Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 viewsRohini 81419952242
Rohini 81419952242
Uploaded by
kargbojohn375Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Scrib 2Document4 pagesScrib 2Aldwin Abidin50% (2)
- Real Estate Buyers PackageDocument16 pagesReal Estate Buyers PackageTom Joseph100% (3)
- Expert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence PDFDocument2 pagesExpert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence PDFStephanieNo ratings yet
- Integrated ReviewDocument120 pagesIntegrated ReviewChristianNo ratings yet
- CE - Unit 2 - Time Response of System and Time Domain SpecificationsDocument38 pagesCE - Unit 2 - Time Response of System and Time Domain SpecificationsP POORNA CHANDRA REDDYNo ratings yet
- First Order SystemDocument21 pagesFirst Order SystemNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDocument16 pagesMathematical Models of SystemsmansoorNo ratings yet
- 4 - Time Response Analysis of Control SystemDocument34 pages4 - Time Response Analysis of Control SystemEyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS)Document14 pagesControl Systems (CS)Suyash Dahake VlogsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsDocument15 pagesLecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsFahadKhNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Test Signal GeneratorDocument7 pagesInstruction Manual: Test Signal GeneratornileshsawNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument49 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control Systemanasmos danielNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AmplifierDocument6 pagesInstrumentation AmplifierMHM MahinNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lecture3 - 5Document50 pagesInstrumentation Lecture3 - 5Afaaq HussainNo ratings yet
- Op Amp ManualDocument12 pagesOp Amp ManualbndianonymousNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis: Transient and Steady State Response, Standard Test Input Functions For Dynamic SystemsDocument13 pagesTime Response Analysis: Transient and Steady State Response, Standard Test Input Functions For Dynamic SystemsmumtazNo ratings yet
- Control Lec 2Document57 pagesControl Lec 2marivull2811No ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 EEE3001 ETH VL2020210500342 2021-03-04 Reference-Material-IDocument83 pagesWINSEM2020-21 EEE3001 ETH VL2020210500342 2021-03-04 Reference-Material-ISAIKAT MUKHERJEE 19BEE0132No ratings yet
- Week 2Document90 pagesWeek 2Raising StarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Characterstics Final PDFDocument102 pagesDynamic Characterstics Final PDFJay ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BECE302L TH VL2023240100272 2023-05-18 Reference-Material-IIIDocument40 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BECE302L TH VL2023240100272 2023-05-18 Reference-Material-IIIkrishna sanapala2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document60 pagesChapter 3Shumaila NaveedNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document7 pagesExp 8growthman.100No ratings yet
- 58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSDocument15 pages58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSMarilyn PrascillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Instrumentation Equipment Module 1: Introduction To InstrumentationDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Instrumentation Equipment Module 1: Introduction To InstrumentationAkmal ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Time Response AnalysisDocument37 pagesTime Response Analysis7014KANISHKA JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Me55 Control Engineering: Sharanabasava C PilliDocument12 pagesMe55 Control Engineering: Sharanabasava C PilliS C PilliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Engineering Control Systems Time Response of Feedback Control System NotesDocument43 pagesElectrical Engineering Engineering Control Systems Time Response of Feedback Control System NotesRishabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsDocument144 pagesLecture 6-Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Notes 3Document5 pagesNotes 3Joshika sri Ram prabhuNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsDocument132 pagesControl Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsP POORNA CHANDRA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis - First Order SystemDocument32 pagesTime Response Analysis - First Order Systemearnest normanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12-13 Time Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsDocument56 pagesLecture 12-13 Time Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsKemal ZhafNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Systems and Mechatronics: Signal Conditioning: Lecture 3Document42 pagesElectromechanical Systems and Mechatronics: Signal Conditioning: Lecture 3cleytonmarques1991No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab: Delta ModulationDocument8 pagesDigital Communication Lab: Delta ModulationAthul Zac JosephNo ratings yet
- BEC-26 Control Systems UNIT-IIDocument144 pagesBEC-26 Control Systems UNIT-IIcharu singhNo ratings yet
- 54124tpnews 10162020Document16 pages54124tpnews 10162020Divyansh KumarNo ratings yet
- CS Topics1Document30 pagesCS Topics112018012 NAVANEETH NALESH C TNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Week 5) : EE305 Instrumentation and Measurement Teaching Assistant Šejla DžakmićDocument20 pagesLecture 5 (Week 5) : EE305 Instrumentation and Measurement Teaching Assistant Šejla DžakmićFrank WhiteNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument126 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineeringkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter4 PDFDocument24 pages12 Chapter4 PDFnagarajuNo ratings yet
- 01 15mec 314 Metrology Unit 3 Signal+conditioning PDFDocument73 pages01 15mec 314 Metrology Unit 3 Signal+conditioning PDFNithinArvindNo ratings yet
- TestSignals and Laplace TransformDocument35 pagesTestSignals and Laplace Transformadaptive4u4527No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Control SystemDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Control SystemTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ADE - Pspice Lab ManualDocument12 pagesADE - Pspice Lab ManualShashiNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control Systems: Vikas D. HajareDocument65 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control Systems: Vikas D. HajareVikas HajareNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics DOTE Text BookDocument111 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics DOTE Text BookspvigneshNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation (Chapter 2)Document7 pagesInstrumentation (Chapter 2)Yab TadNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument25 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control SystemEti'el Films / ኢትኤል ፊልሞችNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis of Control SystemsDocument6 pagesTime Response Analysis of Control SystemsAnoop Kumar JairathNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Transient Response Analysis of Control SystemsDocument120 pagesLecture-5 Transient Response Analysis of Control SystemsIzhar Ahmed NoohpotoNo ratings yet
- Exp 03 Function Generator Using 741 Op-AmpDocument4 pagesExp 03 Function Generator Using 741 Op-Ampkaushal4053100% (2)
- Week 3Document38 pagesWeek 3Raising StarNo ratings yet
- Ec Formula Notes 11Document369 pagesEc Formula Notes 11Tharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualDocument95 pagesAnalogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualZara ZaraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To What Is Digital Signal ProcessingDocument11 pagesIntroduction To What Is Digital Signal Processingياسين خالدNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kendali Digital - Week 2-2Document25 pagesSistem Kendali Digital - Week 2-2Dedi BobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Discrete Time Control SystemDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Discrete Time Control SystemIzzat AzmanNo ratings yet
- ControllersDocument16 pagesControllersMONIRAJ MONDALNo ratings yet
- Ic Application Lab Viva AnswersDocument26 pagesIc Application Lab Viva AnswersKumaraswamy raoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2Endalk SimegnNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital IC Applications - UNIT-1Document55 pagesLinear and Digital IC Applications - UNIT-1Dr. Ajay Kumar Kushwaha ECENo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- A Battery Technology For Safety of Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesA Battery Technology For Safety of Electric Vehicleskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Estimation and Control of Robotic Radiation-Based ProcessesDocument159 pagesEstimation and Control of Robotic Radiation-Based Processeskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control of Modern High-Degree-of-Freedom TurbochDocument179 pagesModel Predictive Control of Modern High-Degree-of-Freedom Turbochkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Active Suspension Simulation Through Software Interfacing.Document156 pagesActive Suspension Simulation Through Software Interfacing.kargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Clean Combustion Control in A Compression Ignition EngineDocument218 pagesClean Combustion Control in A Compression Ignition Enginekargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Low-Pressure EGR in Spark-Ignition Engines - Combustion Effects SDocument266 pagesLow-Pressure EGR in Spark-Ignition Engines - Combustion Effects Skargbojohn375No ratings yet
- A Multi-Perspective Architecture Framework For Managing Multi-FidDocument229 pagesA Multi-Perspective Architecture Framework For Managing Multi-Fidkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Indianaucasestudy Usingdissertationsforresearch 1Document2 pagesIndianaucasestudy Usingdissertationsforresearch 1kargbojohn375No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument6 pagesAttachmentkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument70 pagesAttachmentkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Combustion Phasing Modeling For Control of Spark-Assisted CompresDocument237 pagesCombustion Phasing Modeling For Control of Spark-Assisted Compreskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- UK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesDocument17 pagesUK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesПриходько РомаNo ratings yet
- MINI PROJECT REPORT DoucmentDocument78 pagesMINI PROJECT REPORT DoucmentVarshini VuraNo ratings yet
- "8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)Document20 pages"8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- PF Aquaforte Brochure - 04.04.12Document2 pagesPF Aquaforte Brochure - 04.04.12ukalNo ratings yet
- Bhide CVDocument3 pagesBhide CVtorosterudNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Math at Home Game TimeDocument1 page1-2 Math at Home Game TimeKarla Panganiban TanNo ratings yet
- TM-2107 Hull Detailed Design - Plate Nesting-Rev4.1Document75 pagesTM-2107 Hull Detailed Design - Plate Nesting-Rev4.1sabarna1No ratings yet
- IIM Calcutta - Job Description Form - Summers 2019: Name of The CompanyDocument2 pagesIIM Calcutta - Job Description Form - Summers 2019: Name of The CompanyVaishnaviRaviNo ratings yet
- Third Party Registration - Real Time CommunicationDocument14 pagesThird Party Registration - Real Time CommunicationSpy CameraNo ratings yet
- Arches Local Year 4 PlanDocument30 pagesArches Local Year 4 PlanStephen PerezNo ratings yet
- Case 3-2017 Waste ManagementDocument18 pagesCase 3-2017 Waste ManagementShaameswary AnnadoraiNo ratings yet
- Bba Swach Bharat AbhiyaanDocument3 pagesBba Swach Bharat AbhiyaanTusharJoshiNo ratings yet
- ICAO Service CodeDocument98 pagesICAO Service CodeAnindita RoyNo ratings yet
- 70-130 Autocreaser Pro 50 Parts Manual REV.7Document29 pages70-130 Autocreaser Pro 50 Parts Manual REV.7Peter GaluszkaNo ratings yet
- Mta1 Can, M1 10P Can, At1 Can, At1 CF Can, M1, At1, AT1 CF, RA 12, RA 23, RA T1, FS 002 CAN, FS 002, T1 Foot CAN, ER 1, ER 1FDocument16 pagesMta1 Can, M1 10P Can, At1 Can, At1 CF Can, M1, At1, AT1 CF, RA 12, RA 23, RA T1, FS 002 CAN, FS 002, T1 Foot CAN, ER 1, ER 1Fmacguyver66No ratings yet
- Mindray BC-2800 - Service ManualDocument108 pagesMindray BC-2800 - Service ManualAvilianaK.Bintari80% (5)
- Bai Tap Unit 2Document4 pagesBai Tap Unit 2Vinh BéoNo ratings yet
- Students AchievementDocument10 pagesStudents AchievementMulubrhan OkbaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemDocument4 pagesChapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemZara KhanNo ratings yet
- Second Revision) : Countersunk Flat Head Screws (Common Head Style) With Type HOR Type Cross Recess - Product Grade ADocument10 pagesSecond Revision) : Countersunk Flat Head Screws (Common Head Style) With Type HOR Type Cross Recess - Product Grade Akumar QANo ratings yet
- National Geographic Kids - 2020 10Document36 pagesNational Geographic Kids - 2020 10Vilius ŽirgulisNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 3Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- OTBI Drill - Down - DocumentationDocument124 pagesOTBI Drill - Down - DocumentationFatema OssmanNo ratings yet
- Risk-Isaca PDFDocument7 pagesRisk-Isaca PDFashwin2005No ratings yet
- Acer Altos IZ75A Ver 1Document2 pagesAcer Altos IZ75A Ver 1utkarshkrishnatreyaNo ratings yet
- Massey Knakal Castellan Press ReleaseDocument1 pageMassey Knakal Castellan Press ReleaseAmelia KingNo ratings yet
Rohini 81419952242
Rohini 81419952242
Uploaded by
kargbojohn3750 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views3 pagesOriginal Title
rohini_81419952242
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views3 pagesRohini 81419952242
Rohini 81419952242
Uploaded by
kargbojohn375Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
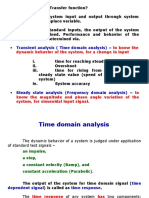
2.3 TYPES OF TEST INPUT
The knowledge of input signal is required to predict the response of a system. In
most of the systems, the input signals are not known ahead of time and also it is difficult
to express the input signals mathematically by simple equations. The characteristics of
actual input signals are a sudden shock, a sudden change, a constant velocity and a
constant acceleration. Hence test signals which resembles these characteristics are used
as input signals to predict the performance of the system. The commonly use test input
signals are impulse, step, ramp, acceleration and sinusoidal signals.
Standard Input Signals
1. Step signal 2. Unit step signal
3. Ramp signal 4. Unit ramp signal
5. Parabolic signal 6. Unit parabolic signal
7. Impulse signal 8. Sinusoidal signal
STEP SIGNAL
The step signal is a signal whose value changes from zero to A at t=0 and remains
constant at A for t>0. The step signal resembles an actual steady input to a system. A
special case of step signal is unit step in which A is unity.
RAMP SIGNAL
The ramp signal is a signal whose value increases linearly with time from an initial
value of zero at t=0. The ramp signal resembles a constant velocity input to the system.
A special case of ramp signal is unit ramp signal in which the value of A is unity.
PARABOLIC SIGNAL
In parabolic signal, the instantaneous value varies as square of the time from an
initial value of zero at t=0. The sketch of the signal with respect to time resembles a
parabola. The parabolic signal resembles a constant acceleration input to the system. A
special case of parabolic signal is unit parabolic signal in which A is unity.
IMPULSE SIGNAL
A signal of very large magnitude which is available for very short duration is called
impulse signal. Ideal impulse signal is a signal with infinite magnitude and zero duration
but with an area of A. The unit impulse signal is a special case, in which A is unity. Since
perfect impulse cannot be achieved in practice, it is usually approximated by a pulse of
IC8451 CONTROL SYSTEMS
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
small width but with area, A. Mathematically an impulse signal is the derivative of a step
signal. Laplace transform of the impulse function is unity.
Figure 2.3.1 Standard test signals
[Source: “Control Systems Engineering” by I J Nagrath, M Gopal, Page: 196]
Input r(t) R(s)
Step input A A/s
Ramp input At A/s2
Parabolic input At2/2 A/s3
Impulse input δ(t) 1
IC8451 CONTROL SYSTEMS
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
IC8451 CONTROL SYSTEMS
You might also like
- Scrib 2Document4 pagesScrib 2Aldwin Abidin50% (2)
- Real Estate Buyers PackageDocument16 pagesReal Estate Buyers PackageTom Joseph100% (3)
- Expert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence PDFDocument2 pagesExpert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence PDFStephanieNo ratings yet
- Integrated ReviewDocument120 pagesIntegrated ReviewChristianNo ratings yet
- CE - Unit 2 - Time Response of System and Time Domain SpecificationsDocument38 pagesCE - Unit 2 - Time Response of System and Time Domain SpecificationsP POORNA CHANDRA REDDYNo ratings yet
- First Order SystemDocument21 pagesFirst Order SystemNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Models of SystemsDocument16 pagesMathematical Models of SystemsmansoorNo ratings yet
- 4 - Time Response Analysis of Control SystemDocument34 pages4 - Time Response Analysis of Control SystemEyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS)Document14 pagesControl Systems (CS)Suyash Dahake VlogsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsDocument15 pagesLecture Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsFahadKhNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Test Signal GeneratorDocument7 pagesInstruction Manual: Test Signal GeneratornileshsawNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument49 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control Systemanasmos danielNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation AmplifierDocument6 pagesInstrumentation AmplifierMHM MahinNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lecture3 - 5Document50 pagesInstrumentation Lecture3 - 5Afaaq HussainNo ratings yet
- Op Amp ManualDocument12 pagesOp Amp ManualbndianonymousNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis: Transient and Steady State Response, Standard Test Input Functions For Dynamic SystemsDocument13 pagesTime Response Analysis: Transient and Steady State Response, Standard Test Input Functions For Dynamic SystemsmumtazNo ratings yet
- Control Lec 2Document57 pagesControl Lec 2marivull2811No ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 EEE3001 ETH VL2020210500342 2021-03-04 Reference-Material-IDocument83 pagesWINSEM2020-21 EEE3001 ETH VL2020210500342 2021-03-04 Reference-Material-ISAIKAT MUKHERJEE 19BEE0132No ratings yet
- Week 2Document90 pagesWeek 2Raising StarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Characterstics Final PDFDocument102 pagesDynamic Characterstics Final PDFJay ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BECE302L TH VL2023240100272 2023-05-18 Reference-Material-IIIDocument40 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BECE302L TH VL2023240100272 2023-05-18 Reference-Material-IIIkrishna sanapala2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document60 pagesChapter 3Shumaila NaveedNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document7 pagesExp 8growthman.100No ratings yet
- 58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSDocument15 pages58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSMarilyn PrascillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Instrumentation Equipment Module 1: Introduction To InstrumentationDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Instrumentation Equipment Module 1: Introduction To InstrumentationAkmal ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Time Response AnalysisDocument37 pagesTime Response Analysis7014KANISHKA JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Me55 Control Engineering: Sharanabasava C PilliDocument12 pagesMe55 Control Engineering: Sharanabasava C PilliS C PilliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Engineering Control Systems Time Response of Feedback Control System NotesDocument43 pagesElectrical Engineering Engineering Control Systems Time Response of Feedback Control System NotesRishabh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsDocument144 pagesLecture 6-Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemsNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Notes 3Document5 pagesNotes 3Joshika sri Ram prabhuNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsDocument132 pagesControl Systems Lab Manual - With Challenging ExperimentsP POORNA CHANDRA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis - First Order SystemDocument32 pagesTime Response Analysis - First Order Systemearnest normanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12-13 Time Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsDocument56 pagesLecture 12-13 Time Domain Analysis of 1st Order SystemsKemal ZhafNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Systems and Mechatronics: Signal Conditioning: Lecture 3Document42 pagesElectromechanical Systems and Mechatronics: Signal Conditioning: Lecture 3cleytonmarques1991No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab: Delta ModulationDocument8 pagesDigital Communication Lab: Delta ModulationAthul Zac JosephNo ratings yet
- BEC-26 Control Systems UNIT-IIDocument144 pagesBEC-26 Control Systems UNIT-IIcharu singhNo ratings yet
- 54124tpnews 10162020Document16 pages54124tpnews 10162020Divyansh KumarNo ratings yet
- CS Topics1Document30 pagesCS Topics112018012 NAVANEETH NALESH C TNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Week 5) : EE305 Instrumentation and Measurement Teaching Assistant Šejla DžakmićDocument20 pagesLecture 5 (Week 5) : EE305 Instrumentation and Measurement Teaching Assistant Šejla DžakmićFrank WhiteNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument126 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineeringkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter4 PDFDocument24 pages12 Chapter4 PDFnagarajuNo ratings yet
- 01 15mec 314 Metrology Unit 3 Signal+conditioning PDFDocument73 pages01 15mec 314 Metrology Unit 3 Signal+conditioning PDFNithinArvindNo ratings yet
- TestSignals and Laplace TransformDocument35 pagesTestSignals and Laplace Transformadaptive4u4527No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Control SystemDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Control SystemTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ADE - Pspice Lab ManualDocument12 pagesADE - Pspice Lab ManualShashiNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control Systems: Vikas D. HajareDocument65 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control Systems: Vikas D. HajareVikas HajareNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics DOTE Text BookDocument111 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics DOTE Text BookspvigneshNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation (Chapter 2)Document7 pagesInstrumentation (Chapter 2)Yab TadNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Analysis of Control SystemDocument25 pagesTime Domain Analysis of Control SystemEti'el Films / ኢትኤል ፊልሞችNo ratings yet
- Time Response Analysis of Control SystemsDocument6 pagesTime Response Analysis of Control SystemsAnoop Kumar JairathNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Transient Response Analysis of Control SystemsDocument120 pagesLecture-5 Transient Response Analysis of Control SystemsIzhar Ahmed NoohpotoNo ratings yet
- Exp 03 Function Generator Using 741 Op-AmpDocument4 pagesExp 03 Function Generator Using 741 Op-Ampkaushal4053100% (2)
- Week 3Document38 pagesWeek 3Raising StarNo ratings yet
- Ec Formula Notes 11Document369 pagesEc Formula Notes 11Tharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualDocument95 pagesAnalogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualZara ZaraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To What Is Digital Signal ProcessingDocument11 pagesIntroduction To What Is Digital Signal Processingياسين خالدNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kendali Digital - Week 2-2Document25 pagesSistem Kendali Digital - Week 2-2Dedi BobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Discrete Time Control SystemDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Discrete Time Control SystemIzzat AzmanNo ratings yet
- ControllersDocument16 pagesControllersMONIRAJ MONDALNo ratings yet
- Ic Application Lab Viva AnswersDocument26 pagesIc Application Lab Viva AnswersKumaraswamy raoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2Endalk SimegnNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital IC Applications - UNIT-1Document55 pagesLinear and Digital IC Applications - UNIT-1Dr. Ajay Kumar Kushwaha ECENo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- A Battery Technology For Safety of Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesA Battery Technology For Safety of Electric Vehicleskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Estimation and Control of Robotic Radiation-Based ProcessesDocument159 pagesEstimation and Control of Robotic Radiation-Based Processeskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control of Modern High-Degree-of-Freedom TurbochDocument179 pagesModel Predictive Control of Modern High-Degree-of-Freedom Turbochkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Active Suspension Simulation Through Software Interfacing.Document156 pagesActive Suspension Simulation Through Software Interfacing.kargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Clean Combustion Control in A Compression Ignition EngineDocument218 pagesClean Combustion Control in A Compression Ignition Enginekargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Low-Pressure EGR in Spark-Ignition Engines - Combustion Effects SDocument266 pagesLow-Pressure EGR in Spark-Ignition Engines - Combustion Effects Skargbojohn375No ratings yet
- A Multi-Perspective Architecture Framework For Managing Multi-FidDocument229 pagesA Multi-Perspective Architecture Framework For Managing Multi-Fidkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Indianaucasestudy Usingdissertationsforresearch 1Document2 pagesIndianaucasestudy Usingdissertationsforresearch 1kargbojohn375No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument6 pagesAttachmentkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument70 pagesAttachmentkargbojohn375No ratings yet
- Combustion Phasing Modeling For Control of Spark-Assisted CompresDocument237 pagesCombustion Phasing Modeling For Control of Spark-Assisted Compreskargbojohn375No ratings yet
- UK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesDocument17 pagesUK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesПриходько РомаNo ratings yet
- MINI PROJECT REPORT DoucmentDocument78 pagesMINI PROJECT REPORT DoucmentVarshini VuraNo ratings yet
- "8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)Document20 pages"8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- PF Aquaforte Brochure - 04.04.12Document2 pagesPF Aquaforte Brochure - 04.04.12ukalNo ratings yet
- Bhide CVDocument3 pagesBhide CVtorosterudNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Math at Home Game TimeDocument1 page1-2 Math at Home Game TimeKarla Panganiban TanNo ratings yet
- TM-2107 Hull Detailed Design - Plate Nesting-Rev4.1Document75 pagesTM-2107 Hull Detailed Design - Plate Nesting-Rev4.1sabarna1No ratings yet
- IIM Calcutta - Job Description Form - Summers 2019: Name of The CompanyDocument2 pagesIIM Calcutta - Job Description Form - Summers 2019: Name of The CompanyVaishnaviRaviNo ratings yet
- Third Party Registration - Real Time CommunicationDocument14 pagesThird Party Registration - Real Time CommunicationSpy CameraNo ratings yet
- Arches Local Year 4 PlanDocument30 pagesArches Local Year 4 PlanStephen PerezNo ratings yet
- Case 3-2017 Waste ManagementDocument18 pagesCase 3-2017 Waste ManagementShaameswary AnnadoraiNo ratings yet
- Bba Swach Bharat AbhiyaanDocument3 pagesBba Swach Bharat AbhiyaanTusharJoshiNo ratings yet
- ICAO Service CodeDocument98 pagesICAO Service CodeAnindita RoyNo ratings yet
- 70-130 Autocreaser Pro 50 Parts Manual REV.7Document29 pages70-130 Autocreaser Pro 50 Parts Manual REV.7Peter GaluszkaNo ratings yet
- Mta1 Can, M1 10P Can, At1 Can, At1 CF Can, M1, At1, AT1 CF, RA 12, RA 23, RA T1, FS 002 CAN, FS 002, T1 Foot CAN, ER 1, ER 1FDocument16 pagesMta1 Can, M1 10P Can, At1 Can, At1 CF Can, M1, At1, AT1 CF, RA 12, RA 23, RA T1, FS 002 CAN, FS 002, T1 Foot CAN, ER 1, ER 1Fmacguyver66No ratings yet
- Mindray BC-2800 - Service ManualDocument108 pagesMindray BC-2800 - Service ManualAvilianaK.Bintari80% (5)
- Bai Tap Unit 2Document4 pagesBai Tap Unit 2Vinh BéoNo ratings yet
- Students AchievementDocument10 pagesStudents AchievementMulubrhan OkbaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemDocument4 pagesChapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemZara KhanNo ratings yet
- Second Revision) : Countersunk Flat Head Screws (Common Head Style) With Type HOR Type Cross Recess - Product Grade ADocument10 pagesSecond Revision) : Countersunk Flat Head Screws (Common Head Style) With Type HOR Type Cross Recess - Product Grade Akumar QANo ratings yet
- National Geographic Kids - 2020 10Document36 pagesNational Geographic Kids - 2020 10Vilius ŽirgulisNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 3Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- OTBI Drill - Down - DocumentationDocument124 pagesOTBI Drill - Down - DocumentationFatema OssmanNo ratings yet
- Risk-Isaca PDFDocument7 pagesRisk-Isaca PDFashwin2005No ratings yet
- Acer Altos IZ75A Ver 1Document2 pagesAcer Altos IZ75A Ver 1utkarshkrishnatreyaNo ratings yet
- Massey Knakal Castellan Press ReleaseDocument1 pageMassey Knakal Castellan Press ReleaseAmelia KingNo ratings yet