Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beee Exp-7 F
Beee Exp-7 F
Uploaded by
dineshrathore977018Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beee Exp-7 F
Beee Exp-7 F
Uploaded by
dineshrathore977018Copyright:
Available Formats
Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore
Department of Electronics & Communication Basic Electrical & Electronics
Engineering Engineering
(BT-104)
Experiment no.07
Date of Performance Date of Submission Grade obtained
Student’s Name Enrollment No Signature of Faculty
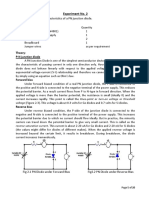
Objective: To Study and verify V-I characteristics of PN junction diode in:
1. Forward bias
2. Reverse bias
Apparatus required: -
1. Analog board of AB01.
2. DC power supplies +12V from external source or ST2612 Analog Lab.
3. Digital Multimeter (2 numbers).
Theory:
Introduction
A diode is an electrical device allowing current to move through it in one
direction with far greater ease than in the other. The most common type of
diode in modem circuit design is the semiconductor diode, although other
diode technologies exist. Semiconductor diodes are symbolized in schematic
diagrams as shown below.
Figure 1
When placed in a simple battery-lamp circuit, the diode will either allow or
prevent current through the lamp, depending on the polarity of the applied
voltage:
BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore
Department of Electronics & Communication Basic electrical & Electronics Engineering
Engineering (BT-104)
Figure 2
When the polarity of the battery is such that electrons are made to flow
through the diode, the diode is said to be forward-biased. Conversely, when
the battery is "backward" and the diode blocks current, the diode is said to be
reverse biased. A diode may be thought of as a kind of switch: "closed"
when forward-biased and "open" when reverse-biased.
The static voltage-current characteristics for a P-N Junction diode are shown
in figure 3.
Figure 3
Forward Characteristic:
When the diode is in forward-biased and the applied voltage is increased from
zero, hardly any current flows through the device in the beginning. It is so
because the external voltage is being opposed by the internal barrier voltage V B
whose value is 0.7V for Si and 0.3V for Ge. As soon as V B is neutralized, current
through the diode increases rapidly with increasing applied supply voltage. It is
found that as a little voltage of 1.0V produces a forward current of about 50mA.
Reverse Characteristic:
When the diode is reverse-biased, majority carrier are blocked and only a
small current (due to minority carrier) flows through the diode. As the
reverse voltage is increased from zero, the reverse current very quickly
reaches its maximum or saturation value Io which is also known as leakage
current. It is of the order of nano-amperes (nA) and microamperes (µA) for
Ge.
As seen from figure 3, when reverse voltage exceeds a certain value called
BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore
Department of Electronics & Communication Basic electrical & Electronics Engineering
Engineering (BT-104)
breakdown voltage VBR, the leakage current suddenly and sharply increases,
the curve indicating zero resistance at this point.
Circuit diagram:
Circuit used to plot different characteristics of Si diode is shown in figure 7.
Figure 4
Procedure:
Connect +12V DC power supplies at their indicated position from
external source or ST2612 Analog Lab.
To plot forward characteristics, proceed as follows
1. Rotate potentiometer P1 fully in CCW (counter clockwise direction).
2. Connect Ammeter between test point 2 and 8 to measure diode current ID
(mA).
3. Connect one voltmeter between test point 1 and 9 to measure voltage VD diode
4. Switch ‘On’ the power supply.
5. Vary the potentiometer P1 so as to increase the value of diode voltage
VD from zero to 1V in step and measure the corresponding values of
diode current ID in an observation Table 1.
6. Plot a curve between diode voltage V D and diode current ID as shown in
figure 3 (First quadrant) using suitable scale with the help of
observation Table 1. This curve is the required forward characteristics
BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore
Department of Electronics & Communication Basic electrical & Electronics Engineering
Engineering (BT-104)
of Si diode.
Observation Table 1:
Diode Diode current ID
S. No.
Voltage (VD) (mA)
1. 0.0V
2. 0.1V
3. 0.2V
4. 0.3V
5. 0.4V
6. 0.5V
7. 0.6V
8. 0.7V
9. 0.8V
10. 0.9V
11. 1.0V
To plot Reverse characteristics of a Si diode, proceed as follows
1. Rotate potentiometer P1 fully in CCW (counter clockwise direction).
2. Connect Ammeter between test point 3 and 8 to measure diode current ID (nA).
3. Connect one voltmeter between test point 1 and 9 to measure voltage VD diode
4. Switch ‘On’ the power supply.
5. Vary the potentiometer P1 so as to increase the value of diode voltage
VD from zero to 10V in step and measure the corresponding values of
diode current ID in an observation Table 2.
6. Plot a curve between diode voltage V D and diode current ID as shown in
figure 3 (third quadrant) using suitable scale with the help of
observation Table 2. This curve is the required forward characteristics
of Si diode.
Observation Table 2:
Diode Voltage
S. No. (VD) Diode current ID (nA)
1. 0.0V
2. 1.0V
3. 2.0V
4. 3.0V
5. 4.0V
6. 5.0V
7. 6.0V
BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore
Department of Electronics & Communication Basic electrical & Electronics Engineering
Engineering (BT-104)
8. 7.0V
9. 8.0V
10. 9.0V
11. 10.0V
RESULT:
The V-I Characteristics of the PN Junction Diode are plotted for the both Forward and
Reverse Bias conditions and Calculated the Cut in Voltage, Dynamic Forward and Reverse
Bias resistance.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Check the wires for continuity before use.
2. Keep the power supply at Zero volts before Start.
3. All the contacts must be intact.
QUESTIONS:
1. Draw the circuit symbol of the Diode?
2. What are the materials used for Anode and Cathode?
3. Draw ideal Diode Volt Ampere Characteristics?
4. What is Cut in Voltage?
5. Explain the working of a Diode as a switch.
BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
You might also like
- Honda Grom Service Manual 150117060710 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument266 pagesHonda Grom Service Manual 150117060710 Conversion Gate01 PDFLê Thành Nam75% (4)
- Climatronic GOLF 4Document2 pagesClimatronic GOLF 4Ionescu Cristina0% (2)
- Lab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesLab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsFasil EndalamawNo ratings yet
- EE Lab Manuls Fast NuDocument88 pagesEE Lab Manuls Fast NuMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Ditch Witch HT25 ManualDocument103 pagesDitch Witch HT25 ManualSara George100% (1)
- Step Less TransmissionDocument5 pagesStep Less TransmissionAsif ali H.Dhalayat100% (1)
- Lytte Instruktion VibraphoneDocument12 pagesLytte Instruktion Vibraphonepaulo silva100% (1)
- Beee Exp-8 FDocument5 pagesBeee Exp-8 Fdineshrathore977018No ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objective: Study of Characteristics of Silicon DiodeUday BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Exp 45Document11 pagesExp 45tanmay sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesElectronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ex 305Document51 pagesEx 305DineshKumarCholkarNo ratings yet
- Exp111 ManualDocument58 pagesExp111 ManualTapan JainNo ratings yet
- EN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesEN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab FileDocument39 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab Filesudipchatterjee059No ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE552Document50 pagesLab Manual EE552s.r.No ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryDocument53 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryKaryampudi RushendrababuNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 3Document9 pagesEDC Lab 3Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocument34 pagesKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsLab - Manual March2010Document64 pagesElectronicsLab - Manual March2010pnarendrareddy.mscNo ratings yet
- Study of Diode CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesStudy of Diode CharacteristicsBhavyaNo ratings yet
- Lab Task Exp-1,2,3Document9 pagesLab Task Exp-1,2,3Ashish patelNo ratings yet
- Expt 3 - Diode CharaDocument5 pagesExpt 3 - Diode Charaokay gNo ratings yet
- LAB1 - Basic of Diode Zener Diode and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesLAB1 - Basic of Diode Zener Diode and ApplicationsjamiNo ratings yet
- LAB1 - Adib EqalDocument15 pagesLAB1 - Adib EqalAdib BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- Ed - Exp - 1 - Student - Manual - 2Document4 pagesEd - Exp - 1 - Student - Manual - 2fahimsahriar200No ratings yet
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDocument27 pagesElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512No ratings yet
- 1-Diode Characteristics and Rectifier CircuitsDocument17 pages1-Diode Characteristics and Rectifier CircuitsAnjan SenguptaNo ratings yet
- EDC 3rd SemDocument52 pagesEDC 3rd Semvijay kumar100% (1)
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsDocument11 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsTalha RiazNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- Lab reportTTDocument13 pagesLab reportTTPaa Kwesi ArhinfulNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Diode CharacteisticsDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 Diode CharacteisticsAbral QureshiNo ratings yet
- PN Zenernv6501Document47 pagesPN Zenernv6501Madhur Patidar0% (1)
- EEE 111 Lab Manual 1Document4 pagesEEE 111 Lab Manual 1SHADOW manNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocument61 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualFadila IsmailNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Ee2207 Electronic Devices and Circuits Laboratory (Revised)Document54 pagesList of Experiments: Ee2207 Electronic Devices and Circuits Laboratory (Revised)prakashkumarNo ratings yet
- Eee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Document32 pagesEee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Ismot Jahan MoniNo ratings yet
- 15e282 18 Lab1Document10 pages15e282 18 Lab1shahid aliNo ratings yet
- EEE111+ (Exp+1) +I v+Characteristics+of+DiodeDocument4 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+1) +I v+Characteristics+of+DiodeFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- 2-1 EDC Lab Manual Jntuk R20 - 201021Document96 pages2-1 EDC Lab Manual Jntuk R20 - 201021Durgasaiteja923 SunnyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualDocument77 pagesElectronic Devices - Circuits Lab ManualpdnkiranNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics PDFDocument16 pagesDiode Characteristics PDFJOECELLE ABLEGINANo ratings yet
- Elce221 Lab 1Document6 pagesElce221 Lab 1Little VoiceNo ratings yet
- Lab 7: Diode Circuits: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLab 7: Diode Circuits: Objectivesbesma bechir grabaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)Document12 pagesLaboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)nikunj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Device Exp 1 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDevice Exp 1 Student Manualgg ezNo ratings yet
- PHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationDocument3 pagesPHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationNurul Naafizah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- BasicElectronics1 Expt10Document3 pagesBasicElectronics1 Expt10H Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Devices Exp 1 - Determination of Characteristic Curve of A DiodeDocument13 pagesElectrical Devices Exp 1 - Determination of Characteristic Curve of A Diodeivy.faraezi15No ratings yet
- Zener Diode CharacteristicsDocument1 pageZener Diode CharacteristicsPercivalEgauNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 3Document8 pagesExperiment - 3arihant gargNo ratings yet
- Edc Studentmanual 16-17Document90 pagesEdc Studentmanual 16-17balasubramanyam200517No ratings yet
- Exp-A2 230224 110136 PDFDocument5 pagesExp-A2 230224 110136 PDFKashish GoyalNo ratings yet
- How To Perfrom PN Diode CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesHow To Perfrom PN Diode CharacteristicskrishnaNo ratings yet
- LAB 9 EE NewDocument9 pagesLAB 9 EE NewtengyanNo ratings yet
- Sir CollgeDocument81 pagesSir CollgemookambigaNo ratings yet
- EC6361 Electronics LaboratoryDocument97 pagesEC6361 Electronics LaboratoryBaskarNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Document18 pagesBASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Mr SpamNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryDocument13 pagesExperiment No. 1: Aim: TheoryAyushiNo ratings yet
- 15E282 18lab1Document10 pages15E282 18lab1Yadhuvanth kumarNo ratings yet
- ZeshanDocument5 pagesZeshanMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- EX # 2 (PN Diode)Document7 pagesEX # 2 (PN Diode)manishNo ratings yet
- C-20 P e Practicle ComletetDocument80 pagesC-20 P e Practicle Comletetamrutha cNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Customer Detail & Data!Document52 pagesCustomer Detail & Data!TaufikNo ratings yet
- GMV-PDM Series Modular ManualDocument40 pagesGMV-PDM Series Modular ManualJuanita Pardo MirandaNo ratings yet
- 107 HP, 380V, 3Ø, Y-D Duplex, Sump Pump, 208amp.1 UnitDocument2 pages107 HP, 380V, 3Ø, Y-D Duplex, Sump Pump, 208amp.1 UnitJose Lorenzo RefelinoNo ratings yet
- 1 PN Junction PDFDocument4 pages1 PN Junction PDFAbhishekh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Blank BOLDocument1 pageBlank BOLIan RockymoreNo ratings yet
- Display DevicesDocument25 pagesDisplay DevicesReyansh RoyNo ratings yet
- MPI Report 012 5inch DP Elevator A109-1Document1 pageMPI Report 012 5inch DP Elevator A109-1John DolanNo ratings yet
- Nte 943Document5 pagesNte 943LUDWINGNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Reactive Power Control: Code: EEE 574Document34 pagesVoltage and Reactive Power Control: Code: EEE 574Fuh Vallery100% (1)
- Diodes Thyristors TransistorsDocument19 pagesDiodes Thyristors TransistorsJayloyd LaraNo ratings yet
- IED-G Manual - ENG (20140922)Document163 pagesIED-G Manual - ENG (20140922)siegfriedNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts & ApplicationsDocument1,875 pagesComputer Concepts & ApplicationsCBSE UGC NET EXAMNo ratings yet
- Rtlo 20913a 0711Document34 pagesRtlo 20913a 0711David J LopezNo ratings yet
- Doc.08.99.01C 2125.sti H-250 V.04 DNC - EN 01CDocument21 pagesDoc.08.99.01C 2125.sti H-250 V.04 DNC - EN 01CMarcos SerrãoNo ratings yet
- TCL Chassis nx56 181 PDFDocument81 pagesTCL Chassis nx56 181 PDFcristi_drgNo ratings yet
- ANSI Device NumbersDocument7 pagesANSI Device Numbersrajpre1213100% (1)
- Flexi CompleteDocument4 pagesFlexi Completeapi-84701884No ratings yet
- Tps-Sch-Bd-Me-Ge-El-0001-A - Cable ScheduleDocument5 pagesTps-Sch-Bd-Me-Ge-El-0001-A - Cable ScheduleBalamurugan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Dk51280-1103a-33t (DP60P5S)Document221 pagesDk51280-1103a-33t (DP60P5S)agus marsito83% (6)
- 2016 Mercedes-Benz CLS 250 D WagonDocument2 pages2016 Mercedes-Benz CLS 250 D WagonFORM700No ratings yet
- FSO Biweekly W#12 PM PLDocument5 pagesFSO Biweekly W#12 PM PLabahaangNo ratings yet
- Very Simple Icroprocessor Anuary: Etienne - Sicard@Document28 pagesVery Simple Icroprocessor Anuary: Etienne - Sicard@Prakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Manual BotoneraDocument1 pageManual BotoneraCCNI, S.A.No ratings yet
- Arteche CT Sdo Oct enDocument12 pagesArteche CT Sdo Oct enRafael GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Software Platform & Architecture For TelematicsDocument52 pagesChapter 3: Software Platform & Architecture For TelematicsRajarathinakumar RajaNo ratings yet