Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Uploaded by
Harsh BhardwajCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- JSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument60 pagesJSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFmichael nwoye100% (1)
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesElementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions ManualChristopherArnoldoqek100% (49)
- 12Document6 pages12api-332361871No ratings yet
- Hypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFDocument9 pagesHypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFRoniAmNo ratings yet
- Reference Coordinate GeometryDocument1 pageReference Coordinate GeometryAnonymous gUySMcpSqNo ratings yet
- 50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDocument26 pages50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDoddy FeryantoNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument5 pagesPolygonKhushi RaniNo ratings yet
- 7 PolygonDocument6 pages7 Polygonneriloc534No ratings yet
- Polygon Angle Sum Packet PDFDocument22 pagesPolygon Angle Sum Packet PDFPrensess BerfinNo ratings yet
- Cylinder: Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesCylinder: Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Property of TrianglesDocument18 pagesProperty of TrianglesviralroshNo ratings yet
- Polygons (UPDATED)Document14 pagesPolygons (UPDATED)Jovialis LlanitaNo ratings yet
- Types of TriangleDocument14 pagesTypes of TriangleKhushi RaniNo ratings yet
- Maths PaperDocument8 pagesMaths PaperMahesh SinghamNo ratings yet
- Day 38 Mensuration 3d 02 (Practice Sheet)Document3 pagesDay 38 Mensuration 3d 02 (Practice Sheet)Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDocument16 pagesSample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDr-Bini Das AshishNo ratings yet
- g7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument40 pagesg7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesTenten Peter100% (1)
- Math Grade7 Quarter3 Module4 Week4Document4 pagesMath Grade7 Quarter3 Module4 Week4ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Line Angle Polygons 39Document8 pagesLine Angle Polygons 39John Adari100% (1)
- Line Angle Polygons 39Document8 pagesLine Angle Polygons 39John AdariNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 004 (19 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 004 (19 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 001 (14 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 001 (14 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Level - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 9 Time: 25 MinDocument7 pagesLevel - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 9 Time: 25 MinGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- 3713203D Mensuration Sheet-2 - CrwillDocument9 pages3713203D Mensuration Sheet-2 - Crwillyadavvv.878No ratings yet
- Math Grade7 Quarter3 Module6 Week6Document3 pagesMath Grade7 Quarter3 Module6 Week6ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Adv Maths - GeometryDocument43 pagesAdv Maths - GeometryYogendra Dwivedi100% (2)
- Neonclass PDFDocument166 pagesNeonclass PDFJohn Mukherjee100% (1)
- F HG I KJ: Maths Mania # 069Document3 pagesF HG I KJ: Maths Mania # 069TUSHAR JALANNo ratings yet
- QA - PolygonsDocument3 pagesQA - PolygonschaostheoristNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 2Document10 pagesGeometry - 2exampreparation1stNo ratings yet
- DAY 40 Maths Sample Paper For CGL CHSL 2021 (Practise Sheet)Document3 pagesDAY 40 Maths Sample Paper For CGL CHSL 2021 (Practise Sheet)Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Geom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketDocument22 pagesGeom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketAnela100% (1)
- Gate Triangle TipsDocument10 pagesGate Triangle TipsHOW TO WORLDNo ratings yet
- l-21 Surface Areas and Volumes ofDocument3 pagesl-21 Surface Areas and Volumes ofsoorya_taNo ratings yet
- 2D MensurationDocument12 pages2D MensurationPushpam JhaNo ratings yet
- Physics B 2019Document15 pagesPhysics B 2019Jeny SharmaNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 002 (15 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 002 (15 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- HBSE 12th Physics A 2018 PaperDocument12 pagesHBSE 12th Physics A 2018 PaperRavjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 3D 20210617114714Document8 pagesMensuration 3D 20210617114714Suneh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7: Applications of PolygonDocument9 pagesGrade 7: Applications of PolygonMa Teneza BarberoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 3D-3Document17 pagesMensuration 3D-3Abaz AbazNo ratings yet
- Quick Review Fundamentals of TrigonometryDocument2 pagesQuick Review Fundamentals of TrigonometryZaid BabarNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 005 (20 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 005 (20 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- 7 January (Evening Shift) - JEE Main 2020 (Memory Based)Document38 pages7 January (Evening Shift) - JEE Main 2020 (Memory Based)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- 13 Dec 2nd Shift CPO 2019Document8 pages13 Dec 2nd Shift CPO 2019pankaj111No ratings yet
- Class Sheet 1636614916. MathDocument37 pagesClass Sheet 1636614916. MathShivam PateriyaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document19 pagesCH 6Itech SwsNo ratings yet
- Izk:I (K.M Olrqfu"B Iz'U : Le % 1 ?kavk Feuv VFRJFDR Iw - KK DDocument8 pagesIzk:I (K.M Olrqfu"B Iz'U : Le % 1 ?kavk Feuv VFRJFDR Iw - KK DAmanNo ratings yet
- 2-D Mensuration Area & Petameter Practice Q Set PDF 263Document22 pages2-D Mensuration Area & Petameter Practice Q Set PDF 263Abhraham Benjamin de VilliersNo ratings yet
- SSC CPO 2022 Maths Chapterwise All QuestionsDocument166 pagesSSC CPO 2022 Maths Chapterwise All QuestionsAarzoo RatheeNo ratings yet
- DPPDocument14 pagesDPPisravelkirubaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 02 (11 Mock Test (2-11) FinalDocument4 pagesMock Test 02 (11 Mock Test (2-11) Finalvayunandanmishra982No ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument30 pagesSolid GeometryRohclem Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument9 pagesGeometryFahim UddinNo ratings yet
- Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesQuestions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Questions: 25 Exercise - 1 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesQuestions: 25 Exercise - 1 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Number System Solution (2011-2021)Document83 pagesNumber System Solution (2011-2021)Sampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Junkai Xie and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Calculations of Vibrational Energy Levels For XY4 Molecules 2: Bending States of MethaneDocument10 pagesJunkai Xie and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Calculations of Vibrational Energy Levels For XY4 Molecules 2: Bending States of MethaneWippetsxzNo ratings yet
- Dha 2Document3 pagesDha 2Gaurav BindalNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Sheet - 5 by Bot of MagnetoDocument3 pagesMensuration Sheet - 5 by Bot of Magneto420walimailidNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 006 (21 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 006 (21 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Investigating (Polygons)Document2 pagesInvestigating (Polygons)aisheykapattersonsba24No ratings yet
- DAY 13 Geometry (16 Days 16 Marathon)Document6 pagesDAY 13 Geometry (16 Days 16 Marathon)digaNo ratings yet
- SSC Mains Maths 19Document26 pagesSSC Mains Maths 19piyush13juNo ratings yet
- Vector and 3-d by Mohit Tyagi SitDocument24 pagesVector and 3-d by Mohit Tyagi SitRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Midline TheoremDocument19 pagesMidline TheoremArlene Polis Delos Reyes100% (4)
- Success Key Test SeriesDocument2 pagesSuccess Key Test SeriesShubham PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Maths Mock 14, Paper 2 (3014)Document14 pagesMaths Mock 14, Paper 2 (3014)。No ratings yet
- Euler's Formula and Poncelet's Porism Lev Emelyanov and Tatiana EmelyanovaDocument4 pagesEuler's Formula and Poncelet's Porism Lev Emelyanov and Tatiana EmelyanovaAltananyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical and Youth Magazine ProblemsDocument52 pagesMathematical and Youth Magazine ProblemsNadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Hyperbolic FunctionDocument10 pagesChapter 1-Hyperbolic Functionhiromiebizuka11No ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFAnonymous m3yrUPNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Andrew Sioson - Lesson HandoutDocument13 pagesKami Export - Andrew Sioson - Lesson HandoutnobdyNo ratings yet
- Kalayaan Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesKalayaan Elementary SchoolEmmanuel MejiaNo ratings yet
- 3D Shapes - KS3 MathsDocument13 pages3D Shapes - KS3 MathsClaudia PinnaNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Document8 pagesDLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Ma Gloria Deocades FlanciaNo ratings yet
- I/B IiDocument22 pagesI/B Iiندى عمريNo ratings yet
- Eometry Ensuration Rigonometry: Review TestDocument37 pagesEometry Ensuration Rigonometry: Review TestRaju RayhanNo ratings yet
- Cds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16Document57 pagesCds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Lines, Angles & TrianglesDocument25 pagesLines, Angles & TrianglesBalachandra MallyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Review Exercise QuestionsDocument10 pagesGeometry: Review Exercise QuestionsMustafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mit18 900s23 Lec1Document5 pagesMit18 900s23 Lec1Htike HtikeNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 RD MathsDocument61 pagesCh-5 RD MathsThe VRAJ GAMESNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3Document3 pagesGeometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3api-252752147No ratings yet
- Euclidean GeometryDocument91 pagesEuclidean GeometryrefilwematotoNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Ch-11 SA N Vol.Document5 pagesClass 9th Ch-11 SA N Vol.ayusharora864No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Triangle PHDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Triangle PHLancelot Gabriel Althuz LatozaNo ratings yet
- G-9 Chapter 10 CirclesDocument5 pagesG-9 Chapter 10 CirclesChetanNo ratings yet
- Trig NoteDocument5 pagesTrig NoteSubin ParkNo ratings yet
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Uploaded by
Harsh BhardwajOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Polygon (Part-01 To 03) New
Uploaded by
Harsh BhardwajCopyright:
Available Formats
By Pushpendra Sir
Part
cgqHkqt 01
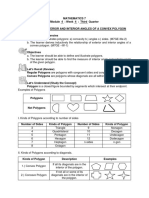
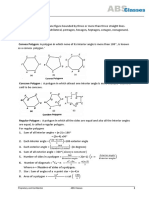
Types of Polygon
Convex Polygon Concave polygon
(each internal angle (each internal angle
VE
less than 180º) more than 180º)
1. Sum of internal and external angle of Polygon is 180º.
2. Sum of all external angle of a polygon is 360º
360º
each external angle =
n
3. Sum of all internal angle of a polygon = (n – 2) 180º
n – 2180º
each internal angle
n
LI
n (n – 3)
4. Total number of diagonal in a polygon
2
a
5. * r = cot
n
2
a
* R= cosec
n
2
r
* = cos
KD
R n
na 2
* Area of polygon = cot
4 n
3 2
6. 3 sided polgon Area = a
4
4 sided polygon Area = a2
5 sided polygon Area = 1.725 a2
3 2
6 sided polygon Area = a 6
4
7 sided polygon Area = 3.64 a2
8 sided polygon Area = 2a 2
2 1
i i = internal Angle
7. n = 2 +1
e e = external Angle
Maths By Pushpendra Sir 1
Formula Based 6. Sum of all interior angle of a polygon is
2160º. Find total number of diagonal of
1. Each interior angle of a regular polygon polygon?
is 120º. The number of sides is?
fdlh cgqHkqt ds lHkh vardks.kksa dk2160º
;ksxiQy
le cgqHkqt ds izR;sd vUr%dks.k dk eku gSA
120º gSA rks cgqHkqt ds fod.kks± dh la[;k crkvks\
rks bldh Hkqtkvksa dh la[;k crkvksA
(A) 70 (B) 60
(A) 10 (B) 8
(C) 77 (D) 87
(C) 6 (D) 9
7. The interior angle of a regular polygon
2. If each interior angle of a regular is 36º more than 5 times of its one
polygon is 4 times its exterior angle. exterior angle. Find the number of
Then find number of sides of a polygon. diagonals in this polygon?
;fn ,d lecgqHkqt ds izR;sd var%dks.k mlds fdlh lecgqHkqt dk vkarfjd dks.k blds cfg"dks.k
dsdh
ckÞ;dks.k dk4 xquk gSA rks cgqHkqt dh Hkqtkvksa 5 xqus ls
36º vf/d gS rc cgqHkqt ds fod.kks±
VE
la[;k crkvks\ dh la[;k crkvks\
(A) 6 (B) 8 (A) 77 (B) 119
(C) 10 (D) 12 (C) 104 (D) 90
3. If one of the interior angle of a regular 8. If the interior angles of a polygon are
polygon is equal to 3/4 times of the in A.P with common difference 5º and
interior angle of a regular hexagon, the smallest angle 120º, then the
Then find out number of sides of a number of sides of the polygon is?
polygon is? cgqHkqt ds vkUrfjd dks.k lekUrj Js.kh esa gS lcls
;fn lecgqHkqt ds ,d vardks.k dk eku le"kV~Hkqt NksVh vkUrfjd dks.k
120º gS vkSj lkok±rj
5º gS rks
Hkqtkvksa dh la[;k crkvks\
LI
ds vardks.k dk3/4 xquk gSA rks cgqHkqt dh Hkqtkvksa
dh la[;k crkvks\ (A) 9 or 16 (B) 9
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 13 (D) 3 or 16
(C) 6 (D) 8 9. In a polygon five interior angles is equal
to 162º and all remaining interior angles
4. A polygon has 27 diagonals. Find
is equal to 150º. Find the number of
number of sides in the polygon? sides of polygon?
,d cgqHkqt ds fod.kks± dh la[;k
27 gSA rks cgqHkqt fdlh cgqHkqt ds ikap vardks.k izR;sd
162º gS
dh Hkqtkvksa dh la[;k crkvksA tcfd 'ks"k vardks.k izR;sd
150º gSA rks cgqHkqt dh
(A) 7 (B) 6 Hkqtkvksa dh la[;k crkvks\
KD
(C) 9 (D) 12 (A) 12 (B) 14
5. Two regular polygon are such that the (C) 16 (D) 18
ratio between their number of sides is
10. There are two regular polygons with
1 : 2 and the ratio of measures of their
number of sides equal to (n – 1) and (n + 2).
interior angles is 3 : 4. Find the number Their exterior angle differ by 6º. Then
of sides of each polygon? value of n is?
nks lecgqHkqt dh Hkqtkvksa dk 1vuqikr
: 2 gS nks lecgqHkqt ftudh Hkqtk,¡ Øe'k%
(n –1) rFkk
tcfd muds vUr%dks.kksa dk vuqikr
3 : 4 gSA izR;sd (n + 2) gSA muds ckÞ;dks.k dk varj
6º gS rks
n
cgqHkqt dh Hkqtkvksa dh la[;k crkvksA dk eku crkvks\
(A) 4, 8 (B) 5, 10 (A) 14 (B) 12
(C) 6, 12 (D) 3, 6 (C) 13 (D) 11
Maths By Pushpendra Sir 2
By Pushpendra Sir
Part
cgqHkqt 02
HEXAGON (le"kV~Hkqt) 14. In the given fig. Find the ratio of shaded
Area to Unshaded Area?
11. ABC DEF is a regular hexagon with side
12 cm. P, Q, R are the mid points of AF, ED, fn;s x;s fp=k esa Nk;afdr rFkk vNk;kafdr Hkkxksa ds
BC respectively. Find out area of DPQR? {ks=kiQyksa dk vuqikr crkb;s\
ABC DEF ,d le"kV~Hkqt gS ftldh izR;sd Hkqtk
B C
dh yEckbZ 12 cm gSAP, Q, R Øe'k%AF, ED,
VE
BC ds eè; fcUnq gSA rks dk {ks=kiQy fudkyks\
DPQR
(A) 80 3 (B) 81 3 A D
(C) 70 3 (D) None
12. In the given fig. PQRSTU is Regular
hexagon. While PRT is equilateral F E
triangle. Find out Area (PQRSTU) : Area
(PRT) = ? 15. ABCDEF is a regular hexagon AOF = 90º.
FO is parallel to ED. What is the ratio
fn;s x;s fp=k esa
PQRSTU ,d le"kV~Hkqt gS tcfd of area of DAOF to the ABCDEF.
PRT ,d leckgq f=kHkqt gS rks nksuksa vkÑfr;ksa ds
ABCDEF ,d le"kV~Hkqt gSA AOF = 90º.
{ks=kiQyksa dk vuqikr crkvks\
LI
FO, ED ds lekUrj gSA rks
DAOF rFkkABCDEF
P Q
ds {ks=kiQyksa dk vuqikrs\crkvk
A B
U R
F O C
T S
(A) 2:1 (B) 1 : 2
(C) 3:1 (D) 1 : 3 E D
KD
13. In a given fig. If the perimeter of DABC
is P, then find the perimeter of Regular (A) 2:9 (B) 1 : 12
hexagon?
(C) 12 : 1 (D) None
fn;s x;s fp=k esa
DABC dk ifjeki P gSA rks le"kV~Hkqt
16. In the given fig find out area of shaded
dk ifjeki crkvks\ portion.
C
fn;s x;s fp=k esa Nk;kafdr Hkkx dk {ks=kiQy fudkyksA
A B
cm
12
P 2 12 cm
(A) (B) P
3 3
(A) 30 3 (B) 36 3
4 3
(C) P (D) P
3 2 (C) 35 3 (D) 46 3
Maths By Pushpendra Sir 3
17. ABCDEF is Regular hexagon. Find 18. ABCDEF is a regular hexagon with side
shaded potion, if area of hexagon is 12 cm. Find area of shaded portion in
45 cm2. given portion.
ABCDEF ,d le"kV~Hkqt gS] rks Nk;kafdr Hkkx dk ABCDEF ,d le"kV~Hkqt gS ftldh Hkqtk dh yEckbZ
{ks=kiQy fudkfy;s ;fn "kVHkqt dk {ks=kiQy 12 cm gSA rks fn;s x;s fp=k esa Nk;kafdr Hkkx dk
45 cm gSA
2
{ks=kiQy fudkyksA
E E D
D
F F C
C
VE
B A B
A
(A) 5 (B) 12 (A) 36 3 (B) 30 3
(C) 20 (D) 36 (C) 35 3 (D) None
LI
KD
Maths By Pushpendra Sir 4
By Pushpendra Sir
Part
cgqHkqt 03
19. ABCDE is a regular pentagon & bisector ,d vk;r dh yEckbZ rFkk pkSM+kbZ8Øe'k% lseh-
of BAE is meets CD at M. If bisector rFkk6 lseh- gSA vk;r dks mlds pkj 'kh"kks± ij bl
of BCD meets AM at P. Find CPM. izdkj dkVk tkrk gS fd feyus okyh vkÑfr ,d
ABCDE ,d leiap Hkqt gSA
BAE dk dks.k le v"VHkqt gSA v"VHkqt dh Hkqtk (ls-eh- esa) D;k gS\
lef¼Hkktd CD ij fcUnqM ij feyrk gSA tcfd
BCD dk dks.k lef¼Hkktd AM ij fcUnqP (A) 3
11 – 7 (B) 5
13 – 8
VE
ij feyrk gS rks CPM dk eku crkvksA
(A) 72º (B) 36º (C) 4 7 – 11 (D) 6
11 – 9
(C) 40º (D) 60º
20. ABCDE is a regular pentagon. Calculate 22. PQRS is a square whose side is 16 cm.
magnitude of BED. What is the value of the side (in cm) of
the largest regular octagon that can be
ABCDE ,d leiapHkqt gS rks BED dk eku cut from the given square?
crkvksA
(A) 36º (B) 72º
PQRS, 16 ls-eh- okyk ,d Hkqtk ,d oxZ gSA fn;s
x;s oxZ ls dkVs tk ldus okys lcls cM+s le
(C) 108º (D) None
v"V~Hkqt dh Hkqtk dk eku (ls-eh- esa) D;k gS\
21. Length and breadth of a rectangle are 8 cm.
LI
and 6 cm. respectively. The rectangle
is cut on its four vertices such that the (A) 8–4 2 (B) 16 + 8 2
resulting fugure is a regular octagon.
What is the side (in cm) of the octagon? (C) 16 2 – 16 (D) 16 – 8 2
KD
Maths By Pushpendra Sir 5
You might also like
- JSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument60 pagesJSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFmichael nwoye100% (1)
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesElementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions ManualChristopherArnoldoqek100% (49)
- 12Document6 pages12api-332361871No ratings yet
- Hypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFDocument9 pagesHypotenuse Leg Theorem Worksheet and Activity PDFRoniAmNo ratings yet
- Reference Coordinate GeometryDocument1 pageReference Coordinate GeometryAnonymous gUySMcpSqNo ratings yet
- 50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDocument26 pages50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDoddy FeryantoNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument5 pagesPolygonKhushi RaniNo ratings yet
- 7 PolygonDocument6 pages7 Polygonneriloc534No ratings yet
- Polygon Angle Sum Packet PDFDocument22 pagesPolygon Angle Sum Packet PDFPrensess BerfinNo ratings yet
- Cylinder: Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesCylinder: Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Property of TrianglesDocument18 pagesProperty of TrianglesviralroshNo ratings yet
- Polygons (UPDATED)Document14 pagesPolygons (UPDATED)Jovialis LlanitaNo ratings yet
- Types of TriangleDocument14 pagesTypes of TriangleKhushi RaniNo ratings yet
- Maths PaperDocument8 pagesMaths PaperMahesh SinghamNo ratings yet
- Day 38 Mensuration 3d 02 (Practice Sheet)Document3 pagesDay 38 Mensuration 3d 02 (Practice Sheet)Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDocument16 pagesSample Test Paper 2015 Acme PDFDr-Bini Das AshishNo ratings yet
- g7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument40 pagesg7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesTenten Peter100% (1)
- Math Grade7 Quarter3 Module4 Week4Document4 pagesMath Grade7 Quarter3 Module4 Week4ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Line Angle Polygons 39Document8 pagesLine Angle Polygons 39John Adari100% (1)
- Line Angle Polygons 39Document8 pagesLine Angle Polygons 39John AdariNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 004 (19 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 004 (19 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 001 (14 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 001 (14 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Level - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 9 Time: 25 MinDocument7 pagesLevel - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 9 Time: 25 MinGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- 3713203D Mensuration Sheet-2 - CrwillDocument9 pages3713203D Mensuration Sheet-2 - Crwillyadavvv.878No ratings yet
- Math Grade7 Quarter3 Module6 Week6Document3 pagesMath Grade7 Quarter3 Module6 Week6ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Adv Maths - GeometryDocument43 pagesAdv Maths - GeometryYogendra Dwivedi100% (2)
- Neonclass PDFDocument166 pagesNeonclass PDFJohn Mukherjee100% (1)
- F HG I KJ: Maths Mania # 069Document3 pagesF HG I KJ: Maths Mania # 069TUSHAR JALANNo ratings yet
- QA - PolygonsDocument3 pagesQA - PolygonschaostheoristNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 2Document10 pagesGeometry - 2exampreparation1stNo ratings yet
- DAY 40 Maths Sample Paper For CGL CHSL 2021 (Practise Sheet)Document3 pagesDAY 40 Maths Sample Paper For CGL CHSL 2021 (Practise Sheet)Sahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Geom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketDocument22 pagesGeom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketAnela100% (1)
- Gate Triangle TipsDocument10 pagesGate Triangle TipsHOW TO WORLDNo ratings yet
- l-21 Surface Areas and Volumes ofDocument3 pagesl-21 Surface Areas and Volumes ofsoorya_taNo ratings yet
- 2D MensurationDocument12 pages2D MensurationPushpam JhaNo ratings yet
- Physics B 2019Document15 pagesPhysics B 2019Jeny SharmaNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 002 (15 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 002 (15 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- HBSE 12th Physics A 2018 PaperDocument12 pagesHBSE 12th Physics A 2018 PaperRavjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 3D 20210617114714Document8 pagesMensuration 3D 20210617114714Suneh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7: Applications of PolygonDocument9 pagesGrade 7: Applications of PolygonMa Teneza BarberoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 3D-3Document17 pagesMensuration 3D-3Abaz AbazNo ratings yet
- Quick Review Fundamentals of TrigonometryDocument2 pagesQuick Review Fundamentals of TrigonometryZaid BabarNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 005 (20 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 005 (20 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- 7 January (Evening Shift) - JEE Main 2020 (Memory Based)Document38 pages7 January (Evening Shift) - JEE Main 2020 (Memory Based)Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- 13 Dec 2nd Shift CPO 2019Document8 pages13 Dec 2nd Shift CPO 2019pankaj111No ratings yet
- Class Sheet 1636614916. MathDocument37 pagesClass Sheet 1636614916. MathShivam PateriyaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document19 pagesCH 6Itech SwsNo ratings yet
- Izk:I (K.M Olrqfu"B Iz'U : Le % 1 ?kavk Feuv VFRJFDR Iw - KK DDocument8 pagesIzk:I (K.M Olrqfu"B Iz'U : Le % 1 ?kavk Feuv VFRJFDR Iw - KK DAmanNo ratings yet
- 2-D Mensuration Area & Petameter Practice Q Set PDF 263Document22 pages2-D Mensuration Area & Petameter Practice Q Set PDF 263Abhraham Benjamin de VilliersNo ratings yet
- SSC CPO 2022 Maths Chapterwise All QuestionsDocument166 pagesSSC CPO 2022 Maths Chapterwise All QuestionsAarzoo RatheeNo ratings yet
- DPPDocument14 pagesDPPisravelkirubaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 02 (11 Mock Test (2-11) FinalDocument4 pagesMock Test 02 (11 Mock Test (2-11) Finalvayunandanmishra982No ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument30 pagesSolid GeometryRohclem Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument9 pagesGeometryFahim UddinNo ratings yet
- Questions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesQuestions: 25 Exercise - 2 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Questions: 25 Exercise - 1 Time: 15 MinDocument5 pagesQuestions: 25 Exercise - 1 Time: 15 MinMatt StarkNo ratings yet
- Number System Solution (2011-2021)Document83 pagesNumber System Solution (2011-2021)Sampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Junkai Xie and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Calculations of Vibrational Energy Levels For XY4 Molecules 2: Bending States of MethaneDocument10 pagesJunkai Xie and Jonathan Tennyson - Variational Calculations of Vibrational Energy Levels For XY4 Molecules 2: Bending States of MethaneWippetsxzNo ratings yet
- Dha 2Document3 pagesDha 2Gaurav BindalNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Sheet - 5 by Bot of MagnetoDocument3 pagesMensuration Sheet - 5 by Bot of Magneto420walimailidNo ratings yet
- Daily Quizzes Series Day 006 (21 June 2024)Document9 pagesDaily Quizzes Series Day 006 (21 June 2024)goluwriter062No ratings yet
- Investigating (Polygons)Document2 pagesInvestigating (Polygons)aisheykapattersonsba24No ratings yet
- DAY 13 Geometry (16 Days 16 Marathon)Document6 pagesDAY 13 Geometry (16 Days 16 Marathon)digaNo ratings yet
- SSC Mains Maths 19Document26 pagesSSC Mains Maths 19piyush13juNo ratings yet
- Vector and 3-d by Mohit Tyagi SitDocument24 pagesVector and 3-d by Mohit Tyagi SitRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Midline TheoremDocument19 pagesMidline TheoremArlene Polis Delos Reyes100% (4)
- Success Key Test SeriesDocument2 pagesSuccess Key Test SeriesShubham PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Maths Mock 14, Paper 2 (3014)Document14 pagesMaths Mock 14, Paper 2 (3014)。No ratings yet
- Euler's Formula and Poncelet's Porism Lev Emelyanov and Tatiana EmelyanovaDocument4 pagesEuler's Formula and Poncelet's Porism Lev Emelyanov and Tatiana EmelyanovaAltananyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical and Youth Magazine ProblemsDocument52 pagesMathematical and Youth Magazine ProblemsNadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Hyperbolic FunctionDocument10 pagesChapter 1-Hyperbolic Functionhiromiebizuka11No ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFAnonymous m3yrUPNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Andrew Sioson - Lesson HandoutDocument13 pagesKami Export - Andrew Sioson - Lesson HandoutnobdyNo ratings yet
- Kalayaan Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesKalayaan Elementary SchoolEmmanuel MejiaNo ratings yet
- 3D Shapes - KS3 MathsDocument13 pages3D Shapes - KS3 MathsClaudia PinnaNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Document8 pagesDLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Ma Gloria Deocades FlanciaNo ratings yet
- I/B IiDocument22 pagesI/B Iiندى عمريNo ratings yet
- Eometry Ensuration Rigonometry: Review TestDocument37 pagesEometry Ensuration Rigonometry: Review TestRaju RayhanNo ratings yet
- Cds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16Document57 pagesCds 1 2020 Maths Solution 16ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Lines, Angles & TrianglesDocument25 pagesLines, Angles & TrianglesBalachandra MallyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Review Exercise QuestionsDocument10 pagesGeometry: Review Exercise QuestionsMustafa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mit18 900s23 Lec1Document5 pagesMit18 900s23 Lec1Htike HtikeNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 RD MathsDocument61 pagesCh-5 RD MathsThe VRAJ GAMESNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3Document3 pagesGeometry - 102714 - 4 2 Worksheet - Angles in A Triangle 1-3api-252752147No ratings yet
- Euclidean GeometryDocument91 pagesEuclidean GeometryrefilwematotoNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Ch-11 SA N Vol.Document5 pagesClass 9th Ch-11 SA N Vol.ayusharora864No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Triangle PHDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Triangle PHLancelot Gabriel Althuz LatozaNo ratings yet
- G-9 Chapter 10 CirclesDocument5 pagesG-9 Chapter 10 CirclesChetanNo ratings yet
- Trig NoteDocument5 pagesTrig NoteSubin ParkNo ratings yet