Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group V III AnaChem Lab Midterm Notes
Group V III AnaChem Lab Midterm Notes
Uploaded by
Kyle LimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group V III AnaChem Lab Midterm Notes
Group V III AnaChem Lab Midterm Notes
Uploaded by
Kyle LimCopyright:
Available Formats
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.
com
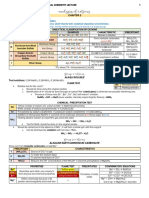
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
Analysis of Cations
The elements maybe classified into two:
1. According to their atomic numbers as you can see in the familiar periodic table.
2. According to the reaction and properties of their ions which lead themselves to analytical
separation and detection.
Analytical classification of cations
1. Group 5 - Alkali Group/Soluble Group
- 𝐾 + , 𝑁𝑎 + , 𝑁𝐻4 + , (𝐿𝑖 + 𝑅𝑏+ 𝐶𝑠 + 𝐹𝑟 + ) – these ions remain in the solution
2. Group 4 - Alkaline Earth Group
- 𝐵𝑎+2 , 𝑆𝑟 +2 , 𝐶𝑎+ , 𝑀𝑔+ – these ions from insoluble carbonates except 𝑀𝑔+
- Group Precipitant: (𝑁𝐻4 )2 𝐶𝑂3, 𝑁𝐻4 + , 𝐶𝑙, 𝑁𝐻4 𝑂𝐻
3. Group 3 - Aluminum -Iron Group (Alkali Insoluble Sulfide Group)
a) Aluminum Group: 𝐴𝑙+3 , 𝐶𝑟 +3 , 𝑍𝑛+2 - ions that will from amphoteric hydroxide
b) Iron Group: 𝐶𝑜 +2 , 𝑁𝑖 +2 , 𝑀𝑛 +2 , 𝐹𝑒 +2 , 𝐹𝑒 +3 - ions that will from non-amphoteric hydroxide
- Group Precipitant: 𝑁𝐻4 𝐶𝑙, (𝑁𝐻4 )2 𝑆, 𝑁𝐻4 𝑂𝐻
4. Group 2- COPPER -ARSENIC GROUP (Acid Insoluble Sulfide Group)
a) Copper Group: 𝐶𝑢+2 , 𝐵𝑖 +3 , 𝐶𝑑 +2 , 𝑃𝑏 +2 , 𝐻𝑔+2 - do not form amphoteric sulfides.
b) Arsenic Group: 𝐴𝑠 +3 , 𝐴𝑠 +5 , 𝑆𝑏+3 , 𝑆𝑏+5 , 𝑆𝑛 +2 , 𝑆𝑛+4 - form amphoteric sulfides
- Group Precipitant: 0.2 − 0.3 𝑀𝐻 + 𝑇𝐴, 𝐻2 𝑂2
5. Group l- SILVER GROUP (Insoluble Chloride Group)
- 𝐴𝑔+ , 𝑃𝑏+2 , 𝐻𝑔2 +2
- Group Precipitant: 6MHCl
Sources of 𝐻2 𝑆
a) 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑆𝑁𝐻2 → 𝐻2 𝑆
- Thioacetamide (CH3CSNH2) is the sulfur analog to acetamide (CH3CONH2)
b) 𝐹𝑒𝑆 + 2 𝐻𝐶𝑙 → 𝐹𝑒𝐶𝑙2 + 𝐻2 𝑆
Note: Test Solutions of Cations are prepared from their nitrate salts. Test solutions of anions are prepared
from their corresponding sodium or potassium salts.
Analysis of Group V Cations: Alkali Group/ Soluble Group
- 𝐾 + , 𝑁𝑎 + , 𝑁𝐻4 + , (𝐿𝑖 + 𝑅𝑏+ 𝐶𝑠 + 𝐹𝑟 + )
- The alkali metal group is sometimes called the "soluble group" for these ions remain in solution after
all the analytical groups of cations have been precipitated
- 𝐾 + , 𝑁𝑎 + - are the most common members of this family and are the ones included in the analytical
procedures.
- 𝑁𝐻4 + - is included in this group since it shows similar properties.
a) having single positive charge
b) most of its salts are soluble in water
- Test Solutions: 0.2 M 𝑁𝑎𝑁𝑂3 , 0.2 M 𝐾𝑁𝑂3 , 0.2 M 𝑁𝐻4 𝑁𝑂3
Detection of these ions
a) Flame Test - a reliable test for 𝐾 + 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑁𝑎 +, should be done using the original solution
b) Chemical Test- Precipitation
Note: For identification of it is necessary to view the flame through an optical filter (cobalt glass) so as to
eliminate any possible interfering ions such as 𝐵𝑎 +2 , 𝑆𝑟 +2 , 𝐶𝑎 + , 𝑁𝑎 + - Presence of these ions will make
invisible. By using cobalt glass, all other ions are filtered out so only 𝐾 + is visible.
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
- 𝐾 + − fleeting lavender flame, alternative test shows yellow precipitate
- 𝑁𝑎 + - persistent yellow flame
Note: Before performing the flame test, add a few drops of 12MHCI to the sample solution, to convert the
salt into a more volatile form. 𝑁𝑎𝑁𝑂3 + 𝐻𝐶𝑙 → 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 + 𝐻𝑁𝑂3 (more volatile). Chlorides impart a brighter
flame.
Chemical Test/ Precipitation:
1. 𝑵𝒂+
- formation of yellow crystals of sodium zinc uranyl acetate.
- formation of white crystals of sodium pyroantimonate.
- Before performing the flame test, add a few drops of 12MHCI to the sample solution, to convert
the salt into a more volatile form.
- Confirmatory reaction: persistent yellow flame. Chlorides (NaCl) impart a brighter flame.
- Confirmatory Equation: 𝑁𝑎𝑁𝑂3 + 𝐻𝐶𝑙 → 𝑧𝑧 𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 + 𝐻𝑁𝑂3 (more volatile).
2. 𝑲+
- precipitated by sodium cobaltinitrite as yellow potassium sodium Cobaltinitrite
Note: this test should be carried out in the absence of NH' since ammonium ion will form a similar
precipitate with this reagent.
3. 𝑵𝑯𝟒 +
- can be removed or destroyed by oxidation with hot conc. 𝐻𝑁𝑂3
- Confirmatory equation (from book): 𝑁𝐻4 + + 𝑂𝐻 → 𝑁𝐻3 + 𝐻2 𝑂
a) Addition of excess strong base (NaOH) to convert the ion to molecular ammonia.
- Confirmatory reaction: Red litmus paper turns to blue
b) heating the alkaline solution to expel ammonia (NH3) gas
- confirmatory reaction: urine like odor
Removal of 𝑁𝐻4 +
1. To 10 drops of the unknown solution containing no members of Group l, Il & Ill, add 15-30 drops of
conc HN03
2. Place unknown solution in an evaporating dish.
3. Heat until no more dense white fumes are formed.
4. Cool then add I ml of distilled HO.
5. Transfer the solution to a vial.
6. Centrifuge if not clear.
7. To the clear centrifugate, add a pinch of sodium cobaltinitrite.
8. Make your own conclusion.
Analysis of Group IV Cations: Alkaline Earth group/ (NH4)2CO3 Group
- Ba+2 Sr+2 Ca+2 Mg+2
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
- These ions form insoluble carbonates except Mg+2
Group pptant: 5M NH4 Cl, 15M NH4 OH, (NH4)2 CO3
a) (NH4)2 Co3 – source of CO3 = to ppt.
b) NH4OH - to make the solution basic
— To prevent hydrolysis of CO3=
c) NH4 Cl – reduces the OH- conc. of the NH4OH and thus prevents precipitation of Mg(OH)2
Sr+2 Ba+2 Ca+2 – resemble each other very closely in their physical and chemical properties
Mg+2 – because of its greater electronegativity and the small size of Mg ++ ion, differs chemically from
the other alkaline earth elements.
Detection of these ions
1. Flame test
Ba +2 – yellow green
Ca+2 – orange/ brick red
Sr +2 – deep/ crimson red
2. Precipitation – formation of white solids
Reagents:
o HAc - to acidity but not to the extent that the
solution will become acidic
Why? because BaCrO4 is soluble
o NH4AC - to buffer excess HAc by decreasing H+
o TEA - Forms a more stable complex ion with
Ca+2 than with Sr+2 so under these
conditions, SrSO4 precipitate out but
CaSO4 does not.
- Triethanolamine
o MgNH4PO4 - Not a reliable test for Mg+2 because all
cations except for the alkali metals
precipitate as phosphate from alkaline
solution
o HCL - Dissolves the precipitate and converts
the salt into a more volatile form
o Buffer - Has a weak acid and its salt or a weak
solution base and its salt
- Has the property of maintaining a near
constant H+ ion concentration if
appreciable acid or base is added to the
solution
o S & O rgt. - Para – nitrobenzeneazoresorcinol
- Derived from Suitzu and Okuma
(Japanese chemists)
CONFIRMATORY EQUATIONS: (from compilation book)
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
1. Ba+2
2. Sr+2
3. Ca+2
4. Mg+2
OXIDATION – REDUCTION REACTANTS
Two categories of chemical reactions:
1. Those in which there is no change in valence or oxidation no.
2. Those in which some elements undergo a change in oxidation no. (Redox)
*for each of these categories; equations an be written either in a molecular or ionic form.
• Molecular equation – where the complete formulas for all reactants and products are written
• Ionic - where only those species (ions or molecules) that participate in the reactions are shown.
Oxidation – reduction also known as “redox”, is a chemical process in which the oxidation no. of an element is
changed
- Reactions which involve the loss and gain of electrons by an atom or ion
Oxidation – occurs whenever the ox. no. of an element increases as a result of losing electrons
Reduction – occurs whenever the ox. no. of an element decreases as a result of gaining electrons
2 types of balancing redox reactions:
▪ Oxidation no. method/molecular method
▪ Half – reaction or Ion-election method
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
Analysis of Group IV Cations: From Lab Manual
B. precipitation of Group IV:
To 3ml of the unknown solution in a vial add 1 ml of 5 M NH4Cl, then 5 M NH4OH drop by drop until basic and
add 3 drops in excess. Heat the solution almost boiling but do not boil. Add 1 ml of (NH4)2C03 reagent, mix and allow
the solution stand for at least five minutes, centrifuge. test for completeness of precipitation by adding a few drops of
the ammonium carbonate reagent. If a cloudiness forms around the drops of reagent added, stir the solution, warm
gently, and then centrifuge again. Test again for completeness of precipitation. When precipitation is complete decant
the supernatant liquid which may contain magnesium ion and group V ions and treat it by procedure C. wash the
precipitate with two 2 ml portions of water and discard the washings.
B-1 Test for Barium Ion
To the precipitate add 6 MHAc dropwise until the solid is just dissolved, or until 10 drops of the HAc solution
have been added. Then add a number of drops of 3 M NH4Ac equal to the number of drops of HAc used in dissolving
the precipitate. Dilute the solution to 2 ml with water. Centrifuge. discard the solid and save the supernatant liquid.
Heat the solution to boiling and add one drop of 1 M K2CrO4-
Ba2+ + CrO42- = BaCro4
If no precipitate forms barium is absent and the solution is treated by B-2. If a precipitate form, heat again and
add a second drop of 1M K2CrO4-
Centrifuge. before decanting the supernatant liquid observe to see that it is yellow. If the solution is colorless,
heat to boiling, add a third drop of 1 M K2CrO4-. Centrifuge. when the supernatant is yellow decant it and treat it by
B-2. Wash the precipitate with two 1 ml portions and discard the washings.
To confirm the presence of barium, dissolve the yellow precipitate in 1 ml of 6 M HCl. Apply the flame test.
BaCrO4 + H+ => BaCr2O7 + H2O
Result:
After the flame test for Barium that was being added with 6 M HCl, it showed a yellow green color confirming the
presence of Barium ion.
To the remaining solution add two drops of 6 M H2SO4-. A white precipitate confirms barium ion. If the color
of the solution makes the precipitate appear yellow, centrifuge and discard the supernatant liquid. Wash the
precipitate with 1 ml of water. Centrifuge again to ascertain whether the precipitate is white.
Result:
The remaining solution after the flame test that was being added with 6 M sulfuric acid which showed an intense
yellow color with white precipitate.
BaCr2O7 + H2SO4 => BaSO4 + H2CrO7
B-2 Test for Strontium Ion
Adjust the volume of solution B-2 to about 2 ml by either evaporation or dilution. Add 15 drops of
triethanolamine and stir with a rod until the solution is homogenous. Add 1 ml of 2M (NH4)2SO4, stir again, and heat
to boiling. Centrifuge and examine the bottom of the tube. A white precipitate indicates the presence of strontium
ion. Decant the supernatant liquid through a filter and save the filtrate for B-3.
To confirm strontium, wash the precipitate with two 1 ml portions of water and discard the washings. To the
washed precipitate add 1 ml of ammonium carbonate reagent, heat and stir. Centrifuge and discard the centrifuge the
centrifugate. Wash the precipitate with two 1 ml portions of water and discard the washings. Dissolve the residue in
three drops of 6 ml HCl and make a flame test on the solution. A deep red flame confirms strontium.
Result:
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
Strontium ion reacts with ammonium sulphate which formed a white precipitate which also showed a crimson red
color to the flame.
Sr 2+ + SO42- => SrSO4
B-3. Test for Calcium Ion
To the filtered solution B-3 add 10 drops of 0.2 M (NH4)2C2O4- . centrifuge, decant and discard supernatant
liquid. Heat the precipitate with the full heat of the burner then allow the tube to cool. Add three drops of 6 M HCl to
the residue and carry out the flame test. An orange red flame confirms the calcium ion. For those who find the color
of the calcium flame difficult to distinguish, the white precipitate with ammonium oxalate may be more reliable test.
Result:
White precipitate was formed which confirmed the presence of calcium ion with orange red flame.
Ca+2 + C2O4-2 => CaC2O4 (white ppt)
C. Test for Magnesium Ion
To the centrifuge C add five drops of 15 M NH4OH and 20 drops of 0.5 M Na2HPO4 solution. Mix and allow to
stand for at least 10 min. centrifuge and discard supernatant liquid. Wash the ppt, with two 1 ml portions of water
and discard the washings. Dissolve the ppt, in three drops of 6 M HCl and dilute with 2 ml water. Add one drops of S
and O reagent, warm the solution slightly, and add 6 M NaOH dropwise until the dye turns purple. A bright blue ppt.
is a positive test for magnesium if the color of the solution obscures the color of the ppt, centrifuge and discard the
supernatant liquid. Suspend the ppt in 1 ml of water containing three drops of 6 M NaOH. (note: if the S and O reagent
is not available, the formation of a white ppt with NaOH will confirm magnesium.
Result:
There was a formation of blue precipitate that confirmed the presence of magnesium ion.
Mg2+ + NH3 + HPO42- => Mg (NH4) PO4
Analysis of Group III Cations: From Lecture Notes
(Al-Fe Group)
Al3+Cr3+Zn2+ Mn3+Fe2+Fe3+Co2+Ni2+
(Al-FE Group)
- Also known as Alkali – Insoluble Sulfide Group
- Ammonium Sulfide Group
- Basic Hydrogen Sulfide Group
A. Aluminum Group
- Al3+Cr3+Zn2+ - forms amphoteric hydroxides
B. Iron Group
- Mn3+Fe2+Fe3+Co2+Ni2+ - forms non-amphoteric hydroxides
Group pptant: 5M NH4 Cl, 15M NH4OH, IM(CH3CSNH2)
The colors of the cations of the Aluminum-iron group are as follows:
Al3+ - colorless Ni2+ - green
Zn2 - colorless Co2+ - reddish pink
Mn3+ - colorless to faint Fe2+ - pale green
pink Fe3+ - reddish brown to
Cr3+ - blue green yellow
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
The colors of the precipitates in this group are:
Cr(OH)3 – dirty green or grayish green
Al(OH)3 – white
Fe(OH)3 – reddish brown
Fe(OH)2 – green
FeS – black
CoS – black
MnS – peach
NiS – black
ZnS – white
Discussion:
1.) Mn3+
MnS – (manganese sulfide) – is the most soluble sulfide of this group
KClO3 in hot conc. HNO3 oxidizes Mn2+ to MnO2
- Separates manganese from all other ions of the Al-Fe group
Mn2+ + 2ClO3- → MnO2 + 2ClO2
NaBiO3 (sodium bismuthate) in HNO3 solution oxidizes Mn2+ to MnO4-
- Formation of purple MnO4-- ion serves as a sensitive test for the detection of manganese
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
- Note: Reducing agents of any kind such as Cl- or S-2 will interfere with the confirmatory test in Mn2+ because
they will reduce MnO4- to Mn 2+ (colorless)
Confirmatory Equation:
Fe2+,Fe3+ test
Fe(OH)3 – ferric hydroxide
- Less soluble than Fe(OH)2
- Differs from hydroxides of Co, Ni, and Zn because it is insoluble in excess NH4OH
3.) Co2+ (cobaltous ion)
- Oxidation of Co2+ compounds in aqueous NH3 gives hexamine cobalt (III) ion, Co(NH3)8++
-Co(OH)2 – cobaltous hydroxide – in cold solutions – blue
- In warm solutions – pink or a rose colored
- Becomes brown upon exposure to air due to partial oxidation into Co3+ or Co(NH3)4++ (cobalt tetraamine)
K3Co((NO2)6 (potassium cobaltinitrite or potassium hexanitrocobaltate (III) – colored yellow)
- Precipitated when KNO2 is added to slightly acidic solution of Co2+ ion
Note: this precipitate is not formed in alkaline or in strongly acidic solutions
In the presence of Na+ ion, the relatively insoluble K-2Na [Co(NO2)6]
Confirmatory Equation:
4.) Ni2+ - (nickelous ion)
- does not form a precipitate with KNO2 in HAc solution, hence does not interfere with cobalt test.
- forms numerous complexes with NH3
Ni(NH3)4++ with 0.1 M NH3
Ni(NH3)5++ with 0.1 M NH3
Ni(NH3)6++ with conc. M NH3 solution
- Forms red ppt. with DMG (dimethyl glyoxime)
- This red ppt. is formed in slightly alkaline solution with NH3 and buffered with NaAc but not in acidic
or strongly ammoniacal solution
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
Confirmatory Equation:
5.) Al3+(aluminum ion)
Al- the only element of the Al-Fe group that is not a transition element
- Aluminum salts have a strong tendency to hydrolyze
- When the acidity of the solution of Al3+ salt is decreased, hydrolysis becomes extensive and at pH 4,
a white gelatinous ppt. of Al(OH)3 appears
- If the pH is increased to 10 or above, the Al(OH) 3 redissolves. Hence, Al(OH)3 is amphoteric
- If HCl is added gradually to the solution containing the Al(OH)4- ion, Al(OH)3 is reprecipitated
or by boiling with excess NH4+ salt
Aluminon rgt. (ammonium salt of aurin tricarboxylic acid) – forms an insoluble red lake ppt. with Al+3
Confirmatory equation:
Note: Interferring ions like Fe3+ and Cr3+ give the same red ppt with aluminon reagent, however, (NH4)2CO3 destroys
them
6.) Cr3+ (Chromium ion)
- in acidic solution, Cr3+ ion is oxidized only by very strong oxidants such as KClO3 in conc. HNO3--
- In alkaline solution it is readily oxidized by H202, even air converts it to Cr(VI)
SrCrO4 – moderately soluble in water
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
- Precipitate in 50% ethanol –H20 mixture
- Sparingly soluble in HAc but all dissolve in strong acid where high concentration of H + ion greatly
favors the formation of dichromate ion
- Where H202 is added to slightly acidic solution of Cr2O72- ion, an unstable blue peroxide of chromium
is formed
Confirmatory equation:
CrO5 is relatively stable in organic solvents and in water at low temperature.
High temperature and high acidity favor its decomposition.
7.) Zn2+(zinc ion)
Zn(OH)2 – dissolve in excess of hydroxide ion solution
- Precipitatation of ZnS is complete in the presence of acetate ion or some other base
Confirmatory equation:
Direct test:
- Under certain conditions, some group III ions maybe tested directly from the original unknown solutions
1. Mn2+
- All manganese salts maybe oxidized to permanganate by sodium bismuthate. Interference (reducing agents)
are removed by the addition of excess NaBiO3
2. Fe3+
- In solution and in acid medium, Fe3+ will give a blood red solution with KSCN
3. CO2+
- Forms a deep blue complex with conc. KSCN or NH4SCN in the presence of acetone or chloroform
- The complex is more stable in organic solvents hence the color is intensified by the addition of acetone
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
- Fe3+ interferes with this test
Removal or Fe3+
4. Ni2+
- Of all the ammonia complexes, only Ni2+ will give a strawberry red ppt. with DMG
5Zn2+
- In the absence of Group I and II ions, Zn2+ is the only ion that will precipitate with T.A (if the sol’n is acidified
with HAc) forming ZnS (in a H2O bath)
Analysis of Group III Cations: From Lab Manual
Prepare a known solution by mixing approximately 1 ml each of manganese nitrate, ferric nitrate, cobalt nitrate, nickel
nitrate, aluminum nitrate, chromium nitrate and zinc nitrate. Dilute with water to make approximately 10 ml of
solution. Analyze as a practice unknown by the following procedure:
E. Precipitation of Group Ill Cations:
To 3 ml of the unknown solution add 1 ml of 5 M NH4CI, 15 M NH4OH until basic plus 5 drops in excess, then
10 drops of 1 M thioacetamide solution. Mix thoroughly and heat the tube in a water bath for 7 to 10 minutes.
Centrifuge. Decant the supernatant liquid into another tube and test for complete precipitation, by adding 5 drops of
thioacetamide and again heating for 5 to 10 minutes. Should a ppt. form, return the suspension to the test tube with
the ppt. and centrifuge again. Repeat the test for complete precipitation. Wash the ppt. with a mixture of 4 drops of
5 M NH4NO3 and 2 ml of water. Centrifuge. Discard the washings and treat the residue according to E-1.
E-1. Separation and Test for Manganese ion:
To the residue add 10 drops of 6 M HNO3. Warm the tube and agitate the suspension. Pour the solution into
a casserole. Remove globules of sulfur, if any, with the tip of a rod. Evaporate the solution to a volume of 2 or 3 drops.
Add 10 drops of 16 M HNO3 and about 0.2 g of potassium chlorate crystals. Evaporate to about 3 drops. Add another
10 drop portion of 16 M HO3 and about 0.1 g of potassium chlorate and again evaporate to three or four drops. (Add
HO3 if the evaporation is carried too far.) Dilute with water to 2 ml. If there is no black stain or ppt. in the casserole,
manganese is absent. Treat the nitric acid solution according to E-F-1. If there is a black ppt. or dark stain in the
casserole, transfer the suspension to a test tube and centrifuge. Decant the supernatant liquid and label it E-F-1. Rinse
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
the stained casserole with 1 ml water, pour the washings into the test tube with the ppt., agitate, centrifuge and
decant the washings into the solution E-F-1.
To the washed ppt. add 10 drops of 6 M HNO3. Warm and add a drop of 3% H,02- Add more drops of H¿O to
dissolve the ppt. if necessary. Pour this solution into the stained casserole. Warm and if necessary to dissolve the black
stain, add a drop or two more H2O2 (If black or brown ppt. begins to form, discontinue the evaporation immediately.)
To the solution in the casserole add 10 drops of 6 M HNO3 and 1 ml water. Add solid sodium bismuthate a pinch at a
time until solid remains undissolved. A pink or purple color in the solution is a test for manganese ion.
E-F-1. Separation of the Aluminum Group from the Iron Group:
To the solution E-F-1 add 6 M NaOH until basic, then 8 drops in excess. Add 5 drops of 3% H2O2 and boil until
bubbles of oxygen are no longer evolved from the hot solution. Centrifuge and decant the supernatant liquid through
a filter. Label the filtrate F-1. Wash the ppt. by warming it with 10 drops 6 M HCI and treat this solution according to
E-2. (A brown or black residue insoluble in the HCI solution is usually MnO2. If the test for manganese was negative,
treat the dark residue by the last paragraph of E-1)
E-2. Separation and Test for Ferric Ion:
Dilute the solution E-2 to 2 ml with water. Add 6 M NH4OH until alkaline, then 5 drops in excess. If there is no ppt.
ferric ion is absent and this solution should then be divided into two equal portions for E-3 and E-4. If a ppt. forms,
centrifuge, decant and divide the supernatant into halves: label one E-3 and the other E-4. Wash the ppt. with 1 ml
water, centrifuge, discard washings. Dissolve the residue in 5 drops of 6 M HCI, dilute to 2 ml, and add 5 drops of 1 M
KSCN solution. A deep red solution is a positive test for ferric ion.
E-3. Test for Cobalt Ion:
To the solution E-3 add 6 M HAc until acidic then 3 drops in excess. Add 1 ml of 6 M KNO2. Warm the solution
and allow to stand for a few minutes. A yellow or olive - colored ppt. indicates the presence of cobalt ion. If no ppt. is
observed, add 3 to 5 drops additional HAc and warm again before concluding that cobalt is absent.
E-4. Test for Nickel Ion:
To the solution E-4 add 4 drops of 1% dimethylglyoxime solution. A red or pink ppt. is a positive test for nickel
ion. If cobalt is present, the first few drops of dimethylglyoxime reagent may react with the cobalt to give a brown
solution. If the brown solution is observed, add 10 additional drops of dimethylglyoxime, centrifuge, decant the
supernatant liquid. A red solid in the tube is a positive test for nickel.
F-1. Test for Aluminum Ion:
To the solution F-1 add 1 ml of 5 M NH4NO3 mix and heat for 5 minutes in a water bath. white gelatinous ppt.
indicates the presence of aluminum ion. Filter and label the filtrate F-2. Wash the filter with 20 drops of water or until
the yellow color of chromate, if present, is removed from the filter. Discard the washings. Dissolve any aluminum
hydroxide on the filter in 5 drops of 6 M HCI. Wash the acid through the filter with 20 drops of water, catching the
water in the same tube with the acid. Add 3 drops of aluminum reagent and 20 drops of 3 M NH4Ac. Warm, allow to
stand for 5 minutes and examine carefully. A red ppt. confirms aluminum.
F-2. Test for Chromium Ion:
If the solution F-2 is colorless, chromium ion was absent in the original solution, and the solution is taken
directly to F-3. If the solution F-2 is yellow, chromate ions are probably present. To confirm chromium, heat the yellow
solution to boiling and add 10 drops of 0.5 M BaCl2 solution. Yellow BaCrO4, white BaSO4, or a mixture of the two
may ppt. Centrifuge, decant the supernatant liquid and label it F-3. Wash the ppt. with two 1 ml portions of water and
after centrifuging, discard the washings. To the residue add 10 drops of 3% H2O2, agitate and then add one drop of 6
M HNO3. A blue color that fades quickly confirms the presence of chromium ion.
F-3. Test for Zinc Ion:
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
To the solution F-3 add drops of thioacetamide. Heat the tube for 5 minutes in a water bath. A white precipitate is a
positive test for zinc.
DIRECT TESTS
Under certain conditions some Group III ions may be tested directly from the original unknown solution without
following the lengthy procedure:
1. Test for Manganese:
To 5 drops of the unknown solution, add 10-15 drops concentrated HNO3. Then add NaBiO3 pinch by pinch
until the solid no longer dissolves. A pink to purple color indicates manganese:
Result: 2Mn(NO3)2 + 5NaBiO3 + 16HNO3 -> 2HMnO4+5Bi(NO3)3 + 5NaNO3 + H20
- when sodium bismuthate is added to manganese ions in dilute nitric acid, the mixture stirred and excess
reagent filtered purple solution of permanganate is produced.
- MnO4- = red ppt
2. Test for Nickel ion:
To 5 drops of the unknown, add 5 drops water, 6M NH4OH dropwise until the ppt. First formed dissolves (or until the
solution smells of ammonia). Centrifuge. To the clear supernatant add a few drops of dimethylglyoxime. A red ppt.
Indicates nickel.
Result: Ni+2CuH7N2O2 -> Ni(C4H7N2O2)
- Ni(DMG)2 = red ppt
3. Test for Ferric ion:
To 5 drops of the unknown, add 6 M HCl until acidic. Add KSCN dropwise. A deep red color indicates ferric ion. If a ppt.
Forms upon addition of KSCN, add excess of the reagent until complete.
Result: FeCl3+3KSCN -> Fe(SCN)3 + 3KCl
- Potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) will give deep red coloration to solutions containing Fe3+
- FeSCN2+ = deep red solution
4. Test for Cobalt ion:
If ferric is present, remove it as follows: To 10 drops of the unknown solution add 6 M HCl until acidic, then add SnCl2
solution dropwise until the solution is almost color-less (or light green)
To test for cobalt, add KSCN and acetone to the solution. A deep blue color indicates the presence of cobalt.
Result: KSCN will give blue color to cobalt, but acetone will enhance/stabilize this complex ion giving deep blue color
that indicates the presence of cobalt.
- Co(SCN)2 = deep blue solution
5. Test for Zinc ion:
To a few drops of the unknown, add 6 M HAc until acidic, 5 drops of thioacetamide. Heat in a water bath. A white ppt.
Indicates zinc ion. (Note: Remove Group 1 and Group 2 ions before performing the test).
Result: Zn(OH)2+C2H5NS -> ZnS+C2H5N(OH)2
- C2H5N5 was added to acidify and distinguish the zinc ion in a presence of white ppt.
- ZnS = white ppt
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
ANAYTICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
Cation V, IV, III
Only aluminum and chromium ions are left for analysis.
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
Schematic Outline for Separation of Cations into Groups:
Ions of Groups I-V
6 M HCl
ppt. sol’n.
Group I Group II- V
0.2- 0.3 M H+
TA, H2O2
ppt. sol’n.
Group II Group III-V
NH4Cl,
NH4OH
TA
ppt. sol’n.
Group III Group IV-V
NH4Cl
NH4OH
(NH4)2CO3
ppt. sol’n.
Group IV Group V
Mg+2
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
Schematic Diagram of Group IV Cations
Ba2+ Sr2+ Ca2+ Mg2+
5M NH4Cl, 15M NH4OH, (NH4)2CO3
ppt: BaCO3, SrCO3, CaCO3 Sol’n Mg2+
Dissolves in 6M HAc Add 15 M NH4OH
Add 3M NH4Ac & 1M K2CrO4 & 0.5 M Na2HPO4
ppt: MgNH4PO4
Add 6 M HCl, S&O
AA Sol’n: Sr2+, Ca2+
ppt: BaCrO4 rgt., 6M NaOH
Add TEA (triethanolamine)
Dissolves in N(C2H4OH)3 & (NH4)2SO4 Mg(OH)2 (White) +
6M HCl dye (blue)
Ba2+
6M
ppt: SrSO4 Sol’n: Ca2+ (Complex)
H2SO4
(NH4)2C2O4
(NH4)2CO3
BaSO4 ppt: SrCO3 ppt: CaC2O4
(white ppt)
Dissolve in
6M HCl Dissolve in 6M HCl
Apply Flame
Test (Yellow- Sr2+ - Flame Test
(Crimson red) Ca2+ - Flame Test
green flame)
(brIck red)
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
This Document has been modified with Flexcil app (Android) https://www.fexcil.com
Group III, IV, & V
NH4Cl, NH4OH, (NH4)2CO3
Group III, IV, & V ppt of group III: Al(OH)3, Cr(OH)3, MnS, Fe2S3, CoS, NiS, ZnS
6M HNO3
ppt of group III: Al(OH)3, Cr(OH)3, MnS, Fe2S3, CoS, NiS, ZnS
KClO3
ppt: MnO2 (brown black) Sol’n: Al3+, Cr2O7^2, CO2+, Ni2+, Zn2+
3% H2O2
NaOH excess,
Mn2+ H2O2, boil, filter
HNO3, NaBiO3
Sol’n: AlO2- or Al(OH)4, ZnO2^2-, or
MnO4 ppt: Fe(OH)3, Co(OH)3, Ni(OH)2 Zn(OH)4^2-, CrO4^2- or CrO2
(purple)
HCl
NH4NH3
Fe3+, Co2+, Ni2+
Excess NH4OH
ppt: Al(OH)3 Sol’n: ZnO2^2-, CrO4^2-
ppt: Fe(OH)3 HCl BaCl2
Sol’n.: Co(NH3)6^2+, Ni(NH3)^2+
Al(OH)4-
HCl To half of the To half of the
or AlO2-
sol’n add sol’n add
Fe3+ excess HAc & DMG NH4Ac, ppt: Sol’n
KNO2 Aluminon BaCrO4 ZnO2^2-
KSCN
rgt. HNO3
ppt: H2S
FeSCN2+ ppt:
K3Co(No2)6 Ni (DMG)2 ppt.
(deep red) Cr2O7^2- ppt. ZnS
(yellow) (red) Al(OH)3
(orange) (white)
(red lake)
HCl
CrO5 (blue) Zn++
NaOH,
TA
ZnS
(white ppt.)
Flexcil - The Smart Study Toolkit & PDF, Annotate, Note
You might also like
- Learning Activity No. 1 Separation of The Basic Constituents Into Groups o LEARNING OBJECTIVES: at The End of The Experiment, The Students CanDocument9 pagesLearning Activity No. 1 Separation of The Basic Constituents Into Groups o LEARNING OBJECTIVES: at The End of The Experiment, The Students Cansampong mga dalere100% (2)
- Module 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptDocument10 pagesModule 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptYuan MasudaNo ratings yet
- Chem (Final)Document17 pagesChem (Final)Jaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes - Acids and Bases - PH - Dry Lab - 2020Document9 pagesElectrolytes - Acids and Bases - PH - Dry Lab - 2020MariaPaulaGonzalezRojasNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Notes: Cedar College Salt Analysis Theory 1Document19 pagesQualitative Analysis Notes: Cedar College Salt Analysis Theory 1Daniyal KhanNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations PDFDocument28 pagesQualitative Analysis of Cations PDFJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations: Group 1 The Silver GroupDocument26 pagesQualitative Analysis of Cations: Group 1 The Silver Group21114 Alfredo SinabutarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 20/21: Separation and Identification of Group IV & Group V Cations (Ba, Ca, MG, Na, K, and NH)Document10 pagesExperiment 20/21: Separation and Identification of Group IV & Group V Cations (Ba, Ca, MG, Na, K, and NH)Noni Iranaya NoniNo ratings yet
- Chem. 112 CationDocument4 pagesChem. 112 CationMhai LgtNo ratings yet
- Kimia-Analitik Analisa-Kation 16651 0Document13 pagesKimia-Analitik Analisa-Kation 16651 0Nur AidaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Qualitative Analysis: PurposeDocument2 pagesLab 4 - Qualitative Analysis: PurposeWilmer AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Exp 2, Group A Cation AnalysisDocument8 pagesExp 2, Group A Cation AnalysisAmahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Intro & Group PropertiesDocument111 pagesChapter 1. Intro & Group PropertiesJoylyn BaligodNo ratings yet
- Classification of The Cations and AnionsDocument17 pagesClassification of The Cations and Anionsachraf73100% (1)
- Comparing AciditiesDocument2 pagesComparing AciditiesKim ThaiNo ratings yet
- Topic VIDocument30 pagesTopic VIEmmarehBucolNo ratings yet
- 5 - Volatile Poisons in Simulated Gastric ContentDocument7 pages5 - Volatile Poisons in Simulated Gastric ContentMedSure PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsNabil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chem Mod 6 #2Document77 pagesChem Mod 6 #2hruthika.schoolNo ratings yet
- CATIONS IV V Post Lab NotesDocument2 pagesCATIONS IV V Post Lab NotesBeatrice AlejeNo ratings yet
- Actinide SeparationDocument35 pagesActinide SeparationZain MSDNo ratings yet
- Experiment 24 Qualitative Analysis I: GoalDocument9 pagesExperiment 24 Qualitative Analysis I: GoalggmmnmcncnnmNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 All About AnionDocument20 pagesLecture1 All About AnionAlma PustaNo ratings yet
- 1 IER FundamentalsDocument54 pages1 IER FundamentalsAdam FendrychNo ratings yet
- Name NIM Class: Nevta Fatikha Ariyani 4411421027 Biology 1ADocument59 pagesName NIM Class: Nevta Fatikha Ariyani 4411421027 Biology 1ANevta FatikhaNo ratings yet
- Chem 5-1st Post Lab DiscussionDocument41 pagesChem 5-1st Post Lab DiscussionJesselie SalayaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Chemistry: Department of Chemistry Opch 101 NOV 2020Document5 pagesCarbonyl Chemistry: Department of Chemistry Opch 101 NOV 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Lab ContDocument13 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lab ContJulianne DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- 05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsDocument5 pages05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Resmi Analisis Kation AnionDocument33 pagesLaporan Resmi Analisis Kation AnionPKU21079 Putri Nurjihan NajlaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical Reactionsreduan sadikNo ratings yet
- 1225 Experiment 07Document8 pages1225 Experiment 07Mahmoud AbdAllah0% (1)
- Chemical ReactionsDocument61 pagesChemical ReactionsJOSHUA NYANGENANo ratings yet
- E5 Lewis Acids and Bases: ComplexationDocument5 pagesE5 Lewis Acids and Bases: ComplexationVirendrakumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Group 7 The HalogensDocument6 pages2.3. Group 7 The HalogensDalton chirchirNo ratings yet
- Detection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesDetection of Functional Groups in Organic CompoundsKiran PatroNo ratings yet
- 3 Monitoring and Management NotesDocument9 pages3 Monitoring and Management NotesPackirisamy NeelagandamNo ratings yet
- 0620 RevisionpackDocument14 pages0620 RevisionpackAnusha MasroorNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity Final AnwersDocument4 pagesLab Activity Final AnwersRhea Angelica CamachoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis (Basic Redicals)Document36 pagesQualitative Analysis (Basic Redicals)gd MNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis (AutoRecovered) - 1Document3 pagesGravimetric Analysis (AutoRecovered) - 1Nour FathyNo ratings yet
- 3E5NA Sci Chem Qualitative Analysis Notes Student'sDocument19 pages3E5NA Sci Chem Qualitative Analysis Notes Student'sAditi Ravi kaushikNo ratings yet
- 1-Organic Chemistry 2015 PDFDocument6 pages1-Organic Chemistry 2015 PDFFariz AzizNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument83 pagesReactions in Aqueous Solutions張婷昀No ratings yet
- AnionsDocument16 pagesAnionsMuna LasenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistr Y Notes: - Solencia HamiltonDocument56 pagesChemistr Y Notes: - Solencia HamiltonManushka ThomasNo ratings yet
- D05MANFesalt PDFDocument9 pagesD05MANFesalt PDFJalil C'boedak TsanpurNo ratings yet
- Chem 3BDocument3 pagesChem 3BWahid Salauddin DiptaNo ratings yet
- Defining Aqueous ReactionsDocument13 pagesDefining Aqueous ReactionspratikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Board Practical Examination - 2023-24Document5 pagesChemistry Board Practical Examination - 2023-24Kevin PNo ratings yet
- Chem 33 Postlabs Expt 10-13Document11 pagesChem 33 Postlabs Expt 10-13BelaNo ratings yet
- PD LABDocument5 pagesPD LABShayden Leslie100% (1)
- Rings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie PeckDocument14 pagesRings, Polymers and Analysis (Unit 4) - OCR Chemistry Notes - Robbie Peckrobbiepeck100% (1)
- Analysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupJan MezoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative-Analysis-Of-Group-1 2 3 4 5 Anions PDFDocument56 pagesQualitative-Analysis-Of-Group-1 2 3 4 5 Anions PDFLucille Beatrice Pablo TanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Qualitative Analysis of Cations Purpose: Develop A Systematic Scheme of Separation and Analysis of A Selected Group of CationsDocument11 pagesExperiment 7: Qualitative Analysis of Cations Purpose: Develop A Systematic Scheme of Separation and Analysis of A Selected Group of CationsMayankNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid ZwiterionDocument6 pagesAmino Acid ZwiterionNaima AmjadNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document4 pagesExperiment 4Lai Zheng Hee KnightNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument28 pagesBusiness PlanKyle LimNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PLAN Word FormatDocument24 pagesBUSINESS PLAN Word FormatKyle LimNo ratings yet
- Letter of Late EnrollmentDocument1 pageLetter of Late EnrollmentKyle Lim0% (1)
- VC Policies Confirmatory SheetDocument1 pageVC Policies Confirmatory SheetKyle LimNo ratings yet
- BIO1A Class ListDocument2 pagesBIO1A Class ListKyle LimNo ratings yet
- Subject 4. - Product Design OCW PDFDocument33 pagesSubject 4. - Product Design OCW PDFJose Luis BarradasNo ratings yet
- Advances Bio Materials Science I To 13Document568 pagesAdvances Bio Materials Science I To 13Alberto Fucarino100% (1)
- Engchem ManualDocument132 pagesEngchem ManualMiriam Llanque Callisaya100% (2)
- CH 9 ChemDocument43 pagesCH 9 ChemCaroline SueperNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 8th Edition McmurryDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 8th Edition McmurryAnthonyRogersydtfp100% (71)
- ChemitryDocument44 pagesChemitrygiridharrajuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3rd Edition by Burdge ISBN Test BankDocument18 pagesChemistry 3rd Edition by Burdge ISBN Test Bankandrea100% (30)
- Physical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETDocument7 pagesPhysical Sciences Table of Specifications NCBTS-BASED For LETAnabelle MaumayNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadDocument23 pagesTopic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadSamihah YaacobNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year T-1Document2 pagesChemistry 1st Year T-1Amir HabibNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid State 1Document8 pagesNcert Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid State 1lueurrNo ratings yet
- 2011 British Chemistry Olympiad TestDocument8 pages2011 British Chemistry Olympiad TestAndrew ChenNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes Made by Students in SPM Chemistry Paper 2Document9 pagesCommon Mistakes Made by Students in SPM Chemistry Paper 2leemayjuin100% (1)
- North Nazimabad Boys Campus Reinforement Worksheet 2Document7 pagesNorth Nazimabad Boys Campus Reinforement Worksheet 2api-262668586No ratings yet
- Module 5 in Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 5 in Physical ScienceDarlyn MontillaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IntroductionDocument12 pagesModule 1 Introductionycca galianNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry by Perkin and KippingDocument373 pagesOrganic Chemistry by Perkin and KippingSanjayShirodkarNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Leah G - Gr7 - FOSIII - Semester1Final - Section1Document9 pagesKami Export - Leah G - Gr7 - FOSIII - Semester1Final - Section1Leah GNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Class IX - 2017-18 SsaDocument9 pagesSyllabus Class IX - 2017-18 SsaBhumika DNo ratings yet
- Year 11 ChemistryDocument18 pagesYear 11 Chemistrymitchell.griggsmteachNo ratings yet
- The Solid State: CBSE Board - Chemistry - 12 NCERT Exercise With SolutionsDocument16 pagesThe Solid State: CBSE Board - Chemistry - 12 NCERT Exercise With SolutionsChittaranjan PaniNo ratings yet
- CHEM 111 E-Learning Material-1Document163 pagesCHEM 111 E-Learning Material-1nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- CAl 3 EDocument7 pagesCAl 3 EAloAgNo ratings yet
- CHM 315 - Instrumental Methods of AnalysisDocument88 pagesCHM 315 - Instrumental Methods of AnalysisTemitope AkinyemiNo ratings yet
- Tibetian Monk - You Forever - Lobsang Rampa - Astral Travel Telepathy Clairvoyance AurasDocument213 pagesTibetian Monk - You Forever - Lobsang Rampa - Astral Travel Telepathy Clairvoyance AurasVandamme Neo100% (1)
- Determination of Pore Size and Pore Size Distribution - 1. Adsorbents and Catalysts PDFDocument31 pagesDetermination of Pore Size and Pore Size Distribution - 1. Adsorbents and Catalysts PDFHenrique SouzaNo ratings yet
- Chem 240 Lab Manual With Problems - 2013Document177 pagesChem 240 Lab Manual With Problems - 2013Mark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- 5.1 The Periodic Table: Chemical Periodicity: Atomic RadiusDocument7 pages5.1 The Periodic Table: Chemical Periodicity: Atomic RadiusPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- PPT's Energy Transaction Post Mid Sem Dec 21Document139 pagesPPT's Energy Transaction Post Mid Sem Dec 21Drishti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lec# 05 Decay ProcessesDocument17 pagesLec# 05 Decay ProcessesVishal MeghwarNo ratings yet