Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 viewsLead Acetate Final-1
Lead Acetate Final-1
Uploaded by
Srijan MalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Strontium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate FinalSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Barium Nitrate CorrectedDocument1 pageBarium Nitrate CorrectedSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride Final-1Document1 pageCalcium Chloride Final-1Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- Barium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageBarium Nitrate Finalswaatiii12No ratings yet
- Strontium Nitrate CorrectedDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate CorrectedSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Zinc Sulphate Final-1Document1 pageZinc Sulphate Final-1Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- 1 - SALT - 01 (PB (NO3) 2)Document2 pages1 - SALT - 01 (PB (NO3) 2)SahanaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1Document28 pagesSalt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1YashikNo ratings yet
- Strontium ChlorideDocument5 pagesStrontium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Ammonium ChlorideDocument5 pagesAmmonium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Lead Acetate SaltDocument5 pagesLead Acetate SaltiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 8Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 8fix my styleNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt-3Document3 pagesUnknown Salt-3PES 21No ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulphate 1Document2 pagesAluminium Sulphate 1Bimal Krishna Biswas60% (5)
- Inorganic Sample 7Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 7Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.lead AcetateDocument3 pages4.lead AcetateCaleb Elisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pbDocument49 pagesSalt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pbsanthoshsingaravelu67No ratings yet
- Updated Salt Analysis ChartDocument7 pagesUpdated Salt Analysis ChartRuben PereiraNo ratings yet
- Lead NitrateDocument3 pagesLead NitrateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 2 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 2 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2Document3 pagesSalt Analysis 2Porkodi MNo ratings yet
- Zinc AcetateDocument4 pagesZinc AcetateAbinaya chettiappanNo ratings yet
- Exp 10. Ammonium SulphateDocument3 pagesExp 10. Ammonium SulphateDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document4 pagesWa0004.Arsh NeilNo ratings yet
- Systematic Analysis of Simple SalDocument22 pagesSystematic Analysis of Simple Sal11 M1 M.BHARATH RAJNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1Siva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- #Analysis of HoneyDocument17 pages#Analysis of HoneyJatin BhasinNo ratings yet
- 7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)Document2 pages7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)sham24102007No ratings yet
- 6 CaCO3Document3 pages6 CaCO3Abhi Suresh100% (3)
- Salt Analysis 2Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 2MithunNo ratings yet
- Salt No - 1Document2 pagesSalt No - 1Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis RecordDocument16 pagesSalt Analysis RecordAbhi SureshNo ratings yet
- Salt Procedure For Copper Nitrate and Copper SulphateDocument8 pagesSalt Procedure For Copper Nitrate and Copper SulphateNeelavathy PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- SALT - 03 (CaCl2)Document2 pagesSALT - 03 (CaCl2)Jeevan RaajNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis IIIDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis IIIrajaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium NitrateDocument3 pagesAluminium NitrateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Calcium No 3Document3 pagesCalcium No 3Ukkeshwaran SNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Amm - Carbonate Lead NitrtaeDocument4 pagesSalt Analysis Amm - Carbonate Lead Nitrtaepradyumn mittalNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Document7 pagesTerm 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Ananya AryaNo ratings yet
- 1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureDocument9 pages1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureGovind Singh KhatiyanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09Document6 pagesChemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09chetan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 1Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 1Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 3 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 3 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 4 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 4 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- EXP5Document3 pagesEXP5suryansu2006No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1sowndharya.abigailNo ratings yet
- 6.SALT ANALYSIS Lead AcetateDocument3 pages6.SALT ANALYSIS Lead Acetatemohnish67% (3)
- Chemistry PracticalsDocument77 pagesChemistry PracticalsSyed Athiq PashaNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument16 pagesSalt AnalysisPrince BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- General Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument10 pagesGeneral Salt Analysis ProcedureAkshat KashyapNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE - 1 - Lead Nitrate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceDocument15 pagesSAMPLE - 1 - Lead Nitrate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceRexlinNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument20 pagesSalt AnalysisPriyansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Qualitative Inorganic AnalysisDocument4 pagesScheme For Qualitative Inorganic Analysisgamingbrothers201510No ratings yet
- Xii-Chemistry-Practical File - Project Work 2024-25Document56 pagesXii-Chemistry-Practical File - Project Work 2024-25The ReaperNo ratings yet
- Ammonium CarbonateDocument3 pagesAmmonium CarbonateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 20Document4 pagesExperiment 20Beenu SinghNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 6Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 6Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aissce Mohr's Salt Vs Kmno4Document2 pagesAissce Mohr's Salt Vs Kmno4Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- 250 Questions OMR SheetDocument1 page250 Questions OMR SheetSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 ElasticityDocument2 pagesAssignment 7 ElasticitySrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Study Material 12-Isothermal and Adiabatic ProcessesDocument14 pagesStudy Material 12-Isothermal and Adiabatic ProcessesSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions Silk RoadDocument5 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions Silk RoadSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Strontium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate FinalSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 FrictionDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 FrictionSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- NameDocument1 pageNameSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Practical Front PageDocument1 pagePractical Front PageSrijan MalNo ratings yet
Lead Acetate Final-1
Lead Acetate Final-1
Uploaded by
Srijan Mal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pageLead Acetate Final-1
Lead Acetate Final-1
Uploaded by
Srijan MalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
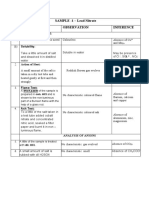
Lead Acetate
To detect the basic and acid radical present in a given unknown salt:
➢ Physical characteristics:
i) Physical state: Solid crystalline
ii) Colour: Colourless
iii) Solubility: Soluble in water
➢ Indicatory test for basic radical:
Experiment Observation Inference
Prepared a paste of the salt with Dull bluish- white flame Pb2+ may be present
conc. HCl and performed the flame
test with a platinum wire.
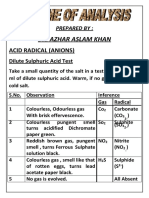
➢ Indicatory test for acid radical:
Experiment Observation Inference
-
A pinch of the salt was taken in a Colourless gas evolved having smell CH3COO may be present
test tube and heated with 1–2 mL of like vinegar which turns blue litmus
dilute sulphuric acid. red.
➢ Preparation of salt solution:
A pinch of salt was taken in a test tube and solution was prepared by adding distilled water to it. The following tests
were performed by using this solution.
➢ Confirmatory test for acid radical:
Experiment Observation Inference
A small amount of the salt solution Deep red colour appears which CH3COO- is present and confirmed
was taken in a test tube. Few drops disappears on boiling and a brown-
of neutral ferric chloride solution red precipitate is formed.
was added to it.
➢ Confirmatory test for basic radical:
Experiment Observation Inference
To a part of sample solution, added White ppt. formed
1-2 ml of dil. HCl
Dissolved the ppt. in boiling water.
To a part of the above solution,
added a few drops of potassium Yellow ppt. formed Pb2+ is present and confirmed
iodide solution.
Result: The given salt contains
Acid radical: Acetate (CH3COO-)
Basic radical: Lead (Pb2+)
You might also like
- Strontium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate FinalSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Barium Nitrate CorrectedDocument1 pageBarium Nitrate CorrectedSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Calcium Chloride Final-1Document1 pageCalcium Chloride Final-1Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- Barium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageBarium Nitrate Finalswaatiii12No ratings yet
- Strontium Nitrate CorrectedDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate CorrectedSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Zinc Sulphate Final-1Document1 pageZinc Sulphate Final-1Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- 1 - SALT - 01 (PB (NO3) 2)Document2 pages1 - SALT - 01 (PB (NO3) 2)SahanaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1Document28 pagesSalt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pb-1YashikNo ratings yet
- Strontium ChlorideDocument5 pagesStrontium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Ammonium ChlorideDocument5 pagesAmmonium ChlorideAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Lead Acetate SaltDocument5 pagesLead Acetate SaltiskypiskybruhNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 8Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 8fix my styleNo ratings yet
- Unknown Salt-3Document3 pagesUnknown Salt-3PES 21No ratings yet
- Aluminium Sulphate 1Document2 pagesAluminium Sulphate 1Bimal Krishna Biswas60% (5)
- Inorganic Sample 7Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 7Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.lead AcetateDocument3 pages4.lead AcetateCaleb Elisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pbDocument49 pagesSalt Analysis I - Lead Acetate - (Ch3coo) 2pbsanthoshsingaravelu67No ratings yet
- Updated Salt Analysis ChartDocument7 pagesUpdated Salt Analysis ChartRuben PereiraNo ratings yet
- Lead NitrateDocument3 pagesLead NitrateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 2 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 2 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2Document3 pagesSalt Analysis 2Porkodi MNo ratings yet
- Zinc AcetateDocument4 pagesZinc AcetateAbinaya chettiappanNo ratings yet
- Exp 10. Ammonium SulphateDocument3 pagesExp 10. Ammonium SulphateDebadrito RayNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document4 pagesWa0004.Arsh NeilNo ratings yet
- Systematic Analysis of Simple SalDocument22 pagesSystematic Analysis of Simple Sal11 M1 M.BHARATH RAJNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1Siva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- #Analysis of HoneyDocument17 pages#Analysis of HoneyJatin BhasinNo ratings yet
- 7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)Document2 pages7 - SALT - 07 (NH4Cl)sham24102007No ratings yet
- 6 CaCO3Document3 pages6 CaCO3Abhi Suresh100% (3)
- Salt Analysis 2Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 2MithunNo ratings yet
- Salt No - 1Document2 pagesSalt No - 1Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis RecordDocument16 pagesSalt Analysis RecordAbhi SureshNo ratings yet
- Salt Procedure For Copper Nitrate and Copper SulphateDocument8 pagesSalt Procedure For Copper Nitrate and Copper SulphateNeelavathy PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- SALT - 03 (CaCl2)Document2 pagesSALT - 03 (CaCl2)Jeevan RaajNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis IIIDocument5 pagesSalt Analysis IIIrajaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium NitrateDocument3 pagesAluminium NitrateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Calcium No 3Document3 pagesCalcium No 3Ukkeshwaran SNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Amm - Carbonate Lead NitrtaeDocument4 pagesSalt Analysis Amm - Carbonate Lead Nitrtaepradyumn mittalNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Document7 pagesTerm 2 Practicals Experiment No.1Ananya AryaNo ratings yet
- 1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureDocument9 pages1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureGovind Singh KhatiyanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09Document6 pagesChemistry Practical: Experiment No. - 09chetan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 1Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 1Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 3 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 3 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical 4 Sudhir SirDocument1 pageChemistry Practical 4 Sudhir Sirvinamratiwari7278No ratings yet
- EXP5Document3 pagesEXP5suryansu2006No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 1Document2 pagesSalt Analysis 1sowndharya.abigailNo ratings yet
- 6.SALT ANALYSIS Lead AcetateDocument3 pages6.SALT ANALYSIS Lead Acetatemohnish67% (3)
- Chemistry PracticalsDocument77 pagesChemistry PracticalsSyed Athiq PashaNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument16 pagesSalt AnalysisPrince BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- General Salt Analysis ProcedureDocument10 pagesGeneral Salt Analysis ProcedureAkshat KashyapNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE - 1 - Lead Nitrate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceDocument15 pagesSAMPLE - 1 - Lead Nitrate S.No Experiment Observation InferenceRexlinNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument20 pagesSalt AnalysisPriyansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Scheme For Qualitative Inorganic AnalysisDocument4 pagesScheme For Qualitative Inorganic Analysisgamingbrothers201510No ratings yet
- Xii-Chemistry-Practical File - Project Work 2024-25Document56 pagesXii-Chemistry-Practical File - Project Work 2024-25The ReaperNo ratings yet
- Ammonium CarbonateDocument3 pagesAmmonium CarbonateAbinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 20Document4 pagesExperiment 20Beenu SinghNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Sample 6Document2 pagesInorganic Sample 6Baibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aissce Mohr's Salt Vs Kmno4Document2 pagesAissce Mohr's Salt Vs Kmno4Srijan MalNo ratings yet
- 250 Questions OMR SheetDocument1 page250 Questions OMR SheetSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 ElasticityDocument2 pagesAssignment 7 ElasticitySrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Study Material 12-Isothermal and Adiabatic ProcessesDocument14 pagesStudy Material 12-Isothermal and Adiabatic ProcessesSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions Silk RoadDocument5 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions Silk RoadSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Strontium Nitrate FinalDocument1 pageStrontium Nitrate FinalSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 FrictionDocument3 pagesAssignment 4 FrictionSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- NameDocument1 pageNameSrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Practical Front PageDocument1 pagePractical Front PageSrijan MalNo ratings yet