Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Uploaded by
Harold JetterCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionDocument46 pagesTreatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionMichel Bakker100% (5)
- CFSC Level-1 Progressions and Regressions Sheet (January 2016)Document1 pageCFSC Level-1 Progressions and Regressions Sheet (January 2016)Mayank Singh garia100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 01 Mar 2023 PDFDocument3 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Mar 2023 PDFAman SahaNo ratings yet
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Sakunrat Sarikit, MDDocument58 pagesSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Sakunrat Sarikit, MDBelle Sakunrat SarikitNo ratings yet
- Era University Era College of NursingDocument8 pagesEra University Era College of NursingAru Verma100% (1)
- Special Test Tests For... Positive (+) Test: Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special Tests Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special TestsDocument192 pagesSpecial Test Tests For... Positive (+) Test: Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special Tests Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special TestsNikunjNo ratings yet
- Wedel SIGDocument120 pagesWedel SIGMichel BakkerNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPractical 2 Study GuideKStNo ratings yet
- ACL Rhab Protocol HHPCDocument9 pagesACL Rhab Protocol HHPCmusickiller100No ratings yet
- Sacral OMM GuideDocument4 pagesSacral OMM GuideSameer AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Wedel PDFDocument120 pagesWedel PDFAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Glenohumeral (GH) Joint: Diagnosis Gross ROM Minor Glides ImageDocument1 pageGlenohumeral (GH) Joint: Diagnosis Gross ROM Minor Glides ImageHarold JetterNo ratings yet
- Freshmen Final Exam Study GuideDocument17 pagesFreshmen Final Exam Study GuideEddie Agbayani Jr.No ratings yet
- Brunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaDocument9 pagesBrunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaLall JingerppangNo ratings yet
- Gait and Gait Aids-Muscle WeeknessDocument57 pagesGait and Gait Aids-Muscle WeeknessKurniawanFirstNo ratings yet
- 15 PTY121 Lecture 12.1 - 2 Gait YhDocument66 pages15 PTY121 Lecture 12.1 - 2 Gait YhsenoNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument3 pagesNeurology Notesdlynne23No ratings yet
- Fix FaultsDocument31 pagesFix FaultsSamehAlyNo ratings yet
- Passive MovementsDocument1 pagePassive MovementsomhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- A VermeilNEWDocument37 pagesA VermeilNEWokelnard100% (4)
- Examination of The ShoulderDocument33 pagesExamination of The ShoulderAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Lab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument6 pagesLab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDaisy MellaNo ratings yet
- Lower Crossed SyndromeDocument11 pagesLower Crossed SyndromeJúnior Alvacir Camargo50% (2)
- Pathfit101.Notes. 1Document4 pagesPathfit101.Notes. 1Desarie Unciano GuiangNo ratings yet
- Ilio-Sacral Diagnosis and Treatment, Part One-Shears, Upslips and DownslipsDocument4 pagesIlio-Sacral Diagnosis and Treatment, Part One-Shears, Upslips and Downslipstachy2006No ratings yet
- 20 - Deltoids - Ant, Lat, PostDocument34 pages20 - Deltoids - Ant, Lat, Postbreinfout fotos100% (1)
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument7 pagesLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideKeen RunnerNo ratings yet
- Spinal Biomechanics: Posture AnalysisDocument74 pagesSpinal Biomechanics: Posture AnalysisDoddy RenaLdoNo ratings yet
- Fitness Assessment Test: Get Ready With The Following FormsDocument32 pagesFitness Assessment Test: Get Ready With The Following FormsMaricrisNo ratings yet
- Pelvis Spine ThoraxDocument4 pagesPelvis Spine Thoraxteguh triNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument38 pagesMuscleAnonymous BzS0RF1qyNo ratings yet
- OPP Lower ExtremityDocument6 pagesOPP Lower ExtremityLana Naila AmerieNo ratings yet
- Exo Kinetics Explosive Performance and Training PrimerDocument17 pagesExo Kinetics Explosive Performance and Training PrimerHari SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Princy Varghese (PT)Document32 pagesPrincy Varghese (PT)Princy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Marcie Harris Hayes Handout - 3 - Grids and TreatmentDocument25 pagesMarcie Harris Hayes Handout - 3 - Grids and TreatmentMartinKozjanNo ratings yet
- Corrective Exercise The Lumbo Pelvic GirdleDocument9 pagesCorrective Exercise The Lumbo Pelvic GirdlealmaformaNo ratings yet
- Mobility Routine Mobile Printer Friendly VersionDocument2 pagesMobility Routine Mobile Printer Friendly VersionAndreaCoccoNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument51 pagesShoulderIts LaraNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Ab Wheel RolloutsDocument2 pagesThe Complete Guide To Ab Wheel RolloutsEl NegroNo ratings yet
- CP QuadriplegaDocument2 pagesCP QuadriplegaNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic TiltDocument13 pagesPelvic TiltPranidhi ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint BiomechanicsDocument31 pagesHip Joint BiomechanicsAtanu Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Hip, Knee and Ankle RehabDocument4 pagesHip, Knee and Ankle RehabDaniele TomassiNo ratings yet
- Human Movement ScienceDocument34 pagesHuman Movement ScienceJerry LoccNo ratings yet
- Rehab Advantage Pamphlet ExercisesDocument13 pagesRehab Advantage Pamphlet Exercisesapi-743189045No ratings yet
- Pelvic Tilt: Presented To: Sir Shahid Sarwar Presented By: AmmaraaroojDocument13 pagesPelvic Tilt: Presented To: Sir Shahid Sarwar Presented By: AmmaraaroojRonak PatelNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity KinesiologyDocument530 pagesLower Extremity KinesiologyDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM89% (9)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Tulang BelakangDocument35 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Tulang BelakangLeaf CloverNo ratings yet
- Interesting ExercisesDocument22 pagesInteresting ExercisespeppesmatheusNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.13Document30 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.13Mustafa ,GhulamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body MovementsDocument23 pagesAdvanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body Movementseyob yirsaw basaznewNo ratings yet
- Spine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Document29 pagesSpine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Mario Johan Heryputra100% (1)
- Session3 Hip MovementDocument29 pagesSession3 Hip Movementbirijik7979No ratings yet
- The Ankle Joint AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Ankle Joint Answersbrownbra1620No ratings yet
- Session4 Hip MovementDocument21 pagesSession4 Hip Movementbirijik7979No ratings yet
- Week 9 - Lower Body Weightroom Exercise SelectionDocument50 pagesWeek 9 - Lower Body Weightroom Exercise Selectionmatthew o sullivanNo ratings yet
- Sajida Bibi Noonari Lecturer at National Institute of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation and MedicineDocument46 pagesSajida Bibi Noonari Lecturer at National Institute of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation and MedicineSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- Bridging Ortho NotesDocument4 pagesBridging Ortho NotesJonathan TayNo ratings yet
- ForearmExercisesforForearmStrength WristCurlsDocument2 pagesForearmExercisesforForearmStrength WristCurlsforearmexercisesNo ratings yet
- Back Stretching: Back Strengthening And Stretching Exercises For EveryoneFrom EverandBack Stretching: Back Strengthening And Stretching Exercises For EveryoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Uploaded by
Harold JetterOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint: Diagnosis Active Motion Passive Motion
Uploaded by
Harold JetterCopyright:
Available Formats
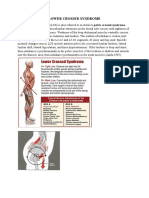
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint
Screening:
Spring superior to inferior on the proximal clavicle bilaterally. Note relative ease or resistance to
motion
Spring anterior to posterior on the proximal clavicle bilaterally. Note relative ease or resistance to
motion
Assess active range of motion
testing of the shoulder to
determine SC with greatest range
of motion restriction.
Reciprocal motion is present at the clavicles
with shoulder depression inducing superior
glide at the SC joints, shoulder elevation
inducing inferior glide at the SC, shoulder
protraction inducing posterior glide at the
SC, and shoulder retraction inducing
anterior glide at the SC joints.
Somatic dysfunction at the SC is often a
combination of anterior or posterior and
superior or inferior somatic dysfunctions.
Diagnose via assessing glide motion at the SC joints during active shoulder motion or via passive motion testing
at SC joint motion:
Diagnosis Active motion Passive motion
Anterior/extension Glides anterior easily with backward shrug Marked resistance to anterior to
somatic dysfunction (shoulder retraction), resists posterior glide posterior pressure on proximal
with forward shrug (shoulder protraction) clavicle
Posterior/flexion SD Glides posterior easily with forwards shrug, Glides easily with anterior to
resists anterior glide with backward shrug posterior pressure on proximal
clavicle
Superior/adduction Glides superior easily with downward shrug Marked resistance to superior to
SD (shoulder depression), resists inferior glide inferior pressure on proximal clavicle
with upward shrug (shoulder elevation)
Inferior/abduction Glides inferior easily with upward shrug, Glides easily with superior to inferior
SD resists superior glide with downward shrug pressure on proximal clavicle
You might also like
- Treatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionDocument46 pagesTreatment of Sacroiliac Joint DysfunctionMichel Bakker100% (5)
- CFSC Level-1 Progressions and Regressions Sheet (January 2016)Document1 pageCFSC Level-1 Progressions and Regressions Sheet (January 2016)Mayank Singh garia100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 01 Mar 2023 PDFDocument3 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Mar 2023 PDFAman SahaNo ratings yet
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Sakunrat Sarikit, MDDocument58 pagesSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Sakunrat Sarikit, MDBelle Sakunrat SarikitNo ratings yet
- Era University Era College of NursingDocument8 pagesEra University Era College of NursingAru Verma100% (1)
- Special Test Tests For... Positive (+) Test: Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special Tests Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special TestsDocument192 pagesSpecial Test Tests For... Positive (+) Test: Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special Tests Wrist/Hand/Fingers Special TestsNikunjNo ratings yet
- Wedel SIGDocument120 pagesWedel SIGMichel BakkerNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPractical 2 Study GuideKStNo ratings yet
- ACL Rhab Protocol HHPCDocument9 pagesACL Rhab Protocol HHPCmusickiller100No ratings yet
- Sacral OMM GuideDocument4 pagesSacral OMM GuideSameer AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Wedel PDFDocument120 pagesWedel PDFAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Glenohumeral (GH) Joint: Diagnosis Gross ROM Minor Glides ImageDocument1 pageGlenohumeral (GH) Joint: Diagnosis Gross ROM Minor Glides ImageHarold JetterNo ratings yet
- Freshmen Final Exam Study GuideDocument17 pagesFreshmen Final Exam Study GuideEddie Agbayani Jr.No ratings yet
- Brunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaDocument9 pagesBrunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaLall JingerppangNo ratings yet
- Gait and Gait Aids-Muscle WeeknessDocument57 pagesGait and Gait Aids-Muscle WeeknessKurniawanFirstNo ratings yet
- 15 PTY121 Lecture 12.1 - 2 Gait YhDocument66 pages15 PTY121 Lecture 12.1 - 2 Gait YhsenoNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument3 pagesNeurology Notesdlynne23No ratings yet
- Fix FaultsDocument31 pagesFix FaultsSamehAlyNo ratings yet
- Passive MovementsDocument1 pagePassive MovementsomhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- A VermeilNEWDocument37 pagesA VermeilNEWokelnard100% (4)
- Examination of The ShoulderDocument33 pagesExamination of The ShoulderAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Lab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDocument6 pagesLab Guide: Musculoskeletal AssessmentDaisy MellaNo ratings yet
- Lower Crossed SyndromeDocument11 pagesLower Crossed SyndromeJúnior Alvacir Camargo50% (2)
- Pathfit101.Notes. 1Document4 pagesPathfit101.Notes. 1Desarie Unciano GuiangNo ratings yet
- Ilio-Sacral Diagnosis and Treatment, Part One-Shears, Upslips and DownslipsDocument4 pagesIlio-Sacral Diagnosis and Treatment, Part One-Shears, Upslips and Downslipstachy2006No ratings yet
- 20 - Deltoids - Ant, Lat, PostDocument34 pages20 - Deltoids - Ant, Lat, Postbreinfout fotos100% (1)
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument7 pagesLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideKeen RunnerNo ratings yet
- Spinal Biomechanics: Posture AnalysisDocument74 pagesSpinal Biomechanics: Posture AnalysisDoddy RenaLdoNo ratings yet
- Fitness Assessment Test: Get Ready With The Following FormsDocument32 pagesFitness Assessment Test: Get Ready With The Following FormsMaricrisNo ratings yet
- Pelvis Spine ThoraxDocument4 pagesPelvis Spine Thoraxteguh triNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument38 pagesMuscleAnonymous BzS0RF1qyNo ratings yet
- OPP Lower ExtremityDocument6 pagesOPP Lower ExtremityLana Naila AmerieNo ratings yet
- Exo Kinetics Explosive Performance and Training PrimerDocument17 pagesExo Kinetics Explosive Performance and Training PrimerHari SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Princy Varghese (PT)Document32 pagesPrincy Varghese (PT)Princy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Marcie Harris Hayes Handout - 3 - Grids and TreatmentDocument25 pagesMarcie Harris Hayes Handout - 3 - Grids and TreatmentMartinKozjanNo ratings yet
- Corrective Exercise The Lumbo Pelvic GirdleDocument9 pagesCorrective Exercise The Lumbo Pelvic GirdlealmaformaNo ratings yet
- Mobility Routine Mobile Printer Friendly VersionDocument2 pagesMobility Routine Mobile Printer Friendly VersionAndreaCoccoNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument51 pagesShoulderIts LaraNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To Ab Wheel RolloutsDocument2 pagesThe Complete Guide To Ab Wheel RolloutsEl NegroNo ratings yet
- CP QuadriplegaDocument2 pagesCP QuadriplegaNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic TiltDocument13 pagesPelvic TiltPranidhi ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint BiomechanicsDocument31 pagesHip Joint BiomechanicsAtanu Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Hip, Knee and Ankle RehabDocument4 pagesHip, Knee and Ankle RehabDaniele TomassiNo ratings yet
- Human Movement ScienceDocument34 pagesHuman Movement ScienceJerry LoccNo ratings yet
- Rehab Advantage Pamphlet ExercisesDocument13 pagesRehab Advantage Pamphlet Exercisesapi-743189045No ratings yet
- Pelvic Tilt: Presented To: Sir Shahid Sarwar Presented By: AmmaraaroojDocument13 pagesPelvic Tilt: Presented To: Sir Shahid Sarwar Presented By: AmmaraaroojRonak PatelNo ratings yet
- Lower Extremity KinesiologyDocument530 pagesLower Extremity KinesiologyDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM89% (9)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Tulang BelakangDocument35 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik Tulang BelakangLeaf CloverNo ratings yet
- Interesting ExercisesDocument22 pagesInteresting ExercisespeppesmatheusNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.13Document30 pagesTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.13Mustafa ,GhulamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body MovementsDocument23 pagesAdvanced Anatomy 2nd. Ed.: Body Movementseyob yirsaw basaznewNo ratings yet
- Spine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Document29 pagesSpine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Mario Johan Heryputra100% (1)
- Session3 Hip MovementDocument29 pagesSession3 Hip Movementbirijik7979No ratings yet
- The Ankle Joint AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Ankle Joint Answersbrownbra1620No ratings yet
- Session4 Hip MovementDocument21 pagesSession4 Hip Movementbirijik7979No ratings yet
- Week 9 - Lower Body Weightroom Exercise SelectionDocument50 pagesWeek 9 - Lower Body Weightroom Exercise Selectionmatthew o sullivanNo ratings yet
- Sajida Bibi Noonari Lecturer at National Institute of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation and MedicineDocument46 pagesSajida Bibi Noonari Lecturer at National Institute of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation and MedicineSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- Bridging Ortho NotesDocument4 pagesBridging Ortho NotesJonathan TayNo ratings yet
- ForearmExercisesforForearmStrength WristCurlsDocument2 pagesForearmExercisesforForearmStrength WristCurlsforearmexercisesNo ratings yet
- Back Stretching: Back Strengthening And Stretching Exercises For EveryoneFrom EverandBack Stretching: Back Strengthening And Stretching Exercises For EveryoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)