Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
Uploaded by
xin nianCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2 - Global Supply Chain Management Simulation v2Document2 pages2 - Global Supply Chain Management Simulation v2prashant30950% (2)
- 1.4. Solution - Design - ERPDocument15 pages1.4. Solution - Design - ERPkhuzaimaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts NotesDocument9 pagesManufacturing Accounts NotesFarrukhsg100% (5)
- Understanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)From EverandUnderstanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Raw Materials Analyst ReportDocument6 pagesRaw Materials Analyst ReportGaurav ChandelNo ratings yet
- Silicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfDocument360 pagesSilicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfuttam pundirNo ratings yet
- Walmart Value Chain AnalysisDocument1 pageWalmart Value Chain AnalysisAmarpreet Singh100% (1)
- 03 Cost of Goods SoldDocument2 pages03 Cost of Goods Soldeduson2013No ratings yet
- What Is Cost of Goods SoldDocument19 pagesWhat Is Cost of Goods SoldRanaNo ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument1 pageCalculationsalaricphineasbransonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Cost Flows and Cost Terminology)Document5 pagesLecture 3 (Cost Flows and Cost Terminology)alomeloNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument9 pagesManufacturing AccountsCrystal Johnson100% (1)
- Key Takeaways: DirectDocument13 pagesKey Takeaways: DirectSB CorporationNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Cost of Goods ManufacturedDocument7 pagesSchedule of Cost of Goods ManufacturedMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Week 4Document28 pagesFabm2 Week 4Jeremy SolomonNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument25 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeAngel Nichole ValenciaNo ratings yet
- What Are Nonmanufacturing Overhead CostsDocument1 pageWhat Are Nonmanufacturing Overhead CostsNana miNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Assignment-02-BUS-5110 Manegerial AccountingDocument5 pagesPortfolio Assignment-02-BUS-5110 Manegerial AccountingRasel SakilNo ratings yet
- Running Head: MASTER BUDGETS 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: MASTER BUDGETS 1Eli KoechNo ratings yet
- Administrative Cost BudgetDocument4 pagesAdministrative Cost BudgetchakriNo ratings yet
- Product CostDocument2 pagesProduct Costmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesDocument4 pagesCost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesAna Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- Retail Net SeDocument15 pagesRetail Net Sepintu82No ratings yet
- DCF Model ExplanationDocument10 pagesDCF Model ExplanationMehak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Suggest Solution Hint For Q1 Q2Document3 pagesSuggest Solution Hint For Q1 Q2Tengku Zulhilmi Al HajNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Cost Accounting and Classification7280895122984483619' With YouDocument10 pagesI Am Sharing 'Cost Accounting and Classification7280895122984483619' With Yousuraj banNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsDocument37 pagesAccounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsTesda CACSNo ratings yet
- Gross MarginDocument13 pagesGross MarginIshita Ghosh100% (1)
- Retail FormulasDocument8 pagesRetail Formulassureshmaddy22No ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument8 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysissachinremaNo ratings yet
- What Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitDocument3 pagesWhat Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitUWatch TVNo ratings yet
- Acc501 GDB 1Document1 pageAcc501 GDB 1Shahbaz AnjumNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument5 pagesBudgetmuktaNo ratings yet
- Cogs VS Cost of SalesDocument9 pagesCogs VS Cost of SalesTjan Tiong GieNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: A Business PartnerDocument24 pagesManagement Accounting: A Business PartnerIsbah INo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - FinalDocument24 pagesChapter 16 - FinalMuhammad Saad UmarNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Control Reviewer Q1Document19 pagesCost Accounting and Control Reviewer Q1angelaang7876No ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument34 pagesCost AccountingRose DallyNo ratings yet
- Cost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesCost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsEduNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis: Margin of SafetyDocument2 pagesBreak-Even Analysis: Margin of SafetyNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- Presupuesto de Ventas y ProducciónDocument6 pagesPresupuesto de Ventas y ProducciónAndrésNo ratings yet
- CH2 Fabm2Document27 pagesCH2 Fabm2Crisson FermalinoNo ratings yet
- Cee 108 ReportDocument9 pagesCee 108 ReportMisael Masauring BasiaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Cost AccountingJappy QuilasNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Notes (Multi-Step Aproach)Document2 pagesFabm 2 Notes (Multi-Step Aproach)Mia Abegail ChuaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Vs Variable CostingDocument2 pagesAbsorption Costing Vs Variable Costingneway gobachew100% (1)
- How To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterDocument16 pagesHow To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterSiti Asma MohamadNo ratings yet
- Definition of Cost PrincipleDocument3 pagesDefinition of Cost PrincipleDickyNo ratings yet
- Types of Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesTypes of Cost AccountingLegends FunanzaNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument3 pagesIncome StatementMamta LallNo ratings yet
- Business Finance FormulaDocument9 pagesBusiness Finance FormulaGeorge Nicole BaybayanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance FormulaDocument9 pagesBusiness Finance FormulaGeorge Nicole BaybayanNo ratings yet
- RoarDocument19 pagesRoarFrank HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument5 pagesCost AccountingNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 Module 3 Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument10 pagesFABM 2 Module 3 Statement of Comprehensive IncomebabyjamskieNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods SoldDocument23 pagesCost of Goods SoldCrizylen Mae Pepito LahoylahoyNo ratings yet
- Fabm ReviewerDocument2 pagesFabm Reviewer治太宰No ratings yet
- Inc StatmentDocument3 pagesInc StatmentDilawarNo ratings yet
- Are Depreciation and Amortization Included in Gross Profit - InvestopediaDocument5 pagesAre Depreciation and Amortization Included in Gross Profit - InvestopediaBob KaneNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts Departmental 1Document12 pagesManufacturing Accounts Departmental 1nandarsoe105No ratings yet
- Kelompok 1Document13 pagesKelompok 1difarafi97No ratings yet
- 27.10 Return On InvestmentDocument11 pages27.10 Return On InvestmentEmin NezirajNo ratings yet
- Accounts lessons 1Document39 pagesAccounts lessons 1senthilnathan25nNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis and ManagementDocument14 pagesFinancial Analysis and Managementvijay_mehta_7No ratings yet
- Best Practice Working Capital Management Techniques For Optimizing Inventories Receivables and PayablesDocument7 pagesBest Practice Working Capital Management Techniques For Optimizing Inventories Receivables and PayablesSenthilSelvaNo ratings yet
- MM Business Process OverviewDocument11 pagesMM Business Process OverviewBrian3911No ratings yet
- Finance Resume TemplateDocument8 pagesFinance Resume Templateafazbsaxi100% (2)
- Project Charter - HR AnalyticsDocument7 pagesProject Charter - HR AnalyticsDhanalaxmi VenkatNo ratings yet
- Porters Five For CK - UpdatedDocument4 pagesPorters Five For CK - UpdateddishaNo ratings yet
- Schilke Hu Helfat. Quo Vadis Dynamic CapabilitiesDocument50 pagesSchilke Hu Helfat. Quo Vadis Dynamic CapabilitiesPedroMotaVeigaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Organization and Management: Basic Education Department School Year 2020-2021 First Quarter PeriodDocument20 pagesGrade 11 Organization and Management: Basic Education Department School Year 2020-2021 First Quarter PeriodLizette Condrea Simon RamosNo ratings yet
- Product Perspective Solutions Perspective: Value PropositionDocument1 pageProduct Perspective Solutions Perspective: Value PropositionPrabhudatta Anup SouravNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and Analysis Enable Accurate Decision Making While Driving EfficienciesDocument4 pagesFinancial Planning and Analysis Enable Accurate Decision Making While Driving Efficienciesanju tharejaNo ratings yet
- Workshop 6 AnsDocument5 pagesWorkshop 6 AnsSAMUEL THOMASNo ratings yet
- Definition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesDefinition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementAnkush RanaNo ratings yet
- Admission Bulletin 2023Document16 pagesAdmission Bulletin 2023Al OkNo ratings yet
- Cost Chapter 1-5Document302 pagesCost Chapter 1-5chingNo ratings yet
- NCE100 Gold Book PDFDocument60 pagesNCE100 Gold Book PDFAnonymous kRIjqBLkNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Standard 01 - Classification of CostDocument28 pagesCost Accounting Standard 01 - Classification of CostShahean AliNo ratings yet
- Developing Modern Applications With Agile OutsourcingDocument17 pagesDeveloping Modern Applications With Agile OutsourcingPaweł PanowiczNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Strategy Planning Template PDFDocument14 pagesDigital Marketing Strategy Planning Template PDFJade Do100% (1)
- Post 716Document2 pagesPost 716RiteshNo ratings yet
- Initial Supply ControlDocument3 pagesInitial Supply ControlKuldeep Chauhan100% (2)
- Internship Report On Studio Bitmap (Event Management Firm)Document20 pagesInternship Report On Studio Bitmap (Event Management Firm)FOuadHasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Environment of Marketing Channels Summary:: The Us Is Have Happen LotDocument3 pagesChapter 3: The Environment of Marketing Channels Summary:: The Us Is Have Happen Lotheize resente0% (1)
- StylumiaDocument3 pagesStylumiasrishNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance QUALITY ASSURANCE PLANDocument40 pagesQuality Assurance QUALITY ASSURANCE PLANDev SurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Feasibility PlanningDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Feasibility Planningrathnakotari63% (8)
- Chapter 11 IS Auditing Standards, Guidelines and Best PracticesDocument9 pagesChapter 11 IS Auditing Standards, Guidelines and Best PracticesMuriithi MurageNo ratings yet
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
Uploaded by
xin nianOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
What Is Cost of Goods Sold
Uploaded by
xin nianCopyright:
Available Formats
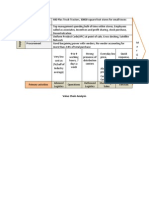
What Is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
Cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the direct costs of producing the
goods sold by a company. This amount includes the cost of the materials
and labor directly used to create the good. It excludes indirect expenses,
such as distribution costs and sales force costs.
Cost of goods sold is also referred to as "cost of sales."
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Cost of goods sold (COGS) includes all of the costs and expenses
directly related to the production of goods.
COGS excludes indirect costs such as overhead and sales and
marketing.
COGS is deducted from revenues (sales) in order to calculate gross
profit and gross margin. Higher COGS results in lower margins.
The value of COGS will change depending on the accounting
standards used in the calculation.
COGS differs from operating expenses (OPEX) in that OPEX
includes expenditures that are not directly tied to the production of
goods or services.
Why Is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Important?
COGS is an important metric on financial statements as it is subtracted
from a company’s revenues to determine its gross profit. Gross profit is a
profitability measure that evaluates how efficient a company is in
managing its labor and supplies in the production process.
or example, COGS for an automaker would include the material costs for
the parts that go into making the car plus the labor costs used to put the
car together. The cost of sending the cars to dealerships and the cost of
the labor used to sell the car would be excluded.
Furthermore, costs incurred on the cars that were not sold during the year
will not be included when calculating COGS, whether the costs are direct
or indirect. In other words, COGS includes the direct cost of producing
goods or services that were purchased by customers during the year. As a
rule of thumb, if you want to know if an expense falls under COGS, ask:
"Would this expense have been an expense even if no sales were
generated?"
COGS only applies to those costs directly related to producing goods
intended for sale.1
What Is the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Formula?
COGS=Beginning Inventory+P−Ending InventorywhereP=Purchas
es during the periodCOGS=Beginning Inventory+P−Ending
InventorywhereP=Purchases during the period
Inventory that is sold appears in the income statement under the COGS
account. The beginning inventory for the year is the inventory left over
from the previous year—that is, the merchandise that was not sold in the
previous year.
Any additional productions or purchases made by a manufacturing or retail
company are added to the beginning inventory. At the end of the year, the
products that were not sold are subtracted from the sum of beginning
inventory and additional purchases. The final number derived from the
calculation is the cost of goods sold for the year.
The balance sheet has an account called the current assets account.
Under this account is an item called inventory. The balance sheet only
captures a company’s financial health at the end of an accounting period.
This means that the inventory value recorded under current assets is the
ending inventory.
You might also like
- 2 - Global Supply Chain Management Simulation v2Document2 pages2 - Global Supply Chain Management Simulation v2prashant30950% (2)
- 1.4. Solution - Design - ERPDocument15 pages1.4. Solution - Design - ERPkhuzaimaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts NotesDocument9 pagesManufacturing Accounts NotesFarrukhsg100% (5)
- Understanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)From EverandUnderstanding Financial Statements (Review and Analysis of Straub's Book)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Raw Materials Analyst ReportDocument6 pagesRaw Materials Analyst ReportGaurav ChandelNo ratings yet
- Silicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfDocument360 pagesSilicon Valley North_ A High-Tech Cluster of Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Technology, Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) (Technology, ... Entrepreneurship and Competitive Strategy) ( PDFDrive.com ).pdfuttam pundirNo ratings yet
- Walmart Value Chain AnalysisDocument1 pageWalmart Value Chain AnalysisAmarpreet Singh100% (1)
- 03 Cost of Goods SoldDocument2 pages03 Cost of Goods Soldeduson2013No ratings yet
- What Is Cost of Goods SoldDocument19 pagesWhat Is Cost of Goods SoldRanaNo ratings yet
- CalculationsDocument1 pageCalculationsalaricphineasbransonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Cost Flows and Cost Terminology)Document5 pagesLecture 3 (Cost Flows and Cost Terminology)alomeloNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument9 pagesManufacturing AccountsCrystal Johnson100% (1)
- Key Takeaways: DirectDocument13 pagesKey Takeaways: DirectSB CorporationNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Cost of Goods ManufacturedDocument7 pagesSchedule of Cost of Goods ManufacturedMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Week 4Document28 pagesFabm2 Week 4Jeremy SolomonNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument25 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeAngel Nichole ValenciaNo ratings yet
- What Are Nonmanufacturing Overhead CostsDocument1 pageWhat Are Nonmanufacturing Overhead CostsNana miNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Assignment-02-BUS-5110 Manegerial AccountingDocument5 pagesPortfolio Assignment-02-BUS-5110 Manegerial AccountingRasel SakilNo ratings yet
- Running Head: MASTER BUDGETS 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: MASTER BUDGETS 1Eli KoechNo ratings yet
- Administrative Cost BudgetDocument4 pagesAdministrative Cost BudgetchakriNo ratings yet
- Product CostDocument2 pagesProduct Costmba departmentNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesDocument4 pagesCost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesAna Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- Retail Net SeDocument15 pagesRetail Net Sepintu82No ratings yet
- DCF Model ExplanationDocument10 pagesDCF Model ExplanationMehak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Suggest Solution Hint For Q1 Q2Document3 pagesSuggest Solution Hint For Q1 Q2Tengku Zulhilmi Al HajNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Cost Accounting and Classification7280895122984483619' With YouDocument10 pagesI Am Sharing 'Cost Accounting and Classification7280895122984483619' With Yousuraj banNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsDocument37 pagesAccounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsTesda CACSNo ratings yet
- Gross MarginDocument13 pagesGross MarginIshita Ghosh100% (1)
- Retail FormulasDocument8 pagesRetail Formulassureshmaddy22No ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument8 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysissachinremaNo ratings yet
- What Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitDocument3 pagesWhat Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitUWatch TVNo ratings yet
- Acc501 GDB 1Document1 pageAcc501 GDB 1Shahbaz AnjumNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument5 pagesBudgetmuktaNo ratings yet
- Cogs VS Cost of SalesDocument9 pagesCogs VS Cost of SalesTjan Tiong GieNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: A Business PartnerDocument24 pagesManagement Accounting: A Business PartnerIsbah INo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - FinalDocument24 pagesChapter 16 - FinalMuhammad Saad UmarNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting and Control Reviewer Q1Document19 pagesCost Accounting and Control Reviewer Q1angelaang7876No ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument34 pagesCost AccountingRose DallyNo ratings yet
- Cost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesCost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsEduNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis: Margin of SafetyDocument2 pagesBreak-Even Analysis: Margin of SafetyNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- Presupuesto de Ventas y ProducciónDocument6 pagesPresupuesto de Ventas y ProducciónAndrésNo ratings yet
- CH2 Fabm2Document27 pagesCH2 Fabm2Crisson FermalinoNo ratings yet
- Cee 108 ReportDocument9 pagesCee 108 ReportMisael Masauring BasiaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Cost AccountingJappy QuilasNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Notes (Multi-Step Aproach)Document2 pagesFabm 2 Notes (Multi-Step Aproach)Mia Abegail ChuaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Vs Variable CostingDocument2 pagesAbsorption Costing Vs Variable Costingneway gobachew100% (1)
- How To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterDocument16 pagesHow To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterSiti Asma MohamadNo ratings yet
- Definition of Cost PrincipleDocument3 pagesDefinition of Cost PrincipleDickyNo ratings yet
- Types of Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesTypes of Cost AccountingLegends FunanzaNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument3 pagesIncome StatementMamta LallNo ratings yet
- Business Finance FormulaDocument9 pagesBusiness Finance FormulaGeorge Nicole BaybayanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance FormulaDocument9 pagesBusiness Finance FormulaGeorge Nicole BaybayanNo ratings yet
- RoarDocument19 pagesRoarFrank HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument5 pagesCost AccountingNiño Rey LopezNo ratings yet
- FABM 2 Module 3 Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument10 pagesFABM 2 Module 3 Statement of Comprehensive IncomebabyjamskieNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods SoldDocument23 pagesCost of Goods SoldCrizylen Mae Pepito LahoylahoyNo ratings yet
- Fabm ReviewerDocument2 pagesFabm Reviewer治太宰No ratings yet
- Inc StatmentDocument3 pagesInc StatmentDilawarNo ratings yet
- Are Depreciation and Amortization Included in Gross Profit - InvestopediaDocument5 pagesAre Depreciation and Amortization Included in Gross Profit - InvestopediaBob KaneNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts Departmental 1Document12 pagesManufacturing Accounts Departmental 1nandarsoe105No ratings yet
- Kelompok 1Document13 pagesKelompok 1difarafi97No ratings yet
- 27.10 Return On InvestmentDocument11 pages27.10 Return On InvestmentEmin NezirajNo ratings yet
- Accounts lessons 1Document39 pagesAccounts lessons 1senthilnathan25nNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis and ManagementDocument14 pagesFinancial Analysis and Managementvijay_mehta_7No ratings yet
- Best Practice Working Capital Management Techniques For Optimizing Inventories Receivables and PayablesDocument7 pagesBest Practice Working Capital Management Techniques For Optimizing Inventories Receivables and PayablesSenthilSelvaNo ratings yet
- MM Business Process OverviewDocument11 pagesMM Business Process OverviewBrian3911No ratings yet
- Finance Resume TemplateDocument8 pagesFinance Resume Templateafazbsaxi100% (2)
- Project Charter - HR AnalyticsDocument7 pagesProject Charter - HR AnalyticsDhanalaxmi VenkatNo ratings yet
- Porters Five For CK - UpdatedDocument4 pagesPorters Five For CK - UpdateddishaNo ratings yet
- Schilke Hu Helfat. Quo Vadis Dynamic CapabilitiesDocument50 pagesSchilke Hu Helfat. Quo Vadis Dynamic CapabilitiesPedroMotaVeigaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Organization and Management: Basic Education Department School Year 2020-2021 First Quarter PeriodDocument20 pagesGrade 11 Organization and Management: Basic Education Department School Year 2020-2021 First Quarter PeriodLizette Condrea Simon RamosNo ratings yet
- Product Perspective Solutions Perspective: Value PropositionDocument1 pageProduct Perspective Solutions Perspective: Value PropositionPrabhudatta Anup SouravNo ratings yet
- Financial Planning and Analysis Enable Accurate Decision Making While Driving EfficienciesDocument4 pagesFinancial Planning and Analysis Enable Accurate Decision Making While Driving Efficienciesanju tharejaNo ratings yet
- Workshop 6 AnsDocument5 pagesWorkshop 6 AnsSAMUEL THOMASNo ratings yet
- Definition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument9 pagesDefinition of Strategic Human Resource ManagementAnkush RanaNo ratings yet
- Admission Bulletin 2023Document16 pagesAdmission Bulletin 2023Al OkNo ratings yet
- Cost Chapter 1-5Document302 pagesCost Chapter 1-5chingNo ratings yet
- NCE100 Gold Book PDFDocument60 pagesNCE100 Gold Book PDFAnonymous kRIjqBLkNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Standard 01 - Classification of CostDocument28 pagesCost Accounting Standard 01 - Classification of CostShahean AliNo ratings yet
- Developing Modern Applications With Agile OutsourcingDocument17 pagesDeveloping Modern Applications With Agile OutsourcingPaweł PanowiczNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Strategy Planning Template PDFDocument14 pagesDigital Marketing Strategy Planning Template PDFJade Do100% (1)
- Post 716Document2 pagesPost 716RiteshNo ratings yet
- Initial Supply ControlDocument3 pagesInitial Supply ControlKuldeep Chauhan100% (2)
- Internship Report On Studio Bitmap (Event Management Firm)Document20 pagesInternship Report On Studio Bitmap (Event Management Firm)FOuadHasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Environment of Marketing Channels Summary:: The Us Is Have Happen LotDocument3 pagesChapter 3: The Environment of Marketing Channels Summary:: The Us Is Have Happen Lotheize resente0% (1)
- StylumiaDocument3 pagesStylumiasrishNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance QUALITY ASSURANCE PLANDocument40 pagesQuality Assurance QUALITY ASSURANCE PLANDev SurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Feasibility PlanningDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Feasibility Planningrathnakotari63% (8)
- Chapter 11 IS Auditing Standards, Guidelines and Best PracticesDocument9 pagesChapter 11 IS Auditing Standards, Guidelines and Best PracticesMuriithi MurageNo ratings yet