Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Uploaded by
govicky565Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dragon Mother A New Look at The Female Psyche by Michael Tsarion - Z Lib - OrgDocument219 pagesDragon Mother A New Look at The Female Psyche by Michael Tsarion - Z Lib - OrgRod P100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- Page 429Document1 pagePage 429AugusteNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell-Cycle and Cell DivisionToby TrollyNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Output (Barraquias, Fatima Shiera H. BS BIO 2C)Document4 pagesMeiosis Output (Barraquias, Fatima Shiera H. BS BIO 2C)Fatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledMikee Jayra NaylesNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionCameron LightbourneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Task 1, 2 and 3Document3 pagesModule 2 Task 1, 2 and 3Ylaine NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesComparison of Mitosis and Meiosisstudent.riya.palsinghNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionlelejfintlskia1we39No ratings yet
- This Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableDocument1 pageThis Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableLaura Cormane100% (1)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis and MeiosisTheSourLemonNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- Meiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsDocument19 pagesMeiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman Geslani100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Document5 pagesChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointRia PerezNo ratings yet
- BLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetIndraragini AnpalakanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesDocument5 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesLeela SNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Activity-SheetDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Activity-SheetHazel Anne TabilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.7 Meiotic DivisionDocument16 pagesChapter 2.7 Meiotic DivisionRACHEL SINDHUNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisSachintha JayamahaNo ratings yet
- A. Different Stages of Mitosis: SimilaritiesDocument2 pagesA. Different Stages of Mitosis: SimilaritiesAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Meiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison Chart Meiosis Mitosis: Type of Reproduction Occurs inDocument2 pagesMeiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison Chart Meiosis Mitosis: Type of Reproduction Occurs inMorena AntesNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesChap 5 Cell DivisionMy fluffy MochiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell Division: Chapter 3: Heredity and VariationDocument18 pages3.1 Cell Division: Chapter 3: Heredity and VariationaliabuabeNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionnamikNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument2 pagesComparisonMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Document14 pagesMeiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Selenia BonoNo ratings yet
- Revision of Mid TermDocument6 pagesRevision of Mid Term؟؟No ratings yet
- Botany Module 3Document6 pagesBotany Module 3Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Significance or Applications of Mitosis/Meiosis: General Biology 1Document26 pagesSignificance or Applications of Mitosis/Meiosis: General Biology 1beaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis A Source of Distinction: Why Do You Share Some But Not All Characters of Each Parent?Document38 pagesMeiosis A Source of Distinction: Why Do You Share Some But Not All Characters of Each Parent?duchessNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10.Document50 pagesChapter 10.eman123elfNo ratings yet
- Science HW MM Compare and ConstrastDocument1 pageScience HW MM Compare and ConstrastjiNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BDocument23 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BJoshlyn AnnabelleNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisEvcha WangagNo ratings yet
- 4 Genetics & The Development of The Human BrainDocument45 pages4 Genetics & The Development of The Human BrainZerefuNo ratings yet
- Tabulate The Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageTabulate The Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisTricia Victoria UmhaoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument39 pagesMeiosisوجدان الشداديNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument4 pagesMeiosis11136843No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 MeiosisDocument37 pagesChapter 13 MeiosisChaehyoung LimNo ratings yet
- CH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument5 pagesCH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cyclesdidua08No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Notes Igcse Edexcel BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter 17 Notes Igcse Edexcel Biologyjhjsxwchk5No ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction and GeneticsDocument53 pagesSexual Reproduction and GeneticsNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- (Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisDocument9 pages(Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Jhon Rey RodeoNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionDocument22 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionJia JiaNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument2 pagesHeredityAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- GB2 Cell CycleDocument9 pagesGB2 Cell Cyclesja254677No ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Neonatal ICUDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Neonatal ICUJasmine KangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.1 Hypothesis Testing One Sample TestDocument14 pagesLesson 6.1 Hypothesis Testing One Sample TestJeline Flor EugenioNo ratings yet
- Guideline No. 402 Diagnosis and Management of Placenta PreviaDocument13 pagesGuideline No. 402 Diagnosis and Management of Placenta PreviaAndrés Gaviria C100% (1)
- Obstetrics Case StudiesDocument5 pagesObstetrics Case StudiesDiane AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Daphne NiDocument12 pagesDaphne NiJenieza D. PabalayNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis 0Document3 pagesOogenesis 0naji 12No ratings yet
- Specific Requirements For Health Centre V1.3Document8 pagesSpecific Requirements For Health Centre V1.3zac mankirNo ratings yet
- S 000 LBLDocument14 pagesS 000 LBLfaisal abbasNo ratings yet
- MM Kit User GuidlineDocument4 pagesMM Kit User GuidlineRussell JohnNo ratings yet
- Midwifery-Led Continum of Care - FindingsDocument20 pagesMidwifery-Led Continum of Care - FindingsAminur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Brown and White Doodle Mind Map Brainstorm GraphDocument1 pageBrown and White Doodle Mind Map Brainstorm GraphAlek SanderNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Ectopic Pregnancy-A Basic View Through LiteratureDocument2 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Ectopic Pregnancy-A Basic View Through LiteraturefprasasyaaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Disorder ProjectDocument10 pagesEnzyme Disorder Projectria wuNo ratings yet
- 1184-Article Text-6181-1-10-20230107Document6 pages1184-Article Text-6181-1-10-20230107NurhalimahNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) John Murtagh's General Practice Companion Handbook 7th Edition John Murtagh - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) John Murtagh's General Practice Companion Handbook 7th Edition John Murtagh - Ebook PDF All Chapterengeadouli8100% (4)
- De Anda - Baby Think It Over-1Document11 pagesDe Anda - Baby Think It Over-1Duyên Vũ PhươngNo ratings yet
- Dissertation BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesDissertation BreastfeedingPaySomeoneToWritePaperCanada100% (1)
- Pre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromeDocument15 pagesPre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromehendraNo ratings yet
- BJOG - 2023 - Regan - Recurrent MiscarriageGreen Top Guideline No 17Document31 pagesBJOG - 2023 - Regan - Recurrent MiscarriageGreen Top Guideline No 17Anuja RajurkarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. Pediatric UnitDocument21 pagesLesson 13. Pediatric UnitPaola ChaconNo ratings yet
- Linder2019 PDFDocument3 pagesLinder2019 PDFDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- Custody Case 1Document3 pagesCustody Case 1Joshua CapispisanNo ratings yet
- Nnc-Buntis CongressDocument26 pagesNnc-Buntis CongressVanessa ChavezNo ratings yet
- Doctors Progress Note - Module 5Document4 pagesDoctors Progress Note - Module 5adrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Embryology (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)Document10 pages3 - Embryology (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)w yNo ratings yet
- TDAH ADHD e Def de Iodo 2004Document7 pagesTDAH ADHD e Def de Iodo 2004Pollyana Furtado JunqueiraNo ratings yet
- OMS Post PartumDocument96 pagesOMS Post PartumcbienbienNo ratings yet
- Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research CentreDocument2 pagesShaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research CentreUsama AjmalNo ratings yet
- The Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been Stopped Walter LastDocument12 pagesThe Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been Stopped Walter Lastevimagg100% (2)
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Uploaded by
govicky565Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Uploaded by
govicky565Copyright:
Available Formats
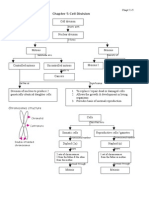
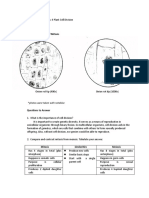
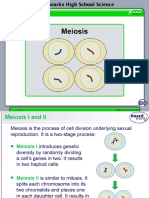
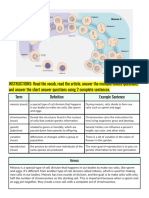
Mitosis Meiosis
Purpose The purpose of mitosis is cell growth, repair, and The purpose of meiosis is the production of gametes
asexual reproduction. for sexual reproduction.
It produces 2 daughter cells that are genetically It involves the reduction of chromosome number by
identical to each other. half, leading to genetic variation in the offspring.
Number of divisions One division, resulting in the formation of 2 daughter Two divisions: meiosis I & meiosis II, resulting in
cells the formation of 4 daughter cells.
Chromosome number Remains the same in daughter and parent cell Halved in the daughter cells (haploid) compared to
(diploid). parent cells (diploid).
Genetic variation Produces genetically identical daughter cells to the Genetic variation introduced through crossing over,
parent cell, so no genetic variation introduced. independent assortment, and random fertilisation,
resulting in genetically diverse daughter cells.
Synapsis and Crossing over No synapsis or crossing over. Synapsis occurs in meiosis I, where homologous
chromosomes pair up and form tetrads.
Crossing over, the exchange of genetic material
between homologous chromosomes, can occur at this
stage, contributing to genetic diversity.
Number of daughter cells 2 daughter cells, each with the same chromosome 4 daughter cells, each with half the chromosome
number as the parent cell. number of the parent cell.
Occurrence Occurs in the somatic (non-reproductive) cells Occurs in the germ cells (cells that give rise to
throughout an organism’s life for growth, repair, and gametes) during the formation of sperm and eggs for
asexual reproduction. sexual reproduction.
You might also like
- Dragon Mother A New Look at The Female Psyche by Michael Tsarion - Z Lib - OrgDocument219 pagesDragon Mother A New Look at The Female Psyche by Michael Tsarion - Z Lib - OrgRod P100% (1)
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- Page 429Document1 pagePage 429AugusteNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell-Cycle and Cell DivisionToby TrollyNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)Document2 pagesWORKSHEET (Cell Division) A. Short Answer: Answer The Following Questions Briefly. (3points Each)gyeojib aeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Output (Barraquias, Fatima Shiera H. BS BIO 2C)Document4 pagesMeiosis Output (Barraquias, Fatima Shiera H. BS BIO 2C)Fatima Shiera BarraquiasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledMikee Jayra NaylesNo ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesBiology Notebook: 03.02 Meiosis: Key Questions and Terms Notes Asexual and Sexual ReproductionCameron LightbourneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Task 1, 2 and 3Document3 pagesModule 2 Task 1, 2 and 3Ylaine NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesComparison of Mitosis and Meiosisstudent.riya.palsinghNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionlelejfintlskia1we39No ratings yet
- This Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableDocument1 pageThis Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableLaura Cormane100% (1)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis and MeiosisTheSourLemonNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- Meiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsDocument19 pagesMeiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsLydia LamNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman Geslani100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Document5 pagesChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointRia PerezNo ratings yet
- BLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBLG143 - Final Exam Cheat SheetIndraragini AnpalakanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesDocument5 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesLeela SNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Activity-SheetDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Activity-SheetHazel Anne TabilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.7 Meiotic DivisionDocument16 pagesChapter 2.7 Meiotic DivisionRACHEL SINDHUNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisSachintha JayamahaNo ratings yet
- A. Different Stages of Mitosis: SimilaritiesDocument2 pagesA. Different Stages of Mitosis: SimilaritiesAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument34 pagesMeiosisJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Meiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison Chart Meiosis Mitosis: Type of Reproduction Occurs inDocument2 pagesMeiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison Chart Meiosis Mitosis: Type of Reproduction Occurs inMorena AntesNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesChap 5 Cell DivisionMy fluffy MochiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell Division: Chapter 3: Heredity and VariationDocument18 pages3.1 Cell Division: Chapter 3: Heredity and VariationaliabuabeNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS OnlineDocument42 pagesMEIOSIS OnlineAltheaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionnamikNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument2 pagesComparisonMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Document14 pagesMeiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Selenia BonoNo ratings yet
- Revision of Mid TermDocument6 pagesRevision of Mid Term؟؟No ratings yet
- Botany Module 3Document6 pagesBotany Module 3Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Significance or Applications of Mitosis/Meiosis: General Biology 1Document26 pagesSignificance or Applications of Mitosis/Meiosis: General Biology 1beaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis A Source of Distinction: Why Do You Share Some But Not All Characters of Each Parent?Document38 pagesMeiosis A Source of Distinction: Why Do You Share Some But Not All Characters of Each Parent?duchessNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10.Document50 pagesChapter 10.eman123elfNo ratings yet
- Science HW MM Compare and ConstrastDocument1 pageScience HW MM Compare and ConstrastjiNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BDocument23 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BJoshlyn AnnabelleNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisEvcha WangagNo ratings yet
- 4 Genetics & The Development of The Human BrainDocument45 pages4 Genetics & The Development of The Human BrainZerefuNo ratings yet
- Tabulate The Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageTabulate The Difference Between Mitosis and MeiosisTricia Victoria UmhaoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesMitosis and MeiosisMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument39 pagesMeiosisوجدان الشداديNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument4 pagesMeiosis11136843No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 MeiosisDocument37 pagesChapter 13 MeiosisChaehyoung LimNo ratings yet
- CH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument5 pagesCH.10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cyclesdidua08No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Notes Igcse Edexcel BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter 17 Notes Igcse Edexcel Biologyjhjsxwchk5No ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction and GeneticsDocument53 pagesSexual Reproduction and GeneticsNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- (Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisDocument9 pages(Unit 2) Cell Division - MeiosisHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2Jhon Rey RodeoNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionDocument22 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation: 3.1 Cell DivisionJia JiaNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument2 pagesHeredityAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- GB2 Cell CycleDocument9 pagesGB2 Cell Cyclesja254677No ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Neonatal ICUDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Neonatal ICUJasmine KangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.1 Hypothesis Testing One Sample TestDocument14 pagesLesson 6.1 Hypothesis Testing One Sample TestJeline Flor EugenioNo ratings yet
- Guideline No. 402 Diagnosis and Management of Placenta PreviaDocument13 pagesGuideline No. 402 Diagnosis and Management of Placenta PreviaAndrés Gaviria C100% (1)
- Obstetrics Case StudiesDocument5 pagesObstetrics Case StudiesDiane AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Daphne NiDocument12 pagesDaphne NiJenieza D. PabalayNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis 0Document3 pagesOogenesis 0naji 12No ratings yet
- Specific Requirements For Health Centre V1.3Document8 pagesSpecific Requirements For Health Centre V1.3zac mankirNo ratings yet
- S 000 LBLDocument14 pagesS 000 LBLfaisal abbasNo ratings yet
- MM Kit User GuidlineDocument4 pagesMM Kit User GuidlineRussell JohnNo ratings yet
- Midwifery-Led Continum of Care - FindingsDocument20 pagesMidwifery-Led Continum of Care - FindingsAminur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Brown and White Doodle Mind Map Brainstorm GraphDocument1 pageBrown and White Doodle Mind Map Brainstorm GraphAlek SanderNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Ectopic Pregnancy-A Basic View Through LiteratureDocument2 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Ectopic Pregnancy-A Basic View Through LiteraturefprasasyaaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Disorder ProjectDocument10 pagesEnzyme Disorder Projectria wuNo ratings yet
- 1184-Article Text-6181-1-10-20230107Document6 pages1184-Article Text-6181-1-10-20230107NurhalimahNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) John Murtagh's General Practice Companion Handbook 7th Edition John Murtagh - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) John Murtagh's General Practice Companion Handbook 7th Edition John Murtagh - Ebook PDF All Chapterengeadouli8100% (4)
- De Anda - Baby Think It Over-1Document11 pagesDe Anda - Baby Think It Over-1Duyên Vũ PhươngNo ratings yet
- Dissertation BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesDissertation BreastfeedingPaySomeoneToWritePaperCanada100% (1)
- Pre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromeDocument15 pagesPre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromehendraNo ratings yet
- BJOG - 2023 - Regan - Recurrent MiscarriageGreen Top Guideline No 17Document31 pagesBJOG - 2023 - Regan - Recurrent MiscarriageGreen Top Guideline No 17Anuja RajurkarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13. Pediatric UnitDocument21 pagesLesson 13. Pediatric UnitPaola ChaconNo ratings yet
- Linder2019 PDFDocument3 pagesLinder2019 PDFDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- Custody Case 1Document3 pagesCustody Case 1Joshua CapispisanNo ratings yet
- Nnc-Buntis CongressDocument26 pagesNnc-Buntis CongressVanessa ChavezNo ratings yet
- Doctors Progress Note - Module 5Document4 pagesDoctors Progress Note - Module 5adrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Embryology (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)Document10 pages3 - Embryology (STRATOG 2015 SBAs)w yNo ratings yet
- TDAH ADHD e Def de Iodo 2004Document7 pagesTDAH ADHD e Def de Iodo 2004Pollyana Furtado JunqueiraNo ratings yet
- OMS Post PartumDocument96 pagesOMS Post PartumcbienbienNo ratings yet
- Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research CentreDocument2 pagesShaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research CentreUsama AjmalNo ratings yet
- The Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been Stopped Walter LastDocument12 pagesThe Borax Conspiracy How The Arthritis Cure Has Been Stopped Walter Lastevimagg100% (2)