Professional Documents
Culture Documents
End of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring Instrument
End of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring Instrument
Uploaded by
108173Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
End of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring Instrument
End of Unit Test Standard (S) : Name Class Date 1 The Drawing Below Shows A Measuring Instrument
Uploaded by
108173Copyright:
Available Formats
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
Name Class Date
1 The drawing below shows a measuring instrument.
(a) Name this instrument.
(1)
(b) What does this instrument measure? Tick one box.
A length
B degrees
C heat
D temperature
(1)
(Total for Question 1 = 2 marks)
2 A boy takes a can of lemonade from the fridge and puts the can on the table.
(a) Explain the direction of energy transfer between the can and the air in the room.
(2)
(b) The boy leaves the can of lemonade on the kitchen table for 6 hours.
Suggest what temperature the lemonade will be after 6 hours.
(1)
(Total for Question 2 = 3 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 1 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
3 The water in this pan is boiling.
(a) State the temperature of boiling
water.
(1)
(b) The main part of the pan is made of metal and the handle is made of wood.
(i) Why is the pan made of metal? Tick one box.
A Metal is a good conductor of heat.
B Metal is a good insulator of heat.
C Metal is a good conductor of electricity.
D Electricity is a good insulator of
electricity.
(1)
(ii) Why is the handle made of wood? Tick one box.
A Wood is a good conductor of heat.
B Wood is a good insulator of heat.
C Wood is a good conductor of electricity.
D Wood is a good insulator of electricity.
(1)
(c) Name one other material that could be used to make a handle that is safe to use.
(1)
(Total for Question 3 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 2 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
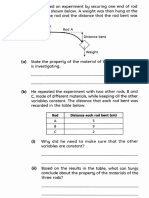
4 The table shows some results from an Material Start Final
insulation experiment. Different materials temperature temperature
were put around beakers of hot water. The (°C) (°C)
temperature of the water was measured at
the start of the experiment. The temperature A 90 73
was measured again after 5 minutes. B 90 82
(a) State which material was best at keeping C 90 75
the water warm. D 90 80
E 90 70
(1)
(b) Many insulating materials contain trapped air. Explain why trapped air is a good insulating
material.
(2)
(Total for Question 4 = 3 marks)
5 These drawings show energy transfers happening.
(a) State the main energy transfer happening in each drawing.
(i) ____________________________ (1) (ii) ____________________________ (1)
(b) Explain how energy is being transferred through the pan in part (a)(i). Use ideas about
particles in your answer.
(4)
(Total for Question 5 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 3 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
6 A man is cooking using two pans of boiling water. Both pans are made of steel, but one pan
has a much thicker base than the other pan.
(a) He turns off the gas on the cooker. Explain why the water in the pan with the thicker base
continues to bubble for longer than the water in the thinner pan.
(2)
(b) The man usually puts a lid on his pans when he is heating water.
Explain two ways a lid helps the water to reach boiling point more quickly.
(2)
(Total for Question 6 = 4 marks)
7 A student is investigating energy transfers using two thermometers.
The bulb of one thermometer is painted black. The bulb of the other thermometer is painted
silver.
The graph shows the results of the experiment.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 4 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
(a) Explain which type of energy transfer the student is investigating.
(2)
(b) State which line represents the black thermometer. Give one reason for your answer.
(1)
(c) The student could have measured the temperature every 5 minutes. Suggest why it was
better to measure the temperature every minute.
(1)
(Total for Question 7 = 4 marks)
8 Kettle A takes 2 minutes to boil 1 dm3 of water
Kettle B takes 2.5 minutes to boil the same volume of water.
Which kettle is the most powerful? Tick one box.
A A is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in a shorter time.
B A is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in a longer time.
C B is more powerful, because it transfers more energy in a shorter time.
D B is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in the same
amount of time.
(Total for Question 8 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 5 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
9 These Sankey diagrams show the energy transfers in two lawn mowers, X and Y.
(a) State two ways in which the lawn mowers transfer wasted energy. Tick one box.
A by sound and by light
B by heating and gravitational potential
C by heating and by sound
D by heating and by electricity
(1)
(b) Which lawn mower is more efficient? Tick one box.
A X, because more energy is wasted
B X, because more energy is transferred as useful energy
C Y, because more energy is wasted
D Y, because more energy is transferred as useful energy
(1)
(Total for Question 9 = 2 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 6 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Standard (S)
10 The energy use of an electric heater is calculated using this equation:
energy use = power rating time
(a) Calculate the energy use of a 1.5 kW heater that heats for 6 hours. Give your answer in
kWh.
(2)
(b) Describe one way in which the person who uses the heater could reduce the amount of
energy they use for heating.
(1)
(Total for Question 10 = 3 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 7 of 7
8K End of Unit Test Higher (H)
Name Class Date
1 A man is cooking using two pans of boiling water. Both pans are made of steel, but one pan
has a much thicker base than the other pan.
(a) Explain how energy is transferred through the metal pans. Write about particles in your
answer.
(2)
(b) The man turns off the gas on the cooker. Explain why the water in the pan with the thicker
base continues to bubble for much more time than the water in the thinner pan.
(2)
(Total for Question 1 = 4 marks)
2 Many insulating materials contain trapped air. Give one reason why trapped air is a good
insulating material.
(Total for Question 2 = 1 mark)
3 A student is investigating energy transfers using
two thermometers.
The bulb of one thermometer is painted black.
The bulb of the other thermometer is painted
silver.
(a) Explain which type of energy transfer the
student is investigating.
(2)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 1 of 5
8K End of Unit Test Higher (H)
The graph shows the results of the experiment.
(b) State which line represents the black
thermometer. Give one reason for your
answer.
(1)
(c) The student could have measured the temperature every 5 minutes. Suggest why it was
better to measure the temperature every minute.
(1)
(Total for Question 3 = 4 marks)
4 Two people are camping. They cover their fresh food with a wet cloth.
(a) How does the wet cloth help to keep the food cool? Tick one box.
A by conduction
B by convection
C by infrared radiation
D by evaporation
(1)
(b) Explain why this method of cooling works. Use ideas about particles in your answer.
(3)
(Total for Question 4 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 2 of 5
8K End of Unit Test Higher (H)
5 Upright freezers usually have drawers to put the food inside. The drawers are metal baskets
with a solid front. The solid front helps to keep the inside of the freezer cold when the door is
opened.
Explain what would happen when the freezer door is opened, if the drawers did not have solid
fronts. Draw a diagram in the space on the right as part of your explanation.
(Total for Question 5 = 3 marks)
6 Kettle A takes 2 minutes to boil 1 dm3 of water.
Kettle B takes 2.5 minutes to boil the same volume of water.
Which kettle is the most powerful? Tick one box.
A A is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in a shorter time.
B A is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in a longer time.
C B is more powerful, because it transfers more energy in a shorter time.
D B is more powerful, because it transfers the same amount of energy in the same
amount of time.
(Total for Question 6 = 1 mark)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 3 of 5
8K End of Unit Test Higher (H)
7 This Sankey diagram shows the energy transfers in a lawn mower.
(a) Give two ways the lawn mower transfers wasted energy. Tick one box.
A by sound and by light
B by heating and gravitational potential
C by heating and by sound
D by heating and by electricity
(1)
(b) Draw and label a Sankey diagram in the space below to show the energy transfers of a
more efficient lawn mower.
(1)
(Total for Question 7 = 2 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 4 of 5
8K End of Unit Test Higher (H)
8 (a) State the meaning of ‘payback time’.
(1)
(b) Washing machine X costs £300 to buy and £30 per year to use.
Machine Y costs £350 to buy and £25 per year to use.
Calculate the payback time for buying the more efficient machine. Tick one box.
A 7 years
B 10 years
C 14 years
D 20 years
(1)
(Total for Question 8 = 2 marks)
9 Explain the advantages to people and to the environment of using more efficient electric
machines.
(Total for Question 9 = 4 marks)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 5 of 5
8K Mark Scheme
Quick Quiz
Answers Marks
Topic Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
8Ka C C B A 4
8Kb D B C A 4
8Kc B D C A 4
8Kd B D A C 4
8Ke A C C D 4
End of Unit Test Mark Scheme Standard (S)
Question Part Step Answer Mark scheme
1 a 1st thermometer 1 mark
b 1st D temperature 1 mark
2 a 4th From the air in the room to the can, because 2 marks – 1 mark for
the air is warmer than the can. direction, 1 mark for
reason
b 2nd The same as the air temperature (or any 1 mark
temperature between 18 °C and 22 °C).
3 a 2nd 100 degrees Celsius (or °C) 1 mark – for value and unit
correct
bi 4th A Metal is a good conductor of heat. 1 mark
b ii 4th B Wood is a good insulator of heat. 1 mark
c 3rd Any solid insulating material – plastic is the 1 mark
most likely answer.
4 a 1st B 1 mark
b 4th Air is a poor conductor; 1 mark
The trapped air stops energy being transferred 1 mark
by convection.
5 ai 3rd conduction 1 mark
a ii 4th convection 1 mark
b 6th Heating makes particles vibrate more; 2 marks – 1 mark for each
the increased vibrations are passed on. point
6 a 6th Any two from: the thicker pan has more mass; 2 marks – 1 mark for each
so it stores more energy; so it takes longer to point
cool down/can still transfer energy to the water
inside the pan.
b 5th Warm air cannot rise so it stops energy transfer 1 mark
by convection;
Evaporated water cannot escape, so it prevents 1 mark
energy transfer by evaporation.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 1 of 6
8K Mark Scheme
Question Part Level Answer Mark scheme
7 a 5th radiation 1 mark
4th Any one from: it is not conduction because air is 1 mark
a poor conductor, or it is not convection
because this would transfer energy upwards in
this situation; radiation is absorbed at different
rates by the black bulb and the silver bulb.
b 6th The top line/line at the highest temperature is 1 mark – answer and
for the one painted black, because black/dark explanation needed
colours are better absorbers.
c 5th It is much easier to see the trend/spot any 1 mark
mistakes in measurements.
8 5th A A is more powerful, because it transfers the 1 mark
same amount of energy in a shorter time.
9 a 4th C by heating and by sound 1 mark
b 4th D Y, because more energy is transferred as 1 mark
useful energy
10 a 4th 1.5 6 = 2 marks – for correct
9 (kWh) answer with or without
calculation, 1 mark for
correct substitution with
incorrect answer
b 5th Any one similar to: use the heater for a shorter 1 mark
time, use a more efficient heater, use a less-
powerful heater for the same (or shorter) time,
insulate the house.
Final Step Calculation
Marks Step
0–6 1st or below
7–8 2nd
9–11 3rd
12–15 4th
16–20 5th
21–24 6th
25+ 7th
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 2 of 6
8K Mark Scheme
End of Unit Test Mark Scheme Higher (H)
Question Part Step Answer Mark scheme
1 a 6th Heating makes particles vibrate more; 2 marks – 1 mark for each
the increased vibrations are passed on. point
b 6th Any two points from: the thicker pan has more 2 marks – 1 mark for each
mass; so it stores more energy; so it takes point
longer to cool down/can still transfer energy to
the water inside the pan.
2 4th trapped air stops energy being transferred by 1 mark
convection
3 a 5th radiation 1 mark
4th Any one from: it is not conduction because air is 1 mark
a poor conductor, or it is not convection
because this would transfer energy upwards in
this situation; radiation is absorbed at different
rates by the black bulb and the silver bulb.
b 6th The top line/line at the highest temperature is 1 mark – answer and
for the one painted black, because black/dark explanation both needed
colours are better absorbers.
c 4th It is much easier to see the trend/spot any 1 mark
mistakes in measurements.
4 a 4th D by evaporation 1 mark
b 7th Any three from: 3 marks – 1 mark for each
the fastest moving particles escape when part point
of a liquid evaporates;
so the ones that are left have lower speeds/are
storing less energy in movement;
so the remaining liquid is cooler;
so energy will be transferred from the milk to
the liquid water remaining in the cloth.
5 6th Cold air inside the freezer will be more dense 3 marks – 1 mark for each
than the air in the kitchen; point
6th so without the solid front, most of the cold air
would fall out when the door was opened;
7th Diagram showing cold air falling out of freezer
and warmer air from room taking its place.
6 5th A A is more powerful, because it transfers the 1 mark
same amount of energy in a shorter time.
7 a 4th C by heating and by sound 1 mark
b 7th Similar diagram but with the useful energy 1 mark
output arrow wider than in the one given.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 3 of 6
8K Mark Scheme
Question Part Step Answer Mark scheme
8 a 5th The time it takes to save (in energy bills) the 1 mark
amount of money spent on buying a more
efficient appliance (or adding insulation).
b 6th B (payback time = £50/£5 =) 10 years 1 mark
9 4th People – cheaper energy bills, because less 4 marks – 1 mark for fact
5th energy is used to carry out the task (e.g. and 1 mark for related
washing, heating). reason for advantage to
5th Environment – any answer similar to the people, 1 mark for fact and
following: 1 mark for related reason
6th less carbon dioxide added to atmosphere (e.g. for advantage to
from burning fossil fuels/generating electricity) environment
which reduces impact on global
warming/climate change
Final Step Calculation
Marks Step
0–6 3rd Step or below
7–9 4th
10–13 5th
14–16 6th
17–20 7th
21+ 8th
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 4 of 6
8K Mark Scheme
Quick Check answers
Quick Check Answers
8Ka Possible questions to fit the answers are:
1 What are the units for measuring temperature?
2 What is another name for internal energy?/What do you have to transfer to
something to make its temperature rise?
3 Why does a tank of hot water store more energy than a cup full of hot water?
4 How can you use the least energy to make a cup of tea?/How can you make a
kettle boil quicker?
5 If two objects are at different temperatures, which way will energy be
transferred?
6 What three things do you need to know to work out how much thermal energy is
stored in something?
7 When does a liquid evaporate fastest?
8 Why does a liquid cool down when some of it evaporates?
8Kb A Conduction through the pan; convection spreads energy throughout the liquid in
the pan; radiation from the hot pan and hot liquid; evaporation from the liquid.
B Mostly radiation from the hot coals; convection from hot air/combustion
products rising; conduction in the solids in the fireplace/horseshoe/tongs.
C Convection from rising hot air/combustion products; radiation from flames
(which explains why their feet will be warmed as well as the upper parts of their
bodies).
D Radiation from Sun to Earth; radiation from hot ground; conduction through
hot ground; convection in the form of sea breezes (if students have done
Explaining 4). Note that convection will not take place in the sea, as the top
part of the sea is warmed so a convection current will not form.
8Kc Hay box:
foil lining – reduces energy transferred by radiation, as shiny, silver surfaces are
good at reflecting radiation
straw-filled bags and straw surrounding pot – reduce energy transferred by
conduction as the straw contains lots of trapped air
cardboard box – mainly to hold straw, but also provides some insulation
Solar cooker:
foil inside top flap and box – increases amount of radiation reaching the pot as it is a
good reflector
glass cover – reduces energy transfer by convection as it prevents warmed air
rising out of the cooker, but still lets radiation go through it
insulation material in walls – keeps inside of cooker hot by reducing energy
transfers by conduction
black pot – increases energy absorbed by radiation, as black is a good absorber
Water purifier:
transparent cover – allows radiation through but reduces energy transfer by
convection as it stops warm air rising, and also prevents escape of evaporated water
black pan – absorbs radiation that has passed through the water, black is a good
absorber, and the hot black pan will then heat the water
reflective surface – increases temperature inside the box by reflecting radiation into
the box
wooden frame – reduces energy transfers by conduction, so helps to keep the
temperature inside the box high
catch trough and tap – allow condensed pure water to be removed
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 5 of 6
8K Mark Scheme
Quick Check Answers
8Kc WS Explanations in all cases should refer to accurate results being close to the target or
true value, and precise results being clustered together (whether or not they are
close to the true value).
1 a low accuracy, high precision b high accuracy, low precision
c low accuracy, low precision d high accuracy, high precision
2 a high accuracy, high precision b low accuracy, high precision
c high accuracy, low precision d low accuracy, low precision
8Kd 3 … and 1 watt is 1 joule per second/ … or kilowatts/ … which measures how fast
energy is transferred by the machine.
4 … and these are more powerful machines/ … and we can work out which these
are from their power ratings.
5 … and some is wasted/ … but the total energy transferred is the same as the
energy supplied.
6 … and the widths of the arrows show the relative amounts of energy/ … and we
can use them to work out the efficiency of a machine.
7 … to find out the percentage of energy that is transferred as useful energy/
… which compares the useful energy to the total energy supplied.
8Ke The energy stored in a substance depends only on its temperature and its mass
[it also depends on the type of material]. When something is heated its temperature
always goes up [unless it is melting/boiling], because the particles start vibrating
more or moving around more. Conduction happens when the vibrations are passed
on in a solid. All solids [metals] are good conductors of energy [but many other solid
materials are not, particularly those containing trapped air].
Energy is spread out through fluids by convection. Part of the fluid is warmer and
becomes denser [less dense], so a convection current starts. Radiation is how
energy is transferred through empty space. Radiation cannot pass through solids
and liquids [it can pass through transparent solids and liquids]. Insulating materials
usually contain trapped air. Shiny, light coloured surfaces are good [poor] absorbers
and emitters of radiation.
Energy can also be transferred by evaporation. When some of a liquid evaporates,
it is only the fastest-moving particles that form a gas. The particles that are left are
not moving as fast so the temperature goes down.
Power is a way of saying how fast energy is being transferred. It is measured in
kilowatt-hours [watts or kilowatts]. Some energy transferred is wasted. Most wasted
energy is transferred by heating. The efficiency of a machine compares the useful
energy transferred to the wasted energy transferred [total energy supplied].
We pay for gas and electricity by the amount of energy used. We can reduce the
amount we have to pay by using less [more] efficient machines. We need to work
out the payback time as sometimes it costs more to buy a new machine than the
amount of money it will save.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2019. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. Page 6 of 6
You might also like
- Fire A Very Short Introduction (Andrew C. Scott)Document183 pagesFire A Very Short Introduction (Andrew C. Scott)Mendo HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Honda Hornet CB250F Owners Manual PDFDocument107 pagesHonda Hornet CB250F Owners Manual PDFvovanhaiqn67% (3)
- Pub - Flame Retardants For Plastics PDFDocument159 pagesPub - Flame Retardants For Plastics PDFDiegoTierradentroNo ratings yet
- Astm E1131Document6 pagesAstm E1131Erick IvánNo ratings yet
- 8kDocument8 pages8ksale7mansour2000No ratings yet
- Es Int 8e Eouts AspDocument6 pagesEs Int 8e Eouts Asprandima.fernandoNo ratings yet
- PM Test C10 (Student)Document7 pagesPM Test C10 (Student)damonchooNo ratings yet
- Paper Test For Thermal PhysicsDocument8 pagesPaper Test For Thermal PhysicsJerrySemuelNo ratings yet
- Class Viii Merge PDFDocument60 pagesClass Viii Merge PDFAkash RajNo ratings yet
- 2009 Promo Paper 1 (Structured)Document14 pages2009 Promo Paper 1 (Structured)Eugene TayNo ratings yet
- Sing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicstestNo ratings yet
- p4 Science Revision MCQ - HeatDocument8 pagesp4 Science Revision MCQ - HeatfranticfoodfrenzyNo ratings yet
- Y9 Science Revision IxDocument20 pagesY9 Science Revision IxfeliciateoxyNo ratings yet
- IX - Science PT2 - 2022-23Document11 pagesIX - Science PT2 - 2022-23avniisplayingytNo ratings yet
- Class 8 ScienceDocument5 pagesClass 8 ScienceShashank JavalgiNo ratings yet
- Oct 2020 p2 QP 1113Document15 pagesOct 2020 p2 QP 1113Lee Jia Bao Bernice0% (1)
- University of Cape Town Department of Physics PHY1032S (General Physics B) Class Test 2: Optics and Thermal PhysicsDocument9 pagesUniversity of Cape Town Department of Physics PHY1032S (General Physics B) Class Test 2: Optics and Thermal Physicslukhanyisojikela12No ratings yet
- Physics Complete SyllabusDocument4 pagesPhysics Complete SyllabusSamridhi JainNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2Document5 pagesICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2madhumitra mohantyNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 10 Pre-Board Paper Semester 2 2021-22Document9 pagesPhysics Grade 10 Pre-Board Paper Semester 2 2021-22OmMen GamingNo ratings yet
- Temperature To Heat Transfer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)Document9 pagesTemperature To Heat Transfer (Pear) Set 1 (Question)6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNo ratings yet
- PGIMER B.SC Nursing Physics Model PaperDocument5 pagesPGIMER B.SC Nursing Physics Model PaperAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Materials ScienceDocument0 pagesMaterials ScienceN Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- Physics Test T9Document1 pagePhysics Test T9Rana ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Sample Paper 6Document5 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Sample Paper 6OverRush AmareshNo ratings yet
- Science PaperDocument4 pagesScience PaperVIMLA BNo ratings yet
- Pawar Public School, Bhandup Class Subject Exam Marks Date Duration No. of Printed Pages X Physics Prelim 2 40 01.02.2022 1 Hours 5Document4 pagesPawar Public School, Bhandup Class Subject Exam Marks Date Duration No. of Printed Pages X Physics Prelim 2 40 01.02.2022 1 Hours 5kim loveNo ratings yet
- SC 2024 SP-4Document17 pagesSC 2024 SP-4Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Sectiona: Multiplechoice (2marks@.24%) : Answer All QuestionsDocument6 pagesSectiona: Multiplechoice (2marks@.24%) : Answer All QuestionsYuki LiNo ratings yet
- HKUGA College: S1 Science Module 2 Test (2021-22) Question & Answer BookletDocument7 pagesHKUGA College: S1 Science Module 2 Test (2021-22) Question & Answer Booklet6A 12 Nathan Leung 梁逸曦No ratings yet
- Practice Mock Paper AdolescenceDocument6 pagesPractice Mock Paper Adolescencesafa sahebNo ratings yet
- UH Science 1Document6 pagesUH Science 1yuniNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 4 HeatDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 March 31 Science Chapter 4 Heatarunadevi30081990No ratings yet
- KS3 TestDocument6 pagesKS3 TestVytheeshwaran Vedagiri80% (5)
- Practice Test Science Grade 9 Set 2Document7 pagesPractice Test Science Grade 9 Set 2Aditya KaushikNo ratings yet
- QP SEM 1 GR 8 2023 24 Combined Science PhysicsDocument8 pagesQP SEM 1 GR 8 2023 24 Combined Science PhysicsSansridh SridharanNo ratings yet
- The United Republic of Tanzania National Examinations Council Certificate of Secondary Education Examination Physics 1Document7 pagesThe United Republic of Tanzania National Examinations Council Certificate of Secondary Education Examination Physics 1Alhamdu Mussa SogoleNo ratings yet
- Heat Paper 1Document2 pagesHeat Paper 1Online SubsNo ratings yet
- Heat Paper 1 PDFDocument2 pagesHeat Paper 1 PDFbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 5-HeatDocument2 pagesPhysics: Chapter 5-HeatSubhadip RoyNo ratings yet
- Materials ScienceDocument42 pagesMaterials ScienceSrimannarayana NandamNo ratings yet
- GeneralScience 52675Document5 pagesGeneralScience 52675Deepa SreenathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Diversity of Materials (Selected QN)Document17 pagesChapter 02 Diversity of Materials (Selected QN)hee.tuitionNo ratings yet
- Name L.T Class Y9G Date 11/26/2020 1 Students Set Up The Apparatus Shown BelowDocument9 pagesName L.T Class Y9G Date 11/26/2020 1 Students Set Up The Apparatus Shown BelowThomasNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 1 SetA Final eDocument5 pagesScicent SQ U2 1 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29 Jun 2024Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 29 Jun 2024IX17-41 Suvayu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Exercise Questions Page Number 45 - 47Document4 pagesExercise Questions Page Number 45 - 47Ricky 's PremiumNo ratings yet
- Tryout Review II Chemistry Written Test 2024Document12 pagesTryout Review II Chemistry Written Test 2024priscillaaudrey24No ratings yet
- Phpy 9 JXL WDocument5 pagesPhpy 9 JXL WAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer BookDocument15 pagesForm 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Eval 1Document2 pagesPhysics Form 4 Eval 1Nkengfac LoiekNo ratings yet
- IB Topic (5) Paper 2 Review Q CardsDocument11 pagesIB Topic (5) Paper 2 Review Q CardsHakkyu KimNo ratings yet
- Icjephpu 07Document11 pagesIcjephpu 07Sharique SyedNo ratings yet
- QP Model Examination Set-BDocument3 pagesQP Model Examination Set-BSharon ShajanNo ratings yet
- Science Question Paper 8Document6 pagesScience Question Paper 8Neha BishlaNo ratings yet
- ISC 2023 Chemistry Question PaperDocument8 pagesISC 2023 Chemistry Question PaperT rud0No ratings yet
- Year 10 Unit 1 States of Matter 11Qn 2013-2019Document23 pagesYear 10 Unit 1 States of Matter 11Qn 2013-2019Rayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Mock Test 3 - PhysicsDocument4 pagesICSE Mock Test 3 - PhysicsYuvraj ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 1 SetB Final eDocument5 pagesScicent SQ U2 1 SetB Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicscappiemunaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Semester 2 Specimen - 521 SCI1Document7 pagesICSE Semester 2 Specimen - 521 SCI1Constantine ByzantineNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Modelling of A Low Nox "Swirl Burner"Document6 pagesAnalysis and Modelling of A Low Nox "Swirl Burner"sonn the greatNo ratings yet
- A Revolution in Fire Suppression Technology: It Really Rocket Science IsDocument6 pagesA Revolution in Fire Suppression Technology: It Really Rocket Science IsEdward MainaNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Unit 4 Thermochem Student PacketDocument28 pagesAP Chem Unit 4 Thermochem Student PacketMiron WolfNo ratings yet
- Basic of Boiler DesignDocument186 pagesBasic of Boiler DesignArielKST100% (2)
- Energies 14 04847Document24 pagesEnergies 14 04847ranjitv10No ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT - Science - Q1 - W3 - Day 1Document99 pagesGrade 5 PPT - Science - Q1 - W3 - Day 1Precilla Halago100% (2)
- 1 s2.0 S036031991930014X MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S036031991930014X MainAmeen KhanNo ratings yet
- 13 Chapter3 PDFDocument49 pages13 Chapter3 PDFmharitmsNo ratings yet
- In Case of FireDocument2 pagesIn Case of FireLiliannaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet H-130 Microbiocide: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet H-130 Microbiocide: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationRahmat Martin PranataNo ratings yet
- EIL Fired Heater Article - PTQ Q1Document4 pagesEIL Fired Heater Article - PTQ Q1aminwahiNo ratings yet
- G51MP Service FilesDocument53 pagesG51MP Service Files74747474No ratings yet
- 4.2 Knocking in SI EngineDocument38 pages4.2 Knocking in SI EngineAshwini SinghNo ratings yet
- Challenges in GT CFD - Lapworth - RR Lec 2008Document27 pagesChallenges in GT CFD - Lapworth - RR Lec 2008get_moin100% (1)
- Air Preheater Seal Upgrades Renew Plant EfficiencyDocument11 pagesAir Preheater Seal Upgrades Renew Plant EfficiencysdiamanNo ratings yet
- High Performance GEARDocument18 pagesHigh Performance GEARcaothucodon322No ratings yet
- Reactions of Non-Metals With OxygenDocument18 pagesReactions of Non-Metals With Oxygen18118100% (1)
- Causes of Air PollutionDocument1 pageCauses of Air PollutionKalimullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Fuel PropertiesDocument19 pagesFuel PropertiesGomathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Deno, Deso, and Co Removal Technology For Power PlantDocument5 pagesDeno, Deso, and Co Removal Technology For Power PlantcumiiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Code of Practice For Aboveground Storage Tank Systems Containing Petroleum ProductsDocument70 pagesEnvironmental Code of Practice For Aboveground Storage Tank Systems Containing Petroleum ProductsMayyouNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Ash in Analysis Sample Coal PDFDocument5 pagesStandard Test Method For Ash in Analysis Sample Coal PDFHidan WLNo ratings yet
- Polaris Extreme ps-4Document6 pagesPolaris Extreme ps-4jonathanNo ratings yet
- Daniel J. Jacob: Atmospheric Chemistry: From Air Pollution To Global Change and BackDocument21 pagesDaniel J. Jacob: Atmospheric Chemistry: From Air Pollution To Global Change and BackKaren AlcedoNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Risk Assessment in Cement Plants - Part4Document10 pagesTraining Manual For Risk Assessment in Cement Plants - Part4Kamran ZafarNo ratings yet