Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANA Terminology
ANA Terminology
Uploaded by
Laura PetiotCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- A&P1 Final Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesA&P1 Final Exam Study GuideRhett Clark100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesMissy Sanders100% (1)
- Skin Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Biology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014Document13 pagesBiology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014santosh.manojNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Fiber Blanket: DescriptionDocument2 pagesCeramic Fiber Blanket: DescriptionKiatchai IttivikulNo ratings yet
- 420-510chapter 1 (4) Types of TissuesDocument6 pages420-510chapter 1 (4) Types of Tissuestomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course Outline. Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course OutlineDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course Outline. Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course OutlineTran9716No ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDocument4 pagesSimple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDimple Lexiry Gloria100% (1)
- Histology 2 EpitheliumDocument53 pagesHistology 2 EpitheliumAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- General Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BDocument133 pagesGeneral Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BHenok GirmaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL HISTOLOGY pdf-1Document22 pagesGENERAL HISTOLOGY pdf-1Dany Samuel100% (1)
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDocument50 pagesSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDocument10 pagesCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Types of TissuesDocument7 pagesTypes of TissuesKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument20 pagesTissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: by Fayez A. ElmabhouhDocument44 pagesAnimal Tissues: by Fayez A. ElmabhouhShamshad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Tissue ReviewerDocument3 pagesTissue ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 EpitheliaDocument5 pagesLecture02 Epitheliaazgaray7No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument49 pagesConnective TissuePaapa MorrisNo ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityDocument14 pagesTissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityroseNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument108 pagesAnimal TissueSumita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and Connective TissuesDocument23 pagesEpithelial and Connective TissuesnasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lab Exam 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio 11 Lab Exam 3 Revieweririsiri28No ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- Lesson IntegumentaryDocument31 pagesLesson IntegumentaryTaryhana FitzgerlandNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionDocument13 pagesTissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionnagahushanamNo ratings yet
- 4) Integrated Small IntestineDocument13 pages4) Integrated Small Intestinektama0331No ratings yet
- HI 2.1 Jaringan EpitelDocument37 pagesHI 2.1 Jaringan EpitelJoanna TaniaNo ratings yet
- Histology LecDocument258 pagesHistology LecBan JMNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Tissues 1.Document2 pagesTissues 1.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lesson IDocument3 pagesAnaphy Lesson IPerpolNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Zoology 100 Notes 6Document9 pagesZoology 100 Notes 6Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial TissueGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium 2021Document40 pagesEpithelium 2021Charmaine LucNo ratings yet
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Document2 pagesJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Shubham PawadeNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Notes - Epithelial and ConnectiveDocument31 pagesAnimal Tissue Notes - Epithelial and ConnectivePrakritiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2-2.3Document15 pagesChapter 2.2-2.3Gerard Bio100% (2)
- Connective Tissue IDocument8 pagesConnective Tissue IElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- 07lect EpitheliumCTissue Summary2017Document4 pages07lect EpitheliumCTissue Summary2017Dan ChoiNo ratings yet
- B 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramDocument27 pagesB 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramSANTHIYA A/P MOHANA SUNDARAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnaphyDocument3 pagesChapter 4 AnaphyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Animal TissueDocument32 pagesStructure and Function of Animal TissueFajar Oktavia RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument16 pagesEpithelial TissuesSubha DeyNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Vertebrate Integumentary System: By: Geonyzl J. Lepiten-AlviolaDocument93 pagesVertebrate Integumentary System: By: Geonyzl J. Lepiten-AlviolaGeonyzl L. AlviolaNo ratings yet
- Epithiliam Tissue OutlineDocument11 pagesEpithiliam Tissue OutlineAleks BlackNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Document166 pagesLecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Selaina NawadraNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Skin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Tds-Smeww 2540 CDocument3 pagesTds-Smeww 2540 Csan chueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry PDFPritishNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerHewlett Pearl BawalanNo ratings yet
- Clariant Brochure Let Your Ideas Flow HOSTAGEL 2014 ENDocument8 pagesClariant Brochure Let Your Ideas Flow HOSTAGEL 2014 ENjefequimicoNo ratings yet
- E14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsDocument4 pagesE14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsGUDANG KARAOKE KITANo ratings yet
- Thermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalDocument27 pagesThermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalThejasjayadeepNo ratings yet
- Arc 1st Mod Arch 503 Building Services Question Bank 15 Mark QuestionsDocument33 pagesArc 1st Mod Arch 503 Building Services Question Bank 15 Mark QuestionsVictor Deb RoyNo ratings yet
- Biosensores Electroquímicos para La Detección de PatógenosDocument30 pagesBiosensores Electroquímicos para La Detección de PatógenosValentina RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ®mowilith LDM 1881: Technical Data Sheet Characteristics StabilizationDocument2 pages®mowilith LDM 1881: Technical Data Sheet Characteristics StabilizationAmr RagabNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Q4 M4Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q4 M4roxan clabria100% (1)
- Openstax College Concepts of Biology Supplemental Test Items Chapter 09: Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesOpenstax College Concepts of Biology Supplemental Test Items Chapter 09: Molecular BiologyFatima BjaijihNo ratings yet
- ElectrophileDocument17 pagesElectrophilemdikramul hoqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument170 pagesLesson 10 - Haloalkanes & HaloarenesAwez FahadNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesMole ConceptAgriye KambojNo ratings yet
- SGS - Price List - Nov 2010 - Full - Up DatedDocument13 pagesSGS - Price List - Nov 2010 - Full - Up DatedabushahadatNo ratings yet
- BT-171130D2 Non Transfer Lip Gross (英文版)Document1 pageBT-171130D2 Non Transfer Lip Gross (英文版)Diyan MayasariNo ratings yet
- 20 HFL 0356 - Whitepaper - Used Oil Analysis Tech Bulletin Whitepaper - v5Document7 pages20 HFL 0356 - Whitepaper - Used Oil Analysis Tech Bulletin Whitepaper - v5DANIEL ZORRONo ratings yet
- August 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDocument11 pagesAugust 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDennis MuzilaNo ratings yet
- Glysantin G64 - Engine Coolant Concentrate PDFDocument6 pagesGlysantin G64 - Engine Coolant Concentrate PDFNicko RizqienggalNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument80 pagesHydrocarbonsina stanevaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Group-13 ElementsDocument5 pagesChemistry of Group-13 ElementsMd. Masud RanaNo ratings yet
- Bohr Effect: Carbon DioxideDocument2 pagesBohr Effect: Carbon DioxideTiToNo ratings yet
- Staining of Connective TissueDocument3 pagesStaining of Connective TissueJey TeeNo ratings yet
- Potential Safety Hazards - DMFDocument16 pagesPotential Safety Hazards - DMFs adhikariNo ratings yet
- Surface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteDocument13 pagesSurface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteGuillaume LepêcheurNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityDocument38 pagesAubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Protein MetabolismDocument78 pagesProtein MetabolismU2002862 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Sec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDocument15 pagesSec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDavid SobralNo ratings yet
ANA Terminology
ANA Terminology
Uploaded by
Laura PetiotOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ANA Terminology
ANA Terminology
Uploaded by
Laura PetiotCopyright:
Available Formats
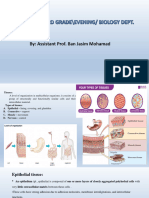
Types of tissues
1. Epithelial tissue: sheets of cells that cover the exterior of the bodies, internal organs and
cavities, glands
2. Connective tissue: Binds cells and organs together. Protection, support, integration
3. Muscle tissue: excitable, responds to stimulation. Skeletal, smooth, cardiac
4. Nervous tissue: excitable, allows for the propagation of nerve impulses. Brain, spinal cord,
nerves.
1. Epithelial tissue: categories, features, functions, basement membrane, junctions,
classifications, glands
1.1 Epithelial tissue: broad categories
1. Epidermis: external surfaces
a. Dermis (connective tissue) -> skin
2. Mesothelium: internal cavities and organs. Pleura (lungs), pericardium (lining around heart),
chest, abdomen
a. Serous membrane: mesothelium + connective tissue -> produces lubricant
3. Endothelium: blood and lymph vessels
4. Lamina propria: connective tissue underneath epidermis that covers surfaces exposed to
the exterior.
a. Mucous membrane: epithelium + lamina propria
1.2 Basement membrane
1. Basement membrane: provides structural support, scaffold for repair and regeneration
2. Apical surface
3. Basal lamina: attached to epithelium. Glycoproteins, collagen
4. Reticular lamina: produced by the connective tissue
1.3 Cellular junctions: tight, anchoring, gap
5. Tight junction
a. Occludin
b. Claudins
c. JAM
6. Anchoring junctions: desmosome, hemidesmosome, adheren
7. Desmosome
a. Plaque: structural protein on the inner surface of the epithelial cell membrane
b. Cadherin: transmembrane glycoprotein that acts as an adhesion molecule; projects
through the membrane and links to other cadherins
c. Keratin: cytoskeletal filaments, project out of the plaque
8. Hemidesmosome
a. Integrin: transmembrane protein
9. Adheren
a. Actin: contractile protein on the cytoplasmic surface of the cells that can form an
actin belt along the lateral aspects of the cells
10. Gap junctions
a. Connexons (composed of connexins): transmembrane proteins that facilitate the
movement of small molecules and ions between the cytoplasm od adjacent cells
1.4 Classifications
1. Squamous cell type: flattened and thin
2. Cuboidal cell type
3. Columnar cell type
4. Stratified: multiple layers
5. Pseudostratified: single layer of irregular cells
6. Transitional epithelium: as the bladder fills up, apical cells’ shape changes from cuboidal to
squamous
1.5 Glands
1. Serous glands: multicellular exocrine glands that develop from simple epithelium and
secrete directly into the internal cavities of the chest/ abdomen
2. Merocrine secretion: product brought to the apical surface of the cell by vesicles, released
by exocytosis
3. Apocrine secretion: product accumulates near the apical surface, which pinches off
4. Holocrine secretion: the entire cell bursts, releasing accumulated product
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- A&P1 Final Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesA&P1 Final Exam Study GuideRhett Clark100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Exam 2 NotesMissy Sanders100% (1)
- Skin Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Biology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014Document13 pagesBiology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014santosh.manojNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Fiber Blanket: DescriptionDocument2 pagesCeramic Fiber Blanket: DescriptionKiatchai IttivikulNo ratings yet
- 420-510chapter 1 (4) Types of TissuesDocument6 pages420-510chapter 1 (4) Types of Tissuestomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course Outline. Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course OutlineDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course Outline. Chapter 4 Tissue - Summary of Notes Which Follows The Course OutlineTran9716No ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDocument4 pagesSimple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDimple Lexiry Gloria100% (1)
- Histology 2 EpitheliumDocument53 pagesHistology 2 EpitheliumAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- General Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BDocument133 pagesGeneral Histology: Unit Three By: Fikre BHenok GirmaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL HISTOLOGY pdf-1Document22 pagesGENERAL HISTOLOGY pdf-1Dany Samuel100% (1)
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDocument50 pagesSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Answer Key-TissuesDocument10 pagesCh05 Answer Key-TissuesGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- Types of TissuesDocument7 pagesTypes of TissuesKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument20 pagesTissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: by Fayez A. ElmabhouhDocument44 pagesAnimal Tissues: by Fayez A. ElmabhouhShamshad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Tissue ReviewerDocument3 pagesTissue ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 EpitheliaDocument5 pagesLecture02 Epitheliaazgaray7No ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument49 pagesConnective TissuePaapa MorrisNo ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityDocument14 pagesTissues, Glands, and Membranes: Ontent Earning CtivityroseNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument108 pagesAnimal TissueSumita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and Connective TissuesDocument23 pagesEpithelial and Connective TissuesnasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 Lab Exam 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio 11 Lab Exam 3 Revieweririsiri28No ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- Lesson IntegumentaryDocument31 pagesLesson IntegumentaryTaryhana FitzgerlandNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionDocument13 pagesTissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionnagahushanamNo ratings yet
- 4) Integrated Small IntestineDocument13 pages4) Integrated Small Intestinektama0331No ratings yet
- HI 2.1 Jaringan EpitelDocument37 pagesHI 2.1 Jaringan EpitelJoanna TaniaNo ratings yet
- Histology LecDocument258 pagesHistology LecBan JMNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Anatomy 1)Document83 pagesTissues (Anatomy 1)nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Tissues 1.Document2 pagesTissues 1.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lesson IDocument3 pagesAnaphy Lesson IPerpolNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIDocument110 pagesAnimal Tissue: Chapter - 10 Std. XIYash Soneji100% (2)
- Zoology 100 Notes 6Document9 pagesZoology 100 Notes 6Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueDocument16 pagesMicroscopic Study of Epithelial Tissue and Connective TissueSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial TissueGhadeer M HassanNo ratings yet
- Epithelium 2021Document40 pagesEpithelium 2021Charmaine LucNo ratings yet
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Document2 pagesJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 7-8Shubham PawadeNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Notes - Epithelial and ConnectiveDocument31 pagesAnimal Tissue Notes - Epithelial and ConnectivePrakritiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2-2.3Document15 pagesChapter 2.2-2.3Gerard Bio100% (2)
- Connective Tissue IDocument8 pagesConnective Tissue IElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- 07lect EpitheliumCTissue Summary2017Document4 pages07lect EpitheliumCTissue Summary2017Dan ChoiNo ratings yet
- B 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramDocument27 pagesB 28-MIBS-Histology Log Book - Model DiagramSANTHIYA A/P MOHANA SUNDARAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnaphyDocument3 pagesChapter 4 AnaphyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Animal TissueDocument32 pagesStructure and Function of Animal TissueFajar Oktavia RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument16 pagesEpithelial TissuesSubha DeyNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- Vertebrate Integumentary System: By: Geonyzl J. Lepiten-AlviolaDocument93 pagesVertebrate Integumentary System: By: Geonyzl J. Lepiten-AlviolaGeonyzl L. AlviolaNo ratings yet
- Epithiliam Tissue OutlineDocument11 pagesEpithiliam Tissue OutlineAleks BlackNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Document166 pagesLecture 5.1: TISSUES - Human Biology (FSM)Selaina NawadraNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Skin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSkin cell, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Tds-Smeww 2540 CDocument3 pagesTds-Smeww 2540 Csan chueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry PDFPritishNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewerHewlett Pearl BawalanNo ratings yet
- Clariant Brochure Let Your Ideas Flow HOSTAGEL 2014 ENDocument8 pagesClariant Brochure Let Your Ideas Flow HOSTAGEL 2014 ENjefequimicoNo ratings yet
- E14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsDocument4 pagesE14015 Bro en A4 v4 Cga Diss Cylinder ConnectionsGUDANG KARAOKE KITANo ratings yet
- Thermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalDocument27 pagesThermal Issues About Li-Ion Batteries and Recent Progress in Battery ThermalThejasjayadeepNo ratings yet
- Arc 1st Mod Arch 503 Building Services Question Bank 15 Mark QuestionsDocument33 pagesArc 1st Mod Arch 503 Building Services Question Bank 15 Mark QuestionsVictor Deb RoyNo ratings yet
- Biosensores Electroquímicos para La Detección de PatógenosDocument30 pagesBiosensores Electroquímicos para La Detección de PatógenosValentina RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ®mowilith LDM 1881: Technical Data Sheet Characteristics StabilizationDocument2 pages®mowilith LDM 1881: Technical Data Sheet Characteristics StabilizationAmr RagabNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Q4 M4Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q4 M4roxan clabria100% (1)
- Openstax College Concepts of Biology Supplemental Test Items Chapter 09: Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesOpenstax College Concepts of Biology Supplemental Test Items Chapter 09: Molecular BiologyFatima BjaijihNo ratings yet
- ElectrophileDocument17 pagesElectrophilemdikramul hoqueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument170 pagesLesson 10 - Haloalkanes & HaloarenesAwez FahadNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument24 pagesMole ConceptAgriye KambojNo ratings yet
- SGS - Price List - Nov 2010 - Full - Up DatedDocument13 pagesSGS - Price List - Nov 2010 - Full - Up DatedabushahadatNo ratings yet
- BT-171130D2 Non Transfer Lip Gross (英文版)Document1 pageBT-171130D2 Non Transfer Lip Gross (英文版)Diyan MayasariNo ratings yet
- 20 HFL 0356 - Whitepaper - Used Oil Analysis Tech Bulletin Whitepaper - v5Document7 pages20 HFL 0356 - Whitepaper - Used Oil Analysis Tech Bulletin Whitepaper - v5DANIEL ZORRONo ratings yet
- August 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDocument11 pagesAugust 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDennis MuzilaNo ratings yet
- Glysantin G64 - Engine Coolant Concentrate PDFDocument6 pagesGlysantin G64 - Engine Coolant Concentrate PDFNicko RizqienggalNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument80 pagesHydrocarbonsina stanevaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Group-13 ElementsDocument5 pagesChemistry of Group-13 ElementsMd. Masud RanaNo ratings yet
- Bohr Effect: Carbon DioxideDocument2 pagesBohr Effect: Carbon DioxideTiToNo ratings yet
- Staining of Connective TissueDocument3 pagesStaining of Connective TissueJey TeeNo ratings yet
- Potential Safety Hazards - DMFDocument16 pagesPotential Safety Hazards - DMFs adhikariNo ratings yet
- Surface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteDocument13 pagesSurface Typochemistry of Hydrothermal PyriteGuillaume LepêcheurNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityDocument38 pagesAubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Protein MetabolismDocument78 pagesProtein MetabolismU2002862 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Sec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDocument15 pagesSec 4.13 - Hydrolysis (Notes) : Group 1 (Alkali Metal Ions) Eg. Li Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Ions) Eg. BeDavid SobralNo ratings yet