Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Com 2ndq
Oral Com 2ndq
Uploaded by
Kei Mark SoberanoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Narrative Report On Presentation of Ipcrf and Rpms of Grade One TeachersDocument8 pagesNarrative Report On Presentation of Ipcrf and Rpms of Grade One TeachersKriselle BañezNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextFrom EverandSpectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Humboldt On LanguageDocument30 pagesHumboldt On Languagemalcrowe100% (1)
- Oral PresentationDocument35 pagesOral Presentationmaegantrish543No ratings yet
- Final Presentation SkillsDocument26 pagesFinal Presentation SkillsFaculty of Economics Center for International AffairsNo ratings yet
- Oc11 Type of Speech According To Purpose and DeliveyDocument29 pagesOc11 Type of Speech According To Purpose and Deliveyapi-615586274No ratings yet
- 2ND Week 3 4Document15 pages2ND Week 3 4BUNNY GGUKNo ratings yet
- OCOM FTA ReviewerDocument5 pagesOCOM FTA ReviewerJulluis DagoNo ratings yet
- Planificacion Del 11C 1Document35 pagesPlanificacion Del 11C 1Lic. Astrid PalmaNo ratings yet
- Wa0066.Document6 pagesWa0066.Lic. Astrid PalmaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 TopicsDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Topicsmichael segundoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33 Speeches Revised and FinalDocument21 pagesLecture 33 Speeches Revised and Finalsnigdhavohra420No ratings yet
- English Creative Writing Paper 1 Checklist DbfsDocument5 pagesEnglish Creative Writing Paper 1 Checklist DbfsPan KNo ratings yet
- Planning Communication - I: Unit 1 - Verbal and Written CommunicationDocument8 pagesPlanning Communication - I: Unit 1 - Verbal and Written CommunicationParul KapoorNo ratings yet
- 2nd Oral-Com NotesDocument2 pages2nd Oral-Com Notesej bagayanNo ratings yet
- Oral. ComDocument5 pagesOral. ComADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- ExtramarksDocument12 pagesExtramarksSonali TripathiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech WritingDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Speech WritingJanice L. LangitNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesBusiness CommunicationRabia NaseemNo ratings yet
- Annual Planning AngieDocument17 pagesAnnual Planning AngieAngie VasquezNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Types of Speech According ToDocument3 pagesPurpose: Types of Speech According ToSolstice OshiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan NovDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Novapi-726071229No ratings yet
- Oral Communication - 4Document4 pagesOral Communication - 4JOYCE ENGARANNo ratings yet
- Ppt3 Types of Speeches Purpose DeliveryDocument21 pagesPpt3 Types of Speeches Purpose DeliveryEden DionisioNo ratings yet
- 1ST QTR Notes (Eng02)Document2 pages1ST QTR Notes (Eng02)Mikaella SantosNo ratings yet
- 3rd Finals ReviewerDocument25 pages3rd Finals Reviewercobra09182007No ratings yet
- Exploring The Essay Understanding An Opinion EssayDocument2 pagesExploring The Essay Understanding An Opinion EssayMichaela MamaradloNo ratings yet
- Formal Presentations - ETC - 3130004Document19 pagesFormal Presentations - ETC - 3130004sameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument25 pagesCommunicative CompetencealfonsosucabNo ratings yet
- 2q-Oralcomm Week16Document15 pages2q-Oralcomm Week16Aleigh Janrah OlivaNo ratings yet
- The Speech Writing Process HandoutDocument3 pagesThe Speech Writing Process HandoutRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- (10.11) - Buku Ajar LSFS-Fitria, Ika, Puput For SKP 2019Document7 pages(10.11) - Buku Ajar LSFS-Fitria, Ika, Puput For SKP 2019SudarmantoNo ratings yet
- Jamal Sir-Class 3 - L-3 - Oral ReportDocument52 pagesJamal Sir-Class 3 - L-3 - Oral ReportmahmudNo ratings yet
- Syllabus DesignDocument12 pagesSyllabus Designmalonamige20No ratings yet
- Paper PresentationDocument4 pagesPaper PresentationPrasad MaratheNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Communication Skills: Mr. Villamin's English ClassDocument27 pagesEnhancing Communication Skills: Mr. Villamin's English ClassJenny Pearl EmeterioNo ratings yet
- Tips For Effective Presentation Design and DeliveryDocument2 pagesTips For Effective Presentation Design and DeliveryJames Manrique100% (1)
- Structuring Your SpeechDocument37 pagesStructuring Your SpeechMirza Adwit RahmanNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingDocument42 pagesExplanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingFatwa KhairaNo ratings yet
- Oral-Com - Act - 1 2Document3 pagesOral-Com - Act - 1 2Fria CariñoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER OralCommDocument3 pagesREVIEWER OralCommaaronmanlapaz4No ratings yet
- OCC Module 11Document13 pagesOCC Module 11Jessa Mae Neri Sardan100% (1)
- (FORMAT) Speech WritingDocument7 pages(FORMAT) Speech WritingDale QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Unificada UpdatedDocument1 pagePlantilla Unificada UpdatedMaría GaviriaNo ratings yet
- Case ReviewerDocument4 pagesCase ReviewerjulianaabelleraNo ratings yet
- OralComPresentation With VideosDocument36 pagesOralComPresentation With VideosPattBolijuanNo ratings yet
- SSLM Q1 Oral ComDocument8 pagesSSLM Q1 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- CRR Strand 1 Strategic Reading Handouts 2023Document11 pagesCRR Strand 1 Strategic Reading Handouts 2023Kathy MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Improving Your Skills: Listening Skills For PTE AcademicDocument4 pagesImproving Your Skills: Listening Skills For PTE AcademicSteven Gaurano100% (1)
- Lesson PLANDocument2 pagesLesson PLANWalton León EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Course General Topic Subtopics A1-1Document8 pagesCourse General Topic Subtopics A1-1Nata DaNo ratings yet
- 2q-Oralcomm Week13Document13 pages2q-Oralcomm Week13John Mario V. Reyes3180675No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan The MetisDocument2 pagesLesson Plan The Metisapi-726071229No ratings yet
- Different Types of Speeches According To Its ReviewrDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Speeches According To Its ReviewrAlfred QuintoNo ratings yet
- Seminars and Oral PresentationsDocument4 pagesSeminars and Oral Presentationsnajimhamidi0900No ratings yet
- Occ (Reviewer 2)Document3 pagesOcc (Reviewer 2)Aljeya EvanchezNo ratings yet
- 14 Story Telling Pedagogy DVKVDocument14 pages14 Story Telling Pedagogy DVKVHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- Bài thuyết trình tiếng anhDocument13 pagesBài thuyết trình tiếng anhHuyền MinhNo ratings yet
- Extemporaneous SpeakingDocument5 pagesExtemporaneous SpeakingkehlaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 English Oralcomm F Quarter 4 Week 4Document11 pagesGrade 12 English Oralcomm F Quarter 4 Week 4Geraldine FerrerasNo ratings yet
- The Academic Term PaperDocument2 pagesThe Academic Term PaperSitong LiuNo ratings yet
- Teaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentFrom EverandTeaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- DVB Scene33Document16 pagesDVB Scene33MAJLIS DAERAH KERIANNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Sample 2Document15 pagesAssessment 1 Sample 2Sam ChawlaNo ratings yet
- 08 August 2000 QSTDocument180 pages08 August 2000 QSTRudik Wid100% (1)
- What My Classroom Looks Like Sounds Like Feels LikeDocument3 pagesWhat My Classroom Looks Like Sounds Like Feels Likeapi-548817489No ratings yet
- Understanding Metaphorical Texts in Foreign LiteratureDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Metaphorical Texts in Foreign LiteratureNeuda LagoNo ratings yet
- Stylish XSS in Magento: When 'Style' Helps YouDocument9 pagesStylish XSS in Magento: When 'Style' Helps YouMSc Ashar Javed100% (1)
- SpringSoft Infotech Business Proposal 2021-22Document39 pagesSpringSoft Infotech Business Proposal 2021-22Satish RikhariNo ratings yet
- Simple Present, Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument18 pagesSimple Present, Simple Past and Present PerfectakbarNo ratings yet
- 10 Case StudiesDocument29 pages10 Case StudiesKr Chandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- ACP Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesACP Lesson Plan Templateapi-316651663No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Di PietroDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Di Pietroapi-303145564No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish GrammarrDocument3 pagesPractice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish Grammarrgweber.gw6380No ratings yet
- Dairy Training de LavalDocument12 pagesDairy Training de LavalAmol PatilNo ratings yet
- Conditions That Hinder Effective CommunicationDocument456 pagesConditions That Hinder Effective CommunicationYohanes Masboi WidodoNo ratings yet
- Teacher ResumeDocument2 pagesTeacher Resumeapi-431676661No ratings yet
- Educ 105 BDocument18 pagesEduc 105 BGlaiza MabantaNo ratings yet
- Daemonolatreiae Libri TresDocument453 pagesDaemonolatreiae Libri TresIan Thomson100% (4)
- GMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Document7 pagesGMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Mobile Technologies SecurityDocument16 pagesMobile Technologies SecurityGi Hyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Booklet N1 - Unit 1Document13 pagesBooklet N1 - Unit 1villameliNo ratings yet
- Graduate School Sorsogon City: Annunciation College of Bacon Sorsogon Unit, IncDocument2 pagesGraduate School Sorsogon City: Annunciation College of Bacon Sorsogon Unit, IncGapas Mary AnnNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 1 - 1Document33 pagesComputer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 1 - 1Ali MemonNo ratings yet
- Sample Template Idea ExemplarDocument3 pagesSample Template Idea ExemplarJaja VictorioNo ratings yet
- Two - Track Approach PresentationDocument32 pagesTwo - Track Approach PresentationDivine Grace Samortin89% (18)
- Serial ProgrammingDocument177 pagesSerial ProgrammingkristofwoutersNo ratings yet
- Tudor Fashion Case StudyDocument3 pagesTudor Fashion Case StudyDines Shinde100% (1)
- Taklimat Proposal DefenceDocument14 pagesTaklimat Proposal DefenceRabeya KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Hernandez #0727088 Library 202 Professor BuenaventuraDocument10 pagesJacqueline Hernandez #0727088 Library 202 Professor Buenaventuralib202No ratings yet
Oral Com 2ndq
Oral Com 2ndq
Uploaded by
Kei Mark SoberanoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oral Com 2ndq
Oral Com 2ndq
Uploaded by
Kei Mark SoberanoCopyright:
Available Formats
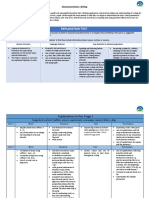
TYPE OF SPEECHES TYPES OF SPEECHES
THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM: (speech writing process) (ACCORDING TO DELIVERY)
1. EXTEMPORANEOUS SPEECH
✓ Speaking with limited preparation
✓ Guided by notes or outline
✓ Delivered conversationally
✓ Most popular type
Speaking Situations
✓ When you are a candidate for a post in a student
government and you deliver your campaign speech before
a voting public.
✓ When you are assigned to report a topic in class.
Tips
✓ Create an outline
✓ Organize your points logically (most important to least
important or vice versa)
✓ Use facts and real-life experiences as your examples
✓ Manage your time well
Audience analysis – entails looking for into the profile of ✓ Rehearse, rehearse, rehearse
your target audience.
Demography – age range, male-female ratio, and 2. IMPROMPTU SPEECH
educational background.
✓ Speaking without advanced preparation
Situation – time, venue, occasion and size.
Psychology – values, beliefs, attitudes, culture, ✓ Unrehearsed speech
preferences. ✓ Spoken conversationally
THREE BASIC TYPES OF SPEECH Speaking Situations
(ACCORDING TO PURPOSE) ✓ In an event where you are asked to say a few words
✓ First day at work or in class, or during an interview
INFORMATIVE SPEECH – It provides the audience
with a clear understanding of the concept or idea presented Tips
by the speaker. ✓ Once you are requested to say something, pause for a
Example: moment to plan in your head what to say.
Teacher telling students about earthquakes,
✓ State your main point briefly and deliver it at a pace your
student talking about her research, a travelogue about
audience can follow.
Chocolate Hills and weatherman speaks updates about the
weather condition the speaker.
3. MANUSCRIPT
- “WHAT?”
➢ Speaking with advanced preparation
PERSUASIVE SPEECH – It provides the audience with ➢ Planned and rehearsed speech
well-argued ideas that can influence their own beliefs and ➢ Reading aloud a written message
decisions.
Example: Speaking Situations
Giving your audience reasons why you should ✓News casting with a TelePrompter or an autocue device
become a club officer, how to improve your grades ✓ Presenting the legal proceedings and verdict in court
through a good habit of reading, the purpose of television ✓ Reading the rules and criteria in a contest
violence influencing the teenagers nowadays and become
a volunteer and change the world.
Tips
- “HOW WILL IT WORK AND WHY IS
IT IMPORTANT?” ✓Rehearse the speech over and over again until you sound
natural.
ENTERTAINMENT SPEECH – provides the audience ✓Observe accomplished news anchors and note how
with amusement, pleasure and enjoyment that make the conversational they sound when they deliver the news.
audience laugh.
Example: 4. MEMORIZED
Comedian delivering punch lines, why videos go ✓ Speaking with advanced preparation
viral, ten fun things to do during exams, why a chicken still ✓ Planned and rehearsed speech
walks even with the head cut off, why is cheating not ✓ Reciting a written message word-for-word from
included in the course curriculum, reasons why I love memory
doing nothing around the house.
- “WHAT WAY AND HOW WILL YOU Speaking Situations
ENTERTAIN?” ✓ When you perform in a stage play
✓ When you deliver a declamation, oratorical, or literary
piece
✓ When an actor or actress in a scene performs a script
from memory
Tips To entertain To entertain Grade 11
✓ Break it down! You cannot memorize a speech in one students with the success
sitting. If your speech has four paragraphs, you should stories of the people in the
focus on one paragraph at a time. Once you have community
memorized the first paragraph, focus on the next one.
✓ Build it up! After memorizing the speech in snippets, 3. TOPIC
you need to put them together. Recite the first paragraph - focal point of your speech
and move on to the second. After this, recite the first and
second paragraphs and move on to the third. 4. NARROWING DOWN A TOPIC
✓ Use note cards! Write one key point on one note card. - Making your main idea more specific and
Bring these note cards wherever you go and take them out focused, narrowing down the topic
whenever you have extra time to memorize, especially through listing.
during idle times of the
5. Gathering Data (Sourcing the Information)
- Seeking out all the available means for
finding materials to support the speech.
(Good sources are newspapers, magazines, books,
journals, or any reading materials full of useful
information.)
PRINCIPLES OF SPEECH DELIVERY
1. MODULATION – The capability to adjust or 6. Selecting a Writing Pattern
manipulate the resonance and timbre of vocal tone. - Structures that will help you organize the
2. ARTICULATION – Pronouncing the words and ideas related to your topic.
speaking with clear diction that effectively transmits
the message of the speaker. Different types of SPEECH WRITING PATTERNS
3. STAGE PRESENCE – The ability to own the stage, 1. Chronological. Historical or time approach like
able to fill the space and project his/her personality to from past to present
the audience. - (BIOGRAPHICAL SPEECH)
4. FACIAL EXPRESSIONS, GESTURES AND Example:
MOVEMENTS – without these non-verbal elements, Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire, the Boxer
the speaker may be judged as boring with flat delivery. Rebellion, or the Arab Spring, which covers the events that
5. RAPPORT WITH THE AUDIENCE - Ability to occurred in the order in which they happened.
deliver a speech that would appeal to the audience,
connection to audience. 2. Spatial or Geographical. Going from one place
to another, from one direction to another.
SPEECH WRITING PROCESS - (ENTERTAINING TRAVEL SPEECH)
1. AUDIENCE ANALYSIS
Demography age range, male-female 3. Causal. Involves a discussion of both cause and
ratio, educational effect of an issue.
background - (SPEECH RELATING CRIME RATE
Situation time, venue, occasion TO DRUG USE)
and size
Psychology values, beliefs, attitudes, 4. Problem-Solution. Explains a problem and
culture, preferences, suggest a possible solution.
Example:
Environmental Problem: What should we do to
2. GENERAL AND SPECIFIS PURPOSES
reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
GENERAL PURPOSE SPECIFIC PURPOSES
Solution 1: Use renewable energy to fuel your
To inform To inform Grade 11
home and vehicles.
students about the
Solution 2: Make recycling within local
importance of effective
communities mandatory.
communication skills in
all fields
To persuade To persuade Grade 11
students to develop their
communication skills
5. Topical/Categorical. Divides the topic into 10. CONCLUSION.
subtopics based on importance or interest value. ✓ Restates the main idea of your speech.
- (LOW TO HIGH IMPORTANCE ) ✓ It provides a summary, emphasizes the message, and
- (BROAD VISION TO SPECIFIC calls for action.
DETAILS)
✓Aims to leave the audience with a memorable statement.
The following are some strategies.
6. Comparison/Contrast. Presents comparison or
contrast of two or three points. ✓ Begin your conclusion with a restatement of your
- Comparing living status (Philippines VS. message.
Australia) ✓ Use positive examples, encouraging words, or
memorable lines from songs or stories familiar to your
7. Preparing an Outline. Organize the speech audience.
itself. ✓ Ask a question or series of questions that can make your
- The best method is an OUTLINE audience reflect or ponder.
11. Editing and Revising. involves correcting errors
in mechanics, such as grammar, punctuation,
capitalization, unity, coherence, and others.
8. INTRODUCTION.
- It is the foundation of your speech.
- Your primary goal is to get the attention of
your audience and present the subject or
main idea of your speech
The following are some strategies.
✓ Use a real-life experience and connect that experience
to your subject.
✓ Use practical examples and explain their connection to
your subject.
✓Start with a familiar or strong quote and then explain 12. Rehearsing. “Constant practice makes perfect.”
what it means.
✓ Use facts or statistics and highlight their importance to
your subject.
✓ Tell a personal story to illustrate your point.
9. BODY OF THE SPEECH. Provides
explanations, examples, or any details that can
help you deliver your purpose and explain the
main idea of your speech.
The following are some strategies to highlight your main
idea.
✓ Present real-life or practical examples
✓ Show statistics
✓ Present comparisons
✓ Share ideas from the experts
You might also like
- Narrative Report On Presentation of Ipcrf and Rpms of Grade One TeachersDocument8 pagesNarrative Report On Presentation of Ipcrf and Rpms of Grade One TeachersKriselle BañezNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextFrom EverandSpectrum Reading for Main Ideas and Details in Informational TextRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Humboldt On LanguageDocument30 pagesHumboldt On Languagemalcrowe100% (1)
- Oral PresentationDocument35 pagesOral Presentationmaegantrish543No ratings yet
- Final Presentation SkillsDocument26 pagesFinal Presentation SkillsFaculty of Economics Center for International AffairsNo ratings yet
- Oc11 Type of Speech According To Purpose and DeliveyDocument29 pagesOc11 Type of Speech According To Purpose and Deliveyapi-615586274No ratings yet
- 2ND Week 3 4Document15 pages2ND Week 3 4BUNNY GGUKNo ratings yet
- OCOM FTA ReviewerDocument5 pagesOCOM FTA ReviewerJulluis DagoNo ratings yet
- Planificacion Del 11C 1Document35 pagesPlanificacion Del 11C 1Lic. Astrid PalmaNo ratings yet
- Wa0066.Document6 pagesWa0066.Lic. Astrid PalmaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 TopicsDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Topicsmichael segundoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33 Speeches Revised and FinalDocument21 pagesLecture 33 Speeches Revised and Finalsnigdhavohra420No ratings yet
- English Creative Writing Paper 1 Checklist DbfsDocument5 pagesEnglish Creative Writing Paper 1 Checklist DbfsPan KNo ratings yet
- Planning Communication - I: Unit 1 - Verbal and Written CommunicationDocument8 pagesPlanning Communication - I: Unit 1 - Verbal and Written CommunicationParul KapoorNo ratings yet
- 2nd Oral-Com NotesDocument2 pages2nd Oral-Com Notesej bagayanNo ratings yet
- Oral. ComDocument5 pagesOral. ComADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- ExtramarksDocument12 pagesExtramarksSonali TripathiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Speech WritingDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Speech WritingJanice L. LangitNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesBusiness CommunicationRabia NaseemNo ratings yet
- Annual Planning AngieDocument17 pagesAnnual Planning AngieAngie VasquezNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Types of Speech According ToDocument3 pagesPurpose: Types of Speech According ToSolstice OshiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan NovDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Novapi-726071229No ratings yet
- Oral Communication - 4Document4 pagesOral Communication - 4JOYCE ENGARANNo ratings yet
- Ppt3 Types of Speeches Purpose DeliveryDocument21 pagesPpt3 Types of Speeches Purpose DeliveryEden DionisioNo ratings yet
- 1ST QTR Notes (Eng02)Document2 pages1ST QTR Notes (Eng02)Mikaella SantosNo ratings yet
- 3rd Finals ReviewerDocument25 pages3rd Finals Reviewercobra09182007No ratings yet
- Exploring The Essay Understanding An Opinion EssayDocument2 pagesExploring The Essay Understanding An Opinion EssayMichaela MamaradloNo ratings yet
- Formal Presentations - ETC - 3130004Document19 pagesFormal Presentations - ETC - 3130004sameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument25 pagesCommunicative CompetencealfonsosucabNo ratings yet
- 2q-Oralcomm Week16Document15 pages2q-Oralcomm Week16Aleigh Janrah OlivaNo ratings yet
- The Speech Writing Process HandoutDocument3 pagesThe Speech Writing Process HandoutRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- (10.11) - Buku Ajar LSFS-Fitria, Ika, Puput For SKP 2019Document7 pages(10.11) - Buku Ajar LSFS-Fitria, Ika, Puput For SKP 2019SudarmantoNo ratings yet
- Jamal Sir-Class 3 - L-3 - Oral ReportDocument52 pagesJamal Sir-Class 3 - L-3 - Oral ReportmahmudNo ratings yet
- Syllabus DesignDocument12 pagesSyllabus Designmalonamige20No ratings yet
- Paper PresentationDocument4 pagesPaper PresentationPrasad MaratheNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Communication Skills: Mr. Villamin's English ClassDocument27 pagesEnhancing Communication Skills: Mr. Villamin's English ClassJenny Pearl EmeterioNo ratings yet
- Tips For Effective Presentation Design and DeliveryDocument2 pagesTips For Effective Presentation Design and DeliveryJames Manrique100% (1)
- Structuring Your SpeechDocument37 pagesStructuring Your SpeechMirza Adwit RahmanNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingDocument42 pagesExplanation Text: Literacy Curriculum - WritingFatwa KhairaNo ratings yet
- Oral-Com - Act - 1 2Document3 pagesOral-Com - Act - 1 2Fria CariñoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER OralCommDocument3 pagesREVIEWER OralCommaaronmanlapaz4No ratings yet
- OCC Module 11Document13 pagesOCC Module 11Jessa Mae Neri Sardan100% (1)
- (FORMAT) Speech WritingDocument7 pages(FORMAT) Speech WritingDale QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Unificada UpdatedDocument1 pagePlantilla Unificada UpdatedMaría GaviriaNo ratings yet
- Case ReviewerDocument4 pagesCase ReviewerjulianaabelleraNo ratings yet
- OralComPresentation With VideosDocument36 pagesOralComPresentation With VideosPattBolijuanNo ratings yet
- SSLM Q1 Oral ComDocument8 pagesSSLM Q1 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- CRR Strand 1 Strategic Reading Handouts 2023Document11 pagesCRR Strand 1 Strategic Reading Handouts 2023Kathy MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Improving Your Skills: Listening Skills For PTE AcademicDocument4 pagesImproving Your Skills: Listening Skills For PTE AcademicSteven Gaurano100% (1)
- Lesson PLANDocument2 pagesLesson PLANWalton León EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Course General Topic Subtopics A1-1Document8 pagesCourse General Topic Subtopics A1-1Nata DaNo ratings yet
- 2q-Oralcomm Week13Document13 pages2q-Oralcomm Week13John Mario V. Reyes3180675No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan The MetisDocument2 pagesLesson Plan The Metisapi-726071229No ratings yet
- Different Types of Speeches According To Its ReviewrDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Speeches According To Its ReviewrAlfred QuintoNo ratings yet
- Seminars and Oral PresentationsDocument4 pagesSeminars and Oral Presentationsnajimhamidi0900No ratings yet
- Occ (Reviewer 2)Document3 pagesOcc (Reviewer 2)Aljeya EvanchezNo ratings yet
- 14 Story Telling Pedagogy DVKVDocument14 pages14 Story Telling Pedagogy DVKVHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- Bài thuyết trình tiếng anhDocument13 pagesBài thuyết trình tiếng anhHuyền MinhNo ratings yet
- Extemporaneous SpeakingDocument5 pagesExtemporaneous SpeakingkehlaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 English Oralcomm F Quarter 4 Week 4Document11 pagesGrade 12 English Oralcomm F Quarter 4 Week 4Geraldine FerrerasNo ratings yet
- The Academic Term PaperDocument2 pagesThe Academic Term PaperSitong LiuNo ratings yet
- Teaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentFrom EverandTeaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- DVB Scene33Document16 pagesDVB Scene33MAJLIS DAERAH KERIANNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Sample 2Document15 pagesAssessment 1 Sample 2Sam ChawlaNo ratings yet
- 08 August 2000 QSTDocument180 pages08 August 2000 QSTRudik Wid100% (1)
- What My Classroom Looks Like Sounds Like Feels LikeDocument3 pagesWhat My Classroom Looks Like Sounds Like Feels Likeapi-548817489No ratings yet
- Understanding Metaphorical Texts in Foreign LiteratureDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Metaphorical Texts in Foreign LiteratureNeuda LagoNo ratings yet
- Stylish XSS in Magento: When 'Style' Helps YouDocument9 pagesStylish XSS in Magento: When 'Style' Helps YouMSc Ashar Javed100% (1)
- SpringSoft Infotech Business Proposal 2021-22Document39 pagesSpringSoft Infotech Business Proposal 2021-22Satish RikhariNo ratings yet
- Simple Present, Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument18 pagesSimple Present, Simple Past and Present PerfectakbarNo ratings yet
- 10 Case StudiesDocument29 pages10 Case StudiesKr Chandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- ACP Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesACP Lesson Plan Templateapi-316651663No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Di PietroDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Di Pietroapi-303145564No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish GrammarrDocument3 pagesPractice Makes Perfect - Complete Spanish Grammarrgweber.gw6380No ratings yet
- Dairy Training de LavalDocument12 pagesDairy Training de LavalAmol PatilNo ratings yet
- Conditions That Hinder Effective CommunicationDocument456 pagesConditions That Hinder Effective CommunicationYohanes Masboi WidodoNo ratings yet
- Teacher ResumeDocument2 pagesTeacher Resumeapi-431676661No ratings yet
- Educ 105 BDocument18 pagesEduc 105 BGlaiza MabantaNo ratings yet
- Daemonolatreiae Libri TresDocument453 pagesDaemonolatreiae Libri TresIan Thomson100% (4)
- GMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Document7 pagesGMC India - Competition Timeline (Round 1)Rishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Mobile Technologies SecurityDocument16 pagesMobile Technologies SecurityGi Hyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Booklet N1 - Unit 1Document13 pagesBooklet N1 - Unit 1villameliNo ratings yet
- Graduate School Sorsogon City: Annunciation College of Bacon Sorsogon Unit, IncDocument2 pagesGraduate School Sorsogon City: Annunciation College of Bacon Sorsogon Unit, IncGapas Mary AnnNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 1 - 1Document33 pagesComputer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 1 - 1Ali MemonNo ratings yet
- Sample Template Idea ExemplarDocument3 pagesSample Template Idea ExemplarJaja VictorioNo ratings yet
- Two - Track Approach PresentationDocument32 pagesTwo - Track Approach PresentationDivine Grace Samortin89% (18)
- Serial ProgrammingDocument177 pagesSerial ProgrammingkristofwoutersNo ratings yet
- Tudor Fashion Case StudyDocument3 pagesTudor Fashion Case StudyDines Shinde100% (1)
- Taklimat Proposal DefenceDocument14 pagesTaklimat Proposal DefenceRabeya KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Hernandez #0727088 Library 202 Professor BuenaventuraDocument10 pagesJacqueline Hernandez #0727088 Library 202 Professor Buenaventuralib202No ratings yet