Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GEOMETRY
GEOMETRY
Uploaded by
Sanjay PanickerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GEOMETRY
GEOMETRY
Uploaded by
Sanjay PanickerCopyright:
Available Formats
TEST
GEOMETRY
QUESTIONS
SEC TIO NS
1. GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
Section 1 : GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
1 In the given figure AB || CD, ∠A = 128°, ∠E = 144°. Then, ∠FCD is equal to :
72°
64°
136°
92°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
2 In the trapezium PQRS, QR || PS, ∠Q = 90°, PQ = QR and ∠PRS = 20°. If ∠TSR = θ, then the value of
θ is :
75°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 1 of 54
55°
65°
45°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
3 In the adjoining figure, ∠ABC = 100°, ∠EDC = 120° and AB || DE. Then, ∠BCD is equal to :
80°
60°
40°
20°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
4 In the given figure, AB || CD, ∠ABO = 40° and ∠CDO = 30°. If ∠DOB = x°, then the value of x is
:
35°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 2 of 54
110°
70°
140°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
5 In the given figure, AB || CD, m∠ABF = 45° and m∠CFC = 110°. Then, m∠FDC is :
25°
45°
35°
30°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
6 n the figure given below, ABC is a triangle. BC is parallel to AE. If BC = AC, then what is the
value of ∠CAE?
20°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 3 of 54
30°
40°
50°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
7 In the figure given below, AB is parallel to CD. ∠ABC = 65°, ∠CDE = 15° and AB = AE. What is
the value of ∠AEF?
30°
35°
40°
45°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
8 The angles x°, a°, c° and (π – b)° are indicated in the figure given below. Which one of the following is
correct?
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 4 of 54
x° = a° + c° – b°
x° = b° – a° – c°
x° = a° + b° + c°
x° = a° – b° + c°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
9 Consider the following statements
I. The locus of points which are equidistant from two parallel lines is a line parallel to both of them and drawn
mid way between them.
II. The perpendicular distance of any point on this locus line from two original parallel lines are equal.
Further, no point outside this locus line has this property.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
10 A wheel makes 12 revolutions per min. The angle in radian described by a spoke of the
wheel in 1 s is:
5π/2
2π/5
3π/5
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 5 of 54
4π/5
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
11 A tangent YZ is drawn at any point Y of a circle of radius 3.5 cm. YX1 and YX2 are the two
chords of this circle. If ∠ZYX2 = 45° and O is the centre of the circle, then the length of arc
YX2 is (assume π = 22/7 )
6.5 cm
7 cm
6 cm
5.5 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
12 In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠PRQ = 40°, then what is ∠OPQ?
30°
40°
150°
50°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 6 of 54
13 If a circle is provided with measure of 19° on centre, is it possible to divide the circle into
360 equal parts?
Never
Possible when one more measure of 20 is given
Always
Possible if one more measure of 21 is given
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
14 The distance between two parallel chords of length 6 cm each in a circle of diametre 10 cm
is
8 cm
7 cm
6 cm
5.5 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
15 Three circles of diameter 10 cm each, are bound together by a rubber band, as shown in the
figure. The length of the rubber band, in cm, if it is stretched as shown, is
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 7 of 54
30
30 + 10π
10π
60 + 20π
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
16 PQ is a chord of a circle with centre O and SOR is a line segment originating from a point S
on the circle and intersecting PQ produced at R such that QR = OS. If ∠QRO = 30° then
∠POS = ?
40°
70°
90°
60°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
17 O and O' are repectively the orthocentre and cicumcentre of an acute angled triangle PQR.
the point P and O are joined and produced to meet the side QR at S. If ∠PQS = 60° and
∠QO'R = 130° then ∠RPS = ?
45°
35°
60°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 8 of 54
75°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
18 In the given figure below, ∠AOB = 48° and AC and OB intersect each other at right angles.
What is the measure of ∠OBC? (O is the centre of the circle)
44°
66°
67°
78.5°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
19 In a right angled triangle, the circumcentre of the triangle lies.
inside the triangle
outside the triangle
on the midpoint of hypotenous
on one vertex
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 9 of 54
20 AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O and radius OD is perpendicular to AB. Find the
angle BAD
60°
45°
30°
75°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
21 The sides of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 6. The triangle is :
acute-angled
right-angled
obtuse-angled
either acute-angled or right-angled
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
22 If the circumcentre of a triangle lies outside it, then the triangle is
Equilateral
Acute angled
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 10 of 54
Right angled
Obtuse angled
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
23 Taking any three of the line segments out of segments of length 2 cm, 3 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm,
the number of triangles that can be formed is :
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
24 If the length of the sides of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : 5 : 6 and the inradius of the triangle
is 3 cm, then the altitude of the triangle corresponding to the largest side as base is :
7.5 cm
6 cm
10 cm
8 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 11 of 54
25 ABC is a triangle. The bisectors of the internal angle ∠B and external angle ∠C intersect at
D. if ∠BDC = 50°, then ∠A is
100°
90°
120°
60°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
26 If the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 41 cm and the sum of the other two sides is 49 cm,
find the difference between the other sides.
30 cm
31 cm
32 cm
29 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
27 In a right-angled triangle, the product of two sides is equal to half of the square of the third
side i.e., hypotenuse. One of the acute angle must be
60°
30°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 12 of 54
45°
15°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
28 ABC is an isosceles triangle such that AB = AC and AD is the median to the base BC with
∠ABC = 35°. Then ∠BAD is
35°
55°
70°
110°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
29 An isosceles triangle ABC is right-angled at B. D is a point inside the triangle ABC. P and Q
are the feet of the perpendiculars drawn from D on the side AB and AC respectively of
ΔABC. If AP = a cm, AQ = b cm and ∠BAD = 15°, sin 75° = ?
2b / √3a
a / 2b
√3a / 2b
2a / √3b
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 13 of 54
30 Consider the following statements:
(I). If G is the centroid of ΔABC, then GA = GB = GC.
(II). If H is the orthocentre of ΔABC, then HA = HB = HC.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Only I
Only II
Both I and II
Neither I nor II
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
31 In a Δ ABC, if D and E are the points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
and if AD = x , DB = x – 2 , AE = x + 2 and EC = x – 1. then find the value of x .
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
32 Longest side of a triangle is 20 cm and another side is 10 cm. If area of the triangle is 80
cm2, then what is the length (in cm) of its third side?
260
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 14 of 54
250
256
240
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
33 In a ∆ ABC, the sides AB and AC have been produced to D and E. Bisectors of ∠ CBD and ∠
BCE meet at O. If ∠ A = 64°, then ∠ BOC is :
52°
58°
26°
112°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
34 In ΔABC, AB = AC, ∠B = 70°, ∠BAD = 80°, ∠ADE = ?
150°
135°
140°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 15 of 54
120°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
35 In the above figure, if area of triangle ABC is 64 sq. units, then find the area of triangle PQR,
where D, E and F are mid points of sides of ΔABC and P, Q and R are midpoints of sides of
ΔDEF.
4 sq units
6 sq units
8 sq units
16 sq units
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
36 Two medians PS and RT of ΔPQR intersect at G at right angles. If PS = 9 cm and RT = 6 cm,
then the length of RS in cm is
10
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 16 of 54
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
37 The length of side AB and side BC of a scalene triangle ABC are 12 cm and 8 cm respectively. The value of angle
C is 59°. Find the length of side AC.
10
12
14
16
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
38 The cordinates of the incentre of the triangle whose sides are 3x – 4y = 0, 5x + 12y = 0 and y
– 15 = 0, are
(1, 8)
(–1, 8)
(2, 8)
(2, –8)
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
39 The in-radius of an equilateral triangle is of length 3 cm. Then the length of each of its
medians is
12 cm
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 17 of 54
9 / 2 cm
4 cm
9 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
40 If the orthocentre and the centroid of a triangle are the same, then the triangle is :
Scalene
Right angled
Equilateral
Obtuse angled
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
41 In a cyclic quadrilateral ∠A + ∠C = ∠B + ∠D = ?
270°
360°
90°
180°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 18 of 54
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
42 If ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral in which ∠A = 4x°, ∠B = 7x°, ∠C = 5y°, ∠D = y°, then x : y is
3:4
4:3
5:4
4:5
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
43 A quadrilateral ABCD circumscribes a circle and AB = 6 cm, CD = 5 cm and AD = 7 cm. The
length of side BC is
4 cm
5 cm
3 cm
6 cm
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
44 ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral and AD is a diameter. If ∠BAC = 55° then value of ∠ADC is
55°
35°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 19 of 54
145°
125°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
45 The difference between the exterior and interior angles at a vertex of a regular polygon is
150°. The number of sides of the polygon is
10
15
24
30
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
46 Measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon can never be :
150°
105°
108°
144°
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
47 The sum of all interior angles of a regular polygon is twice the sum of all its exterior angles.
The number of sides of the polygon is
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 20 of 54
10
12
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
48 The ratio between the number of sides of two regular polygons is 1 : 2 and the ratio
between their interior angles is 2 : 3. The number of sides of these polygons is respectively
6, 12
5, 10
4, 8
7, 14
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
49 There are two regular polygons with number of sides equal to (n – 1) and (n + 2). Their
exterior angles differ by 6°. The value of n is
14
12
13
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 21 of 54
11
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
50 If each interior angle of a regular polygon is 150°, the number of sides of the polygon is
10
15
None of these
Correct: +3 · Incorrect: -1
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Questions Page 22 of 54
TEST
GEOMETRY
ANSWERS
SECTIONS
1. GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
Section 1 : GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
1 92°
2 65°
3 40°
4 70°
5 25°
6 50°
7 35°
8 x° = a° + b° + c°
9 Both I and II
10 2π/5
11 5.5 cm
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Answers Page 23 of 54
12 50°
13 Always
14 8 cm
15 30 + 10π
16 90°
17 35°
18 66°
19 on the midpoint of hypotenous
20 45°
21 obtuse-angled
22 Obtuse angled
23 2
24 7.5 cm
25 100°
26 31 cm
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Answers Page 24 of 54
27 45°
28 55°
29 √3a / 2b
30 Neither I nor II
31 4
32 260
33 58°
34 150°
35 4 sq units
36 5
37 14
38 (–1, 8)
39 9 cm
40 Equilateral
41 180°
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Answers Page 25 of 54
42 4 : 3
43 4 cm
44 145°
45 24
46 105°
47 6
48 4, 8
49 13
50 None of these
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Answers Page 26 of 54
TEST
GEOMETRY
SOLUTIONS
SECTIONS
1. GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
Section 1 : GEOMETRY - 50 Questions
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 27 of 54
4
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 28 of 54
7
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 29 of 54
8
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 30 of 54
9
10
11
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 31 of 54
12
13
14
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 32 of 54
15
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 33 of 54
16
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 34 of 54
17
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 35 of 54
18
19
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 36 of 54
20
21
22
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 37 of 54
23
24
25
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 38 of 54
26
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 39 of 54
27
28
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 40 of 54
29
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 41 of 54
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 42 of 54
30
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 43 of 54
31
32
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 44 of 54
33
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 45 of 54
34
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 46 of 54
35
36
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 47 of 54
37
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 48 of 54
38
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 49 of 54
39
40
41
42
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 50 of 54
43
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 51 of 54
44
45
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 52 of 54
46
47
48
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 53 of 54
49
50
GEOMETRY · GEOMETRY · Solutions Page 54 of 54
You might also like
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadDocument38 pagesElementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadCharles Vanhorne100% (30)
- Lines and Angles Maths Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument2 pagesLines and Angles Maths Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- Airfoil Analysis in WorkbenchDocument26 pagesAirfoil Analysis in Workbenchfab19910% (1)
- Class 9 Chapter 6 Worksheet Math Lines and Angles: InstructionsDocument12 pagesClass 9 Chapter 6 Worksheet Math Lines and Angles: InstructionsyounisNo ratings yet
- Ix Maths CH 6 Lines and AnglesDocument14 pagesIx Maths CH 6 Lines and AnglesmjpraveenaNo ratings yet
- Rhombus SquareDocument17 pagesRhombus SquareAltheus Miguel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: Practice Set 5.1Document25 pagesQuadrilaterals: Practice Set 5.1Rohan ChavanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1 Lines and Angle II by KelvinDocument6 pagesMathematics-Form 3-Chapter 1 Lines and Angle II by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- 68 P SJV Ek CKndee VITIs 7Document15 pages68 P SJV Ek CKndee VITIs 7DEBJITA MAITY XI CNo ratings yet
- Math Foundation Review Teacher's Edition: TrigonometryDocument24 pagesMath Foundation Review Teacher's Edition: TrigonometrytwsttwstNo ratings yet
- MTH 202 Course MaterialDocument88 pagesMTH 202 Course MaterialSakote Tobiloba IsaacNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5Document42 pagesUnit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5 Unit 5AjiteshPaddaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11 AnswersDocument10 pagesMaths Class Ix Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 11 Answersyash upasaniNo ratings yet
- TG GeometryDocument135 pagesTG GeometryVivekRajuNo ratings yet
- 7.G.B5 - Angle Relationships - 10QDocument4 pages7.G.B5 - Angle Relationships - 10Qicka83No ratings yet
- Geometry BasicsDocument136 pagesGeometry Basicsmrs raamNo ratings yet
- GEng 111g - TutorialDocument25 pagesGEng 111g - TutorialRomnick MalulanNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 06 Lines and AnglesDocument17 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 09 Chapter 06 Lines and AnglesamitjoulNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lines and Angles: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesDocument9 pagesGrade 7 Lines and Angles: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesRinoanne Blare DumlingNo ratings yet
- Week4 - Trigonometry UpdatedDocument26 pagesWeek4 - Trigonometry Updatedhamz9k1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Guided Notes To TrigonometryDocument10 pagesChapter 1 - Guided Notes To TrigonometryfallonNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 MathsDocument47 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Mathsfunson123No ratings yet
- Module+5+ +Engg+Math+ +trigonometry+ (Part+3)Document14 pagesModule+5+ +Engg+Math+ +trigonometry+ (Part+3)Satoru FujinumaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry BasicsDocument11 pagesTrigonometry BasicsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document81 pagesChapter 7Saurav UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MC35 Geometry Ch01 Handout-209Document8 pagesMC35 Geometry Ch01 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialDocument28 pagesStudy Materialbobadeshraddha8No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lines and Angles inDocument16 pagesGrade 7 Lines and Angles inSourav bhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semster - Lec02 - Angle & Directions PDFDocument26 pages2nd Semster - Lec02 - Angle & Directions PDFDakheel malekoNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Cut by Transversal - TestDocument7 pagesParallel Lines Cut by Transversal - TestNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Lines & AnglesDocument15 pagesLines & AnglesDarkNo ratings yet
- 2025 Week4 Geometry1Document33 pages2025 Week4 Geometry1Sanchit ChopraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MathsDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 MathsSubhashsish GhoshNo ratings yet
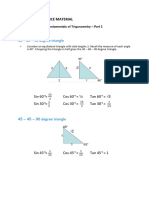
- Fundamentals of Trigonometry - Part 3Document3 pagesFundamentals of Trigonometry - Part 3leilay003No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and AnglesDocument15 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and AnglesDr. J. Josephine JACNo ratings yet
- Polygons TasksDocument16 pagesPolygons TasksнуркызNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument10 pagesMathsRaajeNo ratings yet
- Class IX Maths CH-6 - SOLUTIONSDocument5 pagesClass IX Maths CH-6 - SOLUTIONSshweta shuklaNo ratings yet
- 15 75 90 Triangle ProblemsDocument3 pages15 75 90 Triangle Problemsvidyakumari808940No ratings yet
- Using The Sine RuleDocument7 pagesUsing The Sine RuleJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- Ocr - Xenon Entrance Booklet-2024Document60 pagesOcr - Xenon Entrance Booklet-2024chirag242424jNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledRajarshiNo ratings yet
- 9th GeometryDocument28 pages9th Geometrywww.r2dk2No ratings yet
- Lines and Angles: Sample Question 1Document9 pagesLines and Angles: Sample Question 1tsbaruah202No ratings yet
- 7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 6Document36 pages7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 6Ramesh rajNo ratings yet
- Algebraic FormulaDocument73 pagesAlgebraic Formulagspkishore7953No ratings yet
- (Eduwaves360) CA - 11th (2019C) - EDocument32 pages(Eduwaves360) CA - 11th (2019C) - EAlbertNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZDocument9 pagesSolution:: Ex 3.3 Consider The Following Parallelograms. Find The Values of The Unknowns X, Y, ZpadmaNo ratings yet
- SoalDocument16 pagesSoalrfrmsyahNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine LawDocument6 pagesSine and Cosine Lawmuhamad98No ratings yet
- 8.0 Trigonometry TheoryDocument38 pages8.0 Trigonometry TheoryPramodLomateNo ratings yet
- ExamView - Practice TestDocument13 pagesExamView - Practice Testlornehess100% (2)
- Geometry NotesDocument135 pagesGeometry NotesNAVEEN NELLINo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledHazeel HashimNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 3Document9 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 3nandisunilkumar3No ratings yet
- Lines and Angles AnswersDocument1 pageLines and Angles AnswersAjay Avinash KNo ratings yet
- Geometry PDFDocument12 pagesGeometry PDFGeta Bercaru100% (1)
- 10 DecemberDocument42 pages10 DecemberparodyaanandNo ratings yet
- traversing_chapter_4_31Document10 pagestraversing_chapter_4_31Shaik Mastan ValiNo ratings yet
- Jmap 1384 Regents Book by Chapter GeometryDocument59 pagesJmap 1384 Regents Book by Chapter GeometryRishie Kumar LoganathanNo ratings yet
- 12 Business Studies CH 06 Staffing UnlockedDocument6 pages12 Business Studies CH 06 Staffing UnlockedSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- CLASS 12 Accountancy-PQDocument27 pagesCLASS 12 Accountancy-PQSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- Kvs Jaipur Xii Acc QP & Ms (2nd PB) 23-24 (Set-1)Document11 pagesKvs Jaipur Xii Acc QP & Ms (2nd PB) 23-24 (Set-1)Sanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- The Delegate Handbook - OOWMUNDocument20 pagesThe Delegate Handbook - OOWMUNSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument11 pagesEnglish ProjectSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (M)Document13 pagesAssignment 1 (M)Sanjay Panicker100% (1)
- Geo ProjectDocument20 pagesGeo ProjectSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- Sources of Business FinanceDocument9 pagesSources of Business FinanceSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- Lulu Corp. Marketing AnalysisDocument36 pagesLulu Corp. Marketing AnalysisSanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- QP XI AccountancyDocument13 pagesQP XI AccountancySanjay Panicker100% (1)
- Acc Xi See QP With BP, MS-31-43Document13 pagesAcc Xi See QP With BP, MS-31-43Sanjay PanickerNo ratings yet
- Major Assignment F21 (Friday)Document4 pagesMajor Assignment F21 (Friday)sapna thakurNo ratings yet
- 5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDocument2 pages5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDudeNo ratings yet
- Chapt03 Fta PDFDocument29 pagesChapt03 Fta PDFrodrigo_domNo ratings yet
- Puzzles Asked in Sapient With SolutionsDocument6 pagesPuzzles Asked in Sapient With SolutionsMayank NagpalNo ratings yet
- Breeding Cornell Algebra 1 Semester 1 CBMDocument18 pagesBreeding Cornell Algebra 1 Semester 1 CBMapi-258279393No ratings yet
- Chapter-I-Stress-1 11 21 3Document5 pagesChapter-I-Stress-1 11 21 3Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Optimizing and Interfacing With Cython: Centre de Biophysique Moléculaire (Orléans) Synchrotron Soleil (ST Aubin)Document22 pagesOptimizing and Interfacing With Cython: Centre de Biophysique Moléculaire (Orléans) Synchrotron Soleil (ST Aubin)Nur IzzahudinNo ratings yet
- Selected Books For Electronic Hobby Center (EHC) : A. Books (Available in The Resource Centre)Document9 pagesSelected Books For Electronic Hobby Center (EHC) : A. Books (Available in The Resource Centre)Rajalakshmi BashyamNo ratings yet
- Thesis Using Structural Equation ModelingDocument8 pagesThesis Using Structural Equation Modelingqrikaiiig100% (1)
- New Zealand Adapting Austroads Design Guide 2008Document77 pagesNew Zealand Adapting Austroads Design Guide 2008Ahmad Faathir WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- TRIG FUNCTIONS Lesson Solving Right TrianglesDocument52 pagesTRIG FUNCTIONS Lesson Solving Right TrianglesRudi BerlianNo ratings yet
- Avatarme: Realistically Renderable 3D Facial Reconstruction "In-The-Wild"Document10 pagesAvatarme: Realistically Renderable 3D Facial Reconstruction "In-The-Wild"Joseph OmisNo ratings yet
- CV Albert CH Soewongsono PDFDocument6 pagesCV Albert CH Soewongsono PDFSofia Yusnur RafidaNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic Cost and ComplexityDocument29 pagesAlgorithmic Cost and Complexityhbjethva6977No ratings yet
- Appendix A Worksheet 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesAppendix A Worksheet 1 AnswersdsfjhvbNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Lab Manual 2018-19 5th SemDocument68 pagesMicrocontroller Lab Manual 2018-19 5th Semsandeep sNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument30 pagesHTML NotesSudheer Reddy PothuraiNo ratings yet
- Final Spring07 Solutions SampleDocument15 pagesFinal Spring07 Solutions SampleAnass BNo ratings yet
- 7 - Measurement of VariablesScallingReliabilityDocument49 pages7 - Measurement of VariablesScallingReliabilityRizaNo ratings yet
- ForecastingDocument31 pagesForecastinghananshahid96No ratings yet
- Mindsight CodexDocument87 pagesMindsight CodexFathin NafisaNo ratings yet
- Exam Review - 2012Document3 pagesExam Review - 2012Clement HoangNo ratings yet
- 08 Dummy VariableDocument24 pages08 Dummy VariableZiaNaPiramLiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Compression Member PDFDocument43 pages3 - Compression Member PDFYetty Oktavianita100% (2)
- MODULE 6 ASSIGNMENT 1: How The Konigsberg Bridge Problem Changed MathematicsDocument2 pagesMODULE 6 ASSIGNMENT 1: How The Konigsberg Bridge Problem Changed MathematicsChoco PeanutNo ratings yet
- Prob DDocument4 pagesProb DnozetsubounolifeNo ratings yet
- Constructing Infinitely Many Smooth Structures On Small 4-ManifoldsDocument20 pagesConstructing Infinitely Many Smooth Structures On Small 4-Manifoldsapi-19814561No ratings yet
- Roman NumeralsDocument13 pagesRoman NumeralsJames GabatoNo ratings yet
- Thermo PDFDocument5 pagesThermo PDFjayven minguillanNo ratings yet