Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Language Milestones Rhea Paul 02
Language Milestones Rhea Paul 02
Uploaded by
e.sepulvedaferradaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Language Milestones Rhea Paul 02
Language Milestones Rhea Paul 02
Uploaded by
e.sepulvedaferradaCopyright:
Available Formats
Syntax Phonology
0-2 mo—vegetative sounds
2-4 mo—cooing, laughing
4-6 mo—quasi-resonant nuclei, vocal play
6-10 mo—canonical, reduplicated babbling-CV syllables
Jargon babble with intonation contours of language being learned
First50 words
• Most often have CV shape
• Use same consonants used in early babbling
• Use of reduplication, syllable deletion, assimilation, and
final consonant deletion is common
• Words are selected or avoided for expression based on
favored and avoided sounds
Brown’s Stage I: Basic Semantic Roles and Relations By 24 mo, 9-10 initial and 5-6 final consonants are used
Two-word utterances emerge Speech is 50% intelligible
Word order is consistent 70% of consonants are correct
Utterances are “telegraphic” with few grammatical markers CVC and two-syllable words emerge
Brown’s Stage II: Grammatical Morphemes Awareness of rhyme emerges
Early emerging acquisition: -ing in, on, plural /s/
Use of no, not, can’t, don’t as negation between subject and verb
Questions formed with rising intonation only
Sentences with semi-auxiliaries gonna, wanna, gotta, hafta appear
Brown’s Stage III: Modulation of Simple Sentences Speech is 75% intelligible at 36 mo
Present tense auxiliaries appear (can, will) Ability to produce rhyme emerges
Be verbs used inconsistently
Overgeneralized past-tense forms appear
Brown’s Stage IV: Emergence of Embedded Sentences Use of reduplication, syllable deletion, assimilation, and final consonant
First complex sentence forms appear deletion is less common
Auxiliary verbs are placed correctly in questions and negatives Use of stopping, fronting, cluster reduction, and liquid simplification
Irregular past tense, articles (a, the), possessive (‘s) acquired continues
Brown’s Stage Late IV–Early V Use of cluster reduction decreases
Early emerging complex sentence types, including the following:
• Full prepositional clauses
• Wh- clauses
• Simple infinitives
• Conjoined
Brown’s Stage V Speech is 100% intelligible
Later developing morphemes acquired, including the following: Ability to segment words into syllables emerges
• Be verbs Use of most simplification processes stops; errors on /s/, /r/, /l/, th may
• Regular past persist
• Third person /s/
Past-tense auxiliaries used
• Relative clauses (right branching)
• Infinitive clauses with different subjects
• Gerund clauses
• Wh- infinitive clauses
Basic sentence forms acquired
You might also like
- Speech & Language Development ChartDocument10 pagesSpeech & Language Development ChartYi Ting100% (3)
- Nadina Visan SyntaxDocument374 pagesNadina Visan Syntaxgallivant100% (3)
- Skillful 4 RW TB Unit 1 PDFDocument10 pagesSkillful 4 RW TB Unit 1 PDFAbdikarim Mohamed Mohamoud100% (1)
- A Textbook of Translation - Peter Newmark 1964 - SUMMARYDocument22 pagesA Textbook of Translation - Peter Newmark 1964 - SUMMARYNanang Sharifudin50% (6)
- Anitas Strange DayDocument3 pagesAnitas Strange DayFrancesca Rossi RossiNo ratings yet
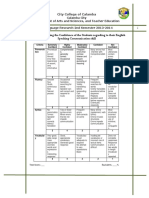
- Rubrics in Assessing The Confidence of The Students Regarding To Their English Speaking Communication SkillDocument1 pageRubrics in Assessing The Confidence of The Students Regarding To Their English Speaking Communication SkillJerwin Patiga100% (1)
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument4 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyKamolpan JammapatNo ratings yet
- Phonics Emmanuel Parent WorkshopDocument21 pagesPhonics Emmanuel Parent Workshopapi-358348442No ratings yet
- LINB10 Week 8 Slides PDFDocument44 pagesLINB10 Week 8 Slides PDFMorgan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Aligns With The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) From Kindergarten To Grade 5 For English Language ArtsDocument8 pagesAligns With The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) From Kindergarten To Grade 5 For English Language ArtsKhuc Huong TraNo ratings yet
- Reading Stages CharacteristicsDocument1 pageReading Stages CharacteristicsvippNo ratings yet
- KEN2570 2 MorphologyDocument22 pagesKEN2570 2 MorphologyGibi GibiNo ratings yet
- Stephanie Thomas Module 6Document16 pagesStephanie Thomas Module 6api-741496929No ratings yet
- Explicit Phonics Mini Lesson CST November 2016Document35 pagesExplicit Phonics Mini Lesson CST November 2016api-353255943No ratings yet
- MorphemeDocument5 pagesMorphemenasyratul100% (2)
- Syllabe TypesDocument18 pagesSyllabe TypesEmmanuel Ruiz SantanaNo ratings yet
- Effective Interventions For Word Decoding and Reading ComprehensionDocument31 pagesEffective Interventions For Word Decoding and Reading ComprehensionLuz Maria LavalleNo ratings yet
- English Grammar in Discourse I - Word ClassesDocument16 pagesEnglish Grammar in Discourse I - Word ClasseshhNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN - CompositionDocument4 pagesLESSON PLAN - CompositionRashida MaynardNo ratings yet
- T RNSX 5 SXD4 Ed T9 V Z3 X 2 Uc RZCil OAFZo An CLRDocument43 pagesT RNSX 5 SXD4 Ed T9 V Z3 X 2 Uc RZCil OAFZo An CLRbaji sharifNo ratings yet
- Branches of Linguistics ExplanationDocument7 pagesBranches of Linguistics ExplanationJaime GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 19 Notes - Phoneme RecognitionDocument37 pages19 Notes - Phoneme RecognitionBebeNo ratings yet
- Gesta Fitz Marie pw5 3Document3 pagesGesta Fitz Marie pw5 3api-659880923No ratings yet
- Lec 1Document14 pagesLec 1Zaira ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Phonics Progression Eyfs KS1 KS2 Year 1 Year 2 YR3 YR4 YR5 YR6Document12 pagesPhonics Progression Eyfs KS1 KS2 Year 1 Year 2 YR3 YR4 YR5 YR6eddie zhouNo ratings yet
- Reading Innovations International Part 3 (Innovations in Reading Materials)Document58 pagesReading Innovations International Part 3 (Innovations in Reading Materials)Sandy LagataNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Speaking RubricDocument1 pageInterpersonal Speaking RubricEuropodians CoursesNo ratings yet
- Lec NLP 01 2015Document107 pagesLec NLP 01 2015B2No ratings yet
- Morphology 3Document27 pagesMorphology 3Veronica BulacioNo ratings yet
- Phoneme Cards: Teaching ResourceDocument25 pagesPhoneme Cards: Teaching ResourceFarooq Butt100% (1)
- Scholastic Reading Assessments (Short & Long Vowels, Digraphs)Document52 pagesScholastic Reading Assessments (Short & Long Vowels, Digraphs)Kendra WongNo ratings yet
- Outline 5 - FARKAS PDFDocument6 pagesOutline 5 - FARKAS PDFAlexis GogoașăNo ratings yet
- Leading The Teaching of Literacy: All About Jolly GrammarDocument31 pagesLeading The Teaching of Literacy: All About Jolly GrammarRima Bosco100% (1)
- Tema 24 The Expression of Assertion, Emphasis and ObjectionDocument6 pagesTema 24 The Expression of Assertion, Emphasis and ObjectionCarlotaJardónJuaniNo ratings yet
- Literacy in The Primary GradesDocument48 pagesLiteracy in The Primary Gradesapi-506099136100% (1)
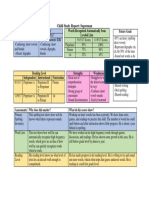
- Progress ReportDocument1 pageProgress Reportapi-404089004No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document10 pagesLesson 1Peter VisuwasamNo ratings yet
- Joann Phonemic Awareness Phonics FluencyDocument82 pagesJoann Phonemic Awareness Phonics FluencyEvelinaNo ratings yet
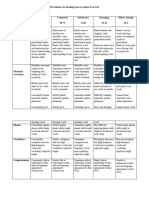
- Reading Rubric Infant 1&2Document2 pagesReading Rubric Infant 1&2alanamaharaj20No ratings yet
- Natural Language Processing Applications: Fabienne Venant Université Nancy2 / Loria 2008/2009Document123 pagesNatural Language Processing Applications: Fabienne Venant Université Nancy2 / Loria 2008/2009praval84No ratings yet
- Spanish and English OrthographyDocument1 pageSpanish and English OrthographychemlordNo ratings yet
- Eslb4034 Phonetics and Phonology Eslb2083 English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesEslb4034 Phonetics and Phonology Eslb2083 English Phonetics and PhonologyXavier David AlleriaNo ratings yet
- Rubric Post-Test RevisiDocument5 pagesRubric Post-Test Revisi11A IndahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language DevelopmentDocument7 pagesTheories of Language DevelopmentTamamaNo ratings yet
- Band 4 (Excellent) 3 (Good) 2 (Poor) 1 (Very Poor) Criteria 1. Pronunciation (Stress)Document2 pagesBand 4 (Excellent) 3 (Good) 2 (Poor) 1 (Very Poor) Criteria 1. Pronunciation (Stress)Lilah Blair100% (2)
- Letters and SoundsDocument32 pagesLetters and Soundsmohammed el erianNo ratings yet
- Letters and SoundsDocument32 pagesLetters and Soundsanna39No ratings yet
- Expo - L'IVDocument13 pagesExpo - L'IVCarolina Flores BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Aula 01 - Meta Language of PhonicsDocument7 pagesAula 01 - Meta Language of PhonicsLeyla AugustoNo ratings yet
- Engl 103Document1 pageEngl 103heartgeoligao13No ratings yet
- How To Go About A Phonemic TranscriptionDocument2 pagesHow To Go About A Phonemic TranscriptionLudmila SeráficaNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Grammar and Punctuation Practice Test PackDocument30 pagesYear 6 Grammar and Punctuation Practice Test Packeng.reham.maher.mNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument41 pagesMorphologyaditya Dutt RaiNo ratings yet
- Course Outline English 2Document5 pagesCourse Outline English 2Noah AnecodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Word-StructureDocument30 pagesLecture 2 Word-StructureАліна ГарникNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Written Text As A Connected DiscourseDocument25 pagesLesson 1. Written Text As A Connected Discoursecstruamero.2002044.chasnNo ratings yet
- Moldova University of European Studies Department of Foreign LanguagesDocument8 pagesMoldova University of European Studies Department of Foreign LanguagesDorinutza PopaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - PhonologyDocument44 pagesChapter 3 - PhonologyMinh Thành NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Morpheme Criteria: Car Garb Break Er ErDocument15 pagesMorpheme Criteria: Car Garb Break Er ErNajwa AlmazroeiNo ratings yet
- Key Terminology Needed For Eng Lit and LangDocument2 pagesKey Terminology Needed For Eng Lit and LangBeheshtaNo ratings yet
- 01 OverviewDocument20 pages01 OverviewJet SalunoyNo ratings yet
- Rubric 6th - Hoja 1Document2 pagesRubric 6th - Hoja 1Poleth DrummerNo ratings yet
- Causality and Subjectivity: The Causal Connectives of Modern Greek Eliza KitisDocument45 pagesCausality and Subjectivity: The Causal Connectives of Modern Greek Eliza Kitisbella_anutza91No ratings yet
- Relative Clause: The Relative Pronouns Are: Pronouns Usage ExamplesDocument10 pagesRelative Clause: The Relative Pronouns Are: Pronouns Usage ExamplesdctfvghjNo ratings yet
- Future Tense AldoDocument7 pagesFuture Tense AldoAldo setiawanNo ratings yet
- Junior Quiz BeeDocument4 pagesJunior Quiz BeeMichael James A. DaligdigNo ratings yet
- Norma Iso de BombasDocument128 pagesNorma Iso de BombasFelipe Miguel GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Engl111 BSN 7Document4 pagesReviewer Engl111 BSN 7priya garciaNo ratings yet
- Lexical Functional Grammar Peter K AustinDocument32 pagesLexical Functional Grammar Peter K Austindenis5555No ratings yet
- Defining Relative ClausesDocument2 pagesDefining Relative ClausesDard TongNo ratings yet
- Janhunen, Juha A. MongolianDocument336 pagesJanhunen, Juha A. MongolianFernando SantosNo ratings yet
- A Grammar of Teiwa by Marian KlamerDocument558 pagesA Grammar of Teiwa by Marian Klamerდავით იაკობიძე100% (1)
- Week 4 EBS 282 Finite and Non Finite ClausesDocument26 pagesWeek 4 EBS 282 Finite and Non Finite ClausesDeva 123No ratings yet
- Quia - Check Your Knowledge of GrammarDocument7 pagesQuia - Check Your Knowledge of GrammarDavinia LongoNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Students - BookDocument214 pages6.5 Students - Bookbai postNo ratings yet
- Book Research EnglishDocument520 pagesBook Research EnglishMuhammad Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- BilalDocument37 pagesBilalpswazirabadsaddarNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument71 pagesNarrative ReportMary Jane LausNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Analysis of Imran Khan's Speech: A Study Based On SFGDocument7 pagesInterpersonal Analysis of Imran Khan's Speech: A Study Based On SFGAJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- 1 Eng 111Document144 pages1 Eng 111Goodnews AntaiNo ratings yet
- Tsuda Review 057 20121130 067-094 HarshbargerDocument28 pagesTsuda Review 057 20121130 067-094 Harshbargerxong queenNo ratings yet
- Clauses Grammar For Unit OneDocument9 pagesClauses Grammar For Unit OneYohnXballsNo ratings yet
- MIdterm Exam in EAPPDocument7 pagesMIdterm Exam in EAPPRalph Jessie Siva CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Grammar For Academic Writing Ism 1Document10 pagesGrammar For Academic Writing Ism 1keeyanNo ratings yet
- Investigations in Cognitive GrammarDocument8 pagesInvestigations in Cognitive GrammarrioNo ratings yet
- English Adverbial ClausesDocument13 pagesEnglish Adverbial ClausesJoele1511No ratings yet
- BCA Part-I (Semester I & II)Document22 pagesBCA Part-I (Semester I & II)Mrinal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Concessive ClauseDocument9 pagesUnit 5 - Concessive Clausedendu nphNo ratings yet