Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig Formulas
Trig Formulas
Uploaded by
Ragini JohariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig Formulas
Trig Formulas
Uploaded by
Ragini JohariCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig formulas
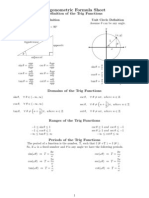
Trigonometric Ratio Formulas
sin θ = Perpendicular/Hypotenuse
cos θ = Base/Hypotenuse
tan θ = Perpendicular/Base
sec θ = Hypotenuse/Base
cosec θ = Hypotenuse/Perpendicular
cot θ = Base/Perpendicular
Reciprocal Identities
cosec θ = 1/sin θ; sin θ = 1/cosec θ
sec θ = 1/cos θ; cos θ = 1/sec θ
cot θ = 1/tan θ; tan θ = 1/cot θ
Pythagorean Identities
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
sec2θ - tan2θ = 1
csc2θ - cot2θ = 1
Trigonometric Ratio Table
Unit Circle Formulas
Co-function Identities(in Degrees)
sin(90° − x) = cos x
cos(90° − x) = sin x
tan(90° − x) = cot x
cot(90° − x) = tan x
sec(90° − x) = cosec x
cosec(90° − x) = sec x
Sum and Difference Identities
The sum and difference identities include the trigonometry formulas of sin(x + y), cos(x - y), cot(x + y),
etc.
sin(x + y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y)
cos(x + y) = cos(x)cos(y) - sin(x)sin(y)
tan(x + y) = (tan x + tan y)/(1 - tan x • tan y)
sin(x – y) = sin(x)cos(y) - cos(x)sin(y)
cos(x – y) = cos(x)cos(y) + sin(x)sin(y)
tan(x − y) = (tan x - tan y)/(1 + tan x • tan y)
Multiple and Sub-Multiple Angles
Trigonometry formulas for multiple and sub-multiple angles can be used to calculate the value of
trigonometric functions for half angle, double angle, triple angle, etc.
Half-Angle Identities
The half angle trigonometric formulas involve x/2 and are as follows.
sin (x/2) = ±√[(1 - cos x)/2]
cos (x/2) = ± √[(1 + cos x)/2]
tan (x/2) = ±√[(1 - cos x)/(1 + cos x)] (or) tan (x/2) = (1 - cos x)/sin x
Double Angle Identities
The double angle trigonometry formulas are used to find the double angle (2x) of trig functions.
sin (2x) = 2sin(x) • cos(x) = [2tan x/(1 + tan2 x)]
cos (2x) = cos2(x) - sin2(x) = [(1 - tan2 x)/(1 + tan2 x)] = 2cos2(x) - 1 = 1 - 2sin2(x)
tan (2x) = [2tan(x)]/ [1 - tan2(x)]
sec (2x) = sec2 x/(2 - sec2 x)
cosec (2x) = (sec x • cosec x)/2
Triple Angle Identities
The trip angle (3x) trig formulas are as follows:
sin 3x = 3sin x - 4sin3x
cos 3x = 4cos3x - 3cos x
tan 3x = [3tanx - tan3x]/[1 - 3tan2x]
Sum and Product Identities
Trigonometric formulas for sum or product identities are used to represent the sum of any two
trigonometric functions in their product form, or vice-versa.
Product to Sum Formulas
sinx⋅ cosy = [sin(x + y) + sin(x − y)]/2
cosx⋅ cosy = [cos(x + y) + cos(x − y)]/2
sinx⋅ siny = [cos(x − y) − cos(x + y)]/2
Sum to Product Formulas
The combination of two acute angles A and B can be presented through the trigonometric ratios, in
the below trigonometry formulas.
sinx + siny = 2[sin((x + y)/2)cos((x − y)/2)]
sinx − siny = 2[cos((x + y)/2)sin((x − y)/2)]
cosx + cosy = 2[cos((x + y)/2)cos((x − y)/2)]
cosx − cosy = −2[sin((x + y)/2)sin((x − y)/2)]
Inverse Trigonometry Formulas
Using the inverse trigonometry formulas, trigonometric ratios are inverted to create the inverse
trigonometric functions, like, sin θ = x and θ = sin −1x. Here x can have values in whole numbers,
decimals, fractions, and exponents.
sin-1 (-x) = -sin-1 x
cos-1 (-x) = π - cos-1 x
tan-1 (-x) = -tan-1 x
cosec-1 (-x) = -cosec-1 x
sec-1 (-x) = π - sec-1 x
cot-1 (-x) = π - cot-1 x
Sine and Cosine Laws
Sine Law: The sine law and the cosine law give a relationship between the sides and angles of a
triangle. The sine law gives the ratio of the sides and the angle opposite to the side. As an example,
the ratio is taken for the side 'a' and its opposite angle 'A'.
(sin A)/a = (sin B)/b = (sin C)/c
Cosine Law: The cosine law helps to find the length of a side, for the given lengths of the other two
sides and the included angle. As an example the length 'a' can be found with the help of the other two
sides 'b' and 'c' and their included angle 'A'.
a2 = b2 + c2 - 2bc cosA
b2 = a2 + c2 - 2ac cosB
c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab cosC
where, a, b, c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and A, B, C are the angles of the triangle.
You might also like
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument13 pagesTrigonometric Identitiesedgenuity dominoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Trigonometry 11th Edition by LialDocument43 pagesSolution Manual For Trigonometry 11th Edition by Liala731759159100% (1)
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument27 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsPrasanth VarrierNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas ListDocument6 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Listkarthik sivarajNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0Document16 pagesIit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0ARYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument5 pagesTRIGONOMETRYMuhamamad ZamanNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions (Edustudy Point) - UnlockedDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Functions (Edustudy Point) - Unlockedsayantannandi9e1roll21No ratings yet
- List of Trigonometry Formulas: Sine Law Cosine LawDocument8 pagesList of Trigonometry Formulas: Sine Law Cosine Lawt tNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Formulas: X X X X X XMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsDocument6 pagesSolutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsPreethiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and Formulas PDFDocument15 pagesTrigonometric Identities and Formulas PDFWagih NabilNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigonometryDocument1 page3 Trigonometrysarthak.kothiyal1576No ratings yet
- Tigonometry Abhas SainiDocument63 pagesTigonometry Abhas SainiAsh ManakNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Lesson Two: Introduction To TrigonometryDocument11 pagesTrigonometry: Lesson Two: Introduction To TrigonometryTimothy S. San JuanNo ratings yet
- TrigonometruyDocument3 pagesTrigonometruyRitu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and FormulasDocument7 pagesTrigonometric Identities and FormulasDeepak ReddyNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulaesDocument7 pagesTrigonometry FormulaesAshutosh AnandNo ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics - TrigonometryDocument12 pagesH2 Mathematics - TrigonometryMin YeeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)Document6 pagesTrigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)ambresh.09No ratings yet
- Mathematics???Document6 pagesMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Math SummaryDocument10 pagesMath SummaryMuadz Abdurrahman RifqiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions of Acute AnglesDocument23 pagesTrigonometric Functions of Acute Anglesbobby4028No ratings yet
- MATH2412-double Angle, Power Reducing, Half Angle Identities PDFDocument5 pagesMATH2412-double Angle, Power Reducing, Half Angle Identities PDFMuhammad Agus Nur SholehNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument13 pagesTrigonometryjobmajuneNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument15 pagesFormulaeProf. M. C. RajuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosDocument2 pagesMathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosSimran GillNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument19 pagesTrigonometryshwpna1979No ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument23 pagesTrigonometryTitis PohanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions QuestionsDocument27 pagesNCERT Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions QuestionsDouglas Beach100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Trigonometric Identitiesnafishahriar02No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and Inverse Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument6 pagesTrigonometric Identities and Inverse Trigonometric IdentitiesOlaf1234321No ratings yet
- Guia Estudio MendelDocument15 pagesGuia Estudio MendelEdward EceincoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities - PurplemathDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Identities - PurplemathIsi ObohNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewDocument27 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewkennedyNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains FormulasDocument17 pagesJee Mains FormulasdevenderNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDocument6 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFAparna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDocument6 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFSUBHADEEP GHOSH100% (2)
- Notes MathDocument4 pagesNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulaDocument3 pagesTrigonometry FormulaAJ Christian MalacapoNo ratings yet
- Opp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan TanDocument3 pagesOpp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan Tanchoosg100% (1)
- Quarter 3 Trig IdentitiesDocument5 pagesQuarter 3 Trig Identitiesapi-288610675No ratings yet
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument14 pagesIntroduction To TrigonometryRishabh Malhotra100% (1)
- TrignometryDocument12 pagesTrignometryVardaan ThakurNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument38 pagesTrigonometric Identitiesetamil87No ratings yet
- "Trigon" Triangle +"metry" Measurement Trigonometry: Review of Trigonometry For CalculusDocument10 pages"Trigon" Triangle +"metry" Measurement Trigonometry: Review of Trigonometry For CalculusAbdulaziz MohammedNo ratings yet
- SAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesSAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric Functionstomcantyyy100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Procurement PlanningDocument4 pagesProcurement PlanningRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Vision of Network: The Business of TodayDocument6 pagesVision of Network: The Business of TodayRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Skills Required For Hotel StaffDocument3 pagesSkills Required For Hotel StaffRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Nutrilite Fruit Drink MixDocument5 pagesNutrilite Fruit Drink MixRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Stress Management: Dr. Ragini Johari Professor, School of Management, Ansal Institute of Technology & ManagementDocument18 pagesStress Management: Dr. Ragini Johari Professor, School of Management, Ansal Institute of Technology & ManagementRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Communication Involves Interdependent PeopleDocument6 pagesInterpersonal Communication Involves Interdependent PeopleRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Telgi ScamDocument3 pagesTelgi ScamRagini JohariNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management CasesDocument14 pagesStrategic Management CasesRagini Johari0% (3)
- HR OutsourcingDocument22 pagesHR OutsourcingRagini Johari50% (4)
- Heron's Formula SolutionsDocument23 pagesHeron's Formula SolutionsAjayNo ratings yet
- T00rigonometryforblockrich PDFDocument236 pagesT00rigonometryforblockrich PDFangela100% (1)
- 1920 Unit 17 Area, Perimeter and Volume (Worksheet)Document14 pages1920 Unit 17 Area, Perimeter and Volume (Worksheet)Kogilan Bama DavenNo ratings yet
- Centroid Work Done in Stretching A Spring: y - Axis X y RDocument3 pagesCentroid Work Done in Stretching A Spring: y - Axis X y RMarche Sebastian100% (1)
- 11th Physics Unit 2 Book Back Questions Solutions English MediumDocument9 pages11th Physics Unit 2 Book Back Questions Solutions English MediumMohana UMNo ratings yet
- 3 - Motion in One DimensionDocument19 pages3 - Motion in One DimensionRitesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Area, VolumeDocument8 pagesArea, VolumeMyla Nazar OcfemiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Angles and Angle MeasureDocument4 pages04 - Angles and Angle MeasureRolando QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Trigo FunctionsDocument14 pagesDerivatives of Trigo FunctionsMaria Jelyn EbdalinNo ratings yet
- CSEC Mathematics June 2018 P2 33pgsDocument33 pagesCSEC Mathematics June 2018 P2 33pgszarzsultan12No ratings yet
- Quiz Date: 12 June 2020: Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For RBI Assistant Mains 2020Document9 pagesQuiz Date: 12 June 2020: Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For RBI Assistant Mains 2020Rahul singhNo ratings yet
- Activity 9: 1. Take A Stand Fitted With 0º-360º Protractor. 2. Consider The Radius of Protractor As 1 UnitDocument3 pagesActivity 9: 1. Take A Stand Fitted With 0º-360º Protractor. 2. Consider The Radius of Protractor As 1 UnitTrupti prangya sahooNo ratings yet
- Physics I (8.012) Fall 2004 Problem Set # 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesPhysics I (8.012) Fall 2004 Problem Set # 2 Solutionscajama79No ratings yet
- Tangent and Secant Angles and Segments MONDAYDocument2 pagesTangent and Secant Angles and Segments MONDAYMaria Eleonor BanaresNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Aliaa AkbarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Cbse Maths MCQDocument4 pagesClass 10 Cbse Maths MCQDhiren Mathur0% (1)
- 1a.rectilinear MotionDocument5 pages1a.rectilinear MotionAtulNo ratings yet
- P6Maths Week 35Document4 pagesP6Maths Week 35tokengeeNo ratings yet
- 4 7 The Law of Sines and The Law of CosinesDocument81 pages4 7 The Law of Sines and The Law of CosinesAnthony WangNo ratings yet
- Physics Lecture Series: HCV ExercisesDocument16 pagesPhysics Lecture Series: HCV ExercisesLalit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics: Guided Learning Activity Kit Static Equilibrium, Rotational Kinematics and Work Done by TorqueDocument24 pagesGen. Physics: Guided Learning Activity Kit Static Equilibrium, Rotational Kinematics and Work Done by TorqueFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Ws - 201 Motion I Amended PDFDocument9 pagesWs - 201 Motion I Amended PDFL LHNo ratings yet
- Indefinite Integral - DPP 1Document2 pagesIndefinite Integral - DPP 1Ashish JhalaniNo ratings yet
- Torsion of A CurveDocument3 pagesTorsion of A CurveewbNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Sheet#1 MSDocument32 pagesTrigonometry Sheet#1 MSretaj 1818No ratings yet
- 50-Increase & Decrease of RatioDocument6 pages50-Increase & Decrease of RatioSameh SalahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Simple CurveDocument66 pagesLesson 1 - Simple CurveFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNo ratings yet
- Angular MeasurementDocument8 pagesAngular MeasurementshivaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Baja LengkapDocument32 pagesTabel Baja LengkapNugroho PratomoNo ratings yet