Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IEMs
IEMs
Uploaded by
bancayanadien3Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- VITO 762 Installation GuideDocument36 pagesVITO 762 Installation GuideThái Ngọc0% (1)
- Inborn Errors or MetabolismDocument25 pagesInborn Errors or MetabolismSamdiSutantoNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathiesDocument2 pagesAminoacidopathiesbarbiegahibNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MRCPCHDocument11 pagesMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNo ratings yet
- All PharmDocument288 pagesAll PharmoliviagbeckNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid DisordersDocument7 pagesAmino Acid DisordersarshehadaNo ratings yet
- Biochem, MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesBiochem, MicrobiologyRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument2 pagesAntimalarial DrugsSushmita VandariNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Diseases / Disorders Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesBiochemistry: Diseases / Disorders Genetic DisordersKailash KhatriNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Feline Hepatic LipidosisDocument46 pagesFeline Hepatic LipidosisAndre Suarez FarfanNo ratings yet
- Disease of Infancy 1Document7 pagesDisease of Infancy 1Cherie thompsonNo ratings yet
- ANTIPARASITICDocument4 pagesANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- IEM ScreeningDocument68 pagesIEM ScreeningKota AnuroopNo ratings yet
- CalciumDocument2 pagesCalciumNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINS TRACE AND TOXICOLOGY StudentsDocument17 pagesVITAMINS TRACE AND TOXICOLOGY StudentsRapada, Rowelyn S.No ratings yet
- Biochem Quick Review by Haji MuhammadDocument7 pagesBiochem Quick Review by Haji Muhammadimran dilawarNo ratings yet
- Different Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetDocument12 pagesDifferent Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetRyan DaetNo ratings yet
- Summary Nelsons Chapter 84Document2 pagesSummary Nelsons Chapter 84Michael John Yap Casipe100% (1)
- Inborn Errors of MetabolismDocument45 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolismzekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- MCB Diseases Exam 1 - CVDocument7 pagesMCB Diseases Exam 1 - CVaucukagapeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Deficiency Related DiseasesDocument10 pagesEnzyme Deficiency Related DiseasesOzzie FagiriNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument8 pagesAntidotedeanelaylayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraNo ratings yet
- ANTIPARASITICDocument5 pagesANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors Metabolism - Sept 2014Document28 pagesInborn Errors Metabolism - Sept 2014Tahta PambudiNo ratings yet
- Table of AntidotesDocument5 pagesTable of Antidotesangelotisbe1120No ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismDocument36 pagesGlucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismTHENEXTSTEPNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Document4 pagesCommon Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Maryam Khushbakhat50% (2)
- Disorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesDisorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument2 pagesAlcoholsJustin Victor AngNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument47 pagesBiochemistry PDFMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-AnemiaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Anti-AnemiaChelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersMitch Ibay100% (1)
- Perinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in ManagementDocument31 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in Managementokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Lipidosis HepaticaDocument45 pagesLipidosis HepaticaJojoa E WilNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument5 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualwarishNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument55 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismRahil singh chauhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Fate of Carbon Skeleton in Amino Acid Catabolism - DR Max Efui Annani-AkollorDocument50 pages2 Fate of Carbon Skeleton in Amino Acid Catabolism - DR Max Efui Annani-AkollorMax Annani-akollorNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Cpliver 1Document4 pagesCpliver 1isahNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument5 pagesAntidoteMaynard ArandaNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism Student LectureDocument81 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism Student LectureFavourNo ratings yet
- Tropical SprueDocument3 pagesTropical SprueAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- 020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Document12 pages020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Sargonan RaviNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 2Document2 pagesTable For Exam 2raybuaNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- ANTHELMINTICSDocument2 pagesANTHELMINTICSMarie PaclebNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument2 pagesWater Soluble Vitaminsnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument37 pagesVitaminsMaryNo ratings yet
- Disease Compendium UpdatedDocument9 pagesDisease Compendium UpdatedKing-son LinNo ratings yet
- Anti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDocument1 pageAnti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDan PobanNo ratings yet
- Tc1057-Eng-10004 0 002 PDFDocument507 pagesTc1057-Eng-10004 0 002 PDFKenaia AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Sample Baby Meal Plans - NilanjanaDocument2 pagesSample Baby Meal Plans - NilanjanahailscribdNo ratings yet
- RABE - Sexual Imagery On The Phantasmagorical Castles at KhajurahoDocument30 pagesRABE - Sexual Imagery On The Phantasmagorical Castles at KhajurahoMarco PassavantiNo ratings yet
- Generalbio2 StecDocument105 pagesGeneralbio2 StecJohn V. LabradorNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture Aeration ModulesDocument7 pagesAquaculture Aeration ModulesecosafeNo ratings yet
- Energy System EngineeringDocument116 pagesEnergy System EngineeringAila DarNo ratings yet
- E BookDocument64 pagesE BookWaqar HassanNo ratings yet
- Brown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyDocument9 pagesBrown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyAneel Nizar AliNo ratings yet
- Texi Post DD ErsatzteillisteDocument52 pagesTexi Post DD ErsatzteillisteJozsef TomoriNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Comprehensive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Si-BasedDocument12 pages2020 - Comprehensive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Si-Basedary.engenharia1244No ratings yet
- Gesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09Document1 pageGesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09ilkay tomlayNo ratings yet
- Percussion Laser DrillingDocument1 pagePercussion Laser DrillingBefzzNo ratings yet
- Product Range: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDocument39 pagesProduct Range: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionssandeepNo ratings yet
- 33 1rv18cv119 Umar BashirDocument10 pages33 1rv18cv119 Umar BashirUMARNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE-tables Lighting Power Density PDFDocument3 pagesASHRAE-tables Lighting Power Density PDFDan MolloyNo ratings yet
- Quickstart Dx35 de en FR Es PT ZH Ja It Ru Im0044955Document2 pagesQuickstart Dx35 de en FR Es PT ZH Ja It Ru Im0044955ROSSNo ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveTeodora PluskoskaNo ratings yet
- Soal OkeDocument12 pagesSoal OkefredyNo ratings yet
- AB 14 para Tranzystorow DarlingtonaDocument23 pagesAB 14 para Tranzystorow DarlingtonavengalamahenderNo ratings yet
- ALLEN-BRADLEY KINETIX 6200 SAFETY MANUAL PDF Download - ManuaLibDocument3 pagesALLEN-BRADLEY KINETIX 6200 SAFETY MANUAL PDF Download - ManuaLibticojfsNo ratings yet
- Catalyst and CatalysisDocument11 pagesCatalyst and CatalysisRehinaNo ratings yet
- Asahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDDocument1 pageAsahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDSUDARSHAN dAWNo ratings yet
- 1 - 语法点1Run-On SentenceDocument11 pages1 - 语法点1Run-On Sentenceihmc_cwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 ForgingDocument21 pagesChapter 14 ForgingNur RokhimNo ratings yet
- PPDocument15 pagesPPdana angela hernandezNo ratings yet
- Mobil PajeroDocument2 pagesMobil Pajeroesemelekete wele2No ratings yet
- STAAD - Pro Plates and Solid Elements (FAQ) - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesDocument15 pagesSTAAD - Pro Plates and Solid Elements (FAQ) - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesKamal RaoNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Module IDocument161 pagesSoft Computing Module INatarajanSubramanyamNo ratings yet
IEMs
IEMs
Uploaded by
bancayanadien3Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IEMs
IEMs
Uploaded by
bancayanadien3Copyright:
Available Formats
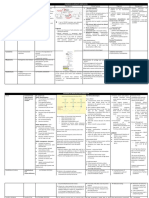
DISORDER PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CLINICAL FEATURES TREATMENT
Galactosemia - abnormal Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase 1 vomiting, Exclusion of galactose from the diet
CARBOHYDRA
accumulation of galactose in body (GALT) diarrhea,
organ systems Galactokinase (GALK) failure to thrive, lactose containing milk and food are substituted with
TE
UPD galactose-4-epimerase (GALE) hepatomegaly, casein hydrolysates and soy milk
splenomegaly,
neonatal jaundice
cataracts (2/2 galactitol accumulation)
Classic organic acidurias - deficiency Accumulation of toxic intermediates sudden onset of encephalopathy and episodic Dietary restrictions of relevant amino acids and
PROTEI
of enzymes in the mitochondrial Disturbance of mitochondrial energy metabolic acidosis avoidance of protein catabolism
metabolism of coenzyme A-activated metabolism and carnitine homeostasis
N
carboxylic acid Supplementation with carnitine and glycine (adjuncts)
Phenylketonuria - phenylalanine is deficiency in the activity of phenylalanine Mentally retarded Intellectual disability Dietary restriction of phenylalanine intake
AROMATIC AMINO ACIDS
metabolized to the phenyl ketones that hydroxylase - catalyzes the conversion of Stunted
are excreted in the urine phenylalanine to tyrosine. light skinned Continuous Phenylalanine restricted diet
Eczematoid rash or intractable itching
Autosomal recessive “musty” or “mousey” smelling individual (2/2 to Modification of phenotypic expression of defective
phenylacetate) gene
Other d/o: microcephaly
Tyrosinemia enamel hypoplasia Definitive: correcting the gene defect
Alkaptonuria hyperactivity with autistic behaviors
Albinism seizures
Hawkinsinuria tremors
athetosis
hyperreflexia
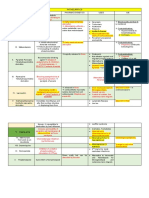
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) - Accumulation of 3 branched chain ketoacids Sudden onset lethargy Inhibit endogenous protein catabolism, sustain protein
passage of urine that has a Alpha ketoisocaproic acid high-pitched crying, synthesis, prevent deficiency of essential amino acids,
sweet, maple syrup-like odor Alpha ketoisovaleric acid feeds poorly, and maintaining normal serum osmolality
becomes opisthotonic, and comatose
BRANCHED CHAIN AMINO ACIDS
Alpha keto B methylvaleric acid
5 phenotypes of MSUD Seizure Peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis
Classic Accumulation of BCAA and 2-hydroxy acids in hypoglycemia
Intermittent the plasma, urine, and CSF Encephalopathy because of cerebral edema Special diets (MSUD powder) and strict protein
Intermediate - Accumulation is a consequence of a spastic restriction
Thiamine-responsive defect in oxidative decarboxylation of intellectually- retarded
E3 deficient branched chain ketoacids
Methylmalonic acidemia Defect methylmalonyl CoA mutase Neonatal ketoacidosis Correction of acidosis and prevention of further
Lethargy catabolism
Vomiting
profound hypotonia, Restriction of isoleucine, methionine, valine, and
profound metabolic acidosis threonine (medical food available)
Hema findings:
Anemia Trail of Vit B12
Leukopenia
thrombocytopenia Growth hormone tried in suboptimal growth
Isovaleric acidemia Isovaleryl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency Stale perspiration, sweaty feat, or ripe cheese Low protein
First week: acidosis, coma L-carnitine
Chronic: lethargy, vomiting, ataxia, and Glycine
ketoacidosis
Glutaric aciduria - Resemble Hypotonia, dystonia, choreoathetosis, and seizure High calorie, low protein diet, carnitine
extrapyramidal cerebral palsy
Macrocephaly, loss of appetite, profuse sweating Give carnitine as supplement
Diagnosis: and hypoglycemia, sleeplessness
Neuroimaging: batwing
appearance (frontotemporal
atrophy)
Caudate atrophy
Bilateral subdural hematoma
Urea Cycle Enzyme Carbamoyl palmytoyl synthese difiiency (CPS) Progressive lethargy, apnea and or seizures Removal of ammonia by peritoneal dialysis or
UREA CYCLE
ENZYME D/O
Ornithine transcarbamoylase deficiency (OTC) Hyperammonemia without metabolic acidosis hemodialysis
Argininosuccinate synthetase deficiency Unexplained vomiting, intermittent headaches,
(Citrullinemia) behavioral changes, or acute encephalopathy
Argininosuccinase deficiency (Argininosuccinic
aciduria)
Ornithinemia
Homocystinuria - Arteriovenous seizures, developmental slowing or cerebrovascular Pyridoxine (100-500 mg/day)
SULFUR-CONTAINING AA
thromboembolism – common cause of accident occur between 5-9 months, regression of
death developmental milestones. Dietary restriction of methionine
Hair is sparse, blond and brittle and multiple Folate (1-15 mg/ day)
Cystathionuria erythematous blotches are seen in the cheeks
Mercaptolactate-cysteine disulfiduria Betaine
Sulfite oxidase deficiency subluxed lens, glaucoma, cataracts, and optic
atrophy Aspirin and dipyridamole
osteoporosis, pectus excavatum, “Marfan-like”
habitus
Fatty Acid Oxidation Hepatic presentation - Hypoketotic, hypoglycemia, Treat it early
hyperammonemia, elevations of serum urea, uric
acid, and liver enzymes Prevent hypoglycemia during infancy
Cardiac - Progressive heart failure between 2-3 Frequent feeding
FAO D/O
years old
Cardiomyopathy is accompanied by acute hepatic
syndrome
Muscles - sudden muscle weakness associated with
myoglobinuria and renal failure during strenuous
exercise
You might also like
- VITO 762 Installation GuideDocument36 pagesVITO 762 Installation GuideThái Ngọc0% (1)
- Inborn Errors or MetabolismDocument25 pagesInborn Errors or MetabolismSamdiSutantoNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathiesDocument2 pagesAminoacidopathiesbarbiegahibNo ratings yet
- Metabolic MRCPCHDocument11 pagesMetabolic MRCPCHJawwad Masood AhmadNo ratings yet
- All PharmDocument288 pagesAll PharmoliviagbeckNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid DisordersDocument7 pagesAmino Acid DisordersarshehadaNo ratings yet
- Biochem, MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesBiochem, MicrobiologyRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument2 pagesAntimalarial DrugsSushmita VandariNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Diseases / Disorders Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesBiochemistry: Diseases / Disorders Genetic DisordersKailash KhatriNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Feline Hepatic LipidosisDocument46 pagesFeline Hepatic LipidosisAndre Suarez FarfanNo ratings yet
- Disease of Infancy 1Document7 pagesDisease of Infancy 1Cherie thompsonNo ratings yet
- ANTIPARASITICDocument4 pagesANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- IEM ScreeningDocument68 pagesIEM ScreeningKota AnuroopNo ratings yet
- CalciumDocument2 pagesCalciumNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- VITAMINS TRACE AND TOXICOLOGY StudentsDocument17 pagesVITAMINS TRACE AND TOXICOLOGY StudentsRapada, Rowelyn S.No ratings yet
- Biochem Quick Review by Haji MuhammadDocument7 pagesBiochem Quick Review by Haji Muhammadimran dilawarNo ratings yet
- Different Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetDocument12 pagesDifferent Hyperglycemic State: Ryan I. DaetRyan DaetNo ratings yet
- Summary Nelsons Chapter 84Document2 pagesSummary Nelsons Chapter 84Michael John Yap Casipe100% (1)
- Inborn Errors of MetabolismDocument45 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolismzekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- MCB Diseases Exam 1 - CVDocument7 pagesMCB Diseases Exam 1 - CVaucukagapeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Deficiency Related DiseasesDocument10 pagesEnzyme Deficiency Related DiseasesOzzie FagiriNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument8 pagesAntidotedeanelaylayNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraNo ratings yet
- ANTIPARASITICDocument5 pagesANTIPARASITICJahn MyrilleeNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors Metabolism - Sept 2014Document28 pagesInborn Errors Metabolism - Sept 2014Tahta PambudiNo ratings yet
- Table of AntidotesDocument5 pagesTable of Antidotesangelotisbe1120No ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismDocument36 pagesGlucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismTHENEXTSTEPNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Document4 pagesCommon Drugs and Their Antidotes - PDF Version 1Maryam Khushbakhat50% (2)
- Disorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesDisorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument2 pagesAlcoholsJustin Victor AngNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument47 pagesBiochemistry PDFMoe KebabNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-AnemiaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Anti-AnemiaChelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic DisordersDocument12 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic DisordersMitch Ibay100% (1)
- Perinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in ManagementDocument31 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in Managementokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Lipidosis HepaticaDocument45 pagesLipidosis HepaticaJojoa E WilNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument5 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualwarishNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument55 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismRahil singh chauhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Fate of Carbon Skeleton in Amino Acid Catabolism - DR Max Efui Annani-AkollorDocument50 pages2 Fate of Carbon Skeleton in Amino Acid Catabolism - DR Max Efui Annani-AkollorMax Annani-akollorNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Cpliver 1Document4 pagesCpliver 1isahNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument5 pagesAntidoteMaynard ArandaNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism Student LectureDocument81 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism Student LectureFavourNo ratings yet
- Tropical SprueDocument3 pagesTropical SprueAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- 020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Document12 pages020 - Metabolism of Proteins 3Sargonan RaviNo ratings yet
- Table For Exam 2Document2 pagesTable For Exam 2raybuaNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- ANTHELMINTICSDocument2 pagesANTHELMINTICSMarie PaclebNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument2 pagesWater Soluble Vitaminsnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument37 pagesVitaminsMaryNo ratings yet
- Disease Compendium UpdatedDocument9 pagesDisease Compendium UpdatedKing-son LinNo ratings yet
- Anti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDocument1 pageAnti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDan PobanNo ratings yet
- Tc1057-Eng-10004 0 002 PDFDocument507 pagesTc1057-Eng-10004 0 002 PDFKenaia AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Sample Baby Meal Plans - NilanjanaDocument2 pagesSample Baby Meal Plans - NilanjanahailscribdNo ratings yet
- RABE - Sexual Imagery On The Phantasmagorical Castles at KhajurahoDocument30 pagesRABE - Sexual Imagery On The Phantasmagorical Castles at KhajurahoMarco PassavantiNo ratings yet
- Generalbio2 StecDocument105 pagesGeneralbio2 StecJohn V. LabradorNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture Aeration ModulesDocument7 pagesAquaculture Aeration ModulesecosafeNo ratings yet
- Energy System EngineeringDocument116 pagesEnergy System EngineeringAila DarNo ratings yet
- E BookDocument64 pagesE BookWaqar HassanNo ratings yet
- Brown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyDocument9 pagesBrown Et Al. 2009 Tribolium A Model For Developmental and Pest BiologyAneel Nizar AliNo ratings yet
- Texi Post DD ErsatzteillisteDocument52 pagesTexi Post DD ErsatzteillisteJozsef TomoriNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Comprehensive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Si-BasedDocument12 pages2020 - Comprehensive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Si-Basedary.engenharia1244No ratings yet
- Gesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09Document1 pageGesab 95131 SCR Chamber 2020-07-09ilkay tomlayNo ratings yet
- Percussion Laser DrillingDocument1 pagePercussion Laser DrillingBefzzNo ratings yet
- Product Range: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDocument39 pagesProduct Range: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionssandeepNo ratings yet
- 33 1rv18cv119 Umar BashirDocument10 pages33 1rv18cv119 Umar BashirUMARNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE-tables Lighting Power Density PDFDocument3 pagesASHRAE-tables Lighting Power Density PDFDan MolloyNo ratings yet
- Quickstart Dx35 de en FR Es PT ZH Ja It Ru Im0044955Document2 pagesQuickstart Dx35 de en FR Es PT ZH Ja It Ru Im0044955ROSSNo ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns: Verb + Infinitive or Verb + - Ing?: Verbs Followed by A To-InfinitiveTeodora PluskoskaNo ratings yet
- Soal OkeDocument12 pagesSoal OkefredyNo ratings yet
- AB 14 para Tranzystorow DarlingtonaDocument23 pagesAB 14 para Tranzystorow DarlingtonavengalamahenderNo ratings yet
- ALLEN-BRADLEY KINETIX 6200 SAFETY MANUAL PDF Download - ManuaLibDocument3 pagesALLEN-BRADLEY KINETIX 6200 SAFETY MANUAL PDF Download - ManuaLibticojfsNo ratings yet
- Catalyst and CatalysisDocument11 pagesCatalyst and CatalysisRehinaNo ratings yet
- Asahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDDocument1 pageAsahi Carbon Black (For Rubber) Physical Chemistry Properties of Main Products - Products - Products and Technology - ASAHI CARBON CO., LTDSUDARSHAN dAWNo ratings yet
- 1 - 语法点1Run-On SentenceDocument11 pages1 - 语法点1Run-On Sentenceihmc_cwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 ForgingDocument21 pagesChapter 14 ForgingNur RokhimNo ratings yet
- PPDocument15 pagesPPdana angela hernandezNo ratings yet
- Mobil PajeroDocument2 pagesMobil Pajeroesemelekete wele2No ratings yet
- STAAD - Pro Plates and Solid Elements (FAQ) - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesDocument15 pagesSTAAD - Pro Plates and Solid Elements (FAQ) - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesKamal RaoNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Module IDocument161 pagesSoft Computing Module INatarajanSubramanyamNo ratings yet