Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motivation
Motivation
Uploaded by
noreen lindaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motivation
Motivation
Uploaded by
noreen lindaCopyright:
Available Formats
Motivation -The fifth and topmost level needs in
-refers to the “process of the hierarchy are called
activating behavior, sustaining it, and self-actualization needs and involve
directing it toward a particular goal.” realizing our full potential as human
This definition is useful because it beings and becoming all that we are
specifies three stages: activating, able to be.
sustaining, and directing actions
towards the achievement of
objectives.
Motivating
-refers to the act of “giving
employees reasons or
incentives... to work to achieve
organizational objectives.”
Factors Contributing to Motivation
- willingness to do a job
- self-confidence in carrying out a task
- needs of satisfaction
Theories of Motivation 2. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
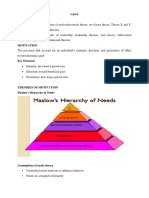
1. Maslow’s Needs Hierachy Theory -Developed by Frederick Herzberg
Abraham Maslow - a psychologist, He indicates that a satisfied employee
theorized that human beings have five is motivated from within to work
basic needs which are as harder and that a dissatisfied
follows: physiological, security, social, employee is not self-motivated.
esteem, and self-actualization. These Two classes of factors associated with
needs are hierarchical, which means, employee satisfaction and dissatisfaction:
one need will have to be satisfied first -Motivational Factors (Satisfiers)
before the other need -Hygiene Factors (Dissatisfiers).
A.PHYSIOLOGICAL NEEDS Motivational Factors
-Those that are concerned with -Factors that directly contribute to job
biological needs like food, drink rest, satisfaction and motivate employees
and sex fall under the category of to perform better. Examples include:
physiological needs. These needs -Achievement
take priority over other needs. -Recognition Advancement
B.SECURITY NEEDS -Opportunities for Personal
-After satisfying that physiological Growth
needs, people will seek to satisfy their Hygiene Factors
safety needs. These needs include -Are aspects of the work environment,
freedom from harm coming from the that, when lacking, can lead to
elements or from other people, dissatisfaction among employees.
financial security which may be Examples include:
affected by loss of job or the -Working Conditions Salary
breadwinner in the family, etc. -Job Security
C.SOCIAL NEEDS -Interpersonal Relationships
-After satisfying his physiological and Hygiene Factors mainly address the
security needs, the employee will no context or environment in which
strive to secure love, affection and the employees work.
need to be accepted by peers. Motivational Factors are related to
D.ESTEEM NEEDS the content of the work itself and how
-The fourth level of needs is called fulfilling it is.
esteem needs and they refer to the
need for a positive self-image and
self-respect and the need to be
respected by others.
E.SELF-ACTUALIZATION NEEDS
3. Expectancy Theory QUALITY CONTROL CIRCLE
-is a motivation model based on -A method of direct employee
the assumption that an individual will participation is the quality circle
work depending on his perception of control (QCC). Th objective of the
the probability of his expectations to QCC is to increase productivity and
happen. The theory poses the idea quality of output.
that motivation is determined by SELF-MANAGED TEAMS
expectancies and valences. -When workers have reached a
-An expectancy is a belief about certain degree of discipline, they may
the likelihood or probability that a be ripe for forming self-managed
particular behavioral act (like teams. Also known as autonomous
attending training sessions) will lead work group or high performance
to a particular outcome (like a teams.
promotion). Valence is the value an
individual places on the expected
outcomes or rewards. Expectancy
theory is based on the following
assumptions
TECHNIQUES OF MOTIVATION
1.Motivation through Rewards
2.Motivation through Employee
Participation
Motivation through Rewards
-Rewards consist of material and
psychological benefits to employees
for performing tasks in the workplace.
Properly administered reward
systems can be improve job
performance and satisfaction.
CLASSIFIED INTO TWO:
1.Extrinsic- refer to payoffs
granted to the individual by
another party.
Examples: are money,
employee benefits, promotions,
recognition, status symbols,
praise, etc
2.Intrinsic - are internally
experienced payoffs which are
self-granted.
Examples: are a sense of
accomplishment, self-esteem
and self-actualization
Motivation through Employee
Participation
-When employees participate in
deciding various aspects of their jobs,
the personal involvement, oftentimes,
is carried up to the point where the
task is completed.
The two popular approaches to
participation includes the following:
1.Quality Control Circles
2.Self-managed Teams
You might also like
- Info Fivesstein Missing: TrackballDocument2 pagesInfo Fivesstein Missing: TrackballSaurabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Functions of Management Functions of Management: MotivatingDocument29 pagesFunctions of Management Functions of Management: MotivatingJam LarsonNo ratings yet
- Engg MNGT Lecture 910Document10 pagesEngg MNGT Lecture 910Diana Rose TanganNo ratings yet
- Em ScriptDocument3 pagesEm ScriptAlyca Chin jansorNo ratings yet
- Motivational TheoryDocument4 pagesMotivational TheorySumit Kr BiswakarmaNo ratings yet
- Buddhism and Modern ManagementDocument17 pagesBuddhism and Modern Managementsadawimala33% (3)
- "Motivating": - Stephen P RobbinsDocument5 pages"Motivating": - Stephen P RobbinsJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 ObDocument1 pageTutorial 4 ObAliff haiqalNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATIONDocument13 pagesMOTIVATIONADITYA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Motivation Introduction:: Desire For Money Success Recognition Job-Satisfaction Team Work, EtcDocument27 pagesMotivation Introduction:: Desire For Money Success Recognition Job-Satisfaction Team Work, EtcRavi MoriNo ratings yet
- Inorman Function of Management MotivatingDocument7 pagesInorman Function of Management MotivatingGilbert CalosaNo ratings yet
- Unit Five OBDocument28 pagesUnit Five OBAbdifatah Ahmed HurreNo ratings yet
- Edited Ob ch-4Document12 pagesEdited Ob ch-4Alex WorkinaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Motivation PDFDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Motivation PDFKrishna ShresthaNo ratings yet
- OM Motivating 1Document27 pagesOM Motivating 1RizeakatsukifakeNo ratings yet
- (PSY 225) 5th Exam ReviewerDocument3 pages(PSY 225) 5th Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- Motivation and Job Design: Republic of The Philippines Central Philippine University School of Graduate StudiesDocument4 pagesMotivation and Job Design: Republic of The Philippines Central Philippine University School of Graduate StudiesmsjoyceeNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy: Needs: Safety NeedsDocument4 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy: Needs: Safety NeedsBaher WilliamNo ratings yet
- International Business Assognment 2Document7 pagesInternational Business Assognment 2Mohammed RaselNo ratings yet
- Motivation and PerformanceDocument23 pagesMotivation and PerformanceHelena QueendomNo ratings yet
- Human Relation Approach Theory G 2Document29 pagesHuman Relation Approach Theory G 2John ReyNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument26 pagesMotivationRahul K PallikkaraNo ratings yet
- Principle of MGTDocument34 pagesPrinciple of MGTKajal MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Dual Tone Multi Frequency SignallingDocument5 pagesDual Tone Multi Frequency SignallingJohn Raphael PonienteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Motivation: Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument2 pagesChapter 16: Motivation: Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsNabila NworinNo ratings yet
- The Four Functions of ManagementDocument5 pagesThe Four Functions of ManagementWaqas IqbalNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoriesDocument15 pagesMotivation Theoriesnisha danielNo ratings yet
- Developmengt of Employeee Moral (HRM)Document5 pagesDevelopmengt of Employeee Moral (HRM)leleahgracebeguiaNo ratings yet
- CCB LeadershipDocument36 pagesCCB LeadershipJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes On MotivationDocument13 pagesNotes On MotivationSharan PatilNo ratings yet
- Group 6: Maria Angela Calderon Zhajill Coronel Hecthor Cuartero Darren Malayas John Patrick TesalonaDocument8 pagesGroup 6: Maria Angela Calderon Zhajill Coronel Hecthor Cuartero Darren Malayas John Patrick TesalonakendallNo ratings yet
- Dr. Azza Abdeldayem AtaDocument15 pagesDr. Azza Abdeldayem Ataheba abd elazizNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Stress ManagementDocument59 pagesMotivation and Stress ManagementGautam BhattaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 MCOBDocument66 pagesUnit-4 MCOBshreya.fruity23No ratings yet
- Module Directing Final FSDocument175 pagesModule Directing Final FSAditi KuteNo ratings yet
- Chap-04 Motivation UpdatedDocument36 pagesChap-04 Motivation UpdatedAl Hasan AbujorNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their ApplicationsDocument11 pagesChapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their ApplicationsAbene Man Wt BreNo ratings yet
- Research On Motivation TheoriesDocument15 pagesResearch On Motivation TheoriesNayeem Md SakibNo ratings yet
- Organization and ManagementDocument14 pagesOrganization and Managementutsav ashishNo ratings yet
- Employee Motivation Assigment Sem 2Document11 pagesEmployee Motivation Assigment Sem 2anishdebnath42No ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Oliver N. OliverosDocument14 pagesEngineering Management: Oliver N. OliverosJ. Robert TanNo ratings yet
- Kathlyn Heart R. Ragudo Tessie Mae O. PagtamaDocument40 pagesKathlyn Heart R. Ragudo Tessie Mae O. PagtamaTessie Mae Onongen PagtamaNo ratings yet
- MTBE - Module - 3Document83 pagesMTBE - Module - 3ABHIJITH V SNo ratings yet
- Hbo FinalsDocument8 pagesHbo FinalsJohn Ford E. MejiaNo ratings yet
- CH6 MOTIVATION in Extension OrganizationDocument70 pagesCH6 MOTIVATION in Extension OrganizationTokkummaa GalatuuNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - 13t - Gary DesslerDocument39 pagesHuman Resource Management - 13t - Gary Desslerhayelom0% (2)
- CCB LeadershipDocument36 pagesCCB LeadershiprajavikramarkaNo ratings yet
- HRM & OB Unit 4Document27 pagesHRM & OB Unit 4jav3d762No ratings yet
- HBC 2105 Principles of Management IIDocument23 pagesHBC 2105 Principles of Management IImoza salimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4Gizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Management TheoriesDocument25 pagesManagement Theoriessakshi malikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document15 pagesUnit 6Manjunath ShivannaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 People in BusinessDocument34 pagesChap 2 People in BusinessDennisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Motivating EmployeesDocument47 pagesChapter 12 - Motivating EmployeessallyNo ratings yet
- Chap 7Document6 pagesChap 7Michelle Francis Manila MoralesNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoryDocument12 pagesMotivation TheoryAnurag kumar89% (9)
- Motivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementDocument30 pagesMotivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementJaspher Jan PasolNo ratings yet
- Motivation ObDocument19 pagesMotivation ObAnkita MahajanNo ratings yet
- WEEK1to7-MOTIVATION THEORIESDocument11 pagesWEEK1to7-MOTIVATION THEORIESJosephine MungaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceFrom EverandUnderstanding Human Behaviour in The WorkplaceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Power of Motivation: Unleashing Your Inner Drive for SuccessFrom EverandThe Power of Motivation: Unleashing Your Inner Drive for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Design ProjectDocument31 pagesDesign ProjectVaibhav Vaidya0% (1)
- Sumitomo Chemical Alumina (ENG)Document16 pagesSumitomo Chemical Alumina (ENG)Lawrence LauNo ratings yet
- Suzlon One EarthDocument1 pageSuzlon One EarthShubhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter #4 - Machine LearningDocument29 pagesChapter #4 - Machine Learningmzoon mohmmedNo ratings yet
- Calculus For Iit Jee PDFDocument510 pagesCalculus For Iit Jee PDFAbhishek Kumar77% (94)
- Lesson 6 Minerals and Rocks S11 12ES Ia 9Document8 pagesLesson 6 Minerals and Rocks S11 12ES Ia 9Christine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflDocument7 pagesNumerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflvinodNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsGerald BaculnaNo ratings yet
- Case 3.1: "Ethical Selling at Perfect Solutions: The Case of The Delayed Product"Document3 pagesCase 3.1: "Ethical Selling at Perfect Solutions: The Case of The Delayed Product"Shan Danielle MortejoNo ratings yet
- Final Test Series - JEE (Main & Adv) 2023 - Phase-IIDocument3 pagesFinal Test Series - JEE (Main & Adv) 2023 - Phase-IIAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Conclusion PolymersDocument1 pageConclusion Polymershuong louNo ratings yet
- Matlab Sheet 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesMatlab Sheet 1 SolutionLonardo WajihNo ratings yet
- Struktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanDocument8 pagesStruktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanSri FamilasariNo ratings yet
- Mingjue-Ebook 2021Document29 pagesMingjue-Ebook 2021Virtualprisonerd100% (1)
- How To Be A SpeakerDocument6 pagesHow To Be A SpeakerGabor KovacsNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer EngineeringDocument79 pagesDepartment of Computer EngineeringTejaswi SuryaNo ratings yet
- EPP E2 Activity 2Document2 pagesEPP E2 Activity 2Hannah Nore TalingtingNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus B.tech 1stDocument12 pagesUG Syllabus B.tech 1stRaunak GuptaNo ratings yet
- DG 1Document161 pagesDG 1Gag PafNo ratings yet
- T 87 PG 101-102 PDFDocument2 pagesT 87 PG 101-102 PDFJossimar PerezNo ratings yet
- Iit Bombay ThesisDocument7 pagesIit Bombay Thesisfjd14f56100% (2)
- TCGI - ESG Diploma BrochureDocument11 pagesTCGI - ESG Diploma BrochureIshtiaque AhmedNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument3 pagesPower SystemMogaka LucasNo ratings yet
- Math Presentation GCF LCMDocument14 pagesMath Presentation GCF LCMblessed joy silvaNo ratings yet
- Material Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)Document4 pagesMaterial Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)krishanNo ratings yet
- WDM11 01 Que 20210304Document32 pagesWDM11 01 Que 20210304윤소리No ratings yet
- Essay Writing PartsDocument14 pagesEssay Writing PartsPAK JANNo ratings yet
- SEMI Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 q4 Week 5Document9 pagesSEMI Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 6 q4 Week 5Christine TevesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Equipment 3Document4 pagesElectronic Equipment 3Dulce DeNo ratings yet