Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 1 .1st Year
Lab 1 .1st Year
Uploaded by
www.mohammed2004sweisy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesOriginal Title
lab 1 .1st year
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesLab 1 .1st Year
Lab 1 .1st Year
Uploaded by
www.mohammed2004sweisyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Lab 1:- Identification of laboratory apparatuses
Aim: To know the use and handling of different apparatus regularly
used in the pharmacy laboratory.
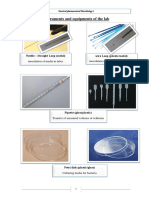
Apparatus name and their use:
Apparatus name Use
Test tube Carrying and reaction chemicals
Graduated test tube Carrying and reaction chemicals (known
volume)
Boiling tube Heating chemicals for long time
Bulb pipette Measure fixed small volume of liquid
Graduated pipette Measure variable small volume of liquid
Burette Used in volumetric titration
Measuring cylinder Measuring and transferring of liquid
beaker Carry liquid as container
Conical flask Carry liquid in volumetric titration
Volumetric flask Prepare standard solution of accurate
volume
Funnel Filtration and transfer of liquid
Hot plate Direct heating <)100 C0(
Water bath Indirect heating (100 > C0 )
Electronic balance Weighing small quantities (1mg to gm)
Mortar and pestle Triturating and mixing of drugs and
additives
Ointment spatula Levigation of ointment bases
Petri dish Microbial growth testing
Buchner flask Vacuum filtration
Desiccators Drying, storage of sample
Filter paper For filtration
General safety information: The goal of safety training is to
manage hazards in order to minimize the risk of accidental
chemical exposure, personal injury, or damage to property or the
environment.
do not work alone in the laboratory. Being alone in a situation
in which accidents can occur can be life-threatening
Always perform an experiment as specified.
Wear clothing that covers and protects your body.
Be aware of others working near you and the hazard associated
with their experiments.
Never eat, drink, or chew gum in the laboratory. Also never
directly inhale or taste any substance.
Read and understand the hazard documentation regarding any
chemicals you plan to you in an experiment.
Know where to find and how to use safety equipment, such as
eye wash station, fire extinguisher, first aid kit and fire alarm
pulls.
Report injuries, accidents and other incidents to instructor.
Properly dispose of chemical waste, Do not dispose of any
chemicals by pouring them down the drain or putting them in
the trash can without approval from your instructor.
Important guidelines:
1. All glassware should be cleaned and dried before use
2. The glassware should be handled with a lot of care
3. Each apparatus should be used as per standard procedure
4. The sensitivity of graduated pipette and burette is 0.1ml
5. In liquid measurement, the lower meniscus should be
considered while measuring the colorless liquids
6. While transferring the liquid by pipette allow the liquid to flow
by gravity . do not below with mouth.
Label: is a piece of paper, plastic film or other material affixed to a
container or product, on which is written or printed information or
symbols about the product or item information printed directly on
a container.
Types of labels:
1-manufacturer label 2- dispersing label
Manufacturer label which contains drug information for the use
of medical practitioners pharmacists distributor of drug
The manufacturer label must have the following:-
1- The name of the preparation
2- Strength and dosage form
3- Quantity
4- Instruction for the use
5- Precaution and warning
6- Registration number
7- Batch number
8- Price
9- Manufacturing and expiry date
10- The address of pharmaceutical industry.
Dispersing label include:-
Drug name and quantity
Patient name
Prescription number
Phone number
Instruction for use
Pharmacy name and addess
You might also like
- Pharmacy Stadard Operating ProcedureDocument5 pagesPharmacy Stadard Operating ProcedureJose Ramon Dalo Bautista100% (1)
- Saes L 125Document22 pagesSaes L 125Shawn LeoNo ratings yet
- GENERAL AND SYSTEMIC VETERINARAY PHARMACOLOGY Practical ManualDocument76 pagesGENERAL AND SYSTEMIC VETERINARAY PHARMACOLOGY Practical ManualSunil100% (2)
- Cleaning and Disinfection Protocol For Infant IncubatorDocument4 pagesCleaning and Disinfection Protocol For Infant Incubatorver_at_work100% (1)
- Anthony Cindy Edward - Investigation 3 LabDocument10 pagesAnthony Cindy Edward - Investigation 3 LabAnthony Hower0% (1)
- The Food Science and Technology - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesThe Food Science and Technology - Lab ManualRameen ShahidNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Class 1 Protocol 2021 DistanceDocument27 pagesMicrobiology Class 1 Protocol 2021 DistanceAhmed KerAtyNo ratings yet
- أجهزة التحاليل الطبية واستخداماتهاDocument22 pagesأجهزة التحاليل الطبية واستخداماتهاDawoodNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochem LabDocument37 pagesClinical Biochem LabJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- 202-NYA-05 Lab Manual Fall 2017Document102 pages202-NYA-05 Lab Manual Fall 2017Hoomehr TayariyanNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 Safety and Microscope 1st 2021-2022Document42 pagesLAB 1 Safety and Microscope 1st 2021-2022Deena Hajj QasemNo ratings yet
- Chem 105L Biochemistry (Lab) : Rachelle C. Mendoza, RCH, MSCDocument7 pagesChem 105L Biochemistry (Lab) : Rachelle C. Mendoza, RCH, MSCFaith BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Safety in The Lab Lab. ApparatusDocument20 pagesSafety in The Lab Lab. Apparatusthegr8 GNo ratings yet
- Laboratory PCOGDocument26 pagesLaboratory PCOGPeter Ray Magat Joves100% (4)
- PHCT311 Prelim ManualDocument23 pagesPHCT311 Prelim ManualFreya AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Practical Biochemistry 1 231023 174408Document103 pagesPractical Biochemistry 1 231023 174408xtnvj5k7xyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document67 pagesLecture 1Shayi HawreNo ratings yet
- Biol1400 2 and 3Document12 pagesBiol1400 2 and 3Richelle Mae B. ButialNo ratings yet
- LG1.1 Definition of Chemistry and Scientific MethodDocument7 pagesLG1.1 Definition of Chemistry and Scientific Methodnejomi_lash2003No ratings yet
- Biological MethodsDocument91 pagesBiological MethodsnahomNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Session One and Two (Biol-1012)Document12 pagesLaboratory Session One and Two (Biol-1012)esiyasmenNo ratings yet
- Micro para Lab - PrelimsDocument7 pagesMicro para Lab - PrelimsEingel Mer EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Manual 2021Document50 pagesChemistry Practical Manual 2021Jagdish PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 OrgchemDocument7 pagesModule 2 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANONo ratings yet
- Disinfection - Testing For DisinfectionDocument26 pagesDisinfection - Testing For DisinfectionRaam NaikNo ratings yet
- GCLAB Manual NewDocument78 pagesGCLAB Manual NewLoay BasemNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Your Science LaboratoryDocument18 pages1.2 Your Science LaboratoryCHAI SZE JIA MoeNo ratings yet
- Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlDocument40 pagesPrinciple, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlAnonymous GcUIZCKNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 Eng-1Document63 pagesBio f4 Eng-1pic6004No ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Practice of Clinical Chemistry, Part 2Document46 pagesBasic Principles and Practice of Clinical Chemistry, Part 2santosh_dhandeNo ratings yet
- Demonstrator/ Reem AmgadDocument14 pagesDemonstrator/ Reem Amgadmohamed 101No ratings yet
- Alanah Jane Garcia - Clin Chem ActivityDocument15 pagesAlanah Jane Garcia - Clin Chem ActivityAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Rules of Safety: by Nayla AklDocument46 pagesLaboratory Rules of Safety: by Nayla AklSirine AjourNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Instructions Aseptic Techniques For Handling MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesLaboratory Instructions Aseptic Techniques For Handling MicroorganismsaliyahNo ratings yet
- Report On Industrial VisitDocument25 pagesReport On Industrial VisitLoki MrPerfectNo ratings yet
- Disinfektan & AntiseptikDocument36 pagesDisinfektan & AntiseptikmaulidyaNo ratings yet
- Friday Morning - Lab1 - GROUP4 - REPORTDocument18 pagesFriday Morning - Lab1 - GROUP4 - REPORTĐạo QuangNo ratings yet
- Antiseptics, Disinfectants and DecontaminationDocument29 pagesAntiseptics, Disinfectants and Decontaminationdannymenard83No ratings yet
- Chemistry Form One & TwoDocument61 pagesChemistry Form One & Twothomaspodo76No ratings yet
- Cy101 Lab ManualDocument30 pagesCy101 Lab ManualsaiNo ratings yet
- Material 2Document41 pagesMaterial 2mounika3No ratings yet
- Exp 6Document12 pagesExp 6Mehul VermaNo ratings yet
- Diluting Fluid A: Intended UseDocument2 pagesDiluting Fluid A: Intended UseCarina Munir SayidiNo ratings yet
- Food Micro Lab ProtocolDocument30 pagesFood Micro Lab ProtocolShahin Kauser ZiaudeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document16 pagesChapter 5Ñãsîrē NåsøyèNo ratings yet
- Medical Instruments (Glasswares)Document14 pagesMedical Instruments (Glasswares)Headcutter OftheNightfallNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Pharmacy: Current Concepts and GMP NormsDocument22 pagesAyurvedic Pharmacy: Current Concepts and GMP NormsanooptiwariNo ratings yet
- Microbiological MethodDocument57 pagesMicrobiological MethodNofrizal100% (1)
- Orientation On Laboratory Safety and Laboratory TechniquesDocument2 pagesOrientation On Laboratory Safety and Laboratory TechniquesJen AntonioNo ratings yet
- English For Chemistry 1Document12 pagesEnglish For Chemistry 1Zulham AliNo ratings yet
- Quantitative CHL242F, DUDocument34 pagesQuantitative CHL242F, DUliz_hobbs79No ratings yet
- Microbiological Monitoring of Water-1Document18 pagesMicrobiological Monitoring of Water-1SolomonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 6 Infection Prevention and Waste Management EditedDocument30 pagesPresentation 6 Infection Prevention and Waste Management EditedLuo MiyandaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Dosage Form IntroductionDocument69 pagesParenteral Dosage Form IntroductionVicky AgroNo ratings yet
- 4 Lab Safety MicrolecDocument123 pages4 Lab Safety MicrolecSophia GoNo ratings yet
- Administering An Intradermal InjectionDocument7 pagesAdministering An Intradermal InjectionRyan InapanNo ratings yet
- Brex Manufacturing EditedDocument291 pagesBrex Manufacturing EditedMing MingNo ratings yet
- Sop Draft Alkaloid TestDocument5 pagesSop Draft Alkaloid TesteyobNo ratings yet
- Mels404 Lab Manual Part 1 2019-2020Document67 pagesMels404 Lab Manual Part 1 2019-2020Rawan Al AbbassiNo ratings yet
- Opaster Anios Fiche Technique 00000 enDocument2 pagesOpaster Anios Fiche Technique 00000 enArwil Fadillah100% (2)
- PDF Review WorkDocument35 pagesPDF Review WorkMd Atif MallickNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids 7Document36 pagesCarboxylic Acids 7www.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- Alkene 2Document59 pagesAlkene 2www.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 1Document45 pagesAlkanes 1www.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- Adsorption SSSDocument5 pagesAdsorption SSSwww.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- ١ - https - - - t.co - u1oylokfyf - - thread - by - ayi986 - - - نوفمبر ١٥، ٢١ - from - rattibhaDocument6 pages١ - https - - - t.co - u1oylokfyf - - thread - by - ayi986 - - - نوفمبر ١٥، ٢١ - from - rattibhawww.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- - - ثريد - - بحط - فيه - - thread - by - kingleoniii - - - نوفمبر ١٧، ١٩ - from - rattibhaDocument8 pages- - ثريد - - بحط - فيه - - thread - by - kingleoniii - - - نوفمبر ١٧، ١٩ - from - rattibhawww.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- Complexometric TitrationsDocument42 pagesComplexometric Titrationswww.mohammed2004sweisyNo ratings yet
- Army Public School No.1 Jabalpur: Chemistry ProjectDocument17 pagesArmy Public School No.1 Jabalpur: Chemistry ProjectJaskarandeep Singh JugrahNo ratings yet
- Go Organic!Document6 pagesGo Organic!ஆதி வேந்தன்No ratings yet
- Cold Plasma Technology: Advanced and Sustainable Approach For Wastewater TreatmentDocument21 pagesCold Plasma Technology: Advanced and Sustainable Approach For Wastewater Treatmenteze_firmatenseNo ratings yet
- Re21010 2017-05 PDFDocument104 pagesRe21010 2017-05 PDFlayetajNo ratings yet
- AntBNC Lemmas Ver 001Document658 pagesAntBNC Lemmas Ver 001Juliet XiongNo ratings yet
- Cables and Conductors - 1Document7 pagesCables and Conductors - 1Mopha BrandyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Lab ReportDocument10 pagesExperiment 3 Lab ReportLilo KuleNo ratings yet
- Flexible R. Joint TwinflexDocument3 pagesFlexible R. Joint TwinflexYuda PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Heat Sterilization: Moist Heat Dry HeatDocument25 pagesHeat Sterilization: Moist Heat Dry HeatRehmatNo ratings yet
- Vit-2 Ref-Eng Ppe&IpeDocument210 pagesVit-2 Ref-Eng Ppe&Ipekristan7No ratings yet
- JD-o3 Detan and DunnyDocument4 pagesJD-o3 Detan and Dunnyjustglow6No ratings yet
- DMR Sekhar: A ProfileDocument38 pagesDMR Sekhar: A ProfileKiran Kumar PediredlaNo ratings yet
- SX2112Document5 pagesSX2112AmenNo ratings yet
- hpv310 e Doc00061 PDFDocument38 pageshpv310 e Doc00061 PDFAnonymous v7XdaQuNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - 28 Elkemposter Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Irons PDFDocument2 pagesDokumen - Tips - 28 Elkemposter Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Irons PDFMD ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Document1 GAS ABSORPTION PRAC Draft 3 Sub FinalDocument16 pagesDocument1 GAS ABSORPTION PRAC Draft 3 Sub Finalziziphomkosana2003No ratings yet
- 000000027828 - 202004222153266xxx계 알루미늄 합금의 경질 아노다이징 피막 형성 특성 연구Document41 pages000000027828 - 202004222153266xxx계 알루미늄 합금의 경질 아노다이징 피막 형성 특성 연구임학진No ratings yet
- Welding Met 1 - Fusion Welding Processes 2020 PDFDocument66 pagesWelding Met 1 - Fusion Welding Processes 2020 PDFfebby andra100% (1)
- Lecture Planner - Chemistry II PDF OnlyDocument1 pageLecture Planner - Chemistry II PDF Onlybjogi0482No ratings yet
- ASTM E 501-94 Standard Rib Tire For Pavement Skid-Resistance TestDocument4 pagesASTM E 501-94 Standard Rib Tire For Pavement Skid-Resistance TestanjanaNo ratings yet
- DLP Grade 7 Concentration of SolutionDocument8 pagesDLP Grade 7 Concentration of SolutionJoy MonteroNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Determination of Acid Detergent Fiber and Lignin in Feed: Interlaboratory StudyDocument17 pagesGravimetric Determination of Acid Detergent Fiber and Lignin in Feed: Interlaboratory StudySV_TokanNo ratings yet
- REC - Module2 THC2 RMASSSDocument9 pagesREC - Module2 THC2 RMASSSJan JanNo ratings yet
- Fracture Toughness K1c and Toughness GCDocument5 pagesFracture Toughness K1c and Toughness GCEric Arriaga AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Crossover ExpDocument4 pagesCrossover ExpMUNISH JAINNo ratings yet
- Homework 6-2 Modern Chemistry AnswersDocument7 pagesHomework 6-2 Modern Chemistry Answersafmtbbasx100% (1)
- Journal Pre-Proof: Polymer TestingDocument42 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Polymer TestingEkansh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bauer 1971Document5 pagesBauer 1971Miranti PuspitasariNo ratings yet