Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beee Experiment No. 3
Beee Experiment No. 3
Uploaded by
Satwik BaraskarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Muhammad Hassan Saeed - 284223-Lab 7Document8 pagesMuhammad Hassan Saeed - 284223-Lab 7Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3Document4 pagesCircuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3D V AnshuNo ratings yet
- CHP 1: Circuit TheoryDocument42 pagesCHP 1: Circuit TheoryjojoNo ratings yet
- EEB501 - Lab 5Document4 pagesEEB501 - Lab 5Rahul DeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument44 pages1 Circuit Theoryamirul aminnNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument44 pages1 Circuit TheoryWinter NaiNo ratings yet
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document82 pages1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21roberto carlos roberto carlosNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument15 pagesRajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyNourin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document16 pagesLecture 04IfhamNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument12 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremISHAAAAAAAAAAANNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits.Document17 pagesDC Circuits.Spandana ReddyNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Name:M.Umer Bin Tariq Registration No: FA19-EEE-070: - Experimental Proof of Thevenin's Theorem ObjectiveDocument7 pagesName:M.Umer Bin Tariq Registration No: FA19-EEE-070: - Experimental Proof of Thevenin's Theorem ObjectiveHajra SwatiNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMDocument47 pages1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-IIDocument44 pagesNA Unit-IIvijayalakshmiv VEMURINo ratings yet
- RC and RL Circuits - FRDocument23 pagesRC and RL Circuits - FRIshtiyaq RafiqiNo ratings yet
- Beee Experiment No. 3Document2 pagesBeee Experiment No. 3Nikhil DaptareNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual Experiment No: 1 (B)Document2 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual Experiment No: 1 (B)Swaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Module - CircuitsDocument6 pagesWEEK 7 Module - CircuitsSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- BeeeDocument66 pagesBeeejaydeep gudetiNo ratings yet
- Skeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIDocument20 pagesSkeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIAsdiyanna Johari0% (1)
- Experiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources AimDocument4 pagesExperiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources Aimnational printersNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument18 pagesCircuit Theorygokulphd100% (1)
- Bsaic of RsistorsDocument33 pagesBsaic of Rsistorsmohamed shabbanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emDocument37 pagesExperiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emakashdeep tickooNo ratings yet
- JA303 Chapter 1Document47 pagesJA303 Chapter 1Apick MuhdNo ratings yet
- Norton + TheveninDocument22 pagesNorton + TheveninMoaaz TahaNo ratings yet
- EC2151 Lecture NotesDocument62 pagesEC2151 Lecture NotesJahith HussainNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDocument28 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualsanjbishtNo ratings yet
- Thevinin and NortonDocument44 pagesThevinin and NortonfareenfarzanawahedNo ratings yet
- EC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualDocument41 pagesEC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualRamkumar Sivakaminathan100% (1)
- Discuss Test 1 - Review: - Kirchoff's Rules For Circuits - Resistors in Series & ParallelDocument33 pagesDiscuss Test 1 - Review: - Kirchoff's Rules For Circuits - Resistors in Series & ParallelSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A CircuitDocument15 pagesDC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A Circuitdeskaug1No ratings yet
- Electromotive Force Resistor Circuits Kirchoff's Rules RC CircuitsDocument19 pagesElectromotive Force Resistor Circuits Kirchoff's Rules RC CircuitsSyed Anas SohailNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Circuits and Internal ResistanceDocument12 pagesDirect Current Circuits and Internal ResistanceEdoku IreneNo ratings yet
- F20F17 Sahil Practical 8Document7 pagesF20F17 Sahil Practical 8Sahil GupteNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- Thevenin Nortons TheoremDocument36 pagesThevenin Nortons TheoremVaneeza EemanNo ratings yet
- BEE Exp 2Document3 pagesBEE Exp 2MD ZunedNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocument50 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd Rzwan0% (1)
- ME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜDocument62 pagesME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜAhmet Salih SEÇGÜNNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Document46 pagesElectrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Shreyansh RajNo ratings yet
- EE 306 ManualDocument55 pagesEE 306 Manualzain khuramNo ratings yet
- Networl Manual (PTDC)Document28 pagesNetworl Manual (PTDC)sadeeskumar.dNo ratings yet
- TheveninsTheorem Lab PDFDocument9 pagesTheveninsTheorem Lab PDFUnknownNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Thevenin TheoremDocument3 pagesLab Manual - Thevenin TheoremPrathamesh Raje UgaleNo ratings yet
- BEE Experiment 2Document3 pagesBEE Experiment 2MD ZunedNo ratings yet
- Superposition TheoremDocument18 pagesSuperposition TheoremShoubhik SahaNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology 08082016Document46 pagesElectrical Technology 08082016AkNo ratings yet
- DC BridgesDocument35 pagesDC BridgesSeanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsDocument39 pages2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsthuanNo ratings yet
- Practical No: 5: Aim: To Study and Verify Thevenin's TheoremDocument10 pagesPractical No: 5: Aim: To Study and Verify Thevenin's TheoremJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- 18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Document57 pages18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Mohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)Document14 pagesElectrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)Karn SudhanshNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
Beee Experiment No. 3
Beee Experiment No. 3
Uploaded by
Satwik BaraskarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beee Experiment No. 3
Beee Experiment No. 3
Uploaded by
Satwik BaraskarCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Electrical & Electronics Engineering
21BTEC001
EXPERIMENT NO. 03
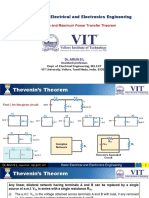
Aim: To verify Thevenin’s theorem and to find the load current for the given circuit.
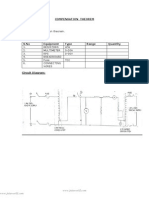
Apparatus: Power supply (0-30 volt), Resistors, Breadboard, connecting wires
Theory: Thevenin’s Theorem states that “Any linear circuit containing several voltages and
resistances can be replaced by just one single voltage in series with a single resistance
connected across the load”. The voltage source is called the Thevenin equivalent voltage,
and the resistor is called the Thevenin equivalent resistance
Steps to apply Thevenin’s theorem
• Remove the load resistance RL.
• Find the open-circuit voltage Voc that appears across the two terminals from where
resistance has removed. It also called Thevenin voltage Vth.
• Compute the resistance of the whole network as looked into from these two terminals after
all sources of e.m.f. have been removed. It also called Thevenin resistance Rth.
• Replace the entire network by single source whose voltage is Vth and whose single
resistance is Rth.
• Connect RL back to its terminals where it previously removed.
• Finally, calculate the current flowing through RL by IL = Vth/(Rth + RL)
Procedure
1) Make the connection on bread board as shown in Circuit diagram.
2) Ensure that supply is on ZERO position at start.
3) Calculate Rth, Vth, IL and IL’
Observation Table:
Vin Vth Rth IL IL’
Theoretical
Practical
Thevenin Equivalent Circuit
IL = Vth / ( Rth + RL)
Result
Hence the Thevenin’s theorem is verified both practically and theoretically in given circuit.
Post Lab Questions
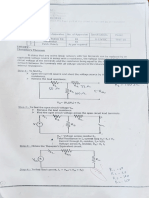
Q1) Apply Thevenin’s theorem to the following circuit and calculate the current flowing
through 2 ohm resistance.
R2
5Ω
R3 R1
V1 8Ω 2Ω
12V
You might also like
- Muhammad Hassan Saeed - 284223-Lab 7Document8 pagesMuhammad Hassan Saeed - 284223-Lab 7Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3Document4 pagesCircuit Theory Lab (Ice) : Experiment No: 3D V AnshuNo ratings yet
- CHP 1: Circuit TheoryDocument42 pagesCHP 1: Circuit TheoryjojoNo ratings yet
- EEB501 - Lab 5Document4 pagesEEB501 - Lab 5Rahul DeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument44 pages1 Circuit Theoryamirul aminnNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument44 pages1 Circuit TheoryWinter NaiNo ratings yet
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document82 pages1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21roberto carlos roberto carlosNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument15 pagesRajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyNourin TasnimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document16 pagesLecture 04IfhamNo ratings yet
- EEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremDocument12 pagesEEE1001 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Thevenin's and Maximum Power Transfer TheoremISHAAAAAAAAAAANNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits.Document17 pagesDC Circuits.Spandana ReddyNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Name:M.Umer Bin Tariq Registration No: FA19-EEE-070: - Experimental Proof of Thevenin's Theorem ObjectiveDocument7 pagesName:M.Umer Bin Tariq Registration No: FA19-EEE-070: - Experimental Proof of Thevenin's Theorem ObjectiveHajra SwatiNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMDocument47 pages1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-IIDocument44 pagesNA Unit-IIvijayalakshmiv VEMURINo ratings yet
- RC and RL Circuits - FRDocument23 pagesRC and RL Circuits - FRIshtiyaq RafiqiNo ratings yet
- Beee Experiment No. 3Document2 pagesBeee Experiment No. 3Nikhil DaptareNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual Experiment No: 1 (B)Document2 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manual Experiment No: 1 (B)Swaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 Module - CircuitsDocument6 pagesWEEK 7 Module - CircuitsSatsuki MomoiNo ratings yet
- BeeeDocument66 pagesBeeejaydeep gudetiNo ratings yet
- Skeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIDocument20 pagesSkeu2033 Circuit Theory IIIAsdiyanna Johari0% (1)
- Experiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources AimDocument4 pagesExperiment 3:toverify Thevenin Theorem and Find Out Thevenin'S Equivalent Circuit Using DC Sources Aimnational printersNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument18 pagesCircuit Theorygokulphd100% (1)
- Bsaic of RsistorsDocument33 pagesBsaic of Rsistorsmohamed shabbanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emDocument37 pagesExperiment No. 1: Verificati O N of TH Eve Nin 'S Theor emakashdeep tickooNo ratings yet
- JA303 Chapter 1Document47 pagesJA303 Chapter 1Apick MuhdNo ratings yet
- Norton + TheveninDocument22 pagesNorton + TheveninMoaaz TahaNo ratings yet
- EC2151 Lecture NotesDocument62 pagesEC2151 Lecture NotesJahith HussainNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDocument28 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualsanjbishtNo ratings yet
- Thevinin and NortonDocument44 pagesThevinin and NortonfareenfarzanawahedNo ratings yet
- EC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualDocument41 pagesEC2155 - Circuits & Devices Lab ManualRamkumar Sivakaminathan100% (1)
- Discuss Test 1 - Review: - Kirchoff's Rules For Circuits - Resistors in Series & ParallelDocument33 pagesDiscuss Test 1 - Review: - Kirchoff's Rules For Circuits - Resistors in Series & ParallelSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A CircuitDocument15 pagesDC Circuits: Review: - Current: The Rate of Flow of Electric Charge Past A Point in A Circuitdeskaug1No ratings yet
- Electromotive Force Resistor Circuits Kirchoff's Rules RC CircuitsDocument19 pagesElectromotive Force Resistor Circuits Kirchoff's Rules RC CircuitsSyed Anas SohailNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Circuits and Internal ResistanceDocument12 pagesDirect Current Circuits and Internal ResistanceEdoku IreneNo ratings yet
- F20F17 Sahil Practical 8Document7 pagesF20F17 Sahil Practical 8Sahil GupteNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- Thevenin Nortons TheoremDocument36 pagesThevenin Nortons TheoremVaneeza EemanNo ratings yet
- BEE Exp 2Document3 pagesBEE Exp 2MD ZunedNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocument50 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd Rzwan0% (1)
- ME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜDocument62 pagesME 214 Mechatronics: Associate Professor Kutay İçöz AGÜAhmet Salih SEÇGÜNNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Document46 pagesElectrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Shreyansh RajNo ratings yet
- EE 306 ManualDocument55 pagesEE 306 Manualzain khuramNo ratings yet
- Networl Manual (PTDC)Document28 pagesNetworl Manual (PTDC)sadeeskumar.dNo ratings yet
- TheveninsTheorem Lab PDFDocument9 pagesTheveninsTheorem Lab PDFUnknownNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Thevenin TheoremDocument3 pagesLab Manual - Thevenin TheoremPrathamesh Raje UgaleNo ratings yet
- BEE Experiment 2Document3 pagesBEE Experiment 2MD ZunedNo ratings yet
- Superposition TheoremDocument18 pagesSuperposition TheoremShoubhik SahaNo ratings yet
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology 08082016Document46 pagesElectrical Technology 08082016AkNo ratings yet
- DC BridgesDocument35 pagesDC BridgesSeanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsDocument39 pages2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsthuanNo ratings yet
- Practical No: 5: Aim: To Study and Verify Thevenin's TheoremDocument10 pagesPractical No: 5: Aim: To Study and Verify Thevenin's TheoremJay SathvaraNo ratings yet
- 18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Document57 pages18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Mohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)Document14 pagesElectrical Ckts Lab Manual (A.c)Karn SudhanshNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet