Professional Documents
Culture Documents
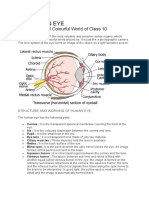
The Human Eye and Colourful World
The Human Eye and Colourful World
Uploaded by
alanaee123Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Human Eye and Colourful World
The Human Eye and Colourful World
Uploaded by
alanaee123Copyright:
Available Formats
The Human Eye And The Colourful World
Vitamin A (raw carrots, broccoli, green vegetables, cod-liver oil, etc.) is necessary for good
vision.
To protect your eyes, the following points should be remembered:
o Avoid reading in dim light.
o Wash your eyes at least four times a day with clean and cold water.
o Wash your eyes quickly if dust particles or small insects enter your eye.
o Visit an eye specialist regularly. Improper vision can cause stress, eyestrain, and even
headaches.
o While reading, maintain a distance of atleast 25 cm between your eyes and the book.
o Do not rub your eyes. If redness in the eye persists, then consult an eye specialist
immediately.
o Avoid direct exposure to sunlight. Exposure to a large amount of light can harm your retina.
Power of accommodation
o Ability of the lens to adjust its focal length
o Thickness of the lens is controlled by ciliary muscles
o Nearest focal distance of lens = 25 cm
Defects
o Myopia/near-sightedness
Problem: Distant objects cannot be seen clearly
Image is formed in front of the retina
Correction –concave lens
Hypermetropia/far-sightedness
o Problem: Near objects are not seen clearly
o Image formed beyond the retina
o Correction – convex lens
Presbyopia – Near-focus distance increases with age
o Power of accommodation decreases
o Correction– Bi-focal lens and concave lens
Refraction through a prism
o Light bends because of refraction that takes place at points B and C .
o The extent of deviation of the light ray from its path BE to path CD is known as the angle of
deviation ( )
The splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours, when it passes
through a glass prism, is called the dispersion of light
o Red → Disperses least
o Violet → Disperses most
o Yellow → Average of all lights
Formation of rainbow is a natural phenomenon in which white sunlight splits into beautiful
colours by water droplets.
Flickering of objects - this is because the air above the fire is relatively hotter than the air
further up in the atmosphere.
Twinkling of stars – caused by changing air density in the atmosphere
Early sunrise and delayed sunset – caused by refraction of light through the atmosphere
The sun and the planets do not twinkle because they are not seen as point sources like
stars, but are considered as extended sources.
Scattering is the phenomenon of absorption and re-emission of light.
The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particle gives rise to Tyndall effect.
Atmospheric particles, smoke, tiny water droplets, suspended particles of dust, and air
molecules scatter sunlight. Therefore, the path of light becomes visible.
Sky is blue- because light near blue wavelength scatters most.
Danger signs are red in colour- because red light scatters least.
You might also like
- Mike's Videos - General Chemistry Lesson Outline PDFDocument63 pagesMike's Videos - General Chemistry Lesson Outline PDFAmandaLe50% (2)
- Lasers in Operative DentistryDocument108 pagesLasers in Operative Dentistryrasagna reddy100% (2)
- Diafiltration A Fast Efficient Method For Desalting or Buffer Exchange of Biological Samples PDFDocument6 pagesDiafiltration A Fast Efficient Method For Desalting or Buffer Exchange of Biological Samples PDFDario Jose Rincon Garcia100% (1)
- CH 4 Human Eye Notes NewDocument10 pagesCH 4 Human Eye Notes Newsatwik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School: Structure of EyeDocument10 pagesDelhi Public School: Structure of Eyekakashi sNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument7 pagesHuman Eyesubham ghoshNo ratings yet
- Human Eye NDADocument7 pagesHuman Eye NDAKushal SahaNo ratings yet
- Humam EyeDocument7 pagesHumam EyeMahamNo ratings yet
- Human Eye - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesHuman Eye - Shobhit NirwanbookssssNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument4 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldVenkataNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934Document5 pagesPhysics 10th Human Eye and Colourful World - 082934defalter090No ratings yet
- Human Eye & Colourful World 1Document71 pagesHuman Eye & Colourful World 1Anoop JoyNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorful WorldDocument53 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorful WorldM SreehithaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye (Prashant Kirad)Document15 pagesHuman Eye (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal1786% (7)
- Light Human Eye 1Document53 pagesLight Human Eye 1Devika ManiNo ratings yet
- Human Eye & WorldDocument5 pagesHuman Eye & WorldSuchita JhaNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document30 pagesCH 11piyushNo ratings yet
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument23 pagesLight-Human Eye and The Colourful Worldapi-268345960No ratings yet
- Note-Human Eye and Colourfull WorldDocument6 pagesNote-Human Eye and Colourfull WorldjamaluddinNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240503-WA0006._removedDocument14 pagesDOC-20240503-WA0006._removedashika2731No ratings yet
- Human Eye Chapter'sDocument17 pagesHuman Eye Chapter'sPratik ChavanNo ratings yet
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument57 pagesLight-Human Eye and The Colourful Worldsmi.29981No ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Document11 pages10 Science Notes 11 Human Eye and Colourful World 1Koustav BiswasNo ratings yet
- RS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23Document6 pagesRS - X - Physics - July - Notes of Human Eye - 2022-23RishikaNo ratings yet
- CHapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldDocument7 pagesCHapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Human Eye & Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesChapter Notes Human Eye & Colourful Worldroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful World NotesDocument7 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful World NotesManisha TanwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction (1)Document12 pagesChapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction (1)ronakdoda1No ratings yet
- Human Eye 20230715152207212Document4 pagesHuman Eye 20230715152207212NEERAV ANANDNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World NotesChetan BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument3 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful WorldVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- 1693407010994.human Eye Lesson NotesDocument7 pages1693407010994.human Eye Lesson NotesNEEL PAREKHNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XADocument17 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XAshashank100% (1)
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful Worldapi-246793885100% (1)
- Physics U2Document6 pagesPhysics U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Copy of LIGHT-HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD.ppt.pptxDocument26 pagesCopy of LIGHT-HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD.ppt.pptxdakshvatsayanNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 2023Document5 pagesHuman Eye 2023arpitashekhawat2No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Revision NotesDocument50 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Revision Notesblazing7875No ratings yet
- Grade 12 Humms Phenomena of LightDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Humms Phenomena of LightJay r DomingoNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument9 pagesHuman EyeNimish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 2 NotesUday ModiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument9 pagesClass 10 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldSunita Kubde100% (1)
- hUMAN EYE 14 - 18Document5 pageshUMAN EYE 14 - 18mannanpass221No ratings yet
- Light-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument23 pagesLight-Human Eye and The Colourful WorldAbhinandan Borad95% (22)
- Human Eye 1Document6 pagesHuman Eye 1Aadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Notes Human EyeDocument9 pagesNotes Human EyeGeetanshi OberoiNo ratings yet
- Handout Gen Physics 2Document5 pagesHandout Gen Physics 2AshleyJaneFuentesNo ratings yet
- 0000Document8 pages0000taetaehyungNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World (PW)Document16 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World (PW)Rahul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesDocument9 pages11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesvenkatNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- (459539) 1.1 BGE 1 - Light Summary NotesDocument8 pages(459539) 1.1 BGE 1 - Light Summary NotesSesê YsäNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument5 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldpaparaoNo ratings yet
- Notes of 10th Cbse Human EyeDocument7 pagesNotes of 10th Cbse Human EyeAvichal TatuNo ratings yet
- Human Eye NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Eye NotesBhavesh KalkhandaNo ratings yet
- Optical Phenomena PDFDocument15 pagesOptical Phenomena PDFRohit KalsiNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Radiometric Correction and Calibration of SAR ImagesDocument7 pagesRadiometric Correction and Calibration of SAR ImagesSimone MeschinoNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2Document12 pagesThermo 2katabayoob11No ratings yet
- Project Report On Lathe MachineDocument33 pagesProject Report On Lathe Machinesanu7blyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 FLSDocument30 pagesChapter 5 FLSnurul najwaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver 1.6Document61 pagesOptical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver 1.6markpriceNo ratings yet
- 6、Field Oriented control (FOC)Document11 pages6、Field Oriented control (FOC)Sol GuiNo ratings yet
- Glassco 2011 2012 Loba LifeDocument60 pagesGlassco 2011 2012 Loba LifeShiv Shankar SahNo ratings yet
- Talyrond 51 Operating InstructionsDocument44 pagesTalyrond 51 Operating InstructionsAnenomeNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Gen Physics Module Week 2Document6 pagesGrade 12 Gen Physics Module Week 2leslie mermeloNo ratings yet
- Force and Acceleration WSDocument2 pagesForce and Acceleration WSMIS NURUL IMAN JakbarNo ratings yet
- Logic ProbeDocument3 pagesLogic ProbeVijay MirjeNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Two Mark Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit - I: Two Mark Questions & Answerssmg26thmayNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Physicspavan kumarNo ratings yet
- Stanford University Most Stupid Professor Leonard SusskindDocument161 pagesStanford University Most Stupid Professor Leonard SusskindJoe Nahhas8% (13)
- Essentials Volume 1 20140115 25744Document8 pagesEssentials Volume 1 20140115 257442bcoatingNo ratings yet
- Speck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsDocument134 pagesSpeck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsSimona Mariana DutuNo ratings yet
- Aryan WilleyDocument8 pagesAryan WilleyAryan DeepNo ratings yet
- FAC Rules e 2015Document267 pagesFAC Rules e 2015Seong Ju KangNo ratings yet
- Vortex Flow Meter User ManualDocument33 pagesVortex Flow Meter User ManualPankaj PadiwalNo ratings yet
- Bose Blackline MastersDocument42 pagesBose Blackline MastersgardeostroNo ratings yet
- ASAT - Volume 17 - Issue AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 17 &ndash April 11 - 13, 2017 - Pages 1-21Document21 pagesASAT - Volume 17 - Issue AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 17 &ndash April 11 - 13, 2017 - Pages 1-21yubrany gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Appendix G: Matrices, Determinants, and Systems of EquationsDocument10 pagesAppendix G: Matrices, Determinants, and Systems of EquationsJustin PolidoNo ratings yet
- HYTEKDocument1 pageHYTEKHeather MurphyNo ratings yet
- Chap13 Et Student SolutionsDocument82 pagesChap13 Et Student SolutionsCody MichelNo ratings yet
- DATEL Application NoteDocument1 pageDATEL Application Noteyousaf_zai_khan81995No ratings yet
- NEP 2020 MathematicsDocument23 pagesNEP 2020 MathematicsAvnish BhattNo ratings yet