Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Botany Updated - 2024
Botany Updated - 2024
Uploaded by
lunalooooo37Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Botany Updated - 2024
Botany Updated - 2024
Uploaded by
lunalooooo37Copyright:
Available Formats
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
BOTANY UPDATED SYLLABUS - 2024
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 1 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 2 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 3 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 4 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 5 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 6 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 7 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 8 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 9 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
Page 10 of 13
Page 11 of 13
VELAMMAL NEET & IIT ACADEMY
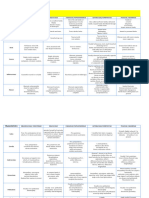
Characteristics BRASSICACEAE/ CRUCIFERAE MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
One of the sub family of Family of
It is known as mustard family. It is known as mallow family.
leguminosae. It is also Also called sun flower family. Advanced cerearls
Mainly Mainly
General description termed as pea family. family. Largest family distributed through ubiquitous
distributed in tropics distributed in tropics
Distributed all over out the world in occurance
and substropics and substropics
the world. largest monocot family
Annual herbs
Habit Annual or perennial herbs Herbs, shrubs and trees. Trees, shrubs, herbs. (Helianthus, Annual or perennial Herbs
Tagetus, Dahlia)
Tap root, fusiform/
Tap root but in
napiform tuberous roots may Tap root with Fibrous roots, stilt roots in maize,
Root Profusely branched tap root. Dahlia fasiculated
found. root nodules. jowar, sugarcane
roots/fibrous roots
Usually herbaceous, erect, much branched
Herbaeous stem with (brancing rare in Grasses have hollow stem at
Erect, branched with Erect or climber,
Stem pungent watery fluid. Dahlia and Helianthus) solid, sometimes internodes. stem is
star-shaped trichormes. herbaceous.
Have stellate hairs. with milky latex. In Helianthus jointed called culm
tuberous stem stores food
Alternate, pinnately Usually alternate but occasionally opposite
Simple, alternate Leaves are narrow
Simple rarely compound, compound or simple (as Helianthus)
palmately lobed, alternate Leaf base is
Leaves alternate, sessile leaves, reticulate or in Whorl (Eupatorium),
stipulate, reticulate sheath like Venation is
exstipulate, reticulate venation. venation, pulvinate leaf base exstipulate, petiolate, simple
venation. parallel, Contain silica, hence hard
stipulate. or compound venation reticulate.
Head or capitulum with involucre of bracts
Usually two types of
florets are found in inflorescence viz,
zygomorphic, ligulate or ray
Solitary terminal or Spike of spikelets
florets and actinomorphic tubular or disc
Inflorescence Corymobse raceme or corymb. axillary cymose or Racemose, (panicle in Dalbergia) In maize, female -spadix,
florets. In inflorescence,
raceme. Male-spike, Wheat-compoud spike
ray florets are found towards the
periphery (they are older in nature)
and disc florets are distributed near
centre (thus younger)
Bracteate, sessile
Bisexual, actinomorphic Sessile, Bracteate,
Bisexual, bracteate, Bisexual, zygomorphic, actinomorphic (disc
(may be zygomorphic), bisexual, unisexual in maize,
actinomorphic, bracteate or ebracteate, florets) or zygomorphic
Flower hypogynous, Zygomorphic hypogynous
complete pentamerous, pentamerous, hypogynous, (ray florets) epigynous
bracteate/ebracteaete, Sterile bracts called glumes are
hypogynous. complete and pentamerous.
tetramerous. present
Page 12 of 13
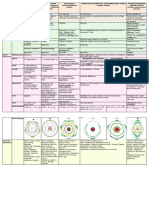
Characteristics BRASSICACEAE/ CRUCIFERAE MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
epicalyx formed by bracteoles
Perianth: Highly reduced, 2 in
is present below the calyx and
Four, free, polysepalous in two Five, gamolous 5 modified into hairs or pappus. number, reduced to pin head like
Calyx is protective in nature. Sepals
whorls, 2+2 valvate aestivation imbricate/valvate aestivation Persistent, help in fruit dispersal lodicules. In bamboo, 3 are
5, fused, gamosepalous,
present
valvate aestivation
Five, polypetalous,
papilionaceous (posterior 5, Gamopetalous,
Four, polypetalous Five, petals free, but
standard, two lateral tubular in disc florets
Corolla cruciform and reduced. basally adnate, twisted
wings, keel enclosing but ligulate in ray
valvate aestivation aestivation.
pistil and stamen), florets, aestivation valvate.
vexillary aestivaiton.
Stamens 5, absent in ray florets.
Numerous stamens Syngenesious (anther lobes are
Usually 3 but sometimes
Monadelphous fused laterally but the filaments are free)
Six stamens arranged in two Ten, diadelphous,(9)+1, 6 (as in Oryza), filament long,
epipetalous, epipetalous, anthers
Androecium whorls, 2+4, polyandrous anther dithecous, anthers versatile,
monothecous, extrorse dithecous fused to form a tube like
tetradynamous, dithecous. introrse. dithecous, dehiscence
anthers reniform, dehiscence structure around the style. Anthers
longitudingal.
transverse introse, dithecous, dehiscence
longitudinal
Monocarpellary (actually
tricarpellary but only one carpel is
Bicarpellary, syncarpous A compund pistil of functional),
monocarpellary, bicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular,
superior ovary with two to many carpels, unilocular, ovary superior, style
Gynoecium unilocular with many superiour ovary. Style long, stigma bifid,
parietal placentation. syncarpous, axile long, stigma 2 and feathery (plants
ovules, single style, Ovary superior single ovule, basal placentation
Replum/false septum is present placentation. are always wind pollinated).
marginal placentation.
Placentation basal.
Usually cross pollination
piston mechanism Usually cross pollination
Usually cross pollination but self pollination in Favoured by protandry and Herkogamy Usually cross pollination
Usually cross pollination
Pollination Entomophily favoured by pisum and lathyrus Entomophily Anemophily
Entomophily
protandry and Herkogamy Entomophily In disc florets some times self pollination favoured by protandry
occurs by saftey mechanism
A single single seeded Caryopsis
Fruit Siliqua or silicula Capsule or schizocarp. Legume/Pod
seeded cypsela.
Page 13 of 13
Characteristics BRASSICACEAE/ CRUCIFERAE MALVACEAE FABACEAE/PAPILIONOIDEAE ASTERACEAE/COMPOSITAE POACEAE /GRAMINAE
Seed with curved embryo and
Seed Small non-endospermic scanty One to many and non-endospermic dicotyledonous, non endospermic monocotyledonous, endospermic
endosperm.
Floral formula
Floral diagram
i) The members of this i) These plants are used i) Members of this family are i) Oil Yielding plants : Helianthus annus i) Members of this family are mainly
family are sources of food, as food, e.g. mainly (sunflower oil), Carthamus (Safflower oil) used as food
e.g. Brassica campestris Abelmoschus esculentus used as food, i.e. pulses, e.g. gram, ii) Medicinal plants: Artemisia, Eclipta 1) Tritium aestivum
(mustard), (lady's finger). arhar, sem, moong, soybean, etc. alba used as hair tonic with (bread wheat) - a natural hexaploid
B. oleracea (cauliflower), Brassica Hibiscus cannabis (gongura) ii) Fodder, e.g. brahmi buti and commonly known as 2) Oryza sativa (Paddy)
rapa (turnip) and Raphanus sativus ii) Ornamentals, e.g. Trifolium, Sesbania, etc. Bringraj, -Chief cereal of India,
(radish). Althaea rosea (gulekhera), iii) Edible oil, e.g. soybean, ground Calendula officinalis bran oil obtained from husk
ii) Medicines, e.g. Iberis Hibiscus rosa-sinensis(China nut iii) Insecticide: Chrysanthemum 3) Zea mays (Maize) - food crop,
amara (gout and rheumatism), rose), iv) For fibres, e.g. sunhemp. cinerariifolium inflorescence unisexual, style
Lobularia (gonorrhoea), Lepidium iii) Medicines: roots and bark v) Ornamentation, e.g. lupin, sweet - Pyrethrum longest.
sativum (asthma and piles) of Urena lobata are used as a pea. iv) Food Yielding plants: Latuca sativa 4) Hordeum vulgare (Barley)
Economic iii) Ornamentals, e.g. Iberis cure for hydrophobia. VI) For the extraction of medicines, (Lettuce or Salad) -Oldest amongst cultivated plants.
Importance amara (candytuft), iv) Fibres, e.g. e.g Cicborium intybus (chikori powder/Coffee 5) Pennisetum typhoidum
Cherianthus cheiri (wall Gossypium sp. (cotton), mulaithi. blend) (Pearl millet or Bajra) -A food
flower), etc. Bombax ceiba (silk cotton) VII) Dye-Indigofera (blue) v) Weeds: Parthenium hysterophorus crop, straw used as fodder.
vi) oil- seeds of Brassica v) Edible oil, e.g. cotton. commonly called ii) Fodder - Cynodon, Panicum,
carrot grass or congress grass. Cymbopogon iii)
vi) Dyes - Carthamus (red), Sugar - Saccharum
Tagetus (Yellow) iv) Building material - Bamboo
v) Paper making - Grasses,
Bamboo
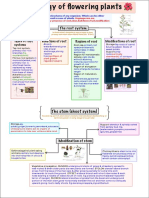
14 Families of Flowering Plants
Exercise - I 7. Shepherd's purse plant belong to
family:-
INTRODUCTION & BRASSICACEAE
1) Cruciferae 2) Malvaceae
1. Number of sepals in mustard flower
3) Solanaceae 4) Leguminosae
1) 5 2) 3 3) 4 4) 6
8. Turnip Brassica rapa) belongs to
2. Replum is:-
family:-
1) False placenta
1) Cruciferae 2) Malvaceae
2) False septum
3) Liliaceae
3) False ovule
4) Cucurbitaceae
4) False thalamus
3. Point out the correct floral formula 9. The Iberis is commonly called as:-
of cruciferae :- 1) Pansy 2) Candy-tuft
1) K2+2 C4 A2+4 G 3) Poppy 4) Snapdragon
2
2) K5 C6 A3 G(2) 10. Cruciform corolla is found in :-
3) K2+2 C2+2 A2+4 G(2) 1) Sunflower 2) China-rose
4) K4 C4 A2 G(2) 3) Radish 4) Pea
4. Placentation of cruciferae plant is:-
11. Tetradynamous androecium is
1) Parietal 2) Axile characterised by-
3) Basal 4) Marginal 1) Outer 2 long and inner 2 short
stamens
5. The special feature of the ovary in
cruciferae is:- 2) Outer 2 short and inner 4 long
1) Hypogyny stamens
2) Polyandry 3) Outer 4 long and inner 2 short
stamens
3) False septum
4) Outer 4 short and inner 2 long
4) One row of ovules on each
stamens
placenta
6. In Brassica oleracea var. capitata the 12. Parietal placentation is found in -
edible part is:- 1) Allium cepa
1) Inflorescence 2) Hibiscus cannabinus
2) Flower bud 3) Brassica
3) Vegetative bud
4) Solanum
4) Stem
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 15
13. The family cruciferae is represented 3) Brassica oleraceae var. gangioids
by the floral formula 4) Brassica caulorapa
1) P3+ 3 or (3 + 3), A3 + 3,G(3)
19. Botanical name of Indian mustard is-
2) K2+2, C4, A2+4 G
2
1) Brassica campestris
3) K 4–5, or (4 – 5), C4-5, A10 G1 2) B. juncea
4) K(5), C(5), A5, G(2) 3) B. nigra 4) B. alba
14. Only herbs are present in - 20. Which of the following plants has a
1) Malvaceae 2) Cruciferae corolla with 4 petals-
3) Compositae 4) Leguminosae 1) Shoe-flower 2) China rose
3) Pea plant 4) Mustard
15. What is the difference between the
flowers of Raphanus sativus & Iberis
FABACEAE
amara-
21. Pulses yielding main family of plants
1) In stamen and Carpels
is :-
2) Colour and size of corolla & fruit
1) Poaceae (Graminae)
3) In symmetry & Inflorescence
2) Cucurbitaceae
4) In stamen & Inflorescence
3) Liliaceae
16. Tetradynamous stamens are the 4) Papilionaceae
characteristic of-
22. The botanical name of ground nut is:
1) Malavaceae – Althea,Hibiscus
1) Cicer arietinum
2) Cruciferae – Mustard,Iberis
2) Glycine max
3) Solanaceae – Nicotiana,Petunia
3) Arachis hypogea
4) Liliaceae – Allium,Asphodilous
4) Lens esculentus
17. An important feature of Brassicaceae is-
23. The floral formula of Pea is
1) Inferior ovary
represented as:-
2) Cruciform corolla
1) Br% K(5) C1+2+(2) A(9)+1 G
3) Axile swollen placentae 1
4) Oblique ovary 2) Br% K5) C5 A1+(9) G1
3) Br% K(5) C1+2+(2) A9+1 G
18. The botanical name for cauliflower is- 1
1) Brassica rapa 4) Ebr or Br% K(5) C1+2+(2) A10 G1
2) Brassica oleracea var. botrytis
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
16 Families of Flowering Plants
24. Which of the following genera is 29. Blue dye is obtained from the leaves
characterised by the production of of:-
geocarpic fruits:- 1) Indigofera tinctoria
1) Cucurbita 2) Pisum 2) Opium
3) Glycine 4) Arachis 3) Aloe
25. The 3 - sub - families of Leguminosae 4) Delbergia sissoo
are distinguished mainly on the
basis of:- 30. In family papilionaceae, 5 petals
form a unique association, In which
1) nature of gynoecium 3 different elements participate,
2) Nature of corolla and stamens these are vexillum, alae & carina.
3) Nature of habit of the plants What is the number of these
elements:-
4) Nature of fruit
1) 1, 2, 2 respectively
26. Most leguminous plants have:- 2) 2, 1, 2 respectively
1) Simple petiolate leaves 3) 1,1,3 respectively
2) Simple sessile leaves 4) 2,2,1 respectively
3) Pinnately compound leaves
31. The name papilionatae and
4) Palmately compound leaves cruciferae is based on:-
27. The leguminous plants are important 1) Corolla 2) Androecium
in agriculture becaue:- 3) Gynoecium 4) Fruit
1) They are disease resistant
32. Keel is characteristic of the flowers
2) They require very little irrigation of:
3) They help in nitrogen economy of 1) Bean 2) Gulmohur
nature
3) Cassia 4) Calotropis
4) Crops of legumes can be produced
in a year 33. Presence of monocarpellary
gynoecium, unilocular ovary and
28. Androecium of Papilionatae family marginal placentation are
is:- characteristics of the family -
1) Monoadelphous 1) Leguminosae
2) Diadelphous 2) Cucurbitaceae
3) Polyadelphous 3) Malvaceae
4) None of these 4) Liliaceae
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 17
34. A crop plant which can grow well 3) Incomplete, zygomorphic,
even in nitrogen deficient soil is- trimerous
1) Helianthus annuus 4) Incomplete, actinomorphic,
2) Gossypium herbaceum pentamerous
3) Brassica campesteris 40. What type of placentation is seen in
4) Cajanus cajan sweet pea-?
1) Marginal 2) Basal
35. Red Gram is-
3) Axile 4) Free central
1) Phaseolus aureus
2) Cicer arietinum SOLANACEAE
3) Cajanus cajan
Br or Ebr K 5 C 5 A5 G
2
4) Phaseolus mungo 41.
is
the floral formula of:-
36. A diagnostic trait for identification of
1) Cruciferae 2) Leguminosae
Fabaceous flower is-
3) Solanaceae 4) Papilionatae
1) Tetradynamous androecium
2) Inferior ovary 42. Inflorescence in Solanaceae is:-
3) Cruciform corolla 1) Racemose 2) Cymose
4) Vexillary aestivation 3) Hypanthodium 4) Verticillaster
37. Family Fabaceae belongs to series- 43. The carpels of Solanum flower are
1) Inferae obliquely placed because:-
2) Thalamiflorae 1) Posterior and anterior carpels turn
o
3) Calyciflorae 4) Disciflorae by 180
38. In the flowers of Fabaceae one of the 2) Posterior and anterior carpels
following immediately encloses the move to the left
essential organs- 3) Posterior carpels turn to right and
1) Anterior petals anterior to the left
2) Posterior petals 4) Posterior carpels turn to left and
anterior to the right
3) Lateral petals 4) Sepals
44. Lycopersicon esculentum belongs to
39. The flower in Fabaceae is-
family:-
1) Complete, zygomorphic,
1) Solanaceae 2) Malvaceae
pentamerous
2) Complete, actinomorphic 3) Cruciferae
trimerous 4) Cucurbitaceae
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
18 Families of Flowering Plants
45. From which part of Atropa 52. Atropa belladona, a medicinal plant
belladona, the drug belladona is belongs to-
obtained:- 1) Liliaceae 2) Brassicaceae
1) Roots 2) bark 3) Solanaceae 4) Poaceae
3) Stem
4) All parts of the plant 53. Floral formula of Tomato/Tobacco
is-
46. Persistant calyx is characteristics of :-
+ K4 – 5 A10 G(2)
1) Allium / Liliaceae 1)
2) Mustard / Cruciferae + K2 + 2 C4 A2 + 4 G1
2)
3) Dalbergia / Papilionatae
+ P2 A3 G1
4) Solanum / solanaceae 3)
47. Bicarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium + K(5) C(5) A5 G(2)
4)
with bilocular ovary axile swollen
placenta and oblique septum occurs 54. Night Queen and Day King belong
in:- to one of the following genera-
1) Cruciferae 2) Solanaceae 1) Sesbania
3) Cucurbitaceae 4) Liliaceae 2) Chrysanthemum
48. Tomato belongs to genus :- 3) Cestrum
1) Brassica 2) Lycopodium 4) Lilium
3) Physalis 4) Lycopersicon
55. Pentamerous, actinomorphic
49. Nicotiana, potato belongs to :- flowers, bicarpellary ovary with
oblique septa, fruit a capsule or
1) Malvaceae 2) Liliaceae berry are characteristic features of-
3) Solanaceae 4) Cruciferae
1) Liliaceae 2) Asteraceae
50. Drug "Henbane" is obtained from:- 3) Brassicaceae 4) Solanaceae
1) Atropa 2) Hyoscyamus POACEAE
3) Withania 4) Nicotiana 56. The inflorescence in Gramineae is a -
51. Which character of malvaceae family 1) Raceme 2) Spike
is completely absent in Solanaceae 3) Spikelet 4) Thyrsus
family-
57. Which of the following families
1) Herbaceous nature provide food rich in carbohydrates-
2) Actinomorphic flower 1) Cruciferae 2) Leguminosae
3) Monothecous anther lobe 3) Gramineae 4) Palmae
4) Axile placentation
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 19
58. Oryza sativa belongs to - 68. Poaceae commonly known as
1) Solanaceae 2) Liliaceae 1) Grass family 2) Potato family
3) Gramineae 4) Palmae 3)pulses family 4) Mustard family
59. Caryopsis fruit is the characteristic of 69. Scutellum present in which family
which family 1) Cruciferae 2) Leguminosae
1) Malvaceae 2) Fabaceae 3) Gramineae 4) Palmae
3) Asteraceae 4) Poaceae
60. Grain of Maize is - MALVACEAE
1) Seed 2) Fruit 70. Number of stamens present in
Malvaceae is:-
3) Neither seed nor fruit
1) Infinite ( ) 2) Five (5)
4) Bud of flower
3) Ten (10) 4) Nine + one (9+1)
61. Feathery stigma are present in -
1) Wheat 2) Pea 71. Fibres are usually obtained from the
members of:-
3) Datura 4) Mustard
1) Solanaceae 2) Malvaceae
62. The inflorescence in Gramineae is :-
3) Leguminosae 4) Cruciferae
1) Raceme 2) Catkin
3) Spike of spikelets 72. In Malvaceae the placentation is:-
4) Thyrsus 1) Marginal 2) Axile
63. Parallel venation occurs in :- 3) Basal 4) Parietal
1) Poaceae 2) Solanaceae 73. Aestivation of petals in family
3) Malvaceae 4) Fabaceae Malvaceae is:-
64. No of stamens in poaceae 1) Valvate 2) Imbricate
1)3 2) 6 3) 9 4) 5 3) Twisted 4) Vexillary
65. No of carpels in poaceae 74. Lady finger belongs to family:-
1)3 2) 1 3) 9 4) 5 1) Malvaceae 2) Cruciferae
66. Perianth of poaceae also known as 3) Compositae 4) Fabaceae
1)lodicules 2) bract
75. Which one of the following groups
3)Lemma 4) spathe. of plants produces fibres of
67. Scientific name of wheat economic importance:-
1)Oryzasativa 1) Gossypium, Hibiscus, Crotalaria
2) Triticum aestivum 2) Gossypium, Cassia, Lycopersicum
3 )Haredeum vulgare 3) Gossypium, Brassica, Glycine
4) Avena sativum 4) Gossypium, Agave, Nicotiana
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
20 Families of Flowering Plants
82. Epipetalous stamens and axile
76. Shoe flower belongs to:-
placentation are found in -
1) Solanaceae 2) Malvaceae
1) Cruciferae 2) Leguminosae
3) Papilionatae 4) Liliaceae
3) Cucurbitaceae 4) Malvaceae
77. Staminal tube is found in:-
83. Presence of epicalyx and
1) Solanaceae 2) Cruciferae monadelphous condition of stamens
3) Malvaceae 4) Poaceae is a characteristic feature of family-
1) Liliaceae 2) Papilionacae
78. Dorsifixed, monothecous anthers are
3) Malvaceae 4) Solanaceae
a special feature of:-
1) Malvaceae/Cotton 84. Flowers are exclusively bisexual in-
2) Solanaceae/Tomato 1) Cucurbits 2) Euphorbia
3) Leguminosae/Pea 3) Malvaceae 4) Asteraceae
4) Liliaceae/Onion ASTERACEAE
79. In which family Pentamerous 85. Plants with inferior ovary belongs
flowers having monoadelphous to:-
stamen and dry dehiscent fruit are
1) Malvaceae 2) Poaceae
persent :-
3) Solanaceae 4) Compositae
1) Leguminosae 2) Malvaceae
3) Cruciferae 4) Solanaceae 86. Basal placentation occurs in:-
1) Asteraceae 2) Solanaceae
80. Aestivation of petals in the flower of
cotton is correctly shown in: 3) Malvaceae 4) Liliaceae
87. Family Compositae can be
distinguished from Solanaceae in:-
1) 2)
1) Capitulum inflorescence
2) Gamopetalous corolla
3) 4) 3) Epipetalous stamens
81. What is epicalyx? 4) Bicarpellary gynoecium
1) An additional calyx 88. Syngenesious anthers and
2) An outgrowth of calyx epipetalous stamens are found in:-
3) A whorl of bracts 1) Liliaceae
4) A whorl of bracteoles 2) Solanaceae
3) Compositae 4) Malvaceae
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 21
89. Inferior ovary, syngenesious anther 95. The plant whose seed give safflower
and cypsela fruit are found in:- oil and the petals an orange dye is -
1) Liliaceae 2) Cruciferae 1) Calendula officinalis
3) Solanaceae 4) Compositae 2) Caesalpinia sappan
3) Pithecelobium dulce
90. Which of the following stands for
4) Carthamus tinctorius
Congress grass:-
1) Cynodon (Gramineae) 96. Tagetes belongs to -
2) Parthenium (Compositae) 1) Compositae 2) Cruciferae
3) Aspidiastra (Liliaceae) 3) Malvaceae 4) Solanaceae
4) Candytuft (Cruciferae) 97. The floral formula of the disc floret
of Compositae would be -
91. Which of the following families have
the largest geographical distribution:- 1) Br, Kpappus, C(2/3), A0, G1
1) Malvaceae 2) Leguminosae 2) Br, Kpappus, C(5), A0, G
2
3) Solanaceae 4) Compositae
3) Br, Kpappus, C A G
5 5 2
92. Which of the following is the largest
family:- 4) Br, Kpappus, C(5), A0, G(2)
1) Leguminosae 2) Cucurbitaceae
98. Pyrethrum insecticide is obtained
3) Solanaceae 4) Compositae from-
1) Pyrethrum anthylmentium
93. Parachute mechanism of fruit and
seed dispersal is common in 2) Chrysanthemum cinerafolium
compositae is due to the structure 3) Parthenium hysterosporus
called:- 4) Helichrysum petiolatum
1) Bracts 2) Thorns
99. Most advanced family of
3) Corolla 4) Pappus.
angiosperms is-
94. A genus of ornamental plants which 1) Asteraceae 2) Leguminosae
is being cultivated for extracting an 3) Graminae
important edible oil from its cypsela 4) Magnoliaceae
fruits is -
1) Helianthus 100. Flowers of Asteraceae are-
2) Brassica 1) Hypogynous
3) Sesamum 2) Epigynous
4) Cocos 3) Perigynous
4) Trimerous
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
22 Families of Flowering Plants
101. Bicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular + K5 C5 A5 G(2)
ovary with basal placentation occurs 1)
in- %+ K5 C5 A5 G(2)
2)
1) Liliaceae 2) Solanaceae
or %+ or + K–pappus C(5) A(5) G(2)
3) Asteraceae 4) Fabaceae 3)
+ K2 + 2 C4A2 + 4G(2)
102. Which is false about Asteraceae- 4)
1) Cypsela fruit 108. Weed of Compositae family is-
2) Syngenesious androecium 1) Congress grass
3) Head inflorescence 2) Argemone mexicana
4) Hypogynous flowers 3) Chenopodium ambrosodies
4) Eichhornia
103. A family delimited by type of
inflorescence is-
109. Which one yields oil from seeds and
1) Fabaceae 2) Asteraceae orange dye from petals-?
3) Solanaceae 4) Liliaceae 1) Helianthus annuus
2) Calendula officinalis
104. Which of these characters do not
belong to compositae- 3) Carthamus tinctorius
1) Ligulate ray florets 4) Tagetus erecta
2) Basal ovules
110. Among bitter gourd, mustard,
3) Syngenesious stamens brinjal, pumpkin, china rose, lupine,
4) 5-lobed stigma cucumber, sunhemp, gram, guava,
bean, chilli, sunflower, petunia,
105. A weed belonging to family tomato, rose, withania, potato,
Asteraceae which has spread in all onion, aloe and tulip - how many
parts of India is- plants have hypogynous flower?
1) Nicotiana 2) Oryza 1) Six 2) Ten
3) Parthenium 4) Hordeum 3) Fifteen 4) Eighteen
106. Fruit dispersal in Asteraceae is
usually by-
1) Mechanical 2) Wind
3) Water 4) Animals
107. The floral formula of Compositae is-
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 23
EXERCISE I – KEY Assertion & Reason
I) If both Assertion & Reason are true
and the reason is the correct
1. 3 2. 2 3. 1 4. 1
explanation of the assertion.
5. 3 6. 3 7. 1 8. 1 II) If both Assertion & Reason are true
9. 2 10. 3 11. 2 12. 3 but the reason is not the correct
13. 2 14. 2 15. 3 16. 2 explanation of the assertion.
III) If A is true statement but R is false
17. 2 18. 2 19. 1 20. 4
IV) If A is false and R is true
21. 4 22. 3 23. 1 24. 4
1. Assertion: Papilionaceous corolla in
25. 2 26. 3 27. 3 28. 2
Fabaceae members help in piston
29. 1 30. 1 31. 1 32. 1 mechanism of pollination
33. 1 34. 4 35. 3 36. 4 Reason: Fabaceae members have
37. 3 38. 1 39. 1 40. 1 their odd petal towards the posterior
side
41. 3 42. 2 43. 3 44. 1
2. Assertion: Muliathi belongs to family
45. 2 46. 4 47. 2 48. 4
Fabaceae
49. 3 50. 2 51. 3 52. 3 Reason: It has zygomorphic flowers
53. 4 54. 3 55. 4 56. 3
3. Assertion: Crotalaria is a Fabaceae
57. 3 58. 3 59. 4 60. 2 member
61. 1 62. 3 63. 1 64. 1 Reason: Crotalaria shows
65. 2 66. 1 67. 2 68. 1 pedicellate, complete, bisexual
flowers
69. 3 70. 1 71. 2 72. 2
73. 3 74. 1 75. 1 76. 2 4. Assertion: Fabaceae flowers are
zygomorphic
77. 3 78. 1 79. 2 80. 3
Reason: Corolla is Papilionaceous in
81. 4 82. 4 83. 3 84. 3 Fabaceae
85. 4 86. 1 87. 1 88. 3
5. Assertion: In Arachis, Pod is
89. 4 90. 2 91. 4 92. 4 indehiscent and geocarpic.
93. 4 94. 1 95. 4 96. 1 Reason: In Arachis, flowers are
97. 3 98. 2 99. 1 100. 2 produced beneath the soil
101. 3 102. 4 103. 2 104. 4 6. Assertion: Pisum is a tendriallar
105. 3 106. 2 107. 3 108. 1 climber
109. 3 110. 3 Reason: In Pisum, basal leaflets of
each compound leaf are modified
into tendrils
Exercise – IIA
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
24 Families of Flowering Plants
7. Assertion: Solanaceae belongs to I) Asetivation of perianth parts
Gamopeatale II) Number of floral parts in each
Reason: The perianth is whorl
dichalmydeous with fused petals in III) Cohesion and adhesion of floral
Solanaceae parts
8. Assertion: Type of vascular bundles IV) Sexuality off the flower
found in the stems of memebers of 1) I and II only
Solanaceae family are bicollateral 2) I, III and IV only
and open
3) I and IV only 4) I, II, III and IV
Reason: Cambium and phloem are
present on the outerside and 3. Which of the following character of
innerside of xylem of the vascular flowers cannot be represented in
bundles floral formula?
9. Assertion: In Solanaceae members A. Sexuality of the flower
seeds are endospermic B. Symmetry of the flower
Reason: Some amount of endosperm C. Number of floral organs in whorl
is leftout in matured seeds of
D. Number of locules in the ovary
Solanaceae memebers.
E. Cohesion of sepals
Exercise II (A) Key: F. Type of faestivation
1. 2 2. 2 3. 2 4. 1 5. 3 1) A, B, C 2) D and F
6. 3 7. 1 8. 1 9. 1 10. 1 3) D alone 4) A, C, E & F
4. A flower of Brassica can show
Exercise – IIB
A) Tetradynamous stamens
1. A flower of Brassica can show B) Polyandrous stamens
A) Polyandrous stamens C) Superior ovary
B) Superior ovary D) Tetramerous condition
C) Parietal plaentation E) Parietal placentation
D) Polypetalous corolla F) Polypetalous corolla
1) A, B, C, D 1) A, B, C, D, E, F
2) Except A 2) All except A
3) Except A & B 3) All except A & B
4) Only B, D 4) All except A, B, F
2. Floral diagram indicates
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 25
5. Which of the following statements B) Pressing down of alae by insect
are correct about information that C) Transfer of pollen to insect body
could be represented in a floral
diagram or of floral formula? D) Pressing down of carina by alae
I) The position of ovary cannot be E) Cross pollination
represented in a floral diagram 1) B, D, C, E, A
II) Number of locules can be 2) B, D, A, E, C
represented in floral diagram but not 3) D, B, C, A, E
in floral formula
4) D, B, A, E, C
III) Placentation cannot be
represented in floral formula 8. Pickout the true statements that are
IV) Cohesion of stamens can be applicable to Fabaceac memebers
represented in floral formula but not I) Flowers with early maturation of
in floral diagram androecium than gynoecium
Correct answer is II) Albuminous seeds
1) I, II, III, IV 2) I, III only III) Filaments of ten stamens are
3) II, IV only 4) I, II, III only fused into two or one bundle
IV) Corolla comprises five equal
6. Study the following characters sized petals
“Bicarpellary ovary, syncarpous 1) Except IV 2) II, III and IV
ovary, bilocular ovary, superior
ovary, unequal lengthed stamens, 3) I and III only 4) I, III and IV
polypetalous corolla, six stamens,
9. Arrange the following aspects
dry fruit, ovules attached to false
related to Tephrosia in descending
septum, Tetramerous flower,
order based on their number
Cruciform Corolla , bisexual flower,
hypogynous flowers”. I) Number of alae in one flower
How many characters from the II) Number of carpels
above list observed in the taxon III) Number of stamens
“Brassica”
IV) Number of sepals
1) 10 2) 6
1) III, IV, I, II
3) 12 4) 13
2) II, I, IV, III
7. Correct sequence of events in the 3) I, II, III, IV
process of “piston mechanism” of 4) IV, III, II, I
insect pollination is
A) Emergence of stigma from the
keel
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
26 Families of Flowering Plants
10. Among the following features III) Protogynous flowers are seen in
which are related to Allium cepa. Solanum, Colchicum and Allium.
I) Non – tunicated bulb IV) Androecium is tilted at an angle
o
II) Presence of radical leaves of 45 in the members of solanaceae.
III) Presence of scape to produce 1) I & II only 2) I, II & III
inflorescence 3) I, II, III, IV 4) III & IV
IV) Presence of poly embryony
13. Arrange the following in ascending
V) Used as a vegetable
order based on the total number of
VI) Epiphyllous stames floral leaves in each flower of the
1) Only III, IV following
2) Only II, IV, V & VI A – Allium,
3) Except – VI B – Female flower of smilax,
4) Except – I C – Mustard,
D – Male flower of Ruscus,
11. Correct the combinations with
respect to the flowers of following E – Trifolium, F – Aswagandha
plants? 1) B, D, A, C, E, F
I) Mustard – Neither cohesion nor 2) B, D, A, F, C, E
adhesion of stamens in a 3) B, D, A, C, F, E
polypetalous flower
4) B, A, D, C, F, E
II) Pisum – Cohesion of sepals and
stamens in a polypetalous flower 14. Identifying the correct descending
III) Solanum – Adhesion of stamens order of the following
with petals in a gamopetalous A. No. of carpels in a flower of
flower mustard (Brassica)
IV) Allium- Adhesion of stamens B. No. of stamens in the bigger
with petals of polypetalous flowers bundle of a flower of Pisum
1) I, II, III & IV 2) III & IV C. No. of locules in the ovary of
3) II & III only 4) I, II & III Gloriosa
D. No. of Stamens in mustard
12. Find the correct statement from the
following E. No. of petals in muliathi
I) Compound leaves and woody 1) B, D,E, C, A
stems are rarely found in the 2) A, C, D, E, B
members of Solanaceae. 3) B, E, D, A, C
II) Most of Liliaceae members are 4) E, B, D, C, A
perennial herbs.
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 27
15. Select correct ratios among the D) Dye yielding plants of Fabaceae –
following Butea, Indigofera
A) Microsporophylls of Mustard and 1) A, B, C, D
Asparagus = 1 : 1 2) B, C, D only
B) Megasporophyll of 3) B, C only
Indigofera,Petunia, Tulip= 1 : 2 : 3
4) A, C only
C) Accessory floral leaves of
sunhemp, chilli = 1 : 1 18. Pick out wrong statement
D) Accessory floral leaves of Brassica 1) In Solanaceae capsule fruit is seen
and Onion = 4 : 3 in Datura, in Liliaceae berry fruit is
1) A, B, C, D 2) B, C, D only seen in Asparagus
3) A, B, D only 4) A, B only. 2) Petunia is an ornamental plant of
Solanaceace, Asparagus is a
16. Analyse the following statements ornamental plant of Liliaceae
choose correct statement: 3) Ground nut,Chilli, Atropa are the
I) Blue dye is extracting from medicinal plants belonging to
Indigofera tinctoria, yellow dye is different families
extracting from Butea monosperma 4) Dicotyledonous, endospermic
II) Day king and Night queen plants seeds are present in the Solanaceae
are belonging to family Solanaceae family members
III) Colchicum is obtained from
19. Analyze the following statement
Fabaceae plant
choose wrong statement:
IV) In Liliaceae family members
I) Gloriosa, Smilax, Pisum and
mostly the flowers are pentacyclic,
Lathyrus plants are tendrilar
bisexual, tetramerous, hypogynous
climbers belonging to different
1) I & II 2) III & IV families
3) II & IV 4) I & IV II) Aloe, Dracaena and Yucca are the
plants, belonging to Dicotyledonae
17. Choose the correct matches from the
following III) In Solanaceae and Liliaceous
members, leaves are exstipulate but
A) Medicinal plants of Fabaceae – in Fabaceae they are stipulate.
Lathyrus, Sesbania
IV) Foliar stipules are present in the
B) Medicinal plants of Solanaceae – Pisum plant.
Atropa, Withania
1) I & III 2) I & IV
C) Medicinal plant of Liliaceae –
Aloe. 3) II & III 4) Only II
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
28 Families of Flowering Plants
20. Read the following statements I II III IV
A) Potato and Brinjal belonging to 1) B C A D
two different genera of different 2) B A D C
families
3) C D B A
B) Cajanus, Sesbania and Indigofera
are belong to same family but 4) C B D A
economically dissimilar plants
23. List – I List – II
C) Flowers in Tulip and Smilax are
A) Belladona I) Atropa
similar in merosity but differ in
symmetry B) Aswagandha II) Soanum nigrum
D) Datura and Allium belong to C) Kamanchi III) Withania
different families but similar in the D) Thorn apple IV) Datura
type of ovule arrangement.
1) A – I, B – III, C – II, D – IV
What is the % of untrue statements
2) A – III, B – II, C – I, D – IV
1) 25% 2) 75%
3) A – I, B – IV, C – II, D – III
3) 50% 4) 100%
4) A – II, B – III, C – I, D – IV
21. List – I List – II
24. List – I List – II
A) Ground nut I) Lathyrus sativus
A) Ornamental plant I)Asparagus
B) Red gram II) Cajanus cajan
B) Medicinal plant II) Petunia
C) Sun hemp III) Arachis hypogea
C) Vegetable III) Aloe
D) Wild pea IV) Crotalaria juncea
D) Spice IV) Garlic
A B C D
1) A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – III
1) II IV III I
2) A – II, B – III, C – I, D – IV
2) III II IV I
3) A – III, B – II, C – I, D – IV
3) III IV II I
4) A – I, B – II, C – III, D – IV
4) II III I IV
25. List – I List – II
A) Meadow saffron I) Allium sativum
22. List – I List – II
B) Garlic II) Yucca gloriosa
I) Red gram A) Sesbania
C) Red dragon
II) Ground nut B) Edible oil
III) Colchicum autumnale
III) Indigofera C) Pulse D) Sarasaparilla
IV) Green manure D) Blue dye IV) Dracaena
V) Smilax zeylanica
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 29
A B C D 27. List - I List – II
1) III I IV V A) Bicollateral I) Fabaceae
2) III I II V vascular bundles
3) III II IV V B)Papilionaceous II) Brassicaceae
4) II I IV V Corolla
C) Trimerous Flower III) Liliaceae
D) Tetramerous flowers
26. List – I List – II
IV) solanaceae
A) Blue dye I) Smilax xeylanica
B) Sarasaparilla II) Butea monosperma
1) A – IV, B – I, C – III, D – II
C) Yellow dye III) Indigofera tinctoria 2) A – I, B – III, C – II, D – IV
D) Chemical IV) Tehrosiia 3) A – II, B – I, C – III, D – IV
mutagen purpurea 4) A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – II
V) Colchicum
autumnale
A B C D
1) II V I IV
2) III I II V
3) III II IV I
4) I II III V
28. Study the following lists:
List – I List – II List – III
A. Arachis P. Monadelphous W. Edible oil
B. Pisum Q. flame of the forest X. Fodder
C. Crotalaria R. Geocarpy Y. Yellow dye
D. Butea S. Self pollination Z. Vegetables
The correct combinations are:
1) ARW, BSZ, CPX, DQY 2) APW, BSZ, CRX, DQY
3) ARZ, BSW, CQX, DPY 4) APW, BSZ, CRX, DQY
29. Plant Fruit Family
I) Pea Pod Fabaceae
II) Nicotiana Capsule Liliaceae
III) Asparagus Berry Liliaceae
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
30 Families of Flowering Plants
IV) Solanum Berry Solanaceae
Find the correct combination from the table given above
1) II & III only 2) IV only 3) Except II 4) II only
30. Plant Character Family
I) Solanum Cymose Solanaceae
II) Allium Umbell Liliaceae
III) Dolichos Twiner Fabaceae
IV) Asparagus Cladophylls Liliaceae
The correct combinations are
1) I only 2) I & II only 3) I, II, III only 4) I, II, III, IV
31. Plant Character – 1 Character – 2
I) Solanum nigrum dithecous anthers Obliquely arranged carpels
II) Crotalaria Hypogynous flower Marginal placentation
III) Nicotiana Fumigatory Bicollateral vascular bundles
IV) Allium Gamopetalous Umbel
The correct combinations are
1) I only 2) I and II only 3) I, II, III only 4) I, II, III, IV
32. Family Scientific name of plant Common name
A) Brassicaeae Brassica nigra Mustard
B) Fabaceae Derris indica Kanuga
C) Solanaceae Solanum tuberosum Potato
D) Liliaceae Allium cepa Onion
The correct combination is
1) C & D 2) D only
3) A, B, C, D 4) A, B, C
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 31
33. Taxon Family Character of statements
I) Datura Solanaceae Diadelphous
II) Allium Liliaceae Epitepalous
III) Petunia Solanaceae epipetalous
IV) Crotalaria Fabaceae Synandry
Choose the incorrect combinations
1) I, II 2) I, III
3) I, IV 4) II, III
34. Three floral diagrams given here. Their respective families are assigned in the
answer key. Find out the families to which these diagrams belongs to
A B C
1) A – Liliaceae , B – Asteraceae, C - Solanaceae
2) A – Asteraceae , B - Solanaceae, C - Brassicaceae
3) A – Poaceae , B - Solanaceae , C – Asteraceae
4) A – Brassicaceae , B – Fabaceae , C - Solanaceae
35. Three floral diagrams given here. Their respective families are assigned in the
answer key. Find out the families to which these diagrams belongs to
A B C
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
32 Families of Flowering Plants
1) A – Liliaceae , B –Cucurbitaceae, C - Asteraceae
2) A – Asteraceae , B - Solanaceae, C - Brassicaceae
3) A – Poaceae , B - Solanaceae , C – Asteraceae
4) A – Brassicaceae , B – Fabaceae , C - Solanaceae
Exercise II(B) – Key: 4. The Replum is present in the ovary
of flower in (2008)
1) sunflower 2) pea
2. 4 3. 2 4. 1 5. 4
1. 1 3) lemon 4) mustard
7. 2 8. 3 9. 1 10. 4
6. 4 5. Flowers are unisexual in (2009)
12. 1 13. 3 14. 1 15. 1
11. 4 1) Onion 2) Pea
17. 3 18. 3 19. 4 20. 3 3) Cucumber 4) China rose
16. 1
22. 4 23. 1 24. 2 25. 1 6. The technical term used for the
21. 2
30. 4 androecium in a flower of China rose
26. 2 27. 1 28. 1 29. 3
(Hibiscus rosasinensis) is (2010)
32. 3 33. 3 34. 4 35. 1 1) Monoadelphous 2) Diadelphous
31. 3
3) Polyandrous 4) Polyadelphous
EXERCISE - III
7. Keel is characteristic of the flowers of
PREVIOUS AIPMT (NEET)
(2010)
1. Bicarpellary gynoecium of oblique 1) Gulmohar 2) Cassia
ovary occur in (2001)
3) Calotropis 4) Bean
1) Mustard 2) Banana
3) Pisum 4) Brinjal 8. Vexillary aestivation is characteristic
of the family (2012)
2. Pentamerous, actinomorphic flowers,
bicarpellary ovary with oblique septa 1) Solanaceae 2) Brassicaceae
and fruit a capsule or berry are 3) Fabaceae 4) Asteraceae
characteristic features of (2006) 9. In China rose the flowers are (2013)
1) Asteraceae 2) Brassicaceae 1) Actinomorphic, hypogynous with
3) Solanaceae 4) Liliaceae twisted aestivation
2) Actinomorphic, epigynous with
3. What type of placentation is seen in valvate aestivation
sweet pea? (2006) 3) Zygomorphic, hypogynous with
1) Basal 2) Axile imbricate aestivation
3) Free central 4) Marginal 4) Zygomorphic, epigynous with
twisted aestivation
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
Families of Flowering Plants 33
10. Keel is the characteristics feature of
flower of (2015)
1) Tomato 2) Tulip
3) Indigofera 4) Aloe
11. The strandard petal of a
papilinaceous corolla is also called
(2016 PHASE I)
1) Carina 2) Pappus
3) Vexillum 4) Corona
12. Tricarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium
is found in flowers of (2016 PHASE I)
1) Liliaceae 2) Solanaceae
3) Fabaceae 4) poaceae
Exercise – III Key:
1. 4 2. 3 3. 4 4. 4 5. 3
6. 1 7. 4 8. 3 9. 1 10. 3
11. 3 12. 1
EXERCISE - IV
NCERT EXEMPLAR
1. Many pulses of daily use belong to
on of the families below (tick the
correct answer)
1) Solanaceae 2) Fabaceae
3) Liliaceae 4) Poaceae
2. Which of the following plants is used
to extract the blue dye?
1) Trifolium 2) Indigofera
3) Lupin 4) Cassia
Exercise – IV Key:
1. 2 2. 2
VELAMMAL UPDATED SYLLABUS
IIT & MEDICAL ACADEMY
You might also like
- Finalize Beta 2018Document14 pagesFinalize Beta 2018elezabeth100% (2)
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapAstha Agrawal89% (9)
- CH 38Document1 pageCH 38Diana Paraiso100% (1)
- Aoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementDocument49 pagesAoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementJordan67% (3)
- Lab Work 6Document3 pagesLab Work 6Bella LopezNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT 23 Rosales and BrassicalesDocument11 pagesLAB REPORT 23 Rosales and BrassicalesKoreen Bayani100% (1)
- Life Span Development Notes-Chapter 3Document9 pagesLife Span Development Notes-Chapter 3Kayelita Wu100% (2)
- Bot - New FamiliesDocument3 pagesBot - New Familiesatiyabegum282No ratings yet
- Table FinalDocument3 pagesTable Finallegendsac2000No ratings yet
- Plant Families NEETDocument2 pagesPlant Families NEETPratyush Raj Saran50% (2)
- Families - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23Document20 pagesFamilies - Comparisions - Sundar Notes Final - 25.10.23priyamprakash0107No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of Flowering PlantsNeil SNo ratings yet
- Poaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Document15 pagesPoaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Cipta Adi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Site planningAutoRecoveredDocument15 pagesSite planningAutoRecoveredRyuuichi KishimaNo ratings yet
- The Exotic Rainforest: Zamioculcas ZamiifoliaDocument15 pagesThe Exotic Rainforest: Zamioculcas ZamiifoliabawadeeNo ratings yet
- List of Endangered Philippine PlantsDocument7 pagesList of Endangered Philippine PlantsResearch AssistanceNo ratings yet
- All FamilyDocument3 pagesAll FamilyRaunak KumarNo ratings yet
- Surf Coast Shire Alternative Plants GuideDocument2 pagesSurf Coast Shire Alternative Plants GuideDavid WhiteNo ratings yet
- Dispersal NotebookDocument4 pagesDispersal NotebookSasha SmithNo ratings yet
- Morphology Chart Eng 1Document1 pageMorphology Chart Eng 1angadgneware0% (1)
- Major Insect-Pest of Fruits of Nepal:: Apple/Peach/ PearDocument6 pagesMajor Insect-Pest of Fruits of Nepal:: Apple/Peach/ PearMamata SubediNo ratings yet
- Pasture Weed Watch - WireweedDocument1 pagePasture Weed Watch - WireweedEKNo ratings yet
- Act 4 PearlasDocument5 pagesAct 4 PearlasAlyssa Pauline PalacioNo ratings yet
- Copy Biodiversity and Conservation WMDocument9 pagesCopy Biodiversity and Conservation WMleagueofkxx00No ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB2 - Weed GardenDocument10 pagesGroup 7 - LAB2 - Weed Gardendario albaNo ratings yet
- Big Key F PDFDocument30 pagesBig Key F PDFAMALIA RIZQI ROSANINGDYAHNo ratings yet
- Plant IdentificationDocument1 pagePlant IdentificationArtjia RepalaNo ratings yet
- LEGUME PhysiologyDocument13 pagesLEGUME PhysiologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants _ Short NotesDocument2 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants _ Short Notespriya9839420311No ratings yet
- Cordage Fiber Overview For ProceedingsDocument10 pagesCordage Fiber Overview For ProceedingsWill JamesNo ratings yet
- Aristolochia FimbriataDocument26 pagesAristolochia FimbriataDiego MyxomycotaNo ratings yet
- Ornamental PlantsDocument10 pagesOrnamental PlantsBrigette SanchezNo ratings yet
- Crops Production ManualDocument12 pagesCrops Production ManualMinayehu WondfrawNo ratings yet
- Exercise in Bio Lab Report 3Document4 pagesExercise in Bio Lab Report 3Ramnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- CabbageDocument5 pagesCabbagemooketsi316No ratings yet
- Plants Morphology XIDocument26 pagesPlants Morphology XINita GosaviNo ratings yet
- The Pest Caterpillars of Cole Crops in VirginiaDocument7 pagesThe Pest Caterpillars of Cole Crops in VirginiafodoNo ratings yet
- 6 DaturaDocument5 pages6 DaturajayNo ratings yet
- FAMILY UpdateDocument17 pagesFAMILY Updateprashant6388kumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12Document7 pagesExercise 12Anna HarietNo ratings yet
- Battandier.m. A., 1896, Notes Sur Quelques Plantes D'algérieDocument9 pagesBattandier.m. A., 1896, Notes Sur Quelques Plantes D'algérieBrahim BabaliNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW Nparks Gov Sgflorafaunawebflora313156Document1 pageHTTPSWWW Nparks Gov Sgflorafaunawebflora313156kohby2014No ratings yet
- Palm Mealybug - 5 - 2014PressQDocument2 pagesPalm Mealybug - 5 - 2014PressQShane DorianNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Half 2 Shorts-1Document11 pagesCH 9 Half 2 Shorts-1muhammad iftikharNo ratings yet
- Rattlesnake Master Species Description PageDocument1 pageRattlesnake Master Species Description PageJaime GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument61 pagesAngiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: Powerpoint Lectures ForDelfin Urbano Jr.No ratings yet
- Gentian Flower and Other GeneraDocument9 pagesGentian Flower and Other GeneraImperfect ArachnoidNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- Maple Petiole BorerDocument2 pagesMaple Petiole BorerSharad BhutoriaNo ratings yet
- Insect AldaDocument7 pagesInsect AldaCatherine AldaNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Document2 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Plants Morphology (Upto - Leaf) - 1Document12 pagesPlants Morphology (Upto - Leaf) - 1Nita GosaviNo ratings yet
- Pteridophyta TableDocument1 pagePteridophyta TableA-0315-12 PRASHARADHA S KUMARNo ratings yet
- Family SystematicsDocument5 pagesFamily SystematicsJoshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Sheryn Common Name Final1Document1 pageSheryn Common Name Final1MJ Maravilla TaboboNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Document8 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Term 1 Week 4 - 2021Mpho MashediNo ratings yet
- Systematic, Anatomy & Development PDFDocument1 pageSystematic, Anatomy & Development PDFAhmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.1 Field Identification of Weed Species: Amaranthaceae CyperaceaeDocument4 pagesActivity 3.1 Field Identification of Weed Species: Amaranthaceae CyperaceaeJAY MARK CUBAONo ratings yet
- Gaint Hogweed Fact FileDocument2 pagesGaint Hogweed Fact Filewing tamNo ratings yet
- Notes-Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument37 pagesNotes-Morphology of Flowering PlantsKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Tuber and Root Crops: Assoc. Prof. Pham Van Hung Department of Food TechnologyDocument14 pagesTuber and Root Crops: Assoc. Prof. Pham Van Hung Department of Food TechnologyDuy Nguyen VuNo ratings yet
- AM Morphology FamiliesDocument11 pagesAM Morphology Familiestechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Flora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeFrom EverandFlora Zambesiaca Volume 13 Part 2:: Eriospermaceae, Dracaenaceae, Arecaceae (Palmae), Pontederiaceae, Bromeliaceae, MayacaceaeNo ratings yet
- Nitrosomonas & NitrobacterDocument2 pagesNitrosomonas & NitrobacterBrian ThomasNo ratings yet
- DR - Fouzia Batool PT - PP-DPT Lecturer, RCRSDocument48 pagesDR - Fouzia Batool PT - PP-DPT Lecturer, RCRSMuhammad Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Phonics Chant Fun Activities Games Pronunciation Exercises Phoni - 15461Document32 pagesPhonics Chant Fun Activities Games Pronunciation Exercises Phoni - 15461DAO NANCYNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Receptors Lec JPDocument55 pagesPhysiology of Receptors Lec JPabhishchheladiya0860No ratings yet
- Wonderful EarthDocument1 pageWonderful EarthĐỗ Quỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- Current Status of Cereals in IndiaDocument20 pagesCurrent Status of Cereals in IndiaManonmani KNo ratings yet
- 05a Neurobiologija UčenjaDocument20 pages05a Neurobiologija Učenjabotoks uwuNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE Annelida MergedDocument32 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE Annelida MergedFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- Biology Experiment Glucose and Carbon Dioxide Fermentation 8642-37602-1-PBDocument4 pagesBiology Experiment Glucose and Carbon Dioxide Fermentation 8642-37602-1-PBmarcelocarcamoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Pathways To Mammalian Heart Development Recent Progress From Manipulation of The Mouse GenomeDocument12 pagesGenetic Pathways To Mammalian Heart Development Recent Progress From Manipulation of The Mouse GenomeCELALEDDİN BAHADIR ŞANLIOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Y2 Met Lecture Revision NotesDocument69 pagesY2 Met Lecture Revision NotesHelen VlotomasNo ratings yet
- Morphological and Molecular Diagnosis of Cuscuta SP Parasitizing Solanaceae Plants in The Middle of Iraqi ProvincesDocument19 pagesMorphological and Molecular Diagnosis of Cuscuta SP Parasitizing Solanaceae Plants in The Middle of Iraqi ProvincesreviewjreNo ratings yet
- Ie5 Reading FinalDocument26 pagesIe5 Reading FinalOanh Nguyễn0% (1)
- Participatory Socioeconomic Analysis: Drawing On Fishermen's Knowledge For Marine Protected Area Planning in CaliforniaDocument15 pagesParticipatory Socioeconomic Analysis: Drawing On Fishermen's Knowledge For Marine Protected Area Planning in CaliforniaJose DGNo ratings yet
- DBT BET Question Paper 2008 With Answer KeyDocument28 pagesDBT BET Question Paper 2008 With Answer KeyAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- INFJ Profile PDFDocument7 pagesINFJ Profile PDFMara100% (2)
- Dr. Suryadi (Itroduction To Medical Phylosophy)Document18 pagesDr. Suryadi (Itroduction To Medical Phylosophy)Danni MahendraNo ratings yet
- Volume 42, Number 21 - November, 2007Document365 pagesVolume 42, Number 21 - November, 2007belleblackNo ratings yet
- The Secret To Success A Positive Mindset Aaron PitmanDocument89 pagesThe Secret To Success A Positive Mindset Aaron PitmanRichel888100% (1)
- Textzoology02parkrich PDFDocument708 pagesTextzoology02parkrich PDFm.osman riazNo ratings yet
- Digoxin: 11820796 190 Cobas e 411 Cobas e 601 Cobas e 602 English Intended UseDocument5 pagesDigoxin: 11820796 190 Cobas e 411 Cobas e 601 Cobas e 602 English Intended UsehairiNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Cell Structure and FunctionDocument28 pagesBacteria Cell Structure and Functionharishkumar kakraniNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale Glossary:: Uc-Shs 1Document43 pagesGeologic Time Scale Glossary:: Uc-Shs 1John Denver AdaoagNo ratings yet
- JFRabajante MS Applied Math ThesisDocument179 pagesJFRabajante MS Applied Math ThesisJomar Rabajante100% (2)
- Sanvi Diagnostics Lpl-Bhubaneshwar PURABI, PLOT NO 2084/4837, GAUTAM Nagar, Bhubnaeswar - 751014Document3 pagesSanvi Diagnostics Lpl-Bhubaneshwar PURABI, PLOT NO 2084/4837, GAUTAM Nagar, Bhubnaeswar - 751014BISHAL PRADHANNo ratings yet