Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Management Note
Project Management Note
Uploaded by
Nsidibe Etim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageOriginal Title
Project management note (30)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageProject Management Note
Project Management Note
Uploaded by
Nsidibe EtimCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
• Providing specific measurements for quality assurance
• Providing recommendations for corrective and preventive actions
• Implementing approved changes as directed by the project’s integrated change control
system.
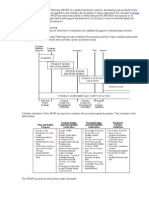
Monitor the Project Quality:
Project managers use quality control focus on project inputs, processes, and outputs. When
considering inputs, a project manager wants to ensure that the assigned people can do their
work. They also work with suppliers to ensure that materials, information, and other inputs
meet the required specifications and perform satisfactorily.
When considering the project processes, the manager wants to minimize rework because it
wastes time, effort, and money, which are in short supply on most projects.
Rework also often has negative impacts on both worker morale and stakeholder relations
because it is very discouraging to make and/or receive an inferior product, even if it is fixed
eventually.
When considering outputs, a project manager may first use internal inspection to ensure the
performance of deliverables before they are sent to the customer.
External inspection may also be required to convince the customer that the deliverables are
developed to meet the desired performance.
While the specifics vary greatly from project to project, there are some useful general lessons
regarding the timing and types of project inspections, including the following:
• Conduct an inspection before a critical or expensive process to make sure the inputs
are good before spending a large amount of money or time on them.
• Process stages in which one worker hands off work to another worker are good times
for both the workers to conduct inspections.
• Milestones identified in the project charter provide good inspection points.
• As practiced in software development, think of an inspection in terms of units
(individual components), integration (how components work together), and the
system (how the deliverable performs).
Quality Control Terms:
Prevention versus Inspection:
Prevention is keeping errors out of a process, while inspection is trying to find errors after they
occur to correct these errors before they reach the customer. Preventing a problem in the first
place is preferred over inspecting it to find a problem. Prevention is the cheaper alternative.
You might also like
- The Strong Breed - Wole SoyinkaDocument20 pagesThe Strong Breed - Wole SoyinkaNsidibe Etim100% (4)
- BridgeDocument25 pagesBridgeamit kandpalNo ratings yet
- Hotel Quality Control PlanDocument21 pagesHotel Quality Control PlanVo Kien Cuong100% (5)
- Project Quality ManagementDocument4 pagesProject Quality ManagementSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Quality AssuranceDocument22 pagesQuality Control and Quality AssurancejswldeepNo ratings yet
- Timber Framing PDFDocument32 pagesTimber Framing PDFNsidibe Etim50% (4)
- Church PlantingDocument167 pagesChurch PlantingNsidibe Etim100% (2)
- Project Management (Project Control Concept)Document31 pagesProject Management (Project Control Concept)joseph100% (1)
- PROJECT QUALITY ManagementDocument10 pagesPROJECT QUALITY ManagementAbdallah BehriNo ratings yet
- Project ControlDocument24 pagesProject ControlMajedNo ratings yet
- Project ControlDocument13 pagesProject ControlsibtikhokharNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument32 pagesProject Quality ManagementLemark R.0% (1)
- May 28 20 QA QCDocument172 pagesMay 28 20 QA QCChristine PaulineNo ratings yet
- SPM Lec#09Document13 pagesSPM Lec#09saleem janNo ratings yet
- Q-4 What Are The Various Steps in Project Monitoring andDocument3 pagesQ-4 What Are The Various Steps in Project Monitoring andbhavin1234567No ratings yet
- CH 11Document29 pagesCH 11MajedNo ratings yet
- Design Validation and Verification PDFDocument31 pagesDesign Validation and Verification PDFgauravkumar bhandariNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring, Evaluation, and Control: Establishing StandardsDocument13 pagesProject Monitoring, Evaluation, and Control: Establishing StandardsClement Ader SekouNo ratings yet
- Project - TQM - Inspection ManagementDocument19 pagesProject - TQM - Inspection ManagementVarsha PraburamNo ratings yet
- Software Inspections: BITS PilaniDocument12 pagesSoftware Inspections: BITS PilanihameethaNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesDocument56 pagesConstruction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesGireesh Gowda GiriNo ratings yet
- Itpm Chapter EightDocument25 pagesItpm Chapter EightMisale FelemaNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesProject Quality ManagementPaul AllenNo ratings yet
- KARTE 04 Installation, Commissioning and TestingDocument41 pagesKARTE 04 Installation, Commissioning and TestingTusenkrish100% (2)
- 13 Project ControlDocument43 pages13 Project Controlpranav guptaNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 3 Project ManagementDocument20 pagesNotes Unit 3 Project ManagementAvni SharmaNo ratings yet
- MEC-7 QualityDocument9 pagesMEC-7 QualityHurram RajaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document5 pagesAssignment 4Aamir MansuriNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Management 05Document28 pagesSoftware Quality Management 05tesfanesh 65tgNo ratings yet
- Topic: Managing A Project From An Idea To ImplementationDocument10 pagesTopic: Managing A Project From An Idea To Implementationsaim raza arif100% (2)
- Week-11 Lecture 21-22Document40 pagesWeek-11 Lecture 21-22Rafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Project Management Leadership EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesProject Management Leadership EntrepreneurshipJane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Engineering, Management and Society Ii CIE:522, EGM 502: Monitoring and Controlling OperationsDocument53 pagesEngineering, Management and Society Ii CIE:522, EGM 502: Monitoring and Controlling OperationsPenelope MalilweNo ratings yet
- Terotechnology SummaryDocument9 pagesTerotechnology SummaryWichard BendixNo ratings yet
- QA - QC Plan For PEP 13-03-2017Document16 pagesQA - QC Plan For PEP 13-03-2017osersNo ratings yet
- S. Jannet Lydia P. Thanga VarshiniDocument10 pagesS. Jannet Lydia P. Thanga VarshiniThanga VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Proj Implementation - ControllingDocument72 pagesProj Implementation - ControllingBhawesh SthaNo ratings yet
- 08 Project Performance DomainsDocument9 pages08 Project Performance DomainsShivansh TulsyanNo ratings yet
- All Tools in OneDocument38 pagesAll Tools in Oneom_3334No ratings yet
- Preparing For Successful Design TransferDocument7 pagesPreparing For Successful Design TransferRahul Dhingra100% (1)
- Software Quality Unit 6 SEDocument12 pagesSoftware Quality Unit 6 SEsrishtisrivastava947No ratings yet
- SE - UNIT3 Part2 PDFDocument83 pagesSE - UNIT3 Part2 PDFPrathamesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8-Construction Project Quality ManagementDocument29 pagesLecture 8-Construction Project Quality ManagementjbjuanzonNo ratings yet
- Quality Planning Management - Summary NotesDocument13 pagesQuality Planning Management - Summary NotesGeorge NjolomaNo ratings yet
- PMP Study NotesDocument24 pagesPMP Study Notesmpbs100100% (2)
- Test ManagementDocument11 pagesTest ManagementMuzammil BalochNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument21 pagesSupply Chain ManagementMacy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Quality& Safety: Construction Management: School of Architecture, S.B.S.S.T.C. FRZDocument8 pagesQuality& Safety: Construction Management: School of Architecture, S.B.S.S.T.C. FRZManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Cost of QDocument6 pagesCost of QManisha Bansal PaulNo ratings yet
- QldaDocument1 pageQldaAnh Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal 2Document5 pagesReflective Journal 2suhasana0305No ratings yet
- Project AuditDocument14 pagesProject AuditKalyan RaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Project Management: MBA - II Section - ADocument20 pagesAssignment On Project Management: MBA - II Section - Adilip_maniyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Construction Project Quality ManagementDocument34 pagesLecture 7-Construction Project Quality ManagementLouise LuyNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance ProjectDocument4 pagesQuality Assurance Projectcharleshutabara951No ratings yet
- PDF Lesson 1 ExamplesDocument6 pagesPDF Lesson 1 ExamplesErwin ObenzaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions ManualDocument40 pagesProject Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manualrowenathuyzdwqr100% (28)
- Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1St Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesProject Management Process Technology and Practice 1St Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFpaulphelanjan100% (13)
- Software Quality AssuranceDocument30 pagesSoftware Quality Assuranceaishdesai31No ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- CPHR HR TextbooksDocument1 pageCPHR HR TextbooksNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Bijan Fazlollahi - Strategies For Ecommerce Success-IRM Press (2002) PDFDocument352 pagesBijan Fazlollahi - Strategies For Ecommerce Success-IRM Press (2002) PDFNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Project Management NoteDocument1 pageProject Management NoteNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Preparing HDG For Paint - American Galvanizers AssociationDocument5 pagesPreparing HDG For Paint - American Galvanizers AssociationNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Prevent Thin and - or Flaking - American Galvanizers AssociationDocument3 pagesPrevent Thin and - or Flaking - American Galvanizers AssociationNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Astm A1055Document9 pagesAstm A1055Nsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Galvanizing Copper Containing - American Galvanizers AssociationDocument2 pagesGalvanizing Copper Containing - American Galvanizers AssociationNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Phenoline 385 PDSDocument5 pagesPhenoline 385 PDSNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Effects of Adding Pure or Scrap - American Galvanizers AssociationDocument2 pagesEffects of Adding Pure or Scrap - American Galvanizers AssociationNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet
- Timber Frame Design Florida Workshop PDFDocument151 pagesTimber Frame Design Florida Workshop PDFNsidibe EtimNo ratings yet