pageSkeletal System: Upgrade Now Invitemaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Skeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionDocument26 pagesSkeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionmeriiNo ratings yet
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- Modeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Document9 pagesModeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Shyam PolacondaNo ratings yet
- TriChapter27 09 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesTriChapter27 09 Muscular Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- Muscoluskeletal SystemDocument1 pageMuscoluskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninNo ratings yet
- Muscoluskeletal SystemDocument1 pageMuscoluskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninNo ratings yet
- 04 Overvew of The Muscular SystemDocument11 pages04 Overvew of The Muscular SystemJanith sandupama RanathungaNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System Anaphy LabDocument12 pagesThe Muscular System Anaphy LabHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 9 Muscular System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document49 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 9 Muscular System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- 303 How Animal Move MuscleDocument14 pages303 How Animal Move MuscleAna RizkaNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsDocument20 pagesJoints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesMuscular System Anatomy and PhysiologyMichelle Tamor100% (1)
- Trumpeta, Kris - Mechanics of Muscle ContractionDocument48 pagesTrumpeta, Kris - Mechanics of Muscle ContractionJunior AbdulcaderNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No.8Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No.8yumi castroNo ratings yet
- '18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?Document7 pages'18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?thanks btNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatDocument14 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues and Its FunctionsDocument1 pageHuman Tissues and Its FunctionsJnnfr BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument12 pagesThe Muscular System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - JointsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - JointsMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartDocument1 pageCbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartAMit100% (2)
- JointsDocument27 pagesJointsJhan BencelNo ratings yet
- Somatic Anatomy Muscles and The Postural FluteDocument6 pagesSomatic Anatomy Muscles and The Postural FlutearonolamNo ratings yet
- MuscolinoDocument6 pagesMuscolinojustnewaroundNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument92 pagesHuman Anatomymohamed.sewaNo ratings yet
- Generalities MyologyDocument14 pagesGeneralities MyologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- #2 Muscular SystemDocument12 pages#2 Muscular SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Tendon TransfersDocument12 pagesBiomechanics of Tendon TransfersBasmah Al-DhafarNo ratings yet
- Musculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Document22 pagesMusculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Anonymous vwR8xcIxNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscles Structure Function Location: SmoothDocument2 pagesTypes of Muscles Structure Function Location: SmoothBabylyn SosaNo ratings yet
- A&P Presentation 20-11-23Document24 pagesA&P Presentation 20-11-23jordanmcmillan04No ratings yet
- Nelson VCE PEDocument23 pagesNelson VCE PEPNo ratings yet
- The JointsDocument7 pagesThe JointsrazondiegoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument35 pagesThe Muscular System: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeTrisha100% (3)
- Bio Cam Clips PresentationDocument5 pagesBio Cam Clips Presentationapi-552227798No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Control of MovementDocument6 pagesChapter 8 - Control of MovementManilyn DacoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument21 pagesMuscular System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Classification of BoneDocument1 pageClassification of Bonezain juttNo ratings yet
- Chap 2. Muscle. The Primary Stabilizer and Mover of The Skeletal SystemDocument48 pagesChap 2. Muscle. The Primary Stabilizer and Mover of The Skeletal SystemHana RVNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM - Power Point PresentationDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM - Power Point PresentationMalchrenNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: by Sisay ADocument34 pagesMuscular System: by Sisay Agobez temariNo ratings yet
- Nuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022Document20 pagesNuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022augustina gaiceanuNo ratings yet
- CMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Document93 pagesCMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Jeremiah PuaNo ratings yet
- Clearias Upsc Prelims Online Mock Test Series 2021 Timetable v1Document58 pagesClearias Upsc Prelims Online Mock Test Series 2021 Timetable v1Silpa KrishnaveniNo ratings yet
- Round Cassette Catalogue - A4Document4 pagesRound Cassette Catalogue - A4Pongalfest byaravNo ratings yet
- Surveying LessonDocument6 pagesSurveying LessonshalenNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Document33 pagesSimply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Anonymous ARMtmNKL100% (1)
- 1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationDocument11 pages1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationMohamed Elsir100% (1)
- Leviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologyDocument5 pagesLeviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologySajeda M. Al-TalafhaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)Document873 pagesEncyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)medNo ratings yet
- Physiological FeelingsDocument202 pagesPhysiological Feelingsoscarin123456789No ratings yet
- Personality Development2022 23Document6 pagesPersonality Development2022 23Veena VaishyNo ratings yet
- DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL Indirapuram, GhaziabadDocument2 pagesDELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL Indirapuram, GhaziabadMonster QueenNo ratings yet
- BlackRock Responsible Investment Engprinciples Global SummaryDocument5 pagesBlackRock Responsible Investment Engprinciples Global SummaryComunicarSe-ArchivoNo ratings yet
- New TAWS Features: Based On EGPWS ExperienceDocument23 pagesNew TAWS Features: Based On EGPWS ExperienceShimeonNo ratings yet
- Why Developmentally Appropriate Practice (Dap) Is Important in KindergartenDocument10 pagesWhy Developmentally Appropriate Practice (Dap) Is Important in KindergartenJoy MoranoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Harvard Style SampleDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Harvard Style Sampleiigheacnd100% (1)
- Homework 2 IENG584Document3 pagesHomework 2 IENG584Frida YoungNo ratings yet
- Bsi BS en 15073 - 2013Document20 pagesBsi BS en 15073 - 2013alferedNo ratings yet
- Name - Section - Date - How To Balance Chemical EquationsDocument2 pagesName - Section - Date - How To Balance Chemical EquationsXazerco LaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodAnonymous 8f2veZf100% (2)
- Introduction To NanotechnologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To NanotechnologyTushar PanditNo ratings yet
- From Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingDocument3 pagesFrom Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingEfra LlebaríaNo ratings yet
- Sameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Document321 pagesSameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Remon SamirNo ratings yet
- Jenitri 3Document7 pagesJenitri 3Zaenal MubaroqNo ratings yet
- Agri CollegesDocument4 pagesAgri Collegesjaimaruthi internetnamakkalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Techno - MauricioDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 - Techno - Mauricioairu mauricioNo ratings yet
- Constructing Basestations July27 RanjithDocument6 pagesConstructing Basestations July27 RanjithAkash MahalikNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
Introduction To Muscles
Introduction To Muscles
Uploaded by
Maria Jesus Bustamante MussoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Muscles
Introduction To Muscles
Uploaded by
Maria Jesus Bustamante MussoCopyright:
Available Formats
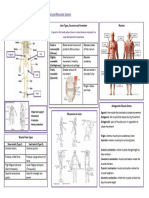
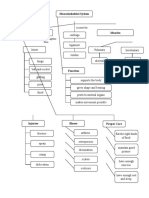
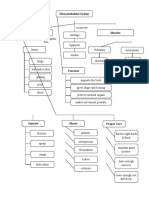
Types of muscle
Introduction contraction
to Muscles
Concentric
Sliding filament Generates movement
theory The insertion points are
approaching.
Eccentric
Generates movement
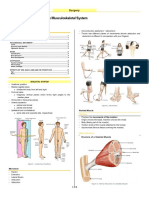
Most abundant tissue in the body. The insertion points
A pencil on a
move away.
More than 430 muscles in pairs on both sides muscle fiber
of the body..
Isometric
Functions of Static There is no movement
Maintains There is no change in
Muscles posture Muscle like a muscle length.
set of pencils
Strength and protection to the skeleton. Within the fiber are the
Load distribution. sarcomeres, where proteins Roles
Shock absorption. Dynamic such as actin and myosin are
found.
Muscle that acts as the
Agonist
Produce movement. main mobilized
Locomotion and
Maintain body posture.
mobility body Actin in the form of a double helix (purple and
Muscle that acts as a
Stabilize joints.
segments
green) and myosin with cross bridges (yellow)
slide between them, generating contraction. stabilizer, in the opposite Antagonist
This is formed in 3d. direction.
You might also like
- Anatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAnatomy - & - Physiology Cheat SheetAlaka71% (17)
- The Cubonomicon v1Document43 pagesThe Cubonomicon v1javandarNo ratings yet
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- Body Mechanics: Psoas Major FunctionDocument15 pagesBody Mechanics: Psoas Major FunctiontokionasNo ratings yet
- SAP 4.7 Installation TutorialDocument54 pagesSAP 4.7 Installation Tutorialrajeev.ashokan8023100% (34)
- 1 Musculoskeletal Mind MapDocument1 page1 Musculoskeletal Mind Mapvn6jydy5gkNo ratings yet
- Reading Assignment 4Document17 pagesReading Assignment 4John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- 1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument5 pages1.15 (Surgery) Review of The Musculoskeletal SystemLeo Mari Go LimNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofDocument20 pages11.2 Movement: Essential Idea: The Roles ofReshma DookarranNo ratings yet
- GCSE PE Paper 1 ContentDocument18 pagesGCSE PE Paper 1 Contentshiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Handout Part IIDocument4 pagesMuscular System Handout Part IIDeenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - KODocument1 pageSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- MM ProjectDocument3 pagesMM ProjectdeuceNo ratings yet
- CHP 11Document71 pagesCHP 11Sophia YounNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument2 pagesMuscle Systemapi-428138727No ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument3 pagesLocomotion and MovementYouTutor PSNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Upgrade Now InviteDocument1 pageSkeletal System: Upgrade Now Invitemaxine janorasNo ratings yet
- Skeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionDocument26 pagesSkeleto-Syste Loco: Muscular Ms and MotionmeriiNo ratings yet
- Muscles Anatomy-Dr - NdukuiDocument62 pagesMuscles Anatomy-Dr - Ndukuiglenian560No ratings yet
- Modeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Document9 pagesModeling of The Musculoskeletal System - 1Shyam PolacondaNo ratings yet
- TriChapter27 09 Muscular SystemDocument18 pagesTriChapter27 09 Muscular Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- Muscoluskeletal SystemDocument1 pageMuscoluskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninNo ratings yet
- Muscoluskeletal SystemDocument1 pageMuscoluskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninNo ratings yet
- 04 Overvew of The Muscular SystemDocument11 pages04 Overvew of The Muscular SystemJanith sandupama RanathungaNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Muscular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System Anaphy LabDocument12 pagesThe Muscular System Anaphy LabHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 9 Muscular System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document49 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 9 Muscular System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- 303 How Animal Move MuscleDocument14 pages303 How Animal Move MuscleAna RizkaNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsDocument20 pagesJoints of The Body & Functional Muscle GroupsOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesMuscular System Anatomy and PhysiologyMichelle Tamor100% (1)
- Trumpeta, Kris - Mechanics of Muscle ContractionDocument48 pagesTrumpeta, Kris - Mechanics of Muscle ContractionJunior AbdulcaderNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No.8Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No.8yumi castroNo ratings yet
- '18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?Document7 pages'18. Movement in humans: What is endoskeleton made up of? 內⾻骼由什麼組成?thanks btNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatDocument14 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues and Its FunctionsDocument1 pageHuman Tissues and Its FunctionsJnnfr BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument12 pagesThe Muscular System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - JointsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - JointsMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartDocument1 pageCbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartAMit100% (2)
- JointsDocument27 pagesJointsJhan BencelNo ratings yet
- Somatic Anatomy Muscles and The Postural FluteDocument6 pagesSomatic Anatomy Muscles and The Postural FlutearonolamNo ratings yet
- MuscolinoDocument6 pagesMuscolinojustnewaroundNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument92 pagesHuman Anatomymohamed.sewaNo ratings yet
- Generalities MyologyDocument14 pagesGeneralities MyologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- #2 Muscular SystemDocument12 pages#2 Muscular SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Tendon TransfersDocument12 pagesBiomechanics of Tendon TransfersBasmah Al-DhafarNo ratings yet
- Musculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Document22 pagesMusculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Anonymous vwR8xcIxNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscles Structure Function Location: SmoothDocument2 pagesTypes of Muscles Structure Function Location: SmoothBabylyn SosaNo ratings yet
- A&P Presentation 20-11-23Document24 pagesA&P Presentation 20-11-23jordanmcmillan04No ratings yet
- Nelson VCE PEDocument23 pagesNelson VCE PEPNo ratings yet
- The JointsDocument7 pagesThe JointsrazondiegoNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument35 pagesThe Muscular System: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeTrisha100% (3)
- Bio Cam Clips PresentationDocument5 pagesBio Cam Clips Presentationapi-552227798No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Control of MovementDocument6 pagesChapter 8 - Control of MovementManilyn DacoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument21 pagesMuscular System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Classification of BoneDocument1 pageClassification of Bonezain juttNo ratings yet
- Chap 2. Muscle. The Primary Stabilizer and Mover of The Skeletal SystemDocument48 pagesChap 2. Muscle. The Primary Stabilizer and Mover of The Skeletal SystemHana RVNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaPhy ReviewerNashleyah AnayatinNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM - Power Point PresentationDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM - Power Point PresentationMalchrenNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: by Sisay ADocument34 pagesMuscular System: by Sisay Agobez temariNo ratings yet
- Nuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022Document20 pagesNuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022augustina gaiceanuNo ratings yet
- CMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Document93 pagesCMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Jeremiah PuaNo ratings yet
- Clearias Upsc Prelims Online Mock Test Series 2021 Timetable v1Document58 pagesClearias Upsc Prelims Online Mock Test Series 2021 Timetable v1Silpa KrishnaveniNo ratings yet
- Round Cassette Catalogue - A4Document4 pagesRound Cassette Catalogue - A4Pongalfest byaravNo ratings yet
- Surveying LessonDocument6 pagesSurveying LessonshalenNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Document33 pagesSimply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Anonymous ARMtmNKL100% (1)
- 1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationDocument11 pages1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationMohamed Elsir100% (1)
- Leviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologyDocument5 pagesLeviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologySajeda M. Al-TalafhaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)Document873 pagesEncyclopedia of Invasive Species 2 Volumes - From Africanized Honey Bees To Zebra Mussels (PDFDrive)medNo ratings yet
- Physiological FeelingsDocument202 pagesPhysiological Feelingsoscarin123456789No ratings yet
- Personality Development2022 23Document6 pagesPersonality Development2022 23Veena VaishyNo ratings yet
- DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL Indirapuram, GhaziabadDocument2 pagesDELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL Indirapuram, GhaziabadMonster QueenNo ratings yet
- BlackRock Responsible Investment Engprinciples Global SummaryDocument5 pagesBlackRock Responsible Investment Engprinciples Global SummaryComunicarSe-ArchivoNo ratings yet
- New TAWS Features: Based On EGPWS ExperienceDocument23 pagesNew TAWS Features: Based On EGPWS ExperienceShimeonNo ratings yet
- Why Developmentally Appropriate Practice (Dap) Is Important in KindergartenDocument10 pagesWhy Developmentally Appropriate Practice (Dap) Is Important in KindergartenJoy MoranoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Harvard Style SampleDocument5 pagesLiterature Review Harvard Style Sampleiigheacnd100% (1)
- Homework 2 IENG584Document3 pagesHomework 2 IENG584Frida YoungNo ratings yet
- Bsi BS en 15073 - 2013Document20 pagesBsi BS en 15073 - 2013alferedNo ratings yet
- Name - Section - Date - How To Balance Chemical EquationsDocument2 pagesName - Section - Date - How To Balance Chemical EquationsXazerco LaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodAnonymous 8f2veZf100% (2)
- Introduction To NanotechnologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To NanotechnologyTushar PanditNo ratings yet
- From Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingDocument3 pagesFrom Haiku To Shinrin-Yoku: A Brief History of Forest BathingEfra LlebaríaNo ratings yet
- Sameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Document321 pagesSameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Remon SamirNo ratings yet
- Jenitri 3Document7 pagesJenitri 3Zaenal MubaroqNo ratings yet
- Agri CollegesDocument4 pagesAgri Collegesjaimaruthi internetnamakkalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Techno - MauricioDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 - Techno - Mauricioairu mauricioNo ratings yet
- Constructing Basestations July27 RanjithDocument6 pagesConstructing Basestations July27 RanjithAkash MahalikNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet