Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTOKEN
TOKEN
Uploaded by
poojabharti17306Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Basic of C - Geeky Shows 1Document4 pagesBasic of C - Geeky Shows 1Tavishi Singh100% (3)
- PC-DMIS 4.3 Reference ManualDocument1,755 pagesPC-DMIS 4.3 Reference ManualCarlosQuelartNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note-01-1Document4 pagesLecture Note-01-1SidtanNo ratings yet
- Constant Variables and Data TypesDocument14 pagesConstant Variables and Data TypesdixitjitekchandNo ratings yet
- Constants Variables and Data TypesDocument7 pagesConstants Variables and Data TypesAhmad syed KhizarNo ratings yet
- 02 C Language BasicsDocument7 pages02 C Language BasicsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Character Set of C: AlphabetsDocument12 pagesCharacter Set of C: AlphabetsWWE OFFICAL MATCH CARDS.No ratings yet
- Chap. 2: All Topics and Points Are Not IncludedDocument9 pagesChap. 2: All Topics and Points Are Not IncludedkkmknNo ratings yet
- Comp 172Document30 pagesComp 172Easy ways2017No ratings yet
- Keywords and IdentifiersDocument9 pagesKeywords and IdentifiersSreedhanya MvNo ratings yet
- C Token: Dr. Sheak Rashed Haider Noori Associate Professor & Associate Head Department of Computer ScienceDocument16 pagesC Token: Dr. Sheak Rashed Haider Noori Associate Professor & Associate Head Department of Computer Sciencethicc boiiNo ratings yet
- C Programming: DR Nazneen AkhterDocument18 pagesC Programming: DR Nazneen Akhternaaz_pinuNo ratings yet
- C++ Tokens: Derived Data TypesDocument3 pagesC++ Tokens: Derived Data TypesArpitha AppiNo ratings yet
- C++ Overview: Appendix ADocument48 pagesC++ Overview: Appendix AchiquicikNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2Document10 pagesUnit - 2abhishekthummar6No ratings yet
- 160 16sccit2-16sccca1-16scccs1 2020051805423333Document27 pages160 16sccit2-16sccca1-16scccs1 2020051805423333jashwanthNo ratings yet
- Character Set Consists ofDocument18 pagesCharacter Set Consists ofEs ENo ratings yet
- PST - Short NotesDocument12 pagesPST - Short Notesmeenakshisankar2013No ratings yet
- Cs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 06 - Tokens in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimDocument9 pagesCs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 06 - Tokens in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimGhazan AqeelNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (Elements of C) PDFDocument9 pagesUnit-2 (Elements of C) PDFSrijit koirlaNo ratings yet
- Language Fundamentals-I: (Character Set, Keywords, Identifiers, Constants, Variables)Document13 pagesLanguage Fundamentals-I: (Character Set, Keywords, Identifiers, Constants, Variables)Pawan NaniNo ratings yet
- DS Notes (Upto Arrays)Document85 pagesDS Notes (Upto Arrays)saiNo ratings yet
- C lANGUAGE BOOKDocument5 pagesC lANGUAGE BOOKmulanidhavalNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument54 pagesC Programskodali_madhav100% (3)
- Constant Variables Chapter-4Document29 pagesConstant Variables Chapter-4Kartik kalaspurkarNo ratings yet
- C Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)Document23 pagesC Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)krupa522No ratings yet
- Course Learning Outcome (Clo) : CLO1 (Apply Knowledge of Basic Concepts and Fundamentals ofDocument104 pagesCourse Learning Outcome (Clo) : CLO1 (Apply Knowledge of Basic Concepts and Fundamentals ofmbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Tokens in CDocument2 pagesTokens in Cravindras4uNo ratings yet
- C-OperatorsDocument33 pagesC-Operatorsjasase6236No ratings yet
- C Data Type NoteDocument22 pagesC Data Type Notevickroid007No ratings yet
- BCP Unit IiDocument34 pagesBCP Unit Iilopogip564No ratings yet
- Introduction To 'C' Language - ModifiedDocument44 pagesIntroduction To 'C' Language - ModifiedunknownNo ratings yet
- CSE1201_lecture1Document46 pagesCSE1201_lecture1nmr69gamingNo ratings yet
- C Programming Notes PDFDocument10 pagesC Programming Notes PDFRamesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit - II C Fundamentals & Decision Control Statements C FundamentalsDocument32 pagesUnit - II C Fundamentals & Decision Control Statements C Fundamentalsyv210904No ratings yet
- CAP100: Programming in CDocument25 pagesCAP100: Programming in CAparsha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- C AllDocument164 pagesC AllBalamurugan VelumaniNo ratings yet
- C Programming and Data Structures Unit-I Introduction To C Language TopicsDocument49 pagesC Programming and Data Structures Unit-I Introduction To C Language TopicsBasheer AhammadNo ratings yet
- C - Basic Syntax C - Basic SyntaxDocument2 pagesC - Basic Syntax C - Basic SyntaxrashNo ratings yet
- Basics of C Language: by Chinnu Edwin A M.Tech. CSDocument18 pagesBasics of C Language: by Chinnu Edwin A M.Tech. CSAugustine VineethNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4Abel IngawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument46 pagesIntroduction To C Programmingmaharjankrisha011No ratings yet
- Introduction To C LanguageDocument47 pagesIntroduction To C LanguageHEMANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- C Programming NotesDocument57 pagesC Programming NotesRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - C Program Data Types, Constants & VariablesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 - C Program Data Types, Constants & VariablesFreddy MutuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes by Rashmi Paneru Pandey (Be-C) : Unit - 3 Variables and Data TypesDocument12 pagesLecture Notes by Rashmi Paneru Pandey (Be-C) : Unit - 3 Variables and Data TypesShani Kumar MandalNo ratings yet
- 5 Tokens Lyst1919Document12 pages5 Tokens Lyst1919suraj nathNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - II Consts Vars and Data TypesDocument36 pagesUnit 1 - II Consts Vars and Data TypesThomas MathewNo ratings yet
- U2Document94 pagesU2Sarmi HarshaNo ratings yet
- Programming in C and C++: Dr. M. Babul IslamDocument15 pagesProgramming in C and C++: Dr. M. Babul IslamMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- C Keywords and IdentifiersDocument2 pagesC Keywords and IdentifiersBasant SinghNo ratings yet
- Pps Unit 2Document189 pagesPps Unit 2afakraipurNo ratings yet
- C Tokens-2Document15 pagesC Tokens-2Malavika VipinNo ratings yet
- Unit2 2Document74 pagesUnit2 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C LanguageDocument37 pagesIntroduction To C LanguageNaishadh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Module1 UpdatedDocument34 pagesModule1 UpdatedrafggajhNo ratings yet
- C Programming NotesDocument96 pagesC Programming NotesNgatia MukereNo ratings yet
- Keywords and IdentifierDocument9 pagesKeywords and IdentifierUthoai MarmaNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Commands Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesRaspberry Pi Commands Cheat SheetAdrian IosifNo ratings yet
- Work Plan Summary TemplateDocument26 pagesWork Plan Summary TemplateThiên HiNo ratings yet
- 3 2 23 989Document6 pages3 2 23 989Dian PriambudiNo ratings yet
- Light Power and Precision ManualDocument112 pagesLight Power and Precision ManualDaniel PantojaNo ratings yet
- GeoMedia Professional 2014 BasicoDocument226 pagesGeoMedia Professional 2014 BasicoJavier AmezcuaNo ratings yet
- Student Management System - Himanshu ProjectDocument51 pagesStudent Management System - Himanshu ProjectmewatihiraNo ratings yet
- How To Develop ABAP RICEF Objects in SDocument23 pagesHow To Develop ABAP RICEF Objects in SAdaikalam Alexander Rayappa50% (2)
- XPrinter User GuideDocument58 pagesXPrinter User GuideRaje FaizulNo ratings yet
- Fusion - 11 Install GuideDocument20 pagesFusion - 11 Install GuideJose Elenilson100% (1)
- UnoCart 2600 ManualDocument4 pagesUnoCart 2600 ManualAndrewColemanNo ratings yet
- HLP21E Service ManualDocument31 pagesHLP21E Service ManualplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Automatic Search External LOVDocument29 pagesAutomatic Search External LOVkorlapati ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Electronics and Communication Engineering: 4040561-Very Large Scale Integration PracticalDocument3 pagesDiploma in Electronics and Communication Engineering: 4040561-Very Large Scale Integration PracticalharivigneshaNo ratings yet
- SAP Dummy - QueriesDocument10 pagesSAP Dummy - QueriesAnonymous aFO3dGACNo ratings yet
- Lesson B Generations of ComputerDocument30 pagesLesson B Generations of ComputerSitsiritsit AlibangbangNo ratings yet
- Konsep KependudukanDocument9 pagesKonsep KependudukanHadi AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Retail Dashboard SynopsisDocument13 pagesRetail Dashboard Synopsisamanraj2009No ratings yet
- Applicable For Students Admitted in Session 2017-18Document8 pagesApplicable For Students Admitted in Session 2017-18Divya soniNo ratings yet
- STM32Cube MCU Package For STM32F4 Series With HAL, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated MiddlewareDocument6 pagesSTM32Cube MCU Package For STM32F4 Series With HAL, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated Middlewarealfredo de la hozNo ratings yet
- DBMSP ReportDocument32 pagesDBMSP ReportThe KingNo ratings yet
- Cosec VMS: User ManualDocument28 pagesCosec VMS: User ManualSijesh ThiruthiyilNo ratings yet
- Grblcontrol CNC Software InstructionsDocument5 pagesGrblcontrol CNC Software Instructionssea13No ratings yet
- Project 8 1c Miniature TrainDocument11 pagesProject 8 1c Miniature Trainapi-282195833100% (1)
- Notas Eletronicas Diagrama A14RM PDFDocument37 pagesNotas Eletronicas Diagrama A14RM PDFJoão VictorNo ratings yet
- Ssmple QP XIIDocument12 pagesSsmple QP XIINØ RÙĪZNo ratings yet
- Resulticks Introduction v2Document8 pagesResulticks Introduction v2Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Isilon - Configure 10 GDocument8 pagesIsilon - Configure 10 GAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Thesis FinalDocument29 pagesThesis FinalDanika Jan100% (2)
- SNMP Feature On Yealink IP PhonesDocument7 pagesSNMP Feature On Yealink IP PhonesdragelecNo ratings yet
TOKEN
TOKEN
Uploaded by
poojabharti173060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesTOKEN
TOKEN
Uploaded by
poojabharti17306Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
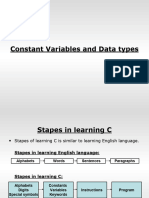
CHAPTER 3
Constants, Variables and Data Types
■ Letters Digits
■ Uppercase A_Z All decimal digits 0..9
CHARACTER SET ■
■
Lowercase a_z
Special Character
■ , comma & ampersand
■ . Period * asterisk
■ The characters that can be used to form ■ ; semicolon - minus
words, numbers and expressions depend
upon the computer on which the program is ■ : colon + plus
run.
■ ? Question mark / slash
■ The characters in C are grouped into the
following categories: ■ ‘ apostrophe \backslash
■ Letters ■ “ quotation mark ~ tilde
■ Digits ■ ! Exclamation mark _ underscore
■ Special characters ■ | vertical bar % percent sign
■ White spaces ■ White Spaces
■ Blank space
■ Horizontal tab
■ Carriage return
■ New line
C Tokens
In a C program the smallest individual units are known as C tokens.
C tokens
keywords constants Strings Operators
Identifiers Special Symbols
KEYWORDS AND IDENTIFIERS
Every C word is classified as either a keyword or an identifier. All keywords have fixed meanings and these meanings
cannot be changed.
Identifiers refer to the names of variables, functions and arrays.
Some keywords
auto double int struct
break else long switch
case enum register typedef
char extern return union
const float short unsigned
continue for signed void
default goto sizeof volatile
do if static while
Rules for Identifiers
1. The first character must be an alphabet (or underscore).
2. Must consist of only letters, digits, or underscore.
3. Only the first 31 characters are significant.
4. Cannot use a keyword.
5. Must not contain white space.
CONSTANTS
Constants in C refers to fixed values that do not change during the execution of a
program.
CONSTANTS
Numeric constants Character constants
Integer Real Single character String
constants constants constants constants
You might also like
- Basic of C - Geeky Shows 1Document4 pagesBasic of C - Geeky Shows 1Tavishi Singh100% (3)
- PC-DMIS 4.3 Reference ManualDocument1,755 pagesPC-DMIS 4.3 Reference ManualCarlosQuelartNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note-01-1Document4 pagesLecture Note-01-1SidtanNo ratings yet
- Constant Variables and Data TypesDocument14 pagesConstant Variables and Data TypesdixitjitekchandNo ratings yet
- Constants Variables and Data TypesDocument7 pagesConstants Variables and Data TypesAhmad syed KhizarNo ratings yet
- 02 C Language BasicsDocument7 pages02 C Language BasicsRaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Character Set of C: AlphabetsDocument12 pagesCharacter Set of C: AlphabetsWWE OFFICAL MATCH CARDS.No ratings yet
- Chap. 2: All Topics and Points Are Not IncludedDocument9 pagesChap. 2: All Topics and Points Are Not IncludedkkmknNo ratings yet
- Comp 172Document30 pagesComp 172Easy ways2017No ratings yet
- Keywords and IdentifiersDocument9 pagesKeywords and IdentifiersSreedhanya MvNo ratings yet
- C Token: Dr. Sheak Rashed Haider Noori Associate Professor & Associate Head Department of Computer ScienceDocument16 pagesC Token: Dr. Sheak Rashed Haider Noori Associate Professor & Associate Head Department of Computer Sciencethicc boiiNo ratings yet
- C Programming: DR Nazneen AkhterDocument18 pagesC Programming: DR Nazneen Akhternaaz_pinuNo ratings yet
- C++ Tokens: Derived Data TypesDocument3 pagesC++ Tokens: Derived Data TypesArpitha AppiNo ratings yet
- C++ Overview: Appendix ADocument48 pagesC++ Overview: Appendix AchiquicikNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2Document10 pagesUnit - 2abhishekthummar6No ratings yet
- 160 16sccit2-16sccca1-16scccs1 2020051805423333Document27 pages160 16sccit2-16sccca1-16scccs1 2020051805423333jashwanthNo ratings yet
- Character Set Consists ofDocument18 pagesCharacter Set Consists ofEs ENo ratings yet
- PST - Short NotesDocument12 pagesPST - Short Notesmeenakshisankar2013No ratings yet
- Cs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 06 - Tokens in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimDocument9 pagesCs112 - Programming Fundamental: Lecture # 06 - Tokens in C Syed Shahrooz ShamimGhazan AqeelNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (Elements of C) PDFDocument9 pagesUnit-2 (Elements of C) PDFSrijit koirlaNo ratings yet
- Language Fundamentals-I: (Character Set, Keywords, Identifiers, Constants, Variables)Document13 pagesLanguage Fundamentals-I: (Character Set, Keywords, Identifiers, Constants, Variables)Pawan NaniNo ratings yet
- DS Notes (Upto Arrays)Document85 pagesDS Notes (Upto Arrays)saiNo ratings yet
- C lANGUAGE BOOKDocument5 pagesC lANGUAGE BOOKmulanidhavalNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument54 pagesC Programskodali_madhav100% (3)
- Constant Variables Chapter-4Document29 pagesConstant Variables Chapter-4Kartik kalaspurkarNo ratings yet
- C Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)Document23 pagesC Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)krupa522No ratings yet
- Course Learning Outcome (Clo) : CLO1 (Apply Knowledge of Basic Concepts and Fundamentals ofDocument104 pagesCourse Learning Outcome (Clo) : CLO1 (Apply Knowledge of Basic Concepts and Fundamentals ofmbagavan 0712No ratings yet
- Tokens in CDocument2 pagesTokens in Cravindras4uNo ratings yet
- C-OperatorsDocument33 pagesC-Operatorsjasase6236No ratings yet
- C Data Type NoteDocument22 pagesC Data Type Notevickroid007No ratings yet
- BCP Unit IiDocument34 pagesBCP Unit Iilopogip564No ratings yet
- Introduction To 'C' Language - ModifiedDocument44 pagesIntroduction To 'C' Language - ModifiedunknownNo ratings yet
- CSE1201_lecture1Document46 pagesCSE1201_lecture1nmr69gamingNo ratings yet
- C Programming Notes PDFDocument10 pagesC Programming Notes PDFRamesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Unit - II C Fundamentals & Decision Control Statements C FundamentalsDocument32 pagesUnit - II C Fundamentals & Decision Control Statements C Fundamentalsyv210904No ratings yet
- CAP100: Programming in CDocument25 pagesCAP100: Programming in CAparsha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- C AllDocument164 pagesC AllBalamurugan VelumaniNo ratings yet
- C Programming and Data Structures Unit-I Introduction To C Language TopicsDocument49 pagesC Programming and Data Structures Unit-I Introduction To C Language TopicsBasheer AhammadNo ratings yet
- C - Basic Syntax C - Basic SyntaxDocument2 pagesC - Basic Syntax C - Basic SyntaxrashNo ratings yet
- Basics of C Language: by Chinnu Edwin A M.Tech. CSDocument18 pagesBasics of C Language: by Chinnu Edwin A M.Tech. CSAugustine VineethNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4Abel IngawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C ProgrammingDocument46 pagesIntroduction To C Programmingmaharjankrisha011No ratings yet
- Introduction To C LanguageDocument47 pagesIntroduction To C LanguageHEMANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- C Programming NotesDocument57 pagesC Programming NotesRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - C Program Data Types, Constants & VariablesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 - C Program Data Types, Constants & VariablesFreddy MutuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes by Rashmi Paneru Pandey (Be-C) : Unit - 3 Variables and Data TypesDocument12 pagesLecture Notes by Rashmi Paneru Pandey (Be-C) : Unit - 3 Variables and Data TypesShani Kumar MandalNo ratings yet
- 5 Tokens Lyst1919Document12 pages5 Tokens Lyst1919suraj nathNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - II Consts Vars and Data TypesDocument36 pagesUnit 1 - II Consts Vars and Data TypesThomas MathewNo ratings yet
- U2Document94 pagesU2Sarmi HarshaNo ratings yet
- Programming in C and C++: Dr. M. Babul IslamDocument15 pagesProgramming in C and C++: Dr. M. Babul IslamMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- C Keywords and IdentifiersDocument2 pagesC Keywords and IdentifiersBasant SinghNo ratings yet
- Pps Unit 2Document189 pagesPps Unit 2afakraipurNo ratings yet
- C Tokens-2Document15 pagesC Tokens-2Malavika VipinNo ratings yet
- Unit2 2Document74 pagesUnit2 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C LanguageDocument37 pagesIntroduction To C LanguageNaishadh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Module1 UpdatedDocument34 pagesModule1 UpdatedrafggajhNo ratings yet
- C Programming NotesDocument96 pagesC Programming NotesNgatia MukereNo ratings yet
- Keywords and IdentifierDocument9 pagesKeywords and IdentifierUthoai MarmaNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Commands Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesRaspberry Pi Commands Cheat SheetAdrian IosifNo ratings yet
- Work Plan Summary TemplateDocument26 pagesWork Plan Summary TemplateThiên HiNo ratings yet
- 3 2 23 989Document6 pages3 2 23 989Dian PriambudiNo ratings yet
- Light Power and Precision ManualDocument112 pagesLight Power and Precision ManualDaniel PantojaNo ratings yet
- GeoMedia Professional 2014 BasicoDocument226 pagesGeoMedia Professional 2014 BasicoJavier AmezcuaNo ratings yet
- Student Management System - Himanshu ProjectDocument51 pagesStudent Management System - Himanshu ProjectmewatihiraNo ratings yet
- How To Develop ABAP RICEF Objects in SDocument23 pagesHow To Develop ABAP RICEF Objects in SAdaikalam Alexander Rayappa50% (2)
- XPrinter User GuideDocument58 pagesXPrinter User GuideRaje FaizulNo ratings yet
- Fusion - 11 Install GuideDocument20 pagesFusion - 11 Install GuideJose Elenilson100% (1)
- UnoCart 2600 ManualDocument4 pagesUnoCart 2600 ManualAndrewColemanNo ratings yet
- HLP21E Service ManualDocument31 pagesHLP21E Service ManualplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Automatic Search External LOVDocument29 pagesAutomatic Search External LOVkorlapati ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Electronics and Communication Engineering: 4040561-Very Large Scale Integration PracticalDocument3 pagesDiploma in Electronics and Communication Engineering: 4040561-Very Large Scale Integration PracticalharivigneshaNo ratings yet
- SAP Dummy - QueriesDocument10 pagesSAP Dummy - QueriesAnonymous aFO3dGACNo ratings yet
- Lesson B Generations of ComputerDocument30 pagesLesson B Generations of ComputerSitsiritsit AlibangbangNo ratings yet
- Konsep KependudukanDocument9 pagesKonsep KependudukanHadi AlamsyahNo ratings yet
- Retail Dashboard SynopsisDocument13 pagesRetail Dashboard Synopsisamanraj2009No ratings yet
- Applicable For Students Admitted in Session 2017-18Document8 pagesApplicable For Students Admitted in Session 2017-18Divya soniNo ratings yet
- STM32Cube MCU Package For STM32F4 Series With HAL, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated MiddlewareDocument6 pagesSTM32Cube MCU Package For STM32F4 Series With HAL, Low-Layer Drivers and Dedicated Middlewarealfredo de la hozNo ratings yet
- DBMSP ReportDocument32 pagesDBMSP ReportThe KingNo ratings yet
- Cosec VMS: User ManualDocument28 pagesCosec VMS: User ManualSijesh ThiruthiyilNo ratings yet
- Grblcontrol CNC Software InstructionsDocument5 pagesGrblcontrol CNC Software Instructionssea13No ratings yet
- Project 8 1c Miniature TrainDocument11 pagesProject 8 1c Miniature Trainapi-282195833100% (1)
- Notas Eletronicas Diagrama A14RM PDFDocument37 pagesNotas Eletronicas Diagrama A14RM PDFJoão VictorNo ratings yet
- Ssmple QP XIIDocument12 pagesSsmple QP XIINØ RÙĪZNo ratings yet
- Resulticks Introduction v2Document8 pagesResulticks Introduction v2Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Isilon - Configure 10 GDocument8 pagesIsilon - Configure 10 GAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Thesis FinalDocument29 pagesThesis FinalDanika Jan100% (2)
- SNMP Feature On Yealink IP PhonesDocument7 pagesSNMP Feature On Yealink IP PhonesdragelecNo ratings yet