Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrition SOM
Nutrition SOM
Uploaded by
sheokandgangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition SOM
Nutrition SOM
Uploaded by
sheokandgangCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition Profile Somalia
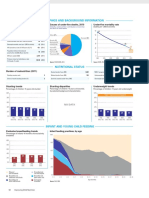
DEMOGRAPHICS
Total population (000) 8,926 (2008)
Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths, 2004
Deaths per 1,000 live births
Others 17% Neonatal
Total under-five population (000) 1,611 (2008) 250 22%
Malaria 3%
Total number of births (000) 395 (2008) 200
200 HIV/AIDS
200
Under-five mortality rate (per 1,000 live Globally, 0%
200 (2008)
births) more than
150
Total number of under-five deaths (000) 76 (2008) one third of
child deaths are
100 67 attributable to
Infant mortality rate (per 1,000 live births) 119 (2008)
undernutrition
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1,000 live Pneumonia
49 (2004) 50 24%
births) MDG
Diarrhoea
HIV prevalence rate (15-49 years, %) 0.5 (2007) Target
18%
0 Injuries 3%
Population below international Measles
- - 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 12%
poverty line of US$1.25 per day (%)
Source: IGME 2009 Source: WHO 2008
Prepared
NUTRITIONAL STATUS
Burden of undernutrition (2008) Stunted (under-fives, 000): 675 Underweight (under-fives, 000): 509
WHO Child Growth Standards
Share of developing world stunting burden (%): 0.3 Wasted (under-fives, 000): 213
Stunting country rank: 47 Severely wasted (under-fives, 000): 69
Current nutritional status Stunting trends Underweight trends
Percentage of children < 5 years old suffering Percentage of children < 5 years old stunted Percentage of children < 5 years old
from: NCHS reference population underweight, NCHS reference population
42 100 % 100 %
Stunting
38 80 80
32 60 60
Underweight
36 40 40
38
13 WHO Child Growth Standards 20 20
Wasting 14 23 18 26 36
NCHS reference population
11 0 0
1997 1999 2006 1997 1999 2006
0 20 40 60 80 100 % MICS MICS MICS MICS MICS MICS
MICS 2006
Source: MICS 2006
• INFANT AND YOUNG CHILD FEEDING
Infant feeding practices, by age
100% Weaned (not breastfed) Breastfed and
non-milk liquids
90 Breastfed and solid/
semi-solid foods Breastfed and plain
water only
80
Breastfed and other Exclusively breastfed
milk/formula
70
60 Exclusive breastfeeding
Percentage of infants < 6 months old
exclusively breastfed
50
100 %
40
80
30
60
20 40
10 20 9 9
0 0
0-1 2-3 4-5 6-7 8-9 10-11 12-13 14-15 16-17 18-19 20-21 22-23 2000 2006
age (months) MICS MICS
Source: MICS 2006
Printed on: 29-Mar-2010
Somalia
MICRONUTRIENTS
Vitamin A supplementation Iodized salt consumption trends* Anaemia
Percentage of children 6-59 months old receiving Percentage of households consuming Prevalence of anaemia among selected populations
two doses of vitamin A during calendar year adequately iodized salt
391,000 newborns are unprotected
100 % against IDD (2008)
100
100 %
80
80
60 60
40 40 No Data
20
20
1
0
14
0 4 2006
MICS
2005 2006 2007 2008
Source: UNICEF 2009
* Estimates may not be comparable.
ESSENTIAL NUTRITION INTERVENTIONS DURING THE LIFE CYCLE
Pregnancy Birth 0-5 months 6-23 months 24-59 months
Use of iron-folic acid Early initiation of breastfeeding International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Substitutes No
- 26%
supplements (within 1 hour of birth) Maternity protection in accordance with ILO Convention 183 No
Household consumption of Exclusive breastfeeding Timely introduction of complementary
1% Infants not weighed at birth - 9% 15%
adequately iodized salt (<6 months) foods (with continued breastfeeding)
Continued breastfeeding at two years 35%
To increase children's chances of survival, improve Full coverage of vitamin A supplementation 100%
development and prevent stunting, nutrition interventions need National guidelines for management of severe acute malnutrition
to be delivered during the mother's pregnancy and the first Partial
incorporating the community-based approach
two years of the child's life.
Policy on new ORS formula and zinc for management of diarrhoea* -
*Information on these policies are being updated Policy on community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics* -
MATERNAL NUTRITION/HEALTH WATER AND SANITATION
Maternal mortality ratio, adjusted Drinking water coverage Sanitation coverage
1,400 (2005) Percentage of population by type of drinking Percentage of population by type of sanitation
(per 100,000 live births)
water source, 2008 facility, 2008
Maternal mortality ratio, reported
(per 100,000 live births)
1,000 (1994-2006)
Piped into dwelling, Other improved Unimproved Improved facility Shared facility
Total number of maternal deaths 5,200 (2005) plot or yard source source Unimproved facility Open defecation
Source: WHO/UNICEF
100% JMP, 2008 100% 3
Lifetime risk of maternal deaths (1 in : ) 12 (2005)
15
Women with low BMI (< 18.5 kg/m2, %) - - 80% 33 80%
54
70 30
Anaemia, non-pregnant woman (<120 g/l, %) - - 60% 16 60% 83
91
Antenatal care (at least one visit, %) 26 (2006) 40% 40% 8
51 15 52
Antenatal care (at least four visits, %) 6 (2006) 20% 11 20% 5
19 23 6
Skilled attendant at birth (%) 33 (2006) 0% 9 0 0% 6
Low birthweight (<2,500 grams, %) - - Total Rural Urban Total Rural Urban
Primary school net enrolment or
21, 25 (2006) Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2010 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2010
attendance ratio (% female, % male)
Gender parity index (primary school net
Prepar
enrolment or attendance ratio) 0.84 (2006) Under-five deaths caused by: Diarrhoea: 18% Pneumonia: 24%
DISPARITIES IN NUTRITION
Gender Residence Wealth quintile
Indicator Ratio of male Ratio of urban to Ratio of richest Source
Male Female Urban Rural Poorest Second Middle Fourth Richest
to female rural to poorest
Stunting prevalence (WHO Child Growth Standards,
43 41 1.0 32 48 0.7 52 52 47 32 25 0.5 MICS 2006
%)
Underweight prevalence (WHO Child Growth
Standards, %) 33 30 1.1 20 38 0.5 42 42 36 23 14 0.3 MICS 2006
Wasting prevalence (WHO Child Growth Standards,
15 12 1.3 9 16 0.6 17 15 16 11 7 0.4 MICS 2006
%)
Infants not weighed at birth (%) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Early initiation of breastfeeding (%) - - - 27 26 1.0 24 29 26 24 30 1.3 MICS 2006
Women with low BMI (<18.5 kg/m2, %) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Prepar
You might also like
- Lesson Plan People As A ResourceDocument2 pagesLesson Plan People As A ResourceAnjali Nim83% (23)
- CHN 2 Questions & Answer KeyDocument33 pagesCHN 2 Questions & Answer KeyWawit A Dela Cerna83% (12)
- Management of LBW BabiesDocument67 pagesManagement of LBW BabiesEllen Angel100% (4)
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocument4 pagesLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Country Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child SurvivalDocument4 pagesCountry Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survivalpaperpin27No ratings yet
- Nutrition LCADocument2 pagesNutrition LCAShernia EliboxNo ratings yet
- Jamaica: Country ProfileDocument4 pagesJamaica: Country ProfileZineil BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Maternal CZEDocument4 pagesMaternal CZEYajie LuoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoNo ratings yet
- Pakistan 2015Document2 pagesPakistan 2015shujahkianiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocument2 pagesNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Ben inDocument1 pageBen incbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Demographics: Maternal and Newborn HealthDocument2 pagesDemographics: Maternal and Newborn Healthmichael8spree8michaeNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Child Health ProfileDocument6 pagesIndonesia: Child Health ProfiledecyoceNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Ye MenDocument1 pageYe MencbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Wmchart2011 PDFDocument2 pagesWmchart2011 PDFcathNo ratings yet
- South Sudan CD2030 2020Document2 pagesSouth Sudan CD2030 2020anjelopaul2017No ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Suiza InformacionDocument1 pageSuiza InformacionZoraida Ortega PoloNo ratings yet
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Document63 pagesKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiNo ratings yet
- Guinea BissauDocument1 pageGuinea BissaucbellsnlNo ratings yet
- gtbr2018 Annex2 PDFDocument61 pagesgtbr2018 Annex2 PDFMumutNo ratings yet
- DemographicsDocument1 pageDemographicscbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Key Health System Indicators: Djibouti: Health Systems ProfileDocument2 pagesKey Health System Indicators: Djibouti: Health Systems ProfilemNo ratings yet
- FINAL KuwaitDocument4 pagesFINAL KuwaitTariq GhareebaNo ratings yet
- Country Health System Fact Sheet 2006 Guinea-BissauDocument8 pagesCountry Health System Fact Sheet 2006 Guinea-BissauJonas WillmerNo ratings yet
- INDICATORS of HealthDocument3 pagesINDICATORS of Healthrajforever17No ratings yet
- Corona Virus Data CompilationDocument16 pagesCorona Virus Data CompilationBenjamin CraigNo ratings yet
- Country ProfileDocument20 pagesCountry ProfileClaudiu LucianNo ratings yet
- Indonesia: Indicators in The Sustainable Development Goals Associated With TB IncidenceDocument1 pageIndonesia: Indicators in The Sustainable Development Goals Associated With TB IncidenceSwitzerland BautistaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Beds (Per 1,000 People) - DataDocument1 pageHospital Beds (Per 1,000 People) - DataRashid ShahNo ratings yet
- ReportsDocument1 pageReportsiracema.rocha8765No ratings yet
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDocument2 pagesMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- Pakistan Apif2006Document1 pagePakistan Apif2006wrangularNo ratings yet
- Mort Afro Tza TanzaniaDocument2 pagesMort Afro Tza TanzaniaJan TanzaniaNo ratings yet
- 1.pediatric Health. 2019Document34 pages1.pediatric Health. 2019Fuad Aman AbjNo ratings yet
- SDG Index - Maharastra Status NoteDocument6 pagesSDG Index - Maharastra Status NoteManohar GolpelwarNo ratings yet
- FINAL ArgentinaDocument4 pagesFINAL Argentinabet52wNo ratings yet
- World Health Statistics 2007Document12 pagesWorld Health Statistics 2007wellunwellNo ratings yet
- DI Profile Kenya PDFDocument4 pagesDI Profile Kenya PDFAnonymous sllHltNo ratings yet
- Sowc07 Fastfacts MenaDocument2 pagesSowc07 Fastfacts Menafaqed ilzakiraNo ratings yet
- Health Status of Pakistan Jan 2014Document18 pagesHealth Status of Pakistan Jan 2014Dr.Abuzar ShiraniNo ratings yet
- Leah Epidemiology and HP 2020Document32 pagesLeah Epidemiology and HP 2020qwerty123No ratings yet
- Burkina FasoDocument1 pageBurkina FasocbellsnlNo ratings yet
- Who My PDFDocument1 pageWho My PDFsuksesNo ratings yet
- Laws of Uganda (Acts) - THE LAW REVISION (FINES AND OTHER FINANCIAL AMOUNTS IN CRIMINAL, MATTERS) ACT 2008Document9 pagesLaws of Uganda (Acts) - THE LAW REVISION (FINES AND OTHER FINANCIAL AMOUNTS IN CRIMINAL, MATTERS) ACT 2008sheokandgangNo ratings yet
- TECT Rio 2016-Practical info2-ENDocument1 pageTECT Rio 2016-Practical info2-ENsheokandgangNo ratings yet
- Bispap 61 GDocument18 pagesBispap 61 GsheokandgangNo ratings yet
- Gold CMA 3rd OctDocument2 pagesGold CMA 3rd OctsheokandgangNo ratings yet
- HaryanaJobs - in HPSC HCS Mains Result 2024Document2 pagesHaryanaJobs - in HPSC HCS Mains Result 2024sheokandgangNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance PresentationDocument15 pagesPreventive Maintenance Presentationabhinav2018100% (2)
- Detroit OIG ReportDocument312 pagesDetroit OIG ReportWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Health Care Systems - Costa Rica vs. ColombiaDocument11 pagesHealth Care Systems - Costa Rica vs. ColombiaFranz EignerNo ratings yet
- $R477RWZDocument37 pages$R477RWZSafwan al ubaiedNo ratings yet
- 2018 Philippine Health StatisticsDocument224 pages2018 Philippine Health StatisticsMark Angelo AquinoNo ratings yet
- Baby DumpingDocument3 pagesBaby Dumpingunic9450% (4)
- Wisconsin Dept of Children and Families and Health Services Home Visitation PlanDocument201 pagesWisconsin Dept of Children and Families and Health Services Home Visitation PlanRick ThomaNo ratings yet
- National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) : Orientation Workshop For ACS/PS/Sec (Health) & MD (NHM)Document18 pagesNational Urban Health Mission (NUHM) : Orientation Workshop For ACS/PS/Sec (Health) & MD (NHM)leoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Practice TestDocument9 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Practice Testjeshema100% (3)
- Ethiopia-National-Expanded-Program-on-Immunization 2021Document122 pagesEthiopia-National-Expanded-Program-on-Immunization 2021mulutugi4No ratings yet
- Inequalities in Health-Definitions - Concepts and TheoriesDocument12 pagesInequalities in Health-Definitions - Concepts and TheoriesElaine MachadoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Economics Ind Devt Ch1Document43 pagesMCQ Economics Ind Devt Ch1Jain AayushNo ratings yet
- Antenantal CareDocument35 pagesAntenantal Carejohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Care in Philadelphia McCool Guidera 2013Document8 pagesPregnancy Care in Philadelphia McCool Guidera 2013Emily ScottNo ratings yet
- If I Was The President of Uganda by Isaac Christopher LubogoDocument69 pagesIf I Was The President of Uganda by Isaac Christopher LubogolubogoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Maternal Newborn and Womens Health Nursing 6th Edition Murray Test BankDocument12 pagesFoundations of Maternal Newborn and Womens Health Nursing 6th Edition Murray Test BankDennisSandersnofpw100% (12)
- New Policies and Protocol On Essential Intrapartal Newborn CareDocument4 pagesNew Policies and Protocol On Essential Intrapartal Newborn CareJam Chelsea ChyNo ratings yet
- CHN NotesDocument7 pagesCHN NotesRoy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- MNH Toolkit 23 11 2013Document196 pagesMNH Toolkit 23 11 2013docsaravananNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument55 pagesCompleteMilkii Du NikusNo ratings yet
- WHO - The Second Ten Years of The World Health OrganizationDocument456 pagesWHO - The Second Ten Years of The World Health OrganizationFloripondio19No ratings yet
- Calibo: PhilippinesDocument11 pagesCalibo: PhilippinesNewborn2013No ratings yet
- Development Studies Revision QuestionsDocument129 pagesDevelopment Studies Revision Questionssbondo britneyNo ratings yet
- Urbanization and ImpactsDocument52 pagesUrbanization and ImpactsDeepnath MajumderNo ratings yet
- The Population Explosion: Causes and ConsequencesDocument11 pagesThe Population Explosion: Causes and ConsequencesShashi CampherNo ratings yet
- Future of HealthcareDocument1 pageFuture of HealthcareSanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Public Health Challenges in India: Seizing The OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesPublic Health Challenges in India: Seizing The OpportunitiesChandana KrishnaNo ratings yet