Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SDL - Cell Structure and Function in Bacteria
SDL - Cell Structure and Function in Bacteria
Uploaded by
govicky565Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SDL - Cell Structure and Function in Bacteria
SDL - Cell Structure and Function in Bacteria
Uploaded by
govicky565Copyright:
Available Formats
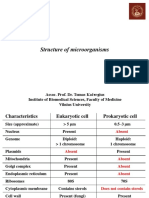
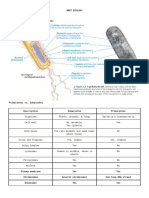
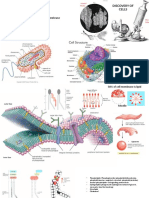
Cell structure and function in bacteria
^ cause of endotoxic
properties
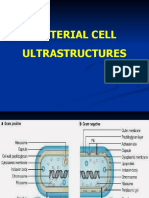
Gram positive Gram negative
Cell wall - Thick - Thinner
- Peptidoglycan composed of N- - Peptidoglycan only - Outer membrane: lipopolysaccharide (LPS) +
acetylglucosamine (NAG) and - Teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid proteins + phospholipids
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) Act as antigen for serological - LPS: toxic = endotoxin (endotoxic shock)
- Made in cytosol and classification. Pyrogenic (induces fever)
transported by carrier molecule: Substrates for autolytic enzymes Activate macrophages and complement.
bactoprenol Bind + supply Mg to cell. Mitogenic for B-lymphocytes
Anchor underlying cell membrane Induces interferon production.
Causes tissue necrosis and tumour
regression.
- Periplasm: gel-like matrix of nutrients
- Peptidoglycan
Structures external to cell wall
Structure Function
Fimbriae and pili - Hair like appendages - Bind to surfaces e.g. mucosal surfaces.
- Pili: cell conjugation (transfer of genetic material from
one bacterium to another)
Flagella - Long, thin whip like appendages - Movement towards or away from stimuli
- Can vary in number: One to hundreds - Immunogenic (evokes immune response)
Capsule - Made of polysaccharides - Evade phagocytosis.
- Virulence factor
- Resist detergents.
- Strongly antigenic
Structures internal to cell wall
Nucleoid - DNA coiled.
- lies in cytoplasm attached to cell
membrane.
- Lacks histone proteins (basically
circular)
Cytoplasmic membrane - Phospholipids and proteins - Active transport
- Site for respiratory chain components
Mesosomes - Invagination of cell membrane - Respiratory activities of the cell
Ribosomes - 70S - Protein synthesis
Cytoplasm - Fluid-like (same as eukaryotes)
Endospores - Spherical - Helps withstand:
- identified by Schaeffer - Bacterial DNA High temps
Fulton stain = green - Ribosomes Desiccation (drying)
- High concs of dipicolinic acid Chemicals e.g. detergents
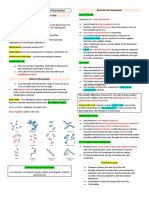
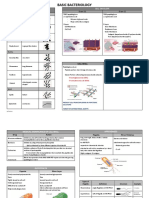
Staining:
Solution Identify
Gram stain Crystal violet iodine stain - Gram positive bacteria’s thick peptidoglycan
cell wall traps the stain = purple
- Gram negative doesn’t = pink
Acid fast Red dye carol fuchsin - High content of mycolic acid in acid fast
bacteria
- Mycobacterium
Endospore staining Malachite green - Stain penetrates endospores
(Schaffer-Fulton) Counterstain: safranin
You might also like
- AQA Biology: 2 Nucleic Acids Exam-Style QuestionsDocument7 pagesAQA Biology: 2 Nucleic Acids Exam-Style Questionsreneehands100% (2)
- CytologyDocument20 pagesCytologykaziba stephen100% (1)
- Class7 - Nutrition in Plants-1Document6 pagesClass7 - Nutrition in Plants-17A04Aditya Mayank75% (4)
- Parts of Frog HistologyDocument6 pagesParts of Frog HistologyVanessa RebancosNo ratings yet
- A Study Course in Nutrition by DR Forrest ShakleeDocument89 pagesA Study Course in Nutrition by DR Forrest ShakleeEmpresario100% (1)
- Part 10 ProkaryoticDocument54 pagesPart 10 ProkaryoticLê Thanh HằngNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 - Micro To paraDocument18 pagesMod 6 - Micro To paraDonzzkie DonNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesBacteria: Prokaryotes EukaryotesJerson Aizpuro SuplementoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Ultra StructureDocument31 pagesBacterial Ultra StructurequrratainiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Presentation2Document57 pagesBacterial Cell Presentation2rehanaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell and StainingDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cell and StainingKriziaoumo P. OrpiaNo ratings yet
- General Microbiology Lecture - No - 2 - Medicine - Autumn SemesterDocument33 pagesGeneral Microbiology Lecture - No - 2 - Medicine - Autumn SemesterCharlie JohnsonNo ratings yet
- OkieDocument3 pagesOkieFebeval CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life - 011321Document73 pagesCell Unit of Life - 011321abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Bacterial StructureDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Bacterial StructureAyat MostafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3 Micro PaperDocument9 pagesChapter 1,2,3 Micro Papermenamamdouh20No ratings yet
- Cell ProkaryotDocument107 pagesCell ProkaryotYani-dha CidHotNo ratings yet
- Mikrobiologi Industri: Dr. Eng. R. DarmawanDocument58 pagesMikrobiologi Industri: Dr. Eng. R. DarmawanSelvi Amelia VNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Bacterial Structure Prokaryotes Eukaryotes and ArchaebacteriaDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Bacterial Structure Prokaryotes Eukaryotes and ArchaebacteriaJoaqin CastroNo ratings yet
- 04 Bacterial CytologyDocument3 pages04 Bacterial CytologyRica Mae Agasen SalazarNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Sel Bakteri2Document41 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Sel Bakteri2Ois SariNo ratings yet
- l4 - Microbiology LecDocument6 pagesl4 - Microbiology LecErika IcawaloNo ratings yet
- 1 ToxonomyDocument48 pages1 ToxonomyroshnayimNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Structure: BacteriaDocument5 pagesBacterial Cell Structure: BacteriaHassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- Biology: 066b4349/Mar-2018-Biology-Notes PDFDocument9 pagesBiology: 066b4349/Mar-2018-Biology-Notes PDFOshein MontimorNo ratings yet
- Micro para 1Document4 pagesMicro para 1Reselle EspirituNo ratings yet
- G9 STE Q3 Biotechnology ReviewerDocument9 pagesG9 STE Q3 Biotechnology ReviewerJoyz Etneilas ArguillesNo ratings yet
- Histo Book (1-3)Document5 pagesHisto Book (1-3)Gwen YosheenNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining: Exercise 3Document4 pagesGram Staining: Exercise 3Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Nmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesNmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cellssavina100% (1)
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesMollyNo ratings yet
- Cells and Microscopy Worksheet 1Document16 pagesCells and Microscopy Worksheet 1George ChanNo ratings yet
- 2-Antibiotic ChemotherapyDocument34 pages2-Antibiotic ChemotherapyYoueel IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- SEM 2 (ImmunoSero - Part1&2)Document8 pagesSEM 2 (ImmunoSero - Part1&2)DayNo ratings yet
- The Microbial World: Bacterial Cell Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesThe Microbial World: Bacterial Cell Structure and Functionluthfiah adzaniNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Prokaryotic Cell UltrastructureDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Prokaryotic Cell UltrastructureFetalvero EddieNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Physiology of Bacteria StudentDocument88 pagesMorphology and Physiology of Bacteria StudentChandana RajuNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Bab 2Document31 pagesBio F4 Bab 2Alwani FarahiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Usmle EndpointDocument208 pagesMicrobiology, Usmle EndpointYazan M Abu-FaraNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell AnatomyDocument3 pagesBacterial Cell AnatomyTreshia SusonNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 4 Microbiology & ParasitologyDocument48 pagesPertemuan 4 Microbiology & ParasitologyRizky BluesNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument15 pagesCell BiologySinchan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Bacterial StructureDocument45 pagesChapter II Bacterial StructureBROOKNo ratings yet
- The Bacterial CellDocument24 pagesThe Bacterial Celljose carlos jimenez huashuayoNo ratings yet
- Morphology of BacteriaDocument44 pagesMorphology of BacteriaDr Harender SimarNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes BioDocument11 pagesSummary Notes Biojerushd05No ratings yet
- Bacterial Virulence FactorsDocument2 pagesBacterial Virulence FactorsJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Morfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDocument47 pagesMorfology AND Citology of Bacteria: Sidarningsih, Drg.,mkesDaffa YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Basic Bacteriology: Bacteria FormsDocument8 pagesBasic Bacteriology: Bacteria FormsKATHE DEANIELLE H. DAYONNo ratings yet
- Microbial Taxonomy - System That Involves in The Organization, Classification, Naming orDocument5 pagesMicrobial Taxonomy - System That Involves in The Organization, Classification, Naming orRedelle Mae NiniNo ratings yet
- Bacillus SPP Dormant: Clinical Bacteriology LecDocument5 pagesBacillus SPP Dormant: Clinical Bacteriology LecJamie BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Biology For Engineer: Microbial Diversity Taxonomy Cell Naming Gram StainDocument42 pagesChapter 1 Basic Biology For Engineer: Microbial Diversity Taxonomy Cell Naming Gram StainDivyashini MohanNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Komal SaparaDocument72 pagesCell Biology: Komal SaparaKomalNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Part LLLDocument36 pagesMicrobiology Notes Part LLLClark KentNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms WorksheetsDocument5 pagesKingdoms WorksheetsTessNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Cell Structure (Lepas)Document36 pagesChapter 5 - Cell Structure (Lepas)MOCHILNo ratings yet
- BACTERIAL MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE - Dr. GuintoDocument4 pagesBACTERIAL MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE - Dr. GuintoMonicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35 Antibacterial DrugsDocument36 pagesChapter 35 Antibacterial Drugstipu94No ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51 during migration in HaCat cellsFrom EverandProtein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51 during migration in HaCat cellsNo ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and DnaDocument5 pagesChromosomes and DnaS. AnsariNo ratings yet
- S1 Nuclease MappingDocument11 pagesS1 Nuclease Mappingstevensb055100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology RevisionDocument88 pagesIGCSE Biology RevisionAlex Parkinson100% (3)
- Secondary School Biology Short Notes and Exercises For Grade 9Document19 pagesSecondary School Biology Short Notes and Exercises For Grade 9Gashaw Fikir AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Biologia de Lombrices PDFDocument332 pagesBiologia de Lombrices PDFJose Tomas Rojas Espinoza0% (1)
- Relationships Between Populations in The BiocoenosisDocument13 pagesRelationships Between Populations in The BiocoenosisSeptim SalvarusNo ratings yet
- Worksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1Document4 pagesWorksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1AreebNo ratings yet
- Q1 Science 9 Module 3Document31 pagesQ1 Science 9 Module 3apudcrizarcellNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper U1Document16 pagesExam Paper U1samantha_ong_22No ratings yet
- 01.wolbachia Masseliensis - YLDocument20 pages01.wolbachia Masseliensis - YLYounes LaidoudiNo ratings yet
- RangayanDocument490 pagesRangayanSneha SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes ch13 Organisms and Populations PDFDocument10 pages12 Biology Notes ch13 Organisms and Populations PDFYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Podcast ScriptDocument7 pagesPodcast Scriptatreyi.2782No ratings yet
- SMJK Sam Tet, Ipoh, Perak Mid Year Examination 2019 Form 4 ScienceDocument6 pagesSMJK Sam Tet, Ipoh, Perak Mid Year Examination 2019 Form 4 SciencejohnNo ratings yet
- Nitrification Libro 2011Document465 pagesNitrification Libro 2011jenny escobarNo ratings yet
- Giant Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of The Breast: A Case Report Etuk EB', Amanari OC', Nwafor CC 2Document5 pagesGiant Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of The Breast: A Case Report Etuk EB', Amanari OC', Nwafor CC 2siti qomaria usuNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument48 pagesBotanyVenky GVNo ratings yet
- Superior Science Degree College Kabirwala: Biology 1 YearDocument8 pagesSuperior Science Degree College Kabirwala: Biology 1 YearZeb Un NisaNo ratings yet
- Formocresol, Still A Controversial Material For Pulpotomy: A Critical Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesFormocresol, Still A Controversial Material For Pulpotomy: A Critical Literature ReviewCristina Androne MihăescuNo ratings yet
- Report STS MH 4 6 - 1stsem23 24Document3 pagesReport STS MH 4 6 - 1stsem23 24Kurt SecretarioNo ratings yet
- PLDH-L GB-D 21 001Document4 pagesPLDH-L GB-D 21 001Nita Sinta BelaNo ratings yet
- The Emotional Brain Fear and The Amygdala PDFDocument13 pagesThe Emotional Brain Fear and The Amygdala PDFANo ratings yet
- Dna RepairDocument34 pagesDna RepairSCRIBEDNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Suhu Terhadap Kerja EnzimDocument6 pagesPengaruh Suhu Terhadap Kerja EnzimAlfrilin PadjaoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy & Phytochemistry I: Practice Question Paper (Unit-02)Document4 pagesPharmacognosy & Phytochemistry I: Practice Question Paper (Unit-02)Krishnendu Ray100% (1)