Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsBiologynotes
Biologynotes
Uploaded by
amazingapple35Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Blood BiochemistryDocument124 pagesBlood BiochemistrySohail AhamdNo ratings yet
- Composition & Functions of BloodDocument15 pagesComposition & Functions of BloodShahroze AlamNo ratings yet
- CH 19 MartiniDocument12 pagesCH 19 MartinijaneNo ratings yet
- Blood - WikipediaDocument106 pagesBlood - WikipediaZoha AliNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument79 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemhed-ikaquinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument39 pagesChapter 10 BloodLovely FinuliarNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingDocument21 pagesAnemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument24 pagesBlood ComponentsJames Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Blood 1Document28 pagesBlood 1Miss KayaniNo ratings yet
- Blood@Wikipedia Org enDocument18 pagesBlood@Wikipedia Org enHelmiNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument103 pagesBloodrizwanbas50% (2)
- BloodDocument14 pagesBloodvardhan_16No ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodKurt HillNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Sem1 Year1 BMwk1 2012 01 27Document10 pagesLec1 Sem1 Year1 BMwk1 2012 01 27sehrish_salamNo ratings yet
- Blood: General Characteristics of BloodDocument9 pagesBlood: General Characteristics of BloodMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofDocument2 pagesBlood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Blood: Blood Is A SpecializedDocument1 pageBlood: Blood Is A Specializedhai haiNo ratings yet
- f3 SC Chap 2Document31 pagesf3 SC Chap 2Chong Yek PhengNo ratings yet
- Online Assignment: Submitted byDocument11 pagesOnline Assignment: Submitted byPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Biology Slides - With BiblioDocument43 pagesBiology Slides - With BiblioJohannes TjendroNo ratings yet
- Hoffman - Hematology. Basic Principles and Practice (3th Edition)Document117 pagesHoffman - Hematology. Basic Principles and Practice (3th Edition)Carmina Lepa100% (1)
- Cells : Further InformationDocument7 pagesCells : Further InformationMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- Functions of BloodDocument10 pagesFunctions of BloodKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument2 pagesBlood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchMichelle E. CapacioNo ratings yet
- Blood STDSDocument49 pagesBlood STDSNaveelaNo ratings yet
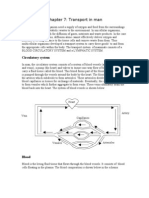
- Chapter 7 Transport in ManDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Transport in ManSheik Mohammud Muzzammil NabybaccusNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument3 pagesBloodRANAAYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 Blood MariebDocument30 pagesChapter17 Blood MariebMario AndersonNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi DARAHDocument31 pagesFisiologi DARAHTririn RinantiNo ratings yet
- Blood ReviewDocument35 pagesBlood ReviewCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- Blood and Clotting FactorsDocument34 pagesBlood and Clotting FactorsAnand KasiNo ratings yet
- BloodphysiologypptDocument103 pagesBloodphysiologypptShfici AdanNo ratings yet
- Text For Reding BloodDocument39 pagesText For Reding BloodFjhvbhhNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument4 pagesBloodatikarahmansuba123No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Blood 11.1 Functions of Blood: - 91% Water - 7% Proteins (Dissolved)Document3 pagesChapter 11: Blood 11.1 Functions of Blood: - 91% Water - 7% Proteins (Dissolved)Jennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Revised Chapter-8 - Google Slide - Hematology - Blood SystemDocument20 pagesRevised Chapter-8 - Google Slide - Hematology - Blood SystemJaded KaysarNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculatoryDocument5 pagesBlood CirculatoryRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 pagesBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - The Human BloodDocument12 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - The Human Bloodxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 10 Cardiovasclar SystemDocument199 pages10 Cardiovasclar SystemjopermongcalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument95 pagesIntroduction To HematologyAhmad Farhan Hassan0% (1)
- CH 12 Blood CellsDocument38 pagesCH 12 Blood CellsAlina GheNo ratings yet
- Composition and Functions: BloodDocument86 pagesComposition and Functions: BloodYeyeh SantosNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology 1Document78 pagesBlood Physiology 1Jude ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Blood ReportDocument15 pagesBlood ReportSaadNo ratings yet
- PSG 712 Blood-1Document54 pagesPSG 712 Blood-1preciousNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Functions of BloodDocument12 pagesFunctions of BloodAngieRamirezNo ratings yet
- Blood Anaphy ReportingDocument52 pagesBlood Anaphy ReportingCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Forensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedDocument205 pagesForensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedNandini SinghNo ratings yet
- The Blood - ReviewerDocument11 pagesThe Blood - Reviewerastraia celesteNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition DR SallamaDocument5 pagesBlood Composition DR SallamaAhmed Ali Assaf100% (1)
Biologynotes
Biologynotes
Uploaded by
amazingapple350 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesBiologynotes
Biologynotes
Uploaded by
amazingapple35Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Key Terms
Blood: fluid transport medium in the cardiovascular system of a mammal that contains blood
cells and
plasma
Plasma: yellow, watery, fluid part of blood consisting of about 90 per cent water and 10 per
cent proteins; carries many substances in either dissolved or suspended form
Platelet: thrombocyte; crescent-shaped fragment of cells produced in the bone marrow; has
afunction in the clotting of blood
Red blood cell: erythrocyte; small biconcave cell containing haemoglobin that is formed in
the bone
marrow
White blood cell: leucocyte; irregularly shaped cell, produced in the bone marrow, that
carries out the
role of defending the body
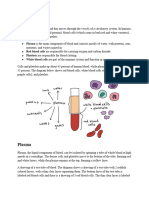
Plasma
Plasma is mostly water. Plasma carries:
Plasma proteins include clotting factors, immunoglobulins, albumen,
enzymes
Nutrients absorbed during digestion
Gases including oxygen and carbon dioxide
Excretory waste products such as urea, uric acid or ammonia
Ions, including sodium, chloride, calcium, magnesium and phosphate
Regulatory substances such as hormones
Other substances such as vitamins
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
transport oxygen. Red blood cells are
formed in bone marrow. As the cell
matures, the nucleus breaks down. A
red pigment called haemoglobin
develops in red blood cells.
Haemoglobin binds with oxygen.
The absence of a nucleus allows each
cell to maximise the amount of
haemoglobin it has. The cells are
small, round, biconcave and
flattened. This makes them more
pliable and elastic.
You might also like
- Blood BiochemistryDocument124 pagesBlood BiochemistrySohail AhamdNo ratings yet
- Composition & Functions of BloodDocument15 pagesComposition & Functions of BloodShahroze AlamNo ratings yet
- CH 19 MartiniDocument12 pagesCH 19 MartinijaneNo ratings yet
- Blood - WikipediaDocument106 pagesBlood - WikipediaZoha AliNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument79 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemhed-ikaquinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument39 pagesChapter 10 BloodLovely FinuliarNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingDocument21 pagesAnemia: Our Lady of Fatima University College of NursingPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument24 pagesBlood ComponentsJames Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Blood 1Document28 pagesBlood 1Miss KayaniNo ratings yet
- Blood@Wikipedia Org enDocument18 pagesBlood@Wikipedia Org enHelmiNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument103 pagesBloodrizwanbas50% (2)
- BloodDocument14 pagesBloodvardhan_16No ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodKurt HillNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Sem1 Year1 BMwk1 2012 01 27Document10 pagesLec1 Sem1 Year1 BMwk1 2012 01 27sehrish_salamNo ratings yet
- Blood: General Characteristics of BloodDocument9 pagesBlood: General Characteristics of BloodMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Document22 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 11 - Blood)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofDocument2 pagesBlood Is A: Haima) For "Blood". in Terms ofMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Blood: Blood Is A SpecializedDocument1 pageBlood: Blood Is A Specializedhai haiNo ratings yet
- f3 SC Chap 2Document31 pagesf3 SC Chap 2Chong Yek PhengNo ratings yet
- Online Assignment: Submitted byDocument11 pagesOnline Assignment: Submitted byPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Biology Slides - With BiblioDocument43 pagesBiology Slides - With BiblioJohannes TjendroNo ratings yet
- Hoffman - Hematology. Basic Principles and Practice (3th Edition)Document117 pagesHoffman - Hematology. Basic Principles and Practice (3th Edition)Carmina Lepa100% (1)
- Cells : Further InformationDocument7 pagesCells : Further InformationMica SaeronNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Blood Is A Specialized Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Suchjeoffrey_castroNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- Functions of BloodDocument10 pagesFunctions of BloodKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchDocument2 pagesBlood Is A Bodily Fluid in Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances SuchMichelle E. CapacioNo ratings yet
- Blood STDSDocument49 pagesBlood STDSNaveelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Transport in ManDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Transport in ManSheik Mohammud Muzzammil NabybaccusNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument3 pagesBloodRANAAYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 Blood MariebDocument30 pagesChapter17 Blood MariebMario AndersonNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi DARAHDocument31 pagesFisiologi DARAHTririn RinantiNo ratings yet
- Blood ReviewDocument35 pagesBlood ReviewCharli ParachinniNo ratings yet
- Blood and Clotting FactorsDocument34 pagesBlood and Clotting FactorsAnand KasiNo ratings yet
- BloodphysiologypptDocument103 pagesBloodphysiologypptShfici AdanNo ratings yet
- Text For Reding BloodDocument39 pagesText For Reding BloodFjhvbhhNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument4 pagesBloodatikarahmansuba123No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Blood 11.1 Functions of Blood: - 91% Water - 7% Proteins (Dissolved)Document3 pagesChapter 11: Blood 11.1 Functions of Blood: - 91% Water - 7% Proteins (Dissolved)Jennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Revised Chapter-8 - Google Slide - Hematology - Blood SystemDocument20 pagesRevised Chapter-8 - Google Slide - Hematology - Blood SystemJaded KaysarNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculatoryDocument5 pagesBlood CirculatoryRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Blood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsDocument24 pagesBlood Is A Body Fluid in Human and Other Animals That Delivers Necessary Substances Such AsPaulo DanielNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - The Human BloodDocument12 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY - The Human Bloodxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- 10 Cardiovasclar SystemDocument199 pages10 Cardiovasclar SystemjopermongcalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument95 pagesIntroduction To HematologyAhmad Farhan Hassan0% (1)
- CH 12 Blood CellsDocument38 pagesCH 12 Blood CellsAlina GheNo ratings yet
- Composition and Functions: BloodDocument86 pagesComposition and Functions: BloodYeyeh SantosNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology 1Document78 pagesBlood Physiology 1Jude ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Blood ReportDocument15 pagesBlood ReportSaadNo ratings yet
- PSG 712 Blood-1Document54 pagesPSG 712 Blood-1preciousNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Functions of BloodDocument12 pagesFunctions of BloodAngieRamirezNo ratings yet
- Blood Anaphy ReportingDocument52 pagesBlood Anaphy ReportingCza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Forensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedDocument205 pagesForensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedNandini SinghNo ratings yet
- The Blood - ReviewerDocument11 pagesThe Blood - Reviewerastraia celesteNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition DR SallamaDocument5 pagesBlood Composition DR SallamaAhmed Ali Assaf100% (1)