Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsLM Sensors
LM Sensors
Uploaded by
sb2505Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Types of ResistorsDocument28 pagesTypes of Resistorsjinto0007100% (3)
- Lecture 5Document14 pagesLecture 5havishalhumNo ratings yet
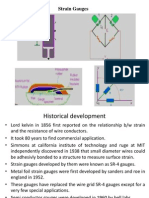
- Strain GaugesDocument35 pagesStrain GaugesSnigdhaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Instrumentation: Strain GaugesDocument58 pagesIndustrial Instrumentation: Strain GaugesBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Straingauge 130703045302 Phpapp02Document22 pagesStraingauge 130703045302 Phpapp02nithiaashreeNo ratings yet
- ME 402 UNIT 4 IC Force Strain InstrumentsDocument43 pagesME 402 UNIT 4 IC Force Strain InstrumentsYASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4yashagrawal.be18aeroNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document23 pagesGroup 4Ankur47No ratings yet
- Thin Film Strain GaugesDocument139 pagesThin Film Strain GaugesmhNo ratings yet
- Piezoresistive Sensors: Strain GaugesDocument17 pagesPiezoresistive Sensors: Strain GaugesAjinkya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Capacitive TransducersDocument18 pagesCapacitive TransducersMSuperManNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument7 pagesStrain GaugeIanosi SorinNo ratings yet
- DP CellDocument18 pagesDP CellbrindaNo ratings yet
- Thin Film CharacterizationDocument11 pagesThin Film CharacterizationPurti SavardekarNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesDocument2 pagesStrain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesanshulNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Nature of MEMSDocument21 pagesMultidisciplinary Nature of MEMSdrn86686No ratings yet
- Strain Gauge: ConstructionDocument11 pagesStrain Gauge: ConstructionpiocasmirNo ratings yet
- Fatigue-Partcle & Whisker Particle Reinforced CompositeDocument26 pagesFatigue-Partcle & Whisker Particle Reinforced Compositenithink100No ratings yet
- Second HalfDocument6 pagesSecond Halfitsmehema12No ratings yet
- Introduction To Strain GaugesDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Strain GaugesManjunatha Babu N.s100% (1)
- Types of Strain GaugesDocument3 pagesTypes of Strain Gaugesprabhushankar05No ratings yet
- p5 En303 Sankalp PurwarDocument14 pagesp5 En303 Sankalp Purwar2K20 EN 63 Sankalp PurwarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Transducers: Lecture - 3.2 Strain GaugeDocument12 pagesUnit - 3 Transducers: Lecture - 3.2 Strain GaugeRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Radiography For Civil Structures Lecture-3Document24 pagesRadiography For Civil Structures Lecture-3pratik anandNo ratings yet
- STNM 4Document33 pagesSTNM 4BME62Thejeswar SeggamNo ratings yet
- Fracture in Fiber Reinforced Composite Material:Mathematical Models and Experimental MethodsDocument54 pagesFracture in Fiber Reinforced Composite Material:Mathematical Models and Experimental MethodsSubayyal IlyasNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Componets 1Document63 pagesPassive and Active Componets 1hellooyeee694No ratings yet
- p5 En303 Sankalp Purwar 2Document14 pagesp5 En303 Sankalp Purwar 22K20 EN 63 Sankalp PurwarNo ratings yet
- Beam Modifiying Devices in Teletherapy Machines: Nilesh Kumar PG Radiation Physics Department of Radiation PhysicsDocument39 pagesBeam Modifiying Devices in Teletherapy Machines: Nilesh Kumar PG Radiation Physics Department of Radiation Physicsnilesh kumar100% (1)
- Strain GaugeDocument3 pagesStrain GaugeNatalio GarzonNo ratings yet
- EMI Shielding: by Divya Balakrishnan Roll No:12 3rd Semester Materials ScienceDocument26 pagesEMI Shielding: by Divya Balakrishnan Roll No:12 3rd Semester Materials ScienceTvarit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Magnetostrictive MaterialsDocument34 pagesChapter 5 - Magnetostrictive MaterialsmilolNo ratings yet
- Resistance Strain GaugeDocument28 pagesResistance Strain GaugeKarunesh PiwaniaNo ratings yet
- 06 - ART - Investigating The Properties of Precision Resistors For The Application in High Voltage DC DividersDocument6 pages06 - ART - Investigating The Properties of Precision Resistors For The Application in High Voltage DC DividersLove for gamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Application of ElectroceramicsDocument46 pagesChapter 10-Application of ElectroceramicsNouf NanoNo ratings yet
- Tensile FinalDocument43 pagesTensile FinalAndres EscobedoNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument35 pagesTransducersm.srinivasa raoNo ratings yet
- Extenso MeterDocument8 pagesExtenso MeterVijayanandh Raja100% (1)
- Physical Operation: Electrical Conductance Electrical Conductor ElasticityDocument4 pagesPhysical Operation: Electrical Conductance Electrical Conductor Elasticitydwarika2006100% (1)
- Electrostatic Sensors and ActuatorsDocument63 pagesElectrostatic Sensors and ActuatorsAnitha Kumari SivathanuNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument57 pagesStatic ElectricityDodo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Mri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiDocument35 pagesMri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiTHE GR8 HUBNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugesDocument7 pagesStrain GaugesRoss Jay MichelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document18 pagesLecture 04khalidhussaineditz786No ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 BECE101L TH VL2021220505673 Reference Material I 04-06-2022 Module 7.2 23Document17 pagesWINSEM2021-22 BECE101L TH VL2021220505673 Reference Material I 04-06-2022 Module 7.2 23gfdffggsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Accelerometer From Polymer: Procedia EngineeringDocument4 pagesMagnetic Accelerometer From Polymer: Procedia EngineeringVacunas AutismoNo ratings yet
- Interpreting PDFDocument7 pagesInterpreting PDFHồ ThắngNo ratings yet
- Beam Modification Devices in Radiotherapy - 3Document45 pagesBeam Modification Devices in Radiotherapy - 3Anirban Halder100% (24)
- EARTHING CorrectedDocument47 pagesEARTHING Correctednihartn2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document22 pagesLecture 9havishalhumNo ratings yet
- Short Wave Diathermy Lecture 2013Document69 pagesShort Wave Diathermy Lecture 2013Faisal Qureshi100% (3)
- Unit 4 - Characterization of Thin Film PropertiesDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Characterization of Thin Film PropertiesSumukh MudalagiriNo ratings yet
- Tensile FinalDocument43 pagesTensile Finalnamrataavyas75% (4)
- Mechanical Problems Associated With Surface Micromachining: Class 7Document24 pagesMechanical Problems Associated With Surface Micromachining: Class 7ShankarAthava100% (1)
- Design and Performance Studies of The Scanning Magnetron in Terms of V-I Characteristics, Dependence of V-I Characteristics On Scanning Speed, Deposition Rate and Substrate TemperatureDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Studies of The Scanning Magnetron in Terms of V-I Characteristics, Dependence of V-I Characteristics On Scanning Speed, Deposition Rate and Substrate TemperatureIjsrnet EditorialNo ratings yet
- Composites Smart MaterialsDocument14 pagesComposites Smart MaterialsSaravanan MadhappaNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 4Document25 pagesUnit IV Part 4VardhanNo ratings yet
- 8-Magnetic CeramicsDocument23 pages8-Magnetic CeramicsbawokeNo ratings yet
- Wide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthFrom EverandWide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthVincent ConsonniNo ratings yet
- New Sensors and Processing ChainFrom EverandNew Sensors and Processing ChainJean-Hugh ThomasNo ratings yet
LM Sensors
LM Sensors
Uploaded by
sb25050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views11 pagesOriginal Title
film sensors
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views11 pagesLM Sensors
LM Sensors
Uploaded by
sb2505Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Film sensors
strain gauges
• which are grid-type resistance structures whose
geometric stretching and compression result in a
measurable resistance change due to length and
thickness differences induced.
strain gauges
• Especially in the case of measuring small forces, the use of conventional foil
strain gauges is limited.
• Strain gauges in thin film technology present a potential solution to
overcome these.
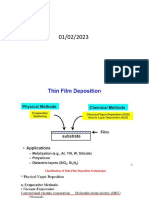
Thin-film sensors
• For a thin-film sensor, four resistors are arranged
on a diaphragm in the form of a Wheatstone
bridge to detect the deformation of the diaphragm
under pressure.
Thin-film Force sensors
Thin film sensor technology
An electrically insulating layer
completely covering the body.
By this layer, an electrical
separation of the metallic and
therefore electrically conducting
deformation element from the
following metallic sensor layer
is achieved.
Thin film sensor technology
• An electrically insulating layer completely covering the body.
• By this layer, an electrical separation of the metallic and therefore
electrically conducting deformation element from the following
metallic sensor layer is achieved.
• To achieve the conductive paths and, thereby, the geometry of the
sensor pattern, the second layer (i.e., the sensor layer) is structured
by photolithography.
Thick-film sensors
• Thick-film sensors, like thin-film sensors, use four resistors grouped
to form a Wheatstone bridge.
• The resistance structures are “printed” onto a base element using
thick-film technology, and afterwards they are burnt-in at high
temperature.
• The resistance change here is also due to the deformation of the
diaphragm, resulting from the geometrical change caused by the
stretching and compression of the material.
You might also like
- Types of ResistorsDocument28 pagesTypes of Resistorsjinto0007100% (3)
- Lecture 5Document14 pagesLecture 5havishalhumNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugesDocument35 pagesStrain GaugesSnigdhaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Instrumentation: Strain GaugesDocument58 pagesIndustrial Instrumentation: Strain GaugesBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Straingauge 130703045302 Phpapp02Document22 pagesStraingauge 130703045302 Phpapp02nithiaashreeNo ratings yet
- ME 402 UNIT 4 IC Force Strain InstrumentsDocument43 pagesME 402 UNIT 4 IC Force Strain InstrumentsYASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4yashagrawal.be18aeroNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document23 pagesGroup 4Ankur47No ratings yet
- Thin Film Strain GaugesDocument139 pagesThin Film Strain GaugesmhNo ratings yet
- Piezoresistive Sensors: Strain GaugesDocument17 pagesPiezoresistive Sensors: Strain GaugesAjinkya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Capacitive TransducersDocument18 pagesCapacitive TransducersMSuperManNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument7 pagesStrain GaugeIanosi SorinNo ratings yet
- DP CellDocument18 pagesDP CellbrindaNo ratings yet
- Thin Film CharacterizationDocument11 pagesThin Film CharacterizationPurti SavardekarNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesDocument2 pagesStrain Gauge: 1. Thin-Film Strain GaugesanshulNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Nature of MEMSDocument21 pagesMultidisciplinary Nature of MEMSdrn86686No ratings yet
- Strain Gauge: ConstructionDocument11 pagesStrain Gauge: ConstructionpiocasmirNo ratings yet
- Fatigue-Partcle & Whisker Particle Reinforced CompositeDocument26 pagesFatigue-Partcle & Whisker Particle Reinforced Compositenithink100No ratings yet
- Second HalfDocument6 pagesSecond Halfitsmehema12No ratings yet
- Introduction To Strain GaugesDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Strain GaugesManjunatha Babu N.s100% (1)
- Types of Strain GaugesDocument3 pagesTypes of Strain Gaugesprabhushankar05No ratings yet
- p5 En303 Sankalp PurwarDocument14 pagesp5 En303 Sankalp Purwar2K20 EN 63 Sankalp PurwarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Transducers: Lecture - 3.2 Strain GaugeDocument12 pagesUnit - 3 Transducers: Lecture - 3.2 Strain GaugeRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- Radiography For Civil Structures Lecture-3Document24 pagesRadiography For Civil Structures Lecture-3pratik anandNo ratings yet
- STNM 4Document33 pagesSTNM 4BME62Thejeswar SeggamNo ratings yet
- Fracture in Fiber Reinforced Composite Material:Mathematical Models and Experimental MethodsDocument54 pagesFracture in Fiber Reinforced Composite Material:Mathematical Models and Experimental MethodsSubayyal IlyasNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Componets 1Document63 pagesPassive and Active Componets 1hellooyeee694No ratings yet
- p5 En303 Sankalp Purwar 2Document14 pagesp5 En303 Sankalp Purwar 22K20 EN 63 Sankalp PurwarNo ratings yet
- Beam Modifiying Devices in Teletherapy Machines: Nilesh Kumar PG Radiation Physics Department of Radiation PhysicsDocument39 pagesBeam Modifiying Devices in Teletherapy Machines: Nilesh Kumar PG Radiation Physics Department of Radiation Physicsnilesh kumar100% (1)
- Strain GaugeDocument3 pagesStrain GaugeNatalio GarzonNo ratings yet
- EMI Shielding: by Divya Balakrishnan Roll No:12 3rd Semester Materials ScienceDocument26 pagesEMI Shielding: by Divya Balakrishnan Roll No:12 3rd Semester Materials ScienceTvarit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Magnetostrictive MaterialsDocument34 pagesChapter 5 - Magnetostrictive MaterialsmilolNo ratings yet
- Resistance Strain GaugeDocument28 pagesResistance Strain GaugeKarunesh PiwaniaNo ratings yet
- 06 - ART - Investigating The Properties of Precision Resistors For The Application in High Voltage DC DividersDocument6 pages06 - ART - Investigating The Properties of Precision Resistors For The Application in High Voltage DC DividersLove for gamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Application of ElectroceramicsDocument46 pagesChapter 10-Application of ElectroceramicsNouf NanoNo ratings yet
- Tensile FinalDocument43 pagesTensile FinalAndres EscobedoNo ratings yet
- TransducersDocument35 pagesTransducersm.srinivasa raoNo ratings yet
- Extenso MeterDocument8 pagesExtenso MeterVijayanandh Raja100% (1)
- Physical Operation: Electrical Conductance Electrical Conductor ElasticityDocument4 pagesPhysical Operation: Electrical Conductance Electrical Conductor Elasticitydwarika2006100% (1)
- Electrostatic Sensors and ActuatorsDocument63 pagesElectrostatic Sensors and ActuatorsAnitha Kumari SivathanuNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument57 pagesStatic ElectricityDodo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Mri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiDocument35 pagesMri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiTHE GR8 HUBNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugesDocument7 pagesStrain GaugesRoss Jay MichelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document18 pagesLecture 04khalidhussaineditz786No ratings yet
- WINSEM2021-22 BECE101L TH VL2021220505673 Reference Material I 04-06-2022 Module 7.2 23Document17 pagesWINSEM2021-22 BECE101L TH VL2021220505673 Reference Material I 04-06-2022 Module 7.2 23gfdffggsNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Accelerometer From Polymer: Procedia EngineeringDocument4 pagesMagnetic Accelerometer From Polymer: Procedia EngineeringVacunas AutismoNo ratings yet
- Interpreting PDFDocument7 pagesInterpreting PDFHồ ThắngNo ratings yet
- Beam Modification Devices in Radiotherapy - 3Document45 pagesBeam Modification Devices in Radiotherapy - 3Anirban Halder100% (24)
- EARTHING CorrectedDocument47 pagesEARTHING Correctednihartn2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document22 pagesLecture 9havishalhumNo ratings yet
- Short Wave Diathermy Lecture 2013Document69 pagesShort Wave Diathermy Lecture 2013Faisal Qureshi100% (3)
- Unit 4 - Characterization of Thin Film PropertiesDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Characterization of Thin Film PropertiesSumukh MudalagiriNo ratings yet
- Tensile FinalDocument43 pagesTensile Finalnamrataavyas75% (4)
- Mechanical Problems Associated With Surface Micromachining: Class 7Document24 pagesMechanical Problems Associated With Surface Micromachining: Class 7ShankarAthava100% (1)
- Design and Performance Studies of The Scanning Magnetron in Terms of V-I Characteristics, Dependence of V-I Characteristics On Scanning Speed, Deposition Rate and Substrate TemperatureDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Studies of The Scanning Magnetron in Terms of V-I Characteristics, Dependence of V-I Characteristics On Scanning Speed, Deposition Rate and Substrate TemperatureIjsrnet EditorialNo ratings yet
- Composites Smart MaterialsDocument14 pagesComposites Smart MaterialsSaravanan MadhappaNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Part 4Document25 pagesUnit IV Part 4VardhanNo ratings yet
- 8-Magnetic CeramicsDocument23 pages8-Magnetic CeramicsbawokeNo ratings yet
- Wide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthFrom EverandWide Band Gap Semiconductor Nanowires 1: Low-Dimensionality Effects and GrowthVincent ConsonniNo ratings yet
- New Sensors and Processing ChainFrom EverandNew Sensors and Processing ChainJean-Hugh ThomasNo ratings yet