Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
Uploaded by
isenathifekisi1Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison: Yusop, Calvin EDocument3 pagesACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison: Yusop, Calvin ECalvin Yusop100% (2)
- Meiosis 21 JUNE 2022 Final - 123759Document58 pagesMeiosis 21 JUNE 2022 Final - 123759SamalaniNo ratings yet
- Botany NotesDocument9 pagesBotany NotesArcelle BraganzaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoDocument43 pages3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoPatrick DingcoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument22 pagesMeiosis and Mitosisyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Ok Mitosis Meiosis 2017 - 12 - 13 12 - 38 - 22 UTCDocument65 pagesOk Mitosis Meiosis 2017 - 12 - 13 12 - 38 - 22 UTCCatherine G. GeraldoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.3: MEIOSISDocument29 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.3: MEIOSISMohammed RidzuwanNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument1 pageMeiosisI aint telling YouNo ratings yet
- G1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointDocument3 pagesG1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointErica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Explanation 1 Meiosis Similarities MitosisDocument4 pagesExplanation 1 Meiosis Similarities MitosisJoy ZeeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis SlidesDocument14 pagesMeiosis SlidesbarsonsNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2019Document151 pagesGenetics 2019Joycee Jatulan-EnajeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesMeiosis: Cell DivisionAthena AretaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663Document20 pagesMeiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663María SalazarNo ratings yet
- Winters Apex - Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageWinters Apex - Mitosis and MeiosisdanishNo ratings yet
- Bio CH6 F4 StudywithadminDocument16 pagesBio CH6 F4 StudywithadminMUHAMMAD AFSARUDDIN RUSYAIDI BIN MOHD AFFENDI MoeNo ratings yet
- 5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsDocument77 pages5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsAlis SyamimiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocument67 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityKareen Joy ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument99 pagesLife ScienceDannydiorNo ratings yet
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument21 pages2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis PPT 1Document38 pagesMitosis, Meiosis PPT 1issacabhishekdaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument51 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionAA ProductionNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230531 210044 0000Document3 pagesPDF 20230531 210044 0000Pooja LaxmieNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionGynewNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument56 pagesMeiosisprincess mangiNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesSession No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisDocument19 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisSaadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocument4 pagesMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNo ratings yet
- Interphase: Haploid Cells With Unreplicated ChromosomesDocument16 pagesInterphase: Haploid Cells With Unreplicated ChromosomesAllen Ray Lopez SaclagNo ratings yet
- Copia de Meiosis Gummy Worm LabDocument8 pagesCopia de Meiosis Gummy Worm Labgopan629No ratings yet
- Lec9 Cell Division and ChromosomeDocument29 pagesLec9 Cell Division and ChromosomeSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1Document47 pagesMEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1exitlagboysNo ratings yet
- Bio S4 C17 Inheritance All Notes SV 2Document87 pagesBio S4 C17 Inheritance All Notes SV 2thomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Puan Suhada Rafizah MD YusofDocument24 pagesCell Division: Puan Suhada Rafizah MD YusofsuhadafadilNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument51 pagesCell CycleZyrene Ann LimNo ratings yet
- 2017.08.30 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - PreDocument29 pages2017.08.30 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - PreZaheer SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ygyktvu7d MEIOSISDocument29 pagesYgyktvu7d MEIOSISsmahlikNo ratings yet
- Activity 1b - Meiosis JuliacamoDocument2 pagesActivity 1b - Meiosis JuliacamoJulia CamoNo ratings yet
- 3 0 MeisosisDocument41 pages3 0 MeisosisThe HushNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
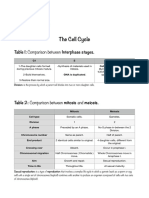
- The Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesBayader ALTLHINo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument8 pagesGeneral BiologyJames BorelaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT Notes PDFDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT Notes PDFJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT NotesDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT NotesNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet No.4: Mitosis and Meiosis, and Their Role in The Cell-Division CycleDocument4 pagesLearning Packet No.4: Mitosis and Meiosis, and Their Role in The Cell-Division CycleSean Lesther100% (1)
- Central Mindanao University: Department of BiologyDocument4 pagesCentral Mindanao University: Department of BiologyNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Common Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinDocument48 pagesCommon Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinJacky Lam JackyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle & DivisionWathiq Khalid IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Document33 pages99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Nicole Xie [Student]No ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction SlidesDocument29 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproduction Slidesmysticgalaxy2823No ratings yet
- 11.cell Division and Cell Cycle - RyanDocument9 pages11.cell Division and Cell Cycle - RyanTatyan YauNo ratings yet
- 6.3 MeiosisDocument24 pages6.3 MeiosisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Pacaldo, Catli, Trapila - Meioreo - Performance TaskDocument3 pagesPacaldo, Catli, Trapila - Meioreo - Performance TaskAnnissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- LP2 MitosisMeiosisGametogenesisDocument61 pagesLP2 MitosisMeiosisGametogenesisTRAIAN GROZESCUNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10Document2 pagesBiology Chapter 10Jon Williams75% (4)
- Meiosis - Quick TestDocument1 pageMeiosis - Quick TestTala ZeerNo ratings yet
- Configuring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubDocument3 pagesConfiguring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubaaaaNo ratings yet
- Dang Cigos2021 FullpaperDocument8 pagesDang Cigos2021 FullpaperTung DangNo ratings yet
- The Next Step in Bevel Gear Metrology: Hermann, J. SladtfeldDocument6 pagesThe Next Step in Bevel Gear Metrology: Hermann, J. Sladtfeldvijay_khandge100% (1)
- WBA Service ManualDocument67 pagesWBA Service ManualsolensiNo ratings yet
- Awesome Ascii Doctor NotebookDocument101 pagesAwesome Ascii Doctor NotebookThiago MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Lab1 SSN IntroductionDocument18 pagesLab1 SSN Introductionzys WdNo ratings yet
- Mod 7Document9 pagesMod 7Muhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- Designing For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFDocument392 pagesDesigning For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFPatrick Creek100% (2)
- Maths Preparation Tracker For All SSC Exams by The PunditsDocument1 pageMaths Preparation Tracker For All SSC Exams by The Punditsanime0001001No ratings yet
- High Frequency Induction Tube and Pipe Welding SolutionsDocument24 pagesHigh Frequency Induction Tube and Pipe Welding Solutionsmahmoud yarahmadiNo ratings yet
- (2017sen) Al CRDocument20 pages(2017sen) Al CRArunNo ratings yet
- Sound Level Measurement On Power TransformersDocument17 pagesSound Level Measurement On Power TransformersvikramvetalNo ratings yet
- Ugrd Cybs6101 Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals Prelim ExamsDocument138 pagesUgrd Cybs6101 Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals Prelim ExamsEumy JL JeonNo ratings yet
- My EMU BASIC, Power & Aux CKTDocument102 pagesMy EMU BASIC, Power & Aux CKTGame RajNo ratings yet
- Graph of A RelationDocument48 pagesGraph of A RelationHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Theory and ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesIonic Theory and ElectrolysisEric carol100% (2)
- Radio Broadcasting Equipment CatalogDocument15 pagesRadio Broadcasting Equipment CatalogManuel ManjateNo ratings yet
- Control Sheet RwadDocument9 pagesControl Sheet RwadrawadNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument40 pagesManualSoundar PandianNo ratings yet
- Ec8681.1 QPDocument4 pagesEc8681.1 QPHdhdhNo ratings yet
- Marelli GeneratorsDocument16 pagesMarelli Generatorsrstepank83% (6)
- For The Following Network and I8.: A. Find The Currents I2, I6, B. Find The Voltages V4 andDocument2 pagesFor The Following Network and I8.: A. Find The Currents I2, I6, B. Find The Voltages V4 andعبدالله عبدالحكيم عامرNo ratings yet
- ISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRDocument6 pagesISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Strut-and-Tie Models Using MulDocument16 pagesStrut-and-Tie Models Using MulwambuigraduationphotosNo ratings yet
- Maths Project 5Document15 pagesMaths Project 5Yash Mahajan0% (1)
- SABCube SpareParts 2010-12Document90 pagesSABCube SpareParts 2010-12Mário OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Promax InstallDocument2 pagesPromax InstallhyugensNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 Formal ReportDocument4 pagesChem 17 Formal Reportchemeister111No ratings yet
- Tut 6Document3 pagesTut 6Jesús Alejandro SantillánNo ratings yet
- FORMAL SPECIFICATION RevisedDocument39 pagesFORMAL SPECIFICATION RevisedRupesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
Uploaded by
isenathifekisi1Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
3meiosis One Pager Eng Memo
Uploaded by
isenathifekisi1Copyright:
Available Formats
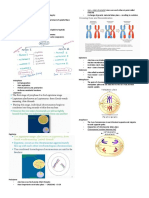
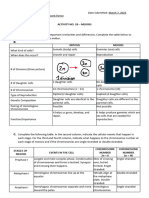
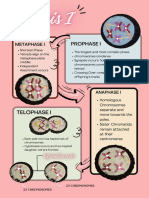
The significance (importance) of Meiosis
MEIOSIS is a type of cell division whereby a diploid cell (somatic cell) divides to form four Production of haploid gametes
different haploid gametes (sex cells). Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes. Haploid cells
only have one set of chromosomes. In males it occurs inside the testes and in female it The halving effect of meiosis overcomes
occurs inside the ovaries . the doubling effect of fertilisation, thus
Meiosis 1 Meiosis 2 maintaining a constant chromosome
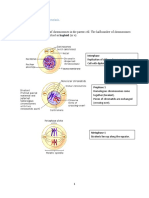
1.1 During which phase does
. number from one generation to the next.
this process takes place? Phase:Prophase 1 Phase: Prophase 2
• Prophase 1 Reason/s: Reason/s:
• Spindle fibres forming - Spindle fibres forming 4.1 How many chromosomes:
1.2 Name the point/region P • Crossing over occurs - Single chromosomes (a) Are present in EACH cell
• Chiasmata •2
• Nuclear membrane visible
Disintegrating Bivalent (b) Were present in the original
1.3 Describe what happens during the process Phase: Metaphase 1 Phase: Metaphase 2 cell at the start of meiosis
shown above Reason/s: Reason/s: •4
• Homologous chromosomes lie next to each other • Homologous chromosomes - Single chromosomes 4.2 The cells in the diagram are NOT identical
• Chromatids overlap/touch at the chiasmata
arranged at the equator arranged at the equator (a) Name TWO processes during meiosis that
• And genetic information is exchanged/swapped lead to the cells being different from one another.
• Crossing over
1.4 Explain the importance of this process Homologous chromosomes Chromosome • Random arrangement
• Introduces genetic variation in gametes Phase: Anaphase 1 Phase: Anaphase 2 (b) Explain the significance to a species of the cells
• May lead to new characteristics (Favourable/un-) Reason/s: Reason/s: being different from one another.
• Affecting the chance of survival of the organism - (Full) chromosomes moves -Chromatids moves •Gametes formed will be genetically different
(natural selection)
to the opposite poles to the opposite poles • leading to variation in the offspring
1.5 Draw a labelled diagram, showing
Chromatids • This increases a species chances of survival
chromosome C, at the end of this process.
4.3 Mention THREE similarities between Meiosis
Phase: Telophase 1 Phase: Telophase 2 and Mitosis
Reason/s: Reason/s: • DNA Replication occurs in both
-Two cells forms with full -Four cells forms with • Spindle fibres forms in both
• Both forms new cells at the end
(replicated)chromosomes unreplicated
4.4 Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
Chromosomes
Meiosis Mitosis
NB…Homologous chromosomes also called ‘BIVALENT’ when crossing over occurs
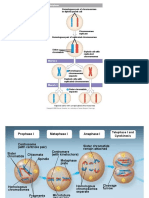
Spindle fibre Chromatid Explain the arrangement of the chromosome at X (diagram on the left).
• Non-disjunction of homologous chromosomes (X) occurred during Anaphase 1
• (Homologous chromosomes failed to separate)
Centriole Explain the disorder that will result, due to the mistake occurring at X, if it represents
chromosome pair 21 in humans.
Random arrangement: During Metaphase 1 (or 2)
………………………………..……….….
homologous chromosomes (or chromosomes) may line
• Non-disjunction of chromosome pair 21 during anaphase I in humans to form abnormal …………………………….……………………………………..…………….
up either way on the equator (see separate document)
X gametes with an extra copy of chromosome 21
Centromere Phase: Anaphase 1 Chromosomes that carry
Homologous chromosomes:……………………………………..
• The fusion between an abnormal gamete (24 chromosomes) and a normal gamete (23 the same set of genes. (Are of the Same size, Same
chromosomes) may lead to Down syndrome ………………………………………………………………………………….
shape and Same length)
Label above diagram
•
•
You might also like
- ACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison: Yusop, Calvin EDocument3 pagesACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison: Yusop, Calvin ECalvin Yusop100% (2)
- Meiosis 21 JUNE 2022 Final - 123759Document58 pagesMeiosis 21 JUNE 2022 Final - 123759SamalaniNo ratings yet
- Botany NotesDocument9 pagesBotany NotesArcelle BraganzaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoDocument43 pages3.0 Cytology-CELL CYCLE UphmoPatrick DingcoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis and MitosisnmrasaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument22 pagesMeiosis and Mitosisyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Ok Mitosis Meiosis 2017 - 12 - 13 12 - 38 - 22 UTCDocument65 pagesOk Mitosis Meiosis 2017 - 12 - 13 12 - 38 - 22 UTCCatherine G. GeraldoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.3: MEIOSISDocument29 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.3: MEIOSISMohammed RidzuwanNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument1 pageMeiosisI aint telling YouNo ratings yet
- G1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointDocument3 pagesG1 Checkpoint - Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint - DNA Damage CheckpointErica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Explanation 1 Meiosis Similarities MitosisDocument4 pagesExplanation 1 Meiosis Similarities MitosisJoy ZeeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis SlidesDocument14 pagesMeiosis SlidesbarsonsNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2019Document151 pagesGenetics 2019Joycee Jatulan-EnajeNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesMeiosis: Cell DivisionAthena AretaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663Document20 pagesMeiosis: Chapter 19 Pages 651 - 663María SalazarNo ratings yet
- Winters Apex - Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageWinters Apex - Mitosis and MeiosisdanishNo ratings yet
- Bio CH6 F4 StudywithadminDocument16 pagesBio CH6 F4 StudywithadminMUHAMMAD AFSARUDDIN RUSYAIDI BIN MOHD AFFENDI MoeNo ratings yet
- 5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsDocument77 pages5a - Topic 4b Cell Cycle - Meiosis & Stem CellsAlis SyamimiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityDocument67 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 Chromosomal Basis of HeredityKareen Joy ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument99 pagesLife ScienceDannydiorNo ratings yet
- 2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument21 pages2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisKinjNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis PPT 1Document38 pagesMitosis, Meiosis PPT 1issacabhishekdaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument51 pagesChapter 6 Cell DivisionAA ProductionNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230531 210044 0000Document3 pagesPDF 20230531 210044 0000Pooja LaxmieNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionGynewNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument56 pagesMeiosisprincess mangiNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesSession No. 1.3. Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisDocument19 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisSaadNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesDocument4 pagesMeiosis Meiosis Halves The Number of Chromosomes in The Parent Cell. The Half Number of ChromosomesTracia WalcottNo ratings yet
- Interphase: Haploid Cells With Unreplicated ChromosomesDocument16 pagesInterphase: Haploid Cells With Unreplicated ChromosomesAllen Ray Lopez SaclagNo ratings yet
- Copia de Meiosis Gummy Worm LabDocument8 pagesCopia de Meiosis Gummy Worm Labgopan629No ratings yet
- Lec9 Cell Division and ChromosomeDocument29 pagesLec9 Cell Division and ChromosomeSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- MEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1Document47 pagesMEIOSIS POWERPOINT Grade 12 Bio Corrected 2024-1exitlagboysNo ratings yet
- Bio S4 C17 Inheritance All Notes SV 2Document87 pagesBio S4 C17 Inheritance All Notes SV 2thomasaquinasrevannoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Puan Suhada Rafizah MD YusofDocument24 pagesCell Division: Puan Suhada Rafizah MD YusofsuhadafadilNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument51 pagesCell CycleZyrene Ann LimNo ratings yet
- 2017.08.30 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - PreDocument29 pages2017.08.30 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - PreZaheer SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ygyktvu7d MEIOSISDocument29 pagesYgyktvu7d MEIOSISsmahlikNo ratings yet
- Activity 1b - Meiosis JuliacamoDocument2 pagesActivity 1b - Meiosis JuliacamoJulia CamoNo ratings yet
- 3 0 MeisosisDocument41 pages3 0 MeisosisThe HushNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Comparison Between Interphase StagesBayader ALTLHINo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument8 pagesGeneral BiologyJames BorelaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT Notes PDFDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT Notes PDFJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PPT NotesDocument10 pagesMeiosis PPT NotesNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet No.4: Mitosis and Meiosis, and Their Role in The Cell-Division CycleDocument4 pagesLearning Packet No.4: Mitosis and Meiosis, and Their Role in The Cell-Division CycleSean Lesther100% (1)
- Central Mindanao University: Department of BiologyDocument4 pagesCentral Mindanao University: Department of BiologyNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Common Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinDocument48 pagesCommon Genetic Problems and Diseases, Stem Cell Research: Rebecca ChinJacky Lam JackyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle & DivisionWathiq Khalid IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Document33 pages99a Genetics Student Workbook Summer 2021Nicole Xie [Student]No ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction SlidesDocument29 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproduction Slidesmysticgalaxy2823No ratings yet
- 11.cell Division and Cell Cycle - RyanDocument9 pages11.cell Division and Cell Cycle - RyanTatyan YauNo ratings yet
- 6.3 MeiosisDocument24 pages6.3 MeiosisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Pacaldo, Catli, Trapila - Meioreo - Performance TaskDocument3 pagesPacaldo, Catli, Trapila - Meioreo - Performance TaskAnnissa PacaldoNo ratings yet
- LP2 MitosisMeiosisGametogenesisDocument61 pagesLP2 MitosisMeiosisGametogenesisTRAIAN GROZESCUNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10Document2 pagesBiology Chapter 10Jon Williams75% (4)
- Meiosis - Quick TestDocument1 pageMeiosis - Quick TestTala ZeerNo ratings yet
- Configuring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubDocument3 pagesConfiguring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubaaaaNo ratings yet
- Dang Cigos2021 FullpaperDocument8 pagesDang Cigos2021 FullpaperTung DangNo ratings yet
- The Next Step in Bevel Gear Metrology: Hermann, J. SladtfeldDocument6 pagesThe Next Step in Bevel Gear Metrology: Hermann, J. Sladtfeldvijay_khandge100% (1)
- WBA Service ManualDocument67 pagesWBA Service ManualsolensiNo ratings yet
- Awesome Ascii Doctor NotebookDocument101 pagesAwesome Ascii Doctor NotebookThiago MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Lab1 SSN IntroductionDocument18 pagesLab1 SSN Introductionzys WdNo ratings yet
- Mod 7Document9 pagesMod 7Muhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- Designing For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFDocument392 pagesDesigning For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFPatrick Creek100% (2)
- Maths Preparation Tracker For All SSC Exams by The PunditsDocument1 pageMaths Preparation Tracker For All SSC Exams by The Punditsanime0001001No ratings yet
- High Frequency Induction Tube and Pipe Welding SolutionsDocument24 pagesHigh Frequency Induction Tube and Pipe Welding Solutionsmahmoud yarahmadiNo ratings yet
- (2017sen) Al CRDocument20 pages(2017sen) Al CRArunNo ratings yet
- Sound Level Measurement On Power TransformersDocument17 pagesSound Level Measurement On Power TransformersvikramvetalNo ratings yet
- Ugrd Cybs6101 Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals Prelim ExamsDocument138 pagesUgrd Cybs6101 Artificial Intelligence Fundamentals Prelim ExamsEumy JL JeonNo ratings yet
- My EMU BASIC, Power & Aux CKTDocument102 pagesMy EMU BASIC, Power & Aux CKTGame RajNo ratings yet
- Graph of A RelationDocument48 pagesGraph of A RelationHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Theory and ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesIonic Theory and ElectrolysisEric carol100% (2)
- Radio Broadcasting Equipment CatalogDocument15 pagesRadio Broadcasting Equipment CatalogManuel ManjateNo ratings yet
- Control Sheet RwadDocument9 pagesControl Sheet RwadrawadNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument40 pagesManualSoundar PandianNo ratings yet
- Ec8681.1 QPDocument4 pagesEc8681.1 QPHdhdhNo ratings yet
- Marelli GeneratorsDocument16 pagesMarelli Generatorsrstepank83% (6)
- For The Following Network and I8.: A. Find The Currents I2, I6, B. Find The Voltages V4 andDocument2 pagesFor The Following Network and I8.: A. Find The Currents I2, I6, B. Find The Voltages V4 andعبدالله عبدالحكيم عامرNo ratings yet
- ISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRDocument6 pagesISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Strut-and-Tie Models Using MulDocument16 pagesStrut-and-Tie Models Using MulwambuigraduationphotosNo ratings yet
- Maths Project 5Document15 pagesMaths Project 5Yash Mahajan0% (1)
- SABCube SpareParts 2010-12Document90 pagesSABCube SpareParts 2010-12Mário OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Promax InstallDocument2 pagesPromax InstallhyugensNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 Formal ReportDocument4 pagesChem 17 Formal Reportchemeister111No ratings yet
- Tut 6Document3 pagesTut 6Jesús Alejandro SantillánNo ratings yet
- FORMAL SPECIFICATION RevisedDocument39 pagesFORMAL SPECIFICATION RevisedRupesh ShresthaNo ratings yet